Selectively cross-linked polyethylene orthopedic devices
a cross-linked polyethylene and orthopedic technology, applied in the direction of prosthesis, other domestic articles, joint implants, etc., can solve the problems of difficult balance to obtain, inability to easily form easily by inexpensive injection molding techniques, and inability to achieve the effect of improving wear resistan
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example
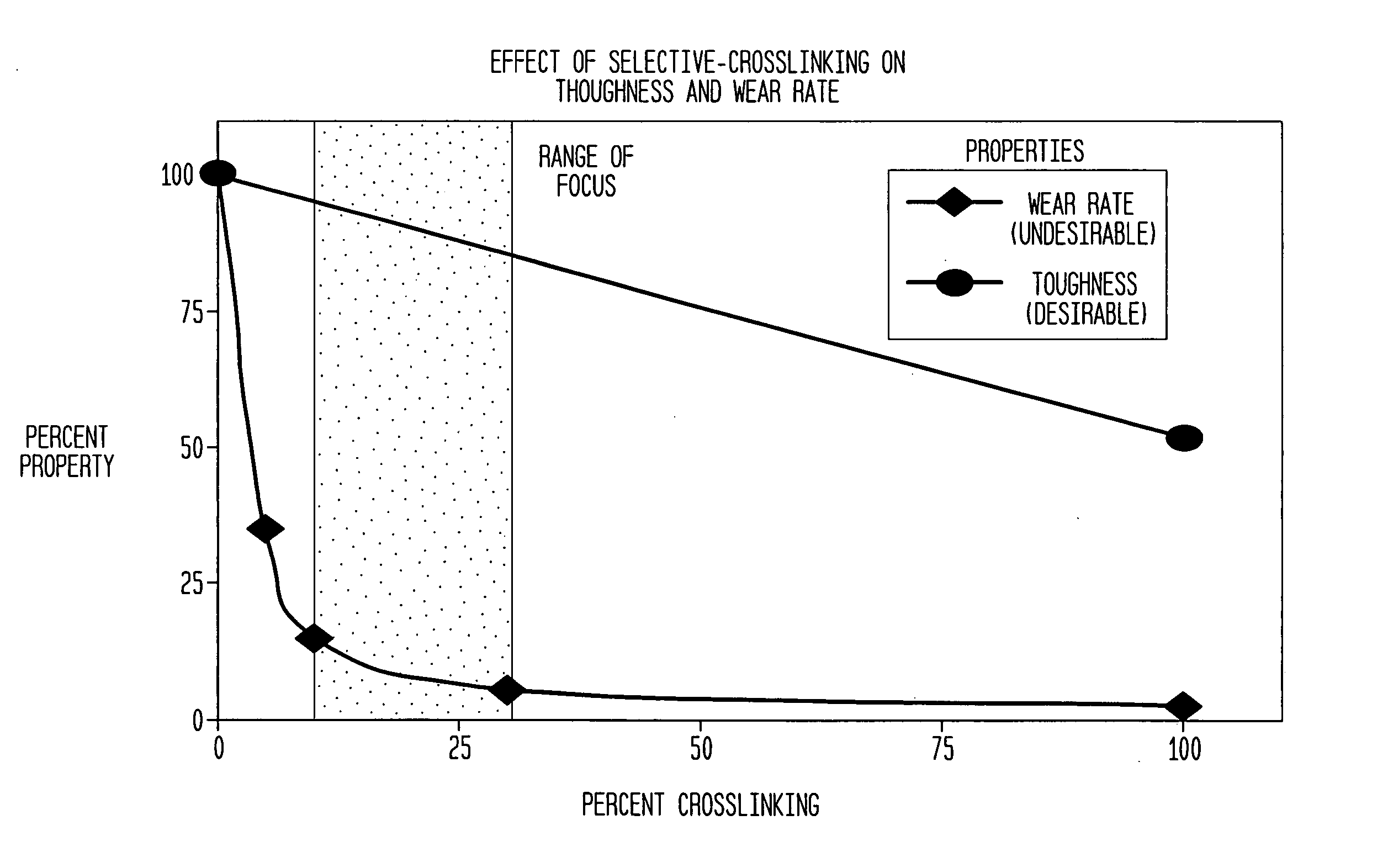
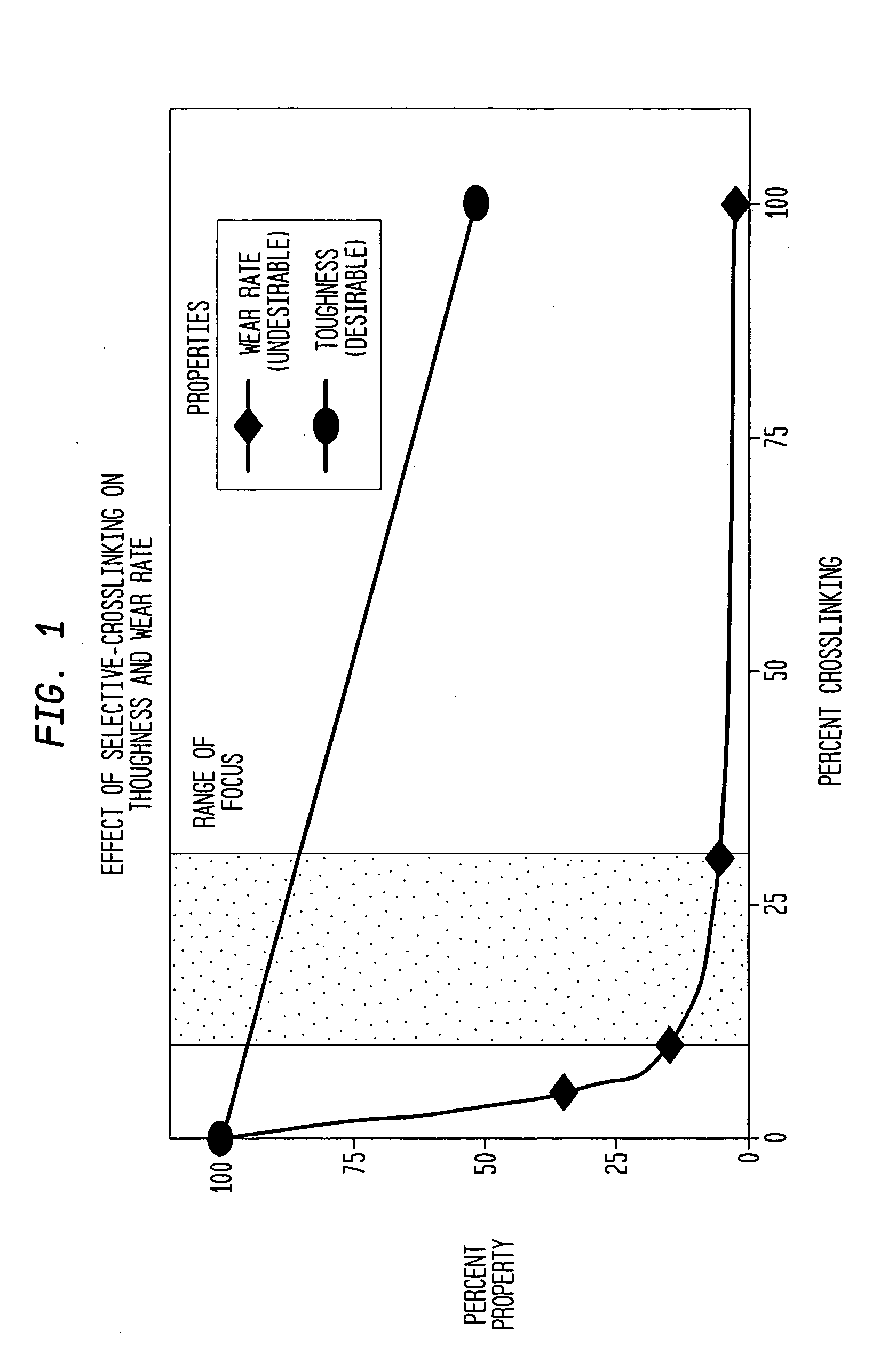
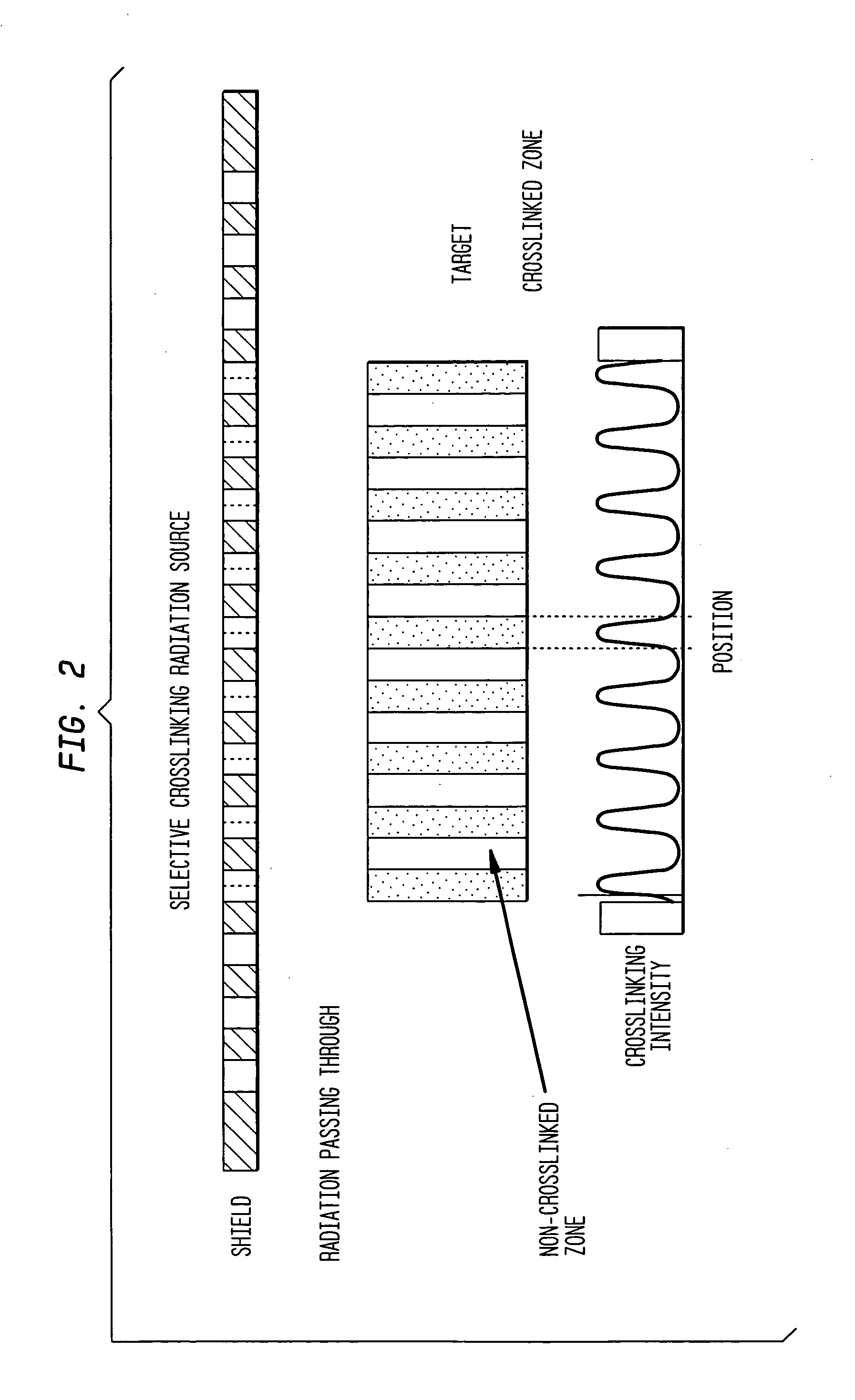
[0062] Several shields were produced from a {fraction (3 / 8)} inch thick steel plate for selective cross-linking treatment of UHMWPE. The overall top surface size for each plate was approximately 5 inches by 5 inches square. Each shield was perforated with a series of 3 mm diameter holes in a geometric arrangement such that each perforation (hole) was equally spaced from all other perforations. One pattern involved 30% porosity or perforation. That is, 30% of the top surface area of the shield was occupied by holes uniformly distributed over the surface of the shield. These parameters (3 mm hole size, equal spacing and 30% surface area) control the total number of holes as well as the inter-hole spacing. An additional shield used a 20% surface area pattern and a third used a 10% pattern.
[0063] A 3.25 inch diameter cylindrical rod of UHMWPE material was sectioned into 1.75 inch thick pieces or “pucks”. This rod was made of GUR 1050 resin and was not treated or cross-linked in any way...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| elongation | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| elongation | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| elongation | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com