Multi-tubular reactors with monolithic catalysts
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
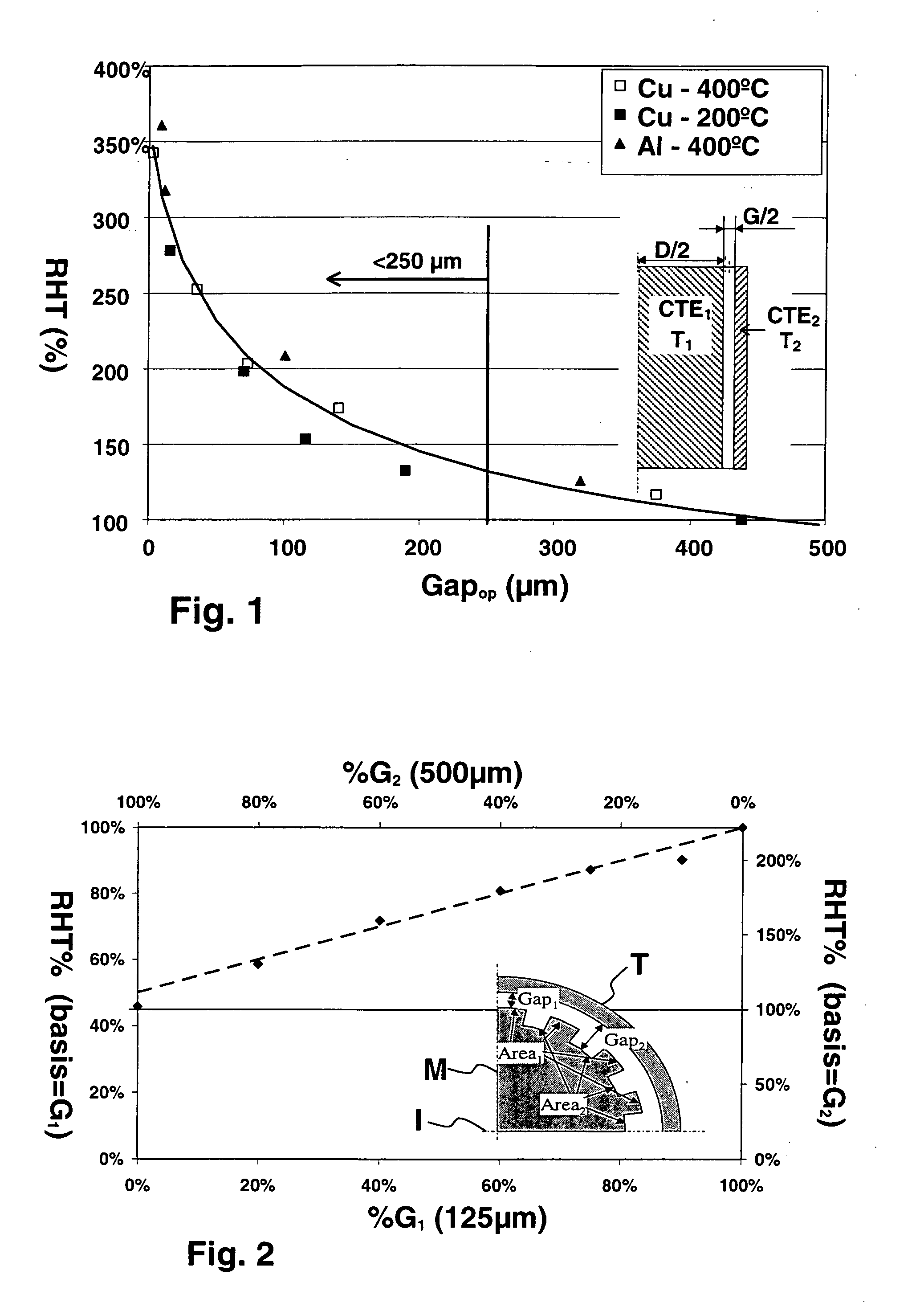
[0023] The effectiveness of the present invention for improving multi-tubular reactor efficiencies can be better appreciated when it is recognized that a single high heat flux resistance in a series of low heat flux resistances will act as thermal “bottleneck”, limiting the amount of heat transfer across the entire series. In such cases no reductions in the latter resistances will have any significant effect on heat flow into or from the reactor. In the case of a multi-tubular reactor incorporating highly conductive metal monolithic catalyst supports and reactor tubes, internal heat flux resistances are generally low, except for the resistance presented by the gap between the monoliths and the inside walls of the tubes. The heat transfer resistance of this gap can vary depending on its size and fluid content, but is typically the largest resistance along the path from the fluid to the outer surfaces of the reactor tubes, particularly where the gap spaces are filled with static air. ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Length | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Fraction | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Fraction | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com