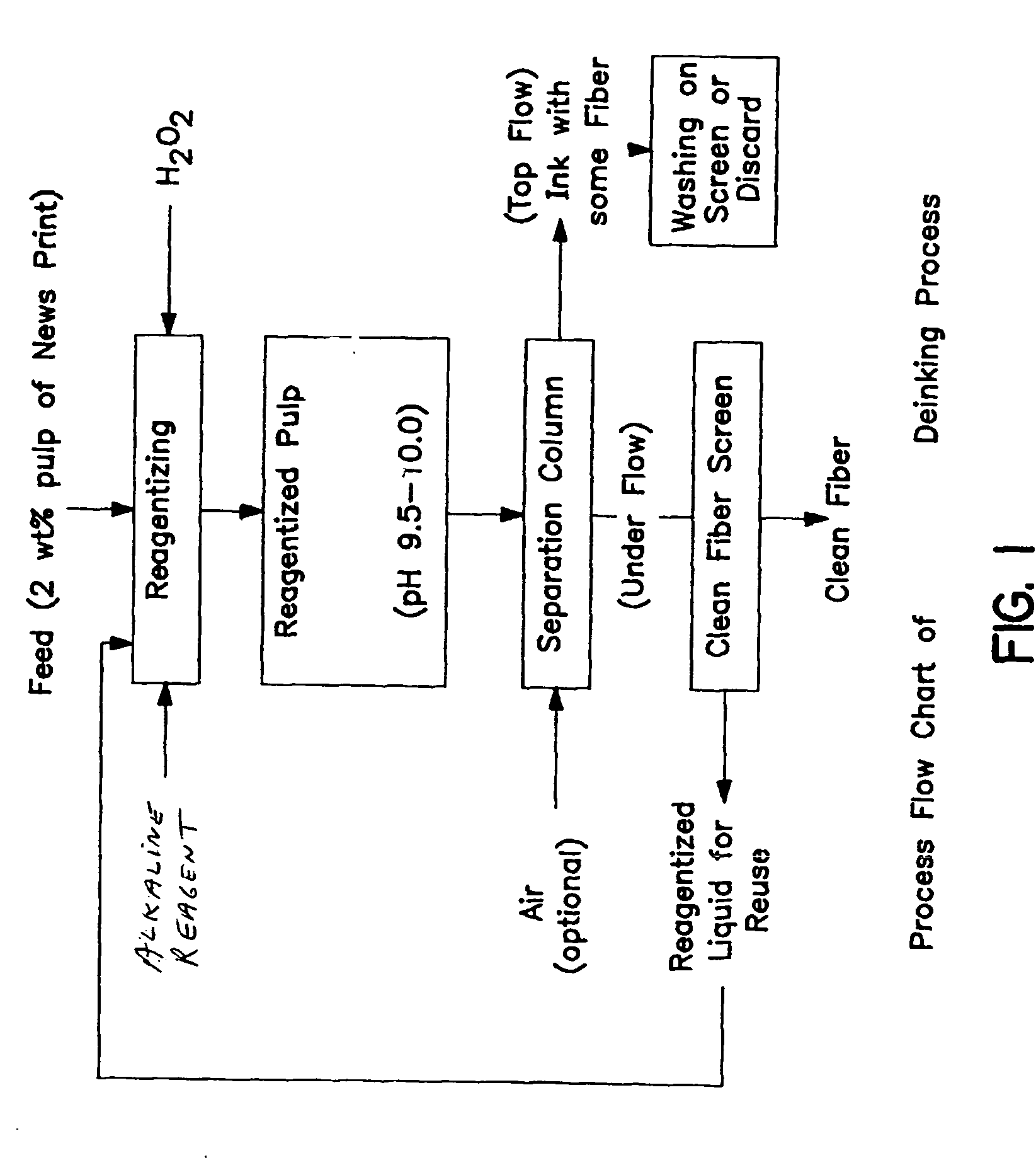
Method of de-inking paper and other cellulosic materials
a cellulosic material and paper technology, applied in papermaking, pretreatment with oxygen-generating compounds, pulping with inorganic bases, etc., can solve the problems of insufficient de-inking methods, inability to remove new types of inks and coating resins, and inability to adapt and adapt de-inking and reclaiming wastepaper by chemical and cooking techniques, etc., to achieve more efficient processes
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example
[0053] Newspaper is first cut into shreds and homogenized. The paper is then pulped at a solids loading of 2 wt. % in a Hamilton Beach blender for two minutes. Hydrogen peroxide is added during the pulping stage at a dosage of 0.5-1.0 wt. % of dry paper. The reagentized pulp is then transferred to a flotation cell and the pH is adjusted to 9.5-10.0 using sodium carbonate. The flotation is performed using a Denver flotation unit for fifteen minutes at 900 rpm. The ink particles are collected in the froth using a manual skimmer. The floated ink particles and the de-inked pulp are then filtered at 0.5 atm vacuum. The filtrate is recycled to subsequent flotation experiments to reduce the reagent consumption by recycling the unreacted reagents. The dewatered pulp is air dried in a convection oven at a temperature of 40° C. for 4-5 hours. In conventional methods, the dewatered pulp is washed and bleached to increase the brightness of the pulp. However, in this example, post flotation proc...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| temperatures | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| pH | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| weight | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com