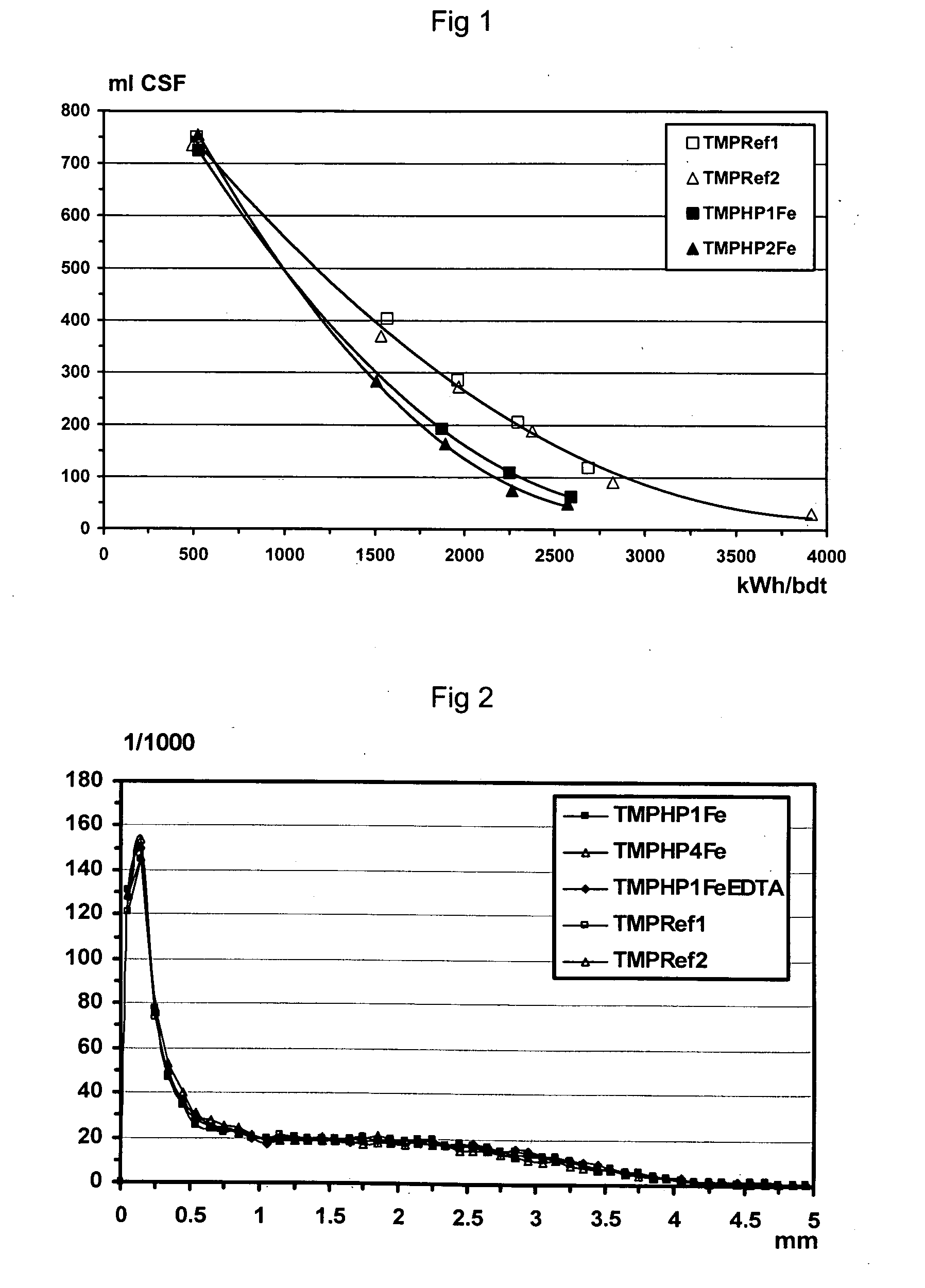
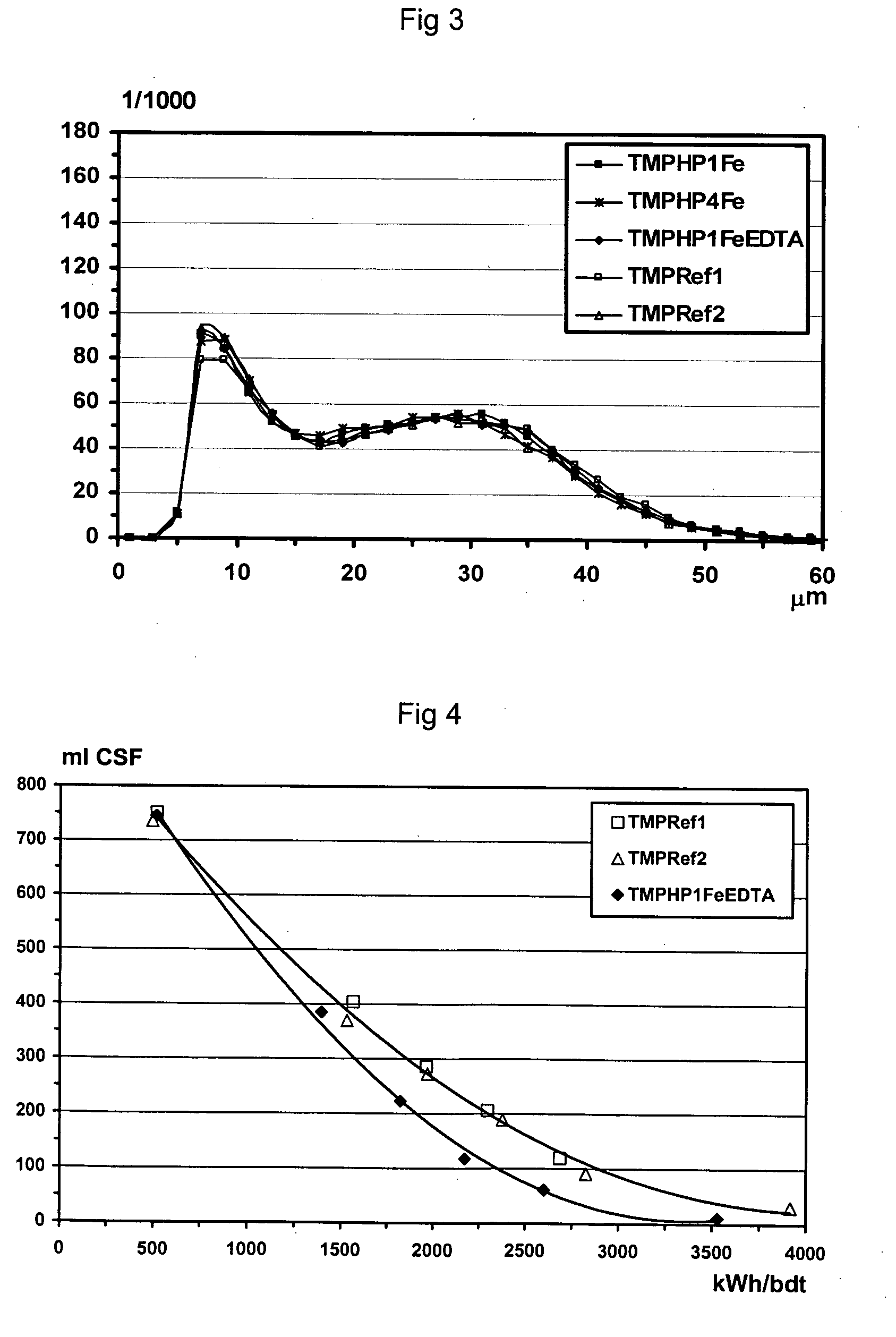
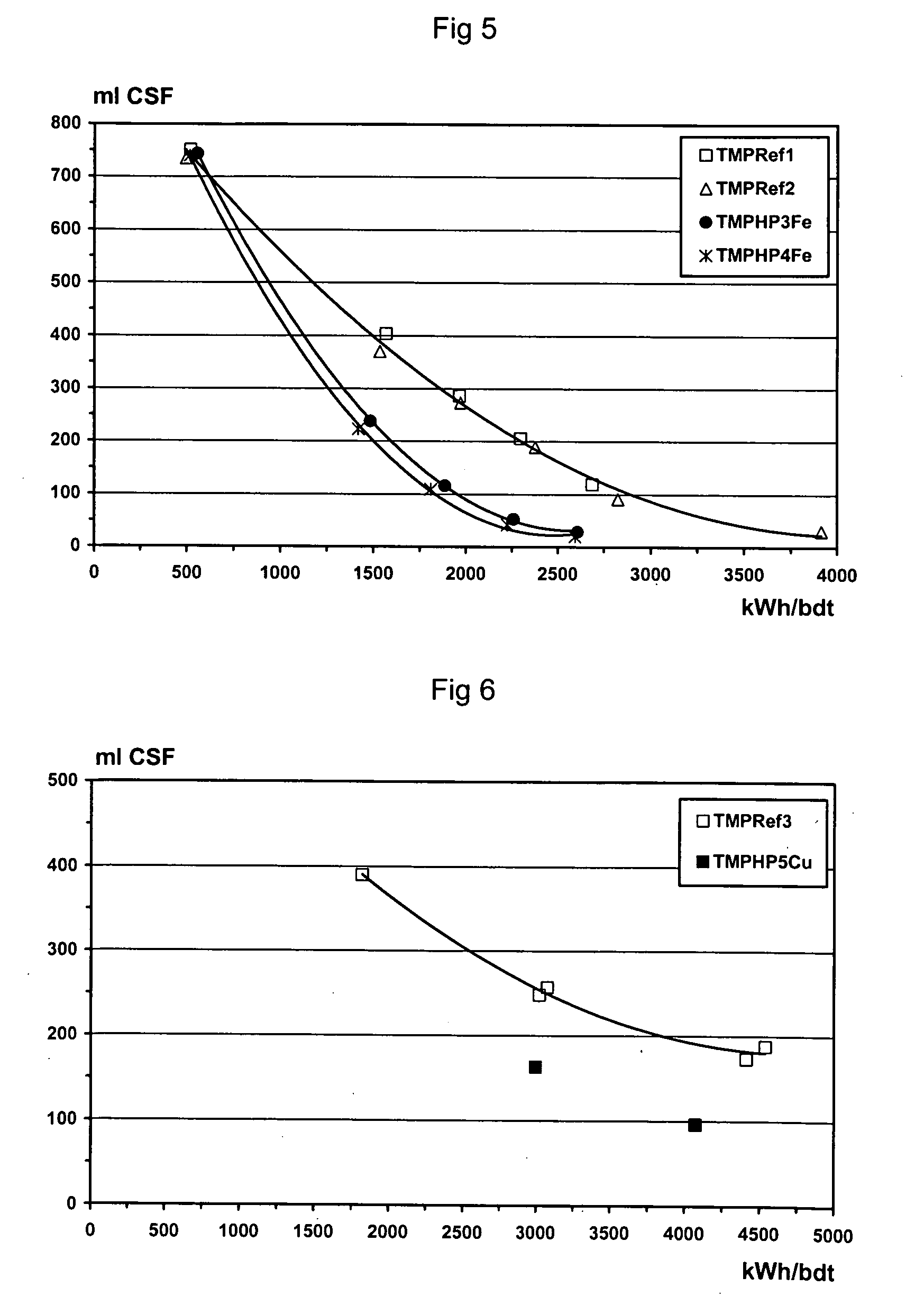
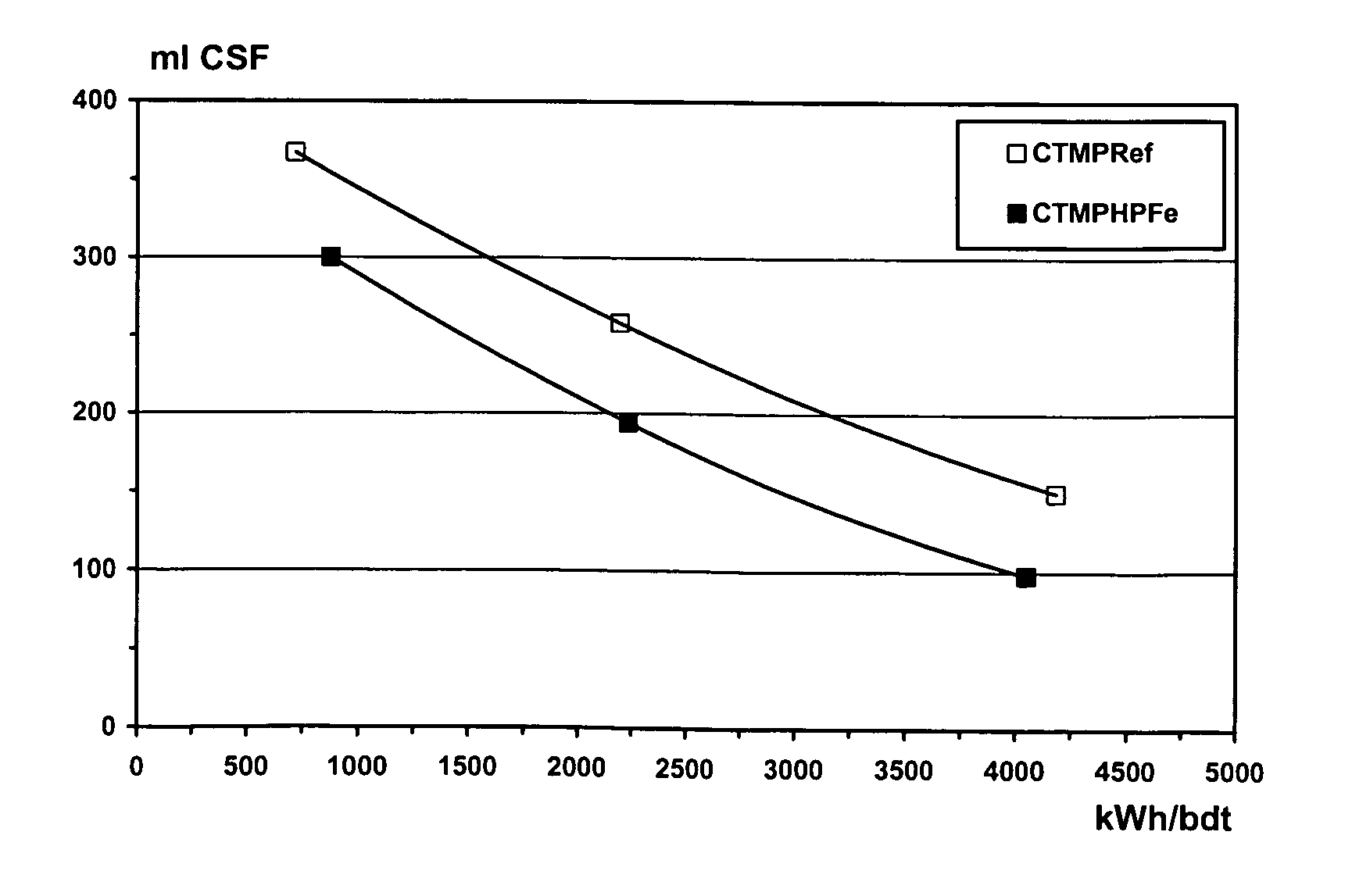
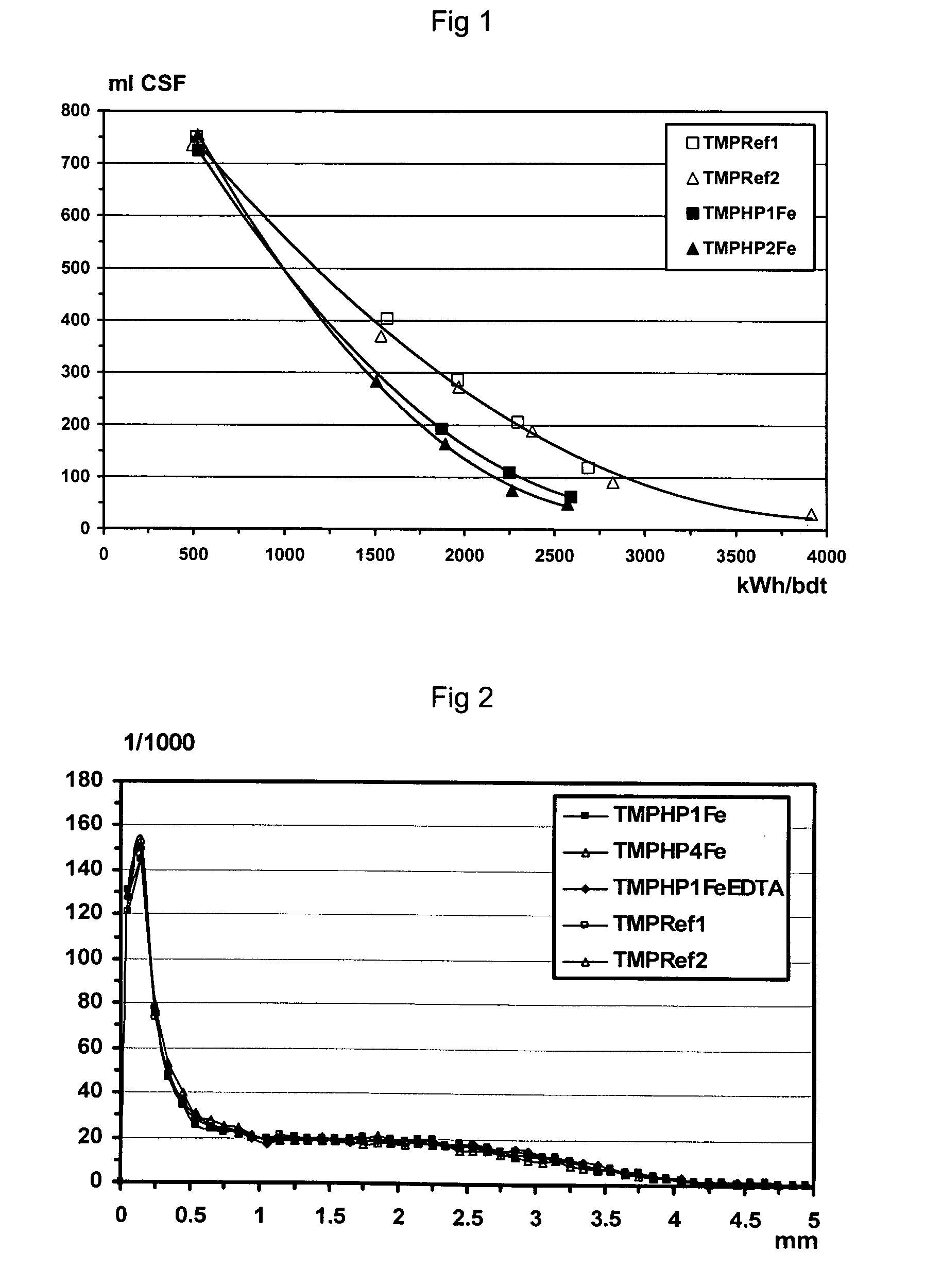
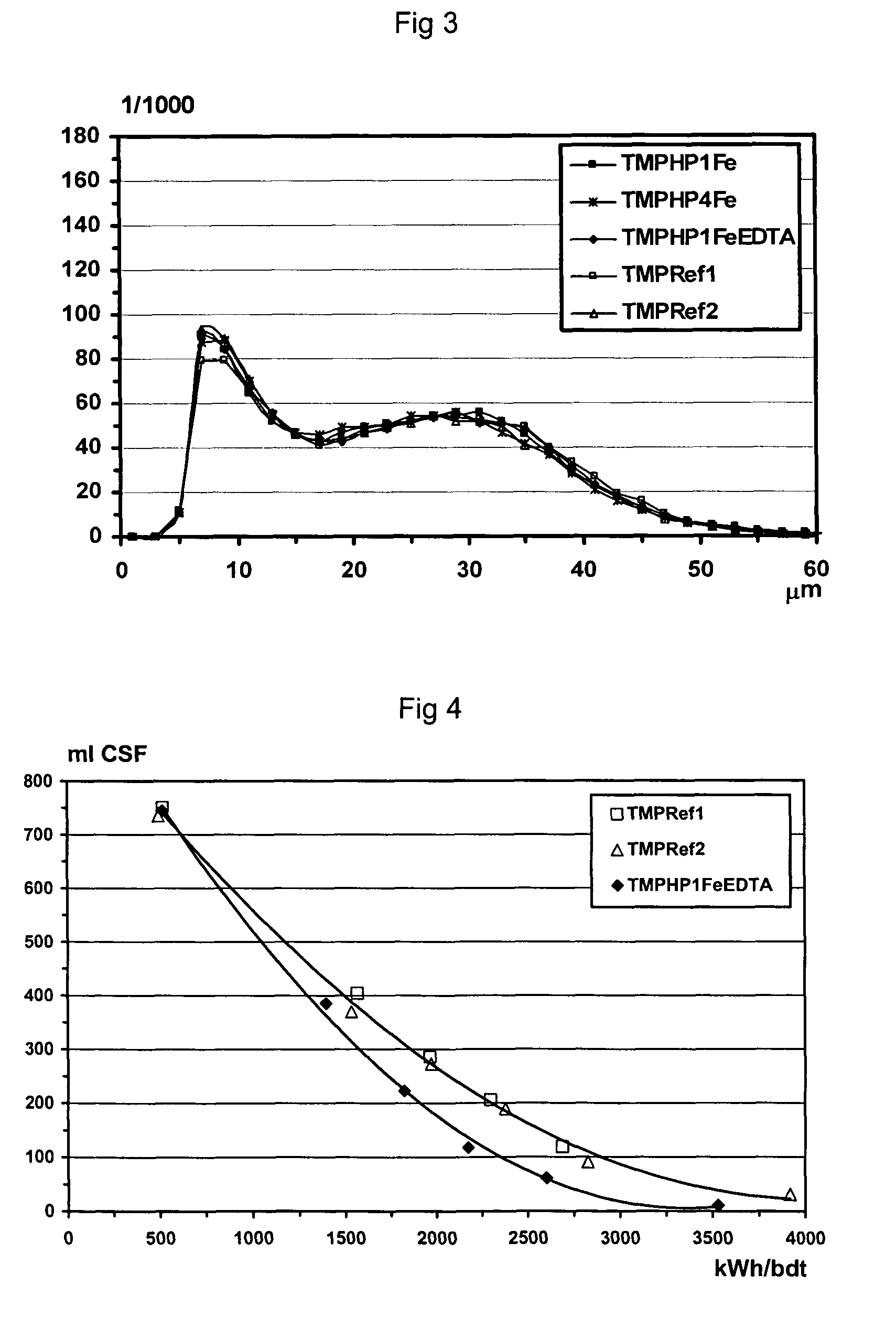
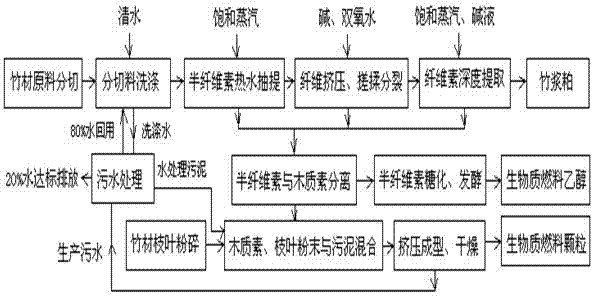
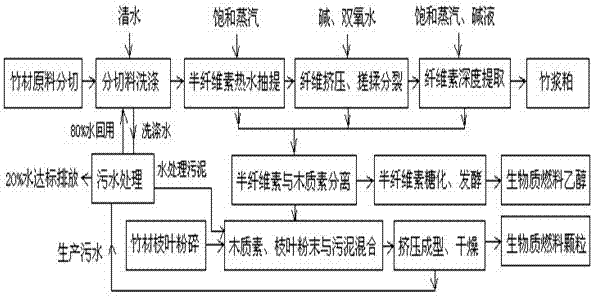
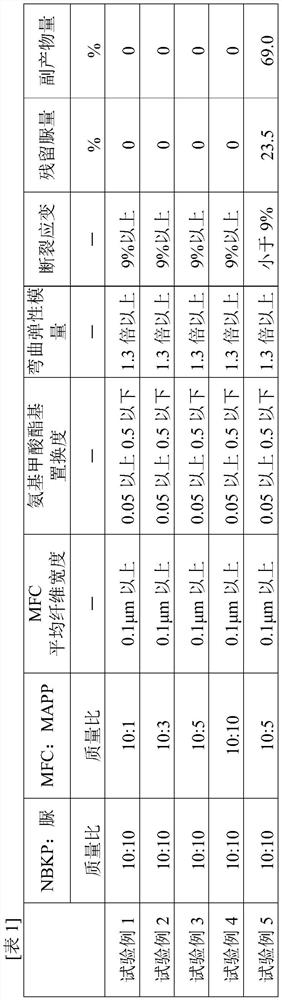
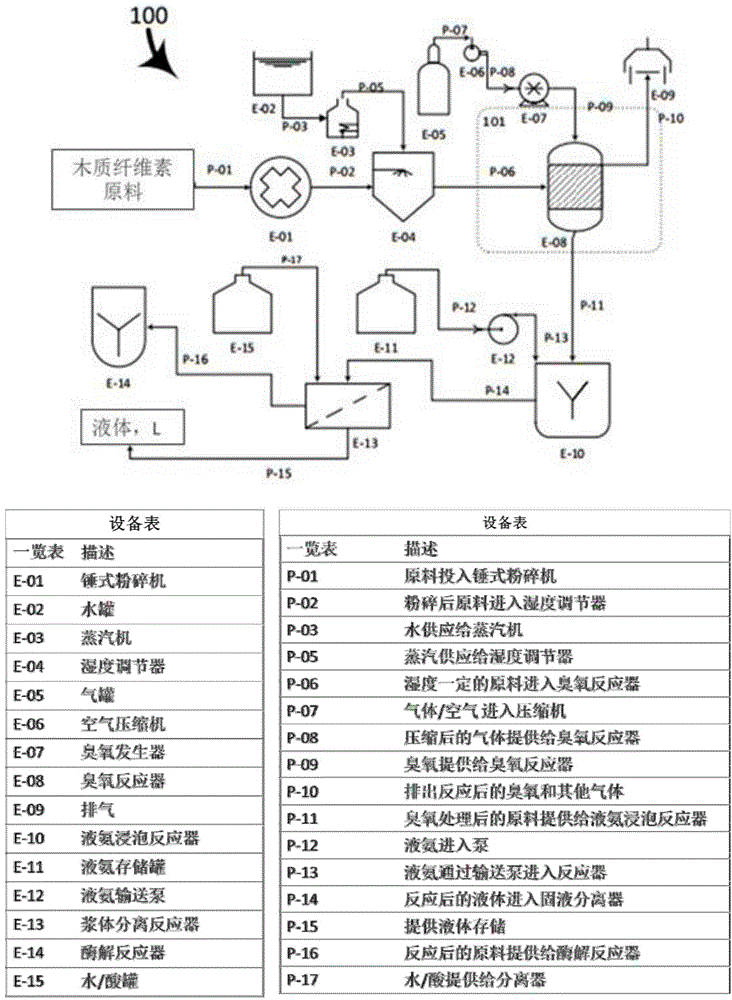
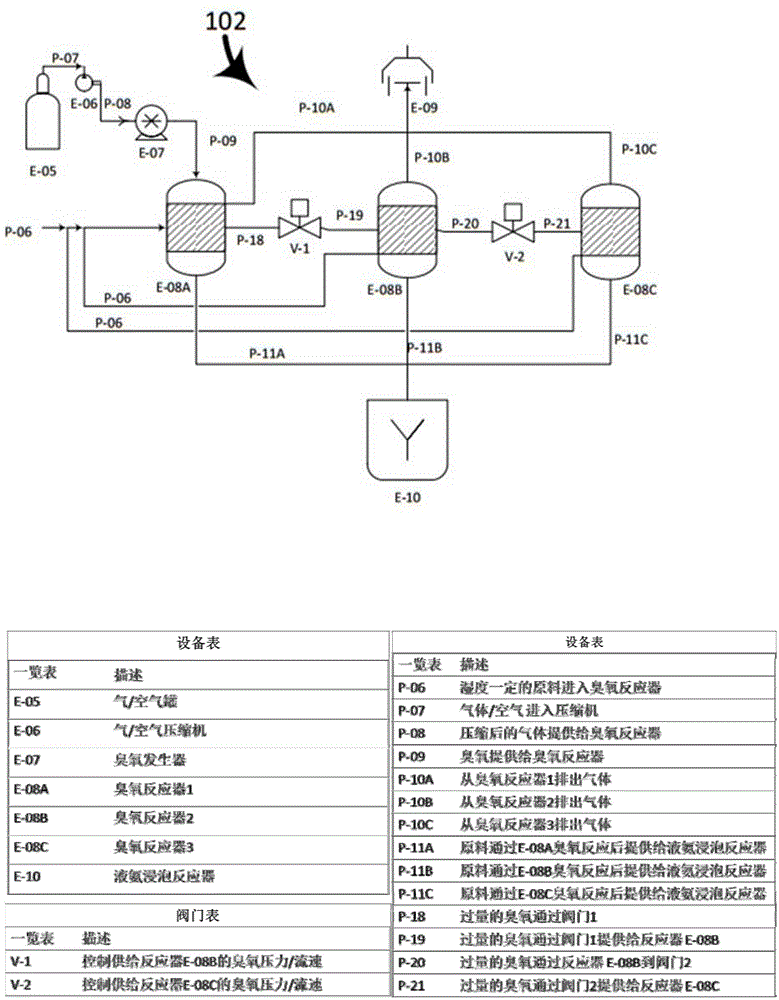
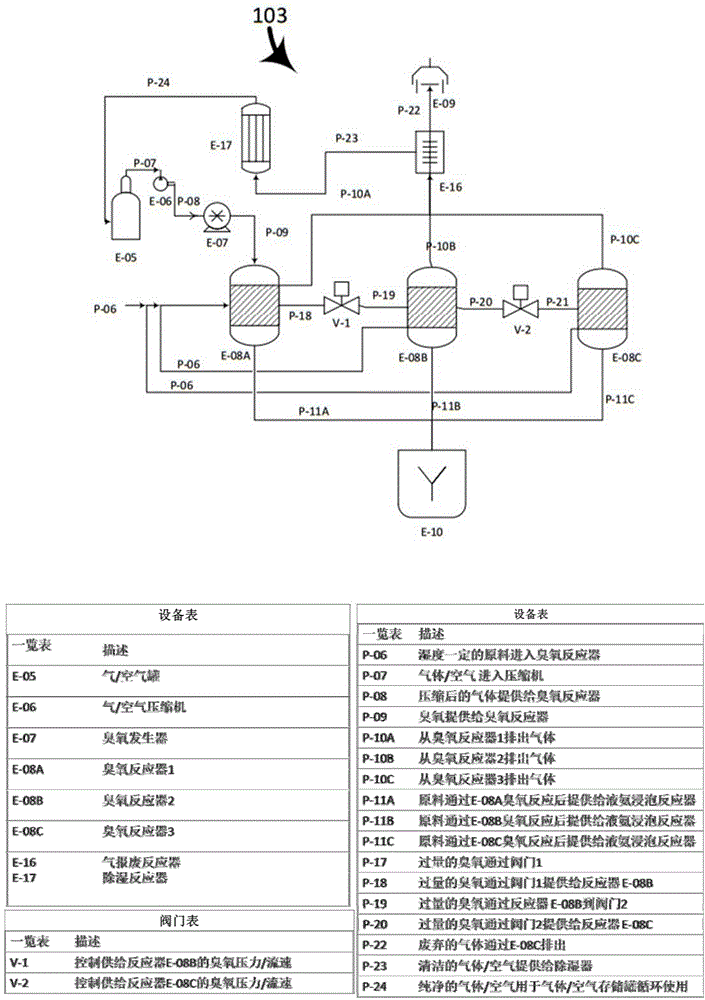
Patents
Literature
43results about "Pretreatment with oxygen-generating compounds" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Process of producing high-yield pulp
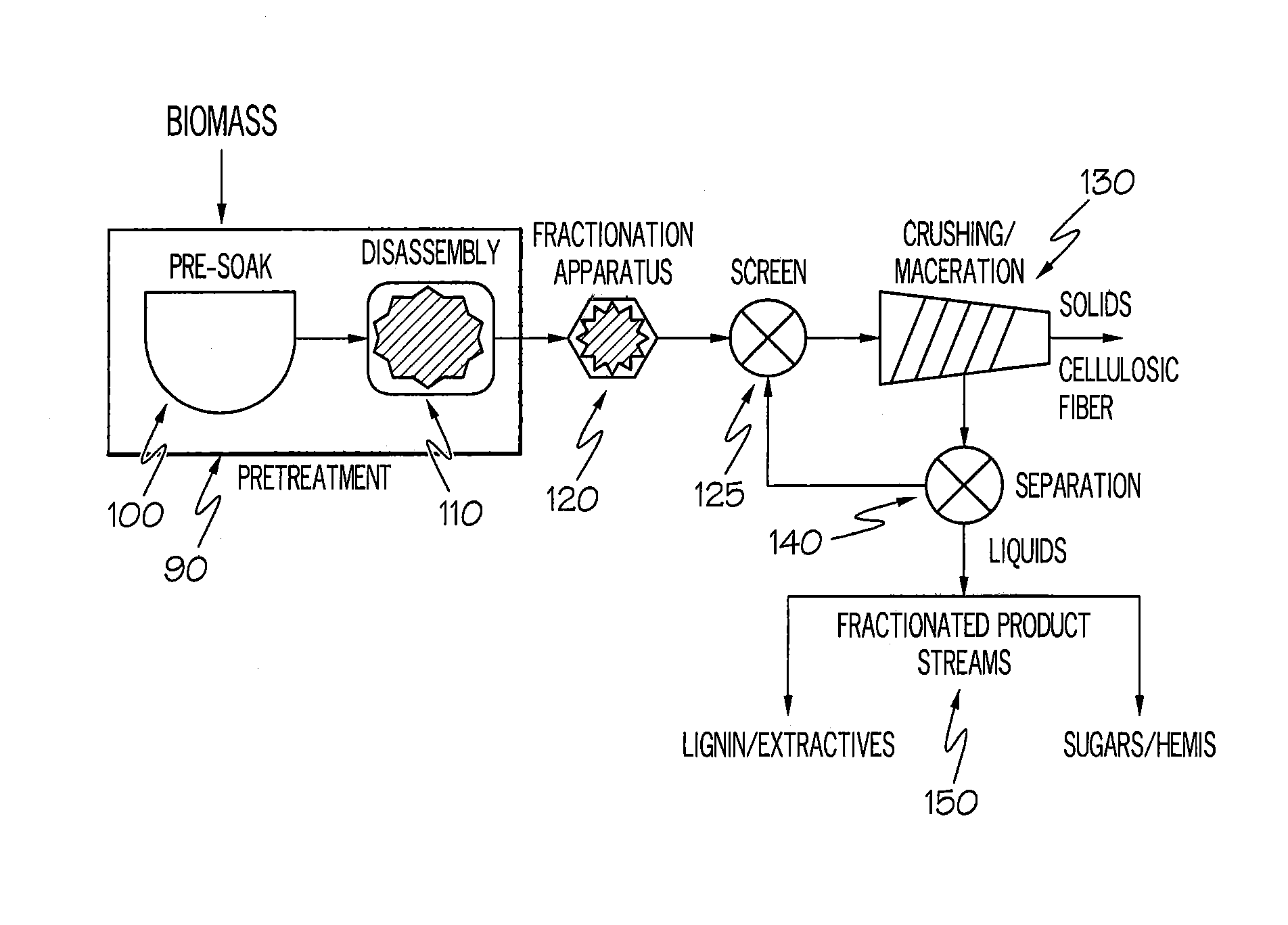
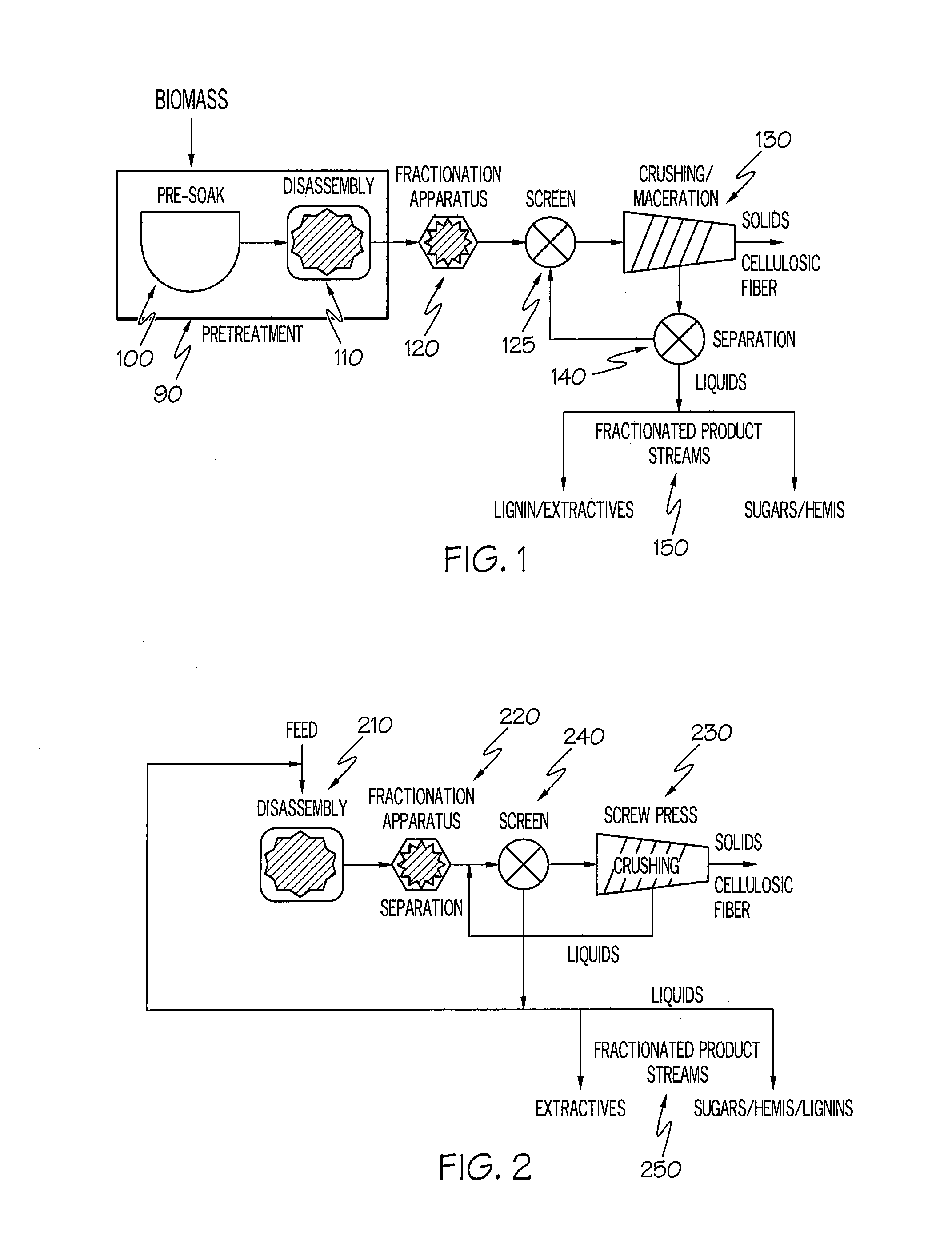
The present invention relates to a process for preparing a high-yield pulp comprising a) treating a lignocellulose containing material chemically by means of an oxidising system comprising at least one non-enzymatic oxidant substantially free from ozone and chlorine dioxide and an activator at a pH from about 2 to about 6.5; and b) treating the lignocellulose containing material mechanically for a time sufficient to produce a high-yield pulp, wherein the lignocellulose containing material is chemically treated prior to and / or during any mechanical treatment stage, and wherein the lignocellulose containing material is not chemically treated at a pH from about 11.5 to about 14 between stages a) and b).
Owner:AKZO NOBEL CHEM INT BV
Process of producing high-yield pulp
InactiveUS8268122B2Pulp bleachingPretreatment with oxygen-generating compoundsCelluloseChemical treatment
The present invention relates to a process for preparing a high-yield pulp comprisinga) treating a lignocellulose containing material chemically by means of an oxidizing system comprising at least one non-enzymatic oxidant substantially free from ozone and chlorine dioxide and an activator at a pH from about 2 to about 6.5; andb) treating the lignocellulose containing material mechanically for a time sufficient to produce a high-yield pulp, wherein the lignocellulose containing material is chemically treated prior to and / or during any mechanical treatment stage, and wherein the lignocellulose containing material is not chemically treated at a pH from about 11.5 to about 14 between stages a) and b).
Owner:NOURYON CHEM INT BV
Process for the production of microfibrillated cellulose in an extruder and microfibrillated cellulose produced according to the process
ActiveUS8747612B2Increase productionEfficient productionCellulosic pulp after-treatmentPretreatment with oxygen-generating compoundsCelluloseFiber
The present invention relates to a process for the production of microfibrillated cellulose wherein the process comprises the steps of, providing a slurry comprising fibers, adding the slurry to an extruder, treating the slurry in the extruder so that the fibers are defibrillated and microfibrillated cellulose is formed. The invention further relates to a microfibrillated cellulose produced.
Owner:STORA ENSO OYJ
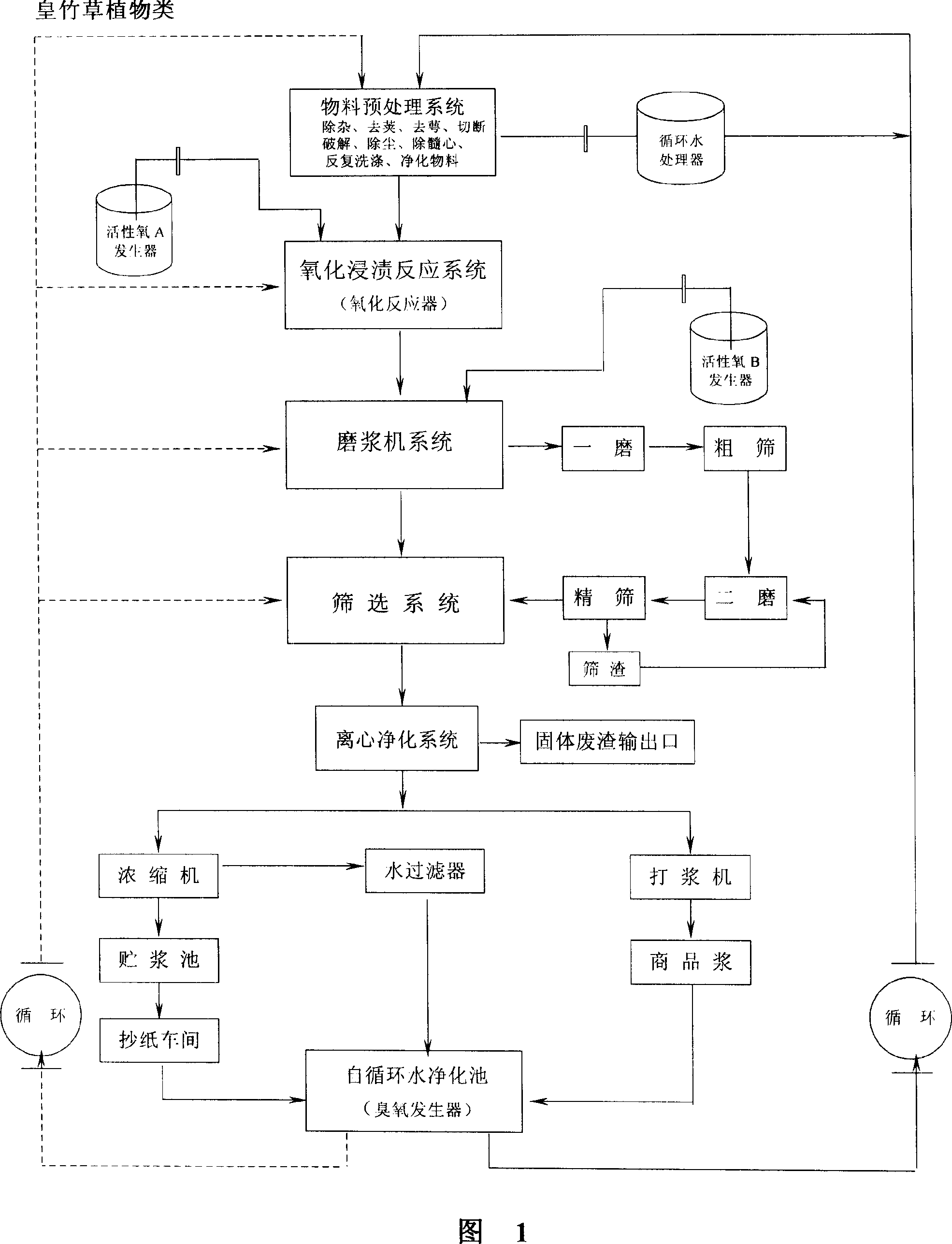
Paper pulp making technology by biological catalytic cracking method
InactiveCN101067284AAvoid pollutionReach the goal of green environmental protectionPretreatment with oxygen-generating compoundsCellulaseSewage
The present invention relates to one kind of paper pulp making biologically catalyzed degradation process. Paper pulp material after being wetted with ozone water is biologically catalyzed degraded under the action of the composite biologically catalyzed degrading agent comprising whiterot fungus, cellulose, pectase, yeast and water, so as to produce slurry. The process has a production period as short as 2 hr, produces no organic compound and sewage, and is environment friendly, simple and low in power consumption.
Owner:杨黎明
Co-production preparation method of bamboo biomass fuel and bamboo pulp
InactiveCN102226317AReduce pollutionReduce degradation damagePretreatment with alkaline reacting compoundsBiofuelsDistillationSludge
The invention relates to a co-production preparation method of bamboo biomass fuel and bamboo pulp, and the method comprises the following steps: (1) performing hot-water extraction for getting a hemicellulose extract liquid; (2) extruding and rubbing cellulose, and extruding for removing a hemicellulose and lignin extract liquid and further getting a filamentous material; (3) performing depth extraction on the cellulose and preparing the bamboo pulp: adding alkali into the filamentous material, performing heating-up treatment, washing, and filtering out a hemicellulose and lignin degradation solution, thus getting the bamboo pulp; (4) preparing biomass fuel ethanol: separating hemicellulose, performing saccharification conversion, further inoculating microzyme for fermentation, and performing distillation and concentration to get the biomass fuel ethanol; and (5) preparing biomass fuel particles: smashing slender bamboo tails, branches and leaves, then mixing with sludge and residual liquid after separating the hemicellulose in the step (4), and performing extrusion forming and drying for getting the biomass fuel particles. The process is advanced; and furthermore, on the premise of not increasing the production cost, the utilization rate of bamboo resources is improved, the economic benefits are increased and the environmental pollution is reduced.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
Low energy consumption clean paper pulp extracting method and papermaking process thereof
InactiveCN101694075AAchieve recyclingGood flexibilityPretreatment with alkaline reacting compoundsPulp de-wateringFiberChemical solution
The invention relates to a low energy consumption clean paper pulp extracting method and a papermaking process thereof, solving the problems that fibrous raw materials need to be boiled at high temperature and pressure in the pulp preparing and papermaking processes and chemical solutions produce a large quantity of black or red liquid in the pulp preparing and papermaking processes to cause great waste to resources and great pollution to the environment in the prior art. The invention adopts the following technical scheme: the low energy consumption clean paper pulp extracting method is realized by removing impurities from biomass raw materials rich of fiber, crushing, softening and soaking, separating organic matters, grinding and pulping, wherein a softening and soaking solution contains the following components in percent by weight: 10-20 sodium oxide, 3-5 sodium carbonate, 0.5-2.5 penetrating agent T, 0.5 magnesium oxide and 0.05-0.15 chelating agent EDTA. The papermaking process matched with the method comprises the following steps: getting materials ready, rubbing to devillicate, soaking to react, separating liquid medicine, spirally squeezing pulp, refining with high consistency, removing slag, coarsely screening and making paper. The pulp preparing process has simple course, no high requirements on environment and equipment condition, easily popularized technology, no requirement on the scale of production, low costs for building production lines and purchasing equipment and less running expense.
Owner:林宣禧
Method for isolating cellulose from a biomass and products provided therefrom
InactiveUS20150152598A1Cellulosic pulp after-treatmentPretreatment with water/steamWater insolubleWater soluble
A pretreated biomass is subjected to high frequency pulses and shear forces without denaturing and / or degrading the individual components of the biomass. The biomass is then subjected to compressive force to separate a first liquid fraction from a first fractionated biomass. The first fractionated biomass may again then be subjected to the same high frequency pulses and shear forces as previously, particularly if there are hemicellulose and / or sugars still present in the first fractionated biomass. Compressive forces are used to separate a second liquid fraction from a second fractionated biomass. The second fractionated biomass is subjected to oxidation. The second fractioned biomass is then subjected to compressive forces to separate out one or more water insoluble components of the biomass in water soluble form and to provide cellulose that has not been denatured and / or degraded and has a lignin contact of less than 7 percent.
Owner:MITCHELL MELVIN
Process for fractionating sugarcane bagasse into high a-cellulose pulp, xylan and lignin
ActiveCN101821320AImprove performancePretreatment with water/steamPulp bleachingXylanCellulose acetate
Sugarcane bagasse consists of mainly three polymeric components, namely cellulose (40-45%), hemicellulose (xylan) (28-30%), and lignin (19-21%). A process is herein disclosed for fractionating sugarcane bagasse into cellulose, hemicellulose and lignin with high purity a-cellulose, which is a useful raw material for preparing cellulose esters like cellulose triacetate and other high value-added cellulose plastics. Co-production and recovery of hemicellulose (xylan) and lignin in high yields and high purities, along with a-cellulose, is another important feature of this process. Sugarcane bagasse consists of a material known as pith which constitutes 30-35% by weight of bagasse. Pith contains cellulose, hemicellulose, and lignin, in addition to various other ingredients and cell mass. The process described herein discloses the use of partially depithed bagasse as a preferred raw material for fractionation. Use of sugarcane bagasse containing pith leads to a product which is lower in yield as well as poorer in color.
Owner:COUNCIL OF SCI & IND RES
Process for fractionating sugarcane bagasse into high a-cellulose pulp, xylan and lignin
ActiveUS20100276093A1High yieldSimple and efficientPretreatment with water/steamFats/resins/pitch/waxes removal in pulpXylanFractionation
Sugarcane bagasse consists of mainly three polymeric components, namely cellulose (40-45%), hemicellulose (xylan) (28-30%), and lignin (19-21%). A process is herein disclosed for fractionating sugarcane bagasse into cellulose, hemicellulose and lignin with high purity α-cellulose, which is a useful raw material for preparing cellulose esters like cellulose triacetate and other high value-added cellulose plastics. Co-production and recovery of hemicellulose (xylan) and lignin in high yields and high purities, along with α-cellulose, is another important feature of this process. Sugarcane bagasse consists of a material known as pith which constitutes 30-35% by weight of bagasse. Pith contains cellulose, hemicellulose, and lignin, in addition to various other ingredients and cell mass. The process described herein discloses the use of partially depithed bagasse as a preferred raw material for fractionation. Use of sugarcane bagasse containing pith leads to a product which is lower in yield as well as poorer in color.
Owner:COUNCIL OF SCI & IND RES
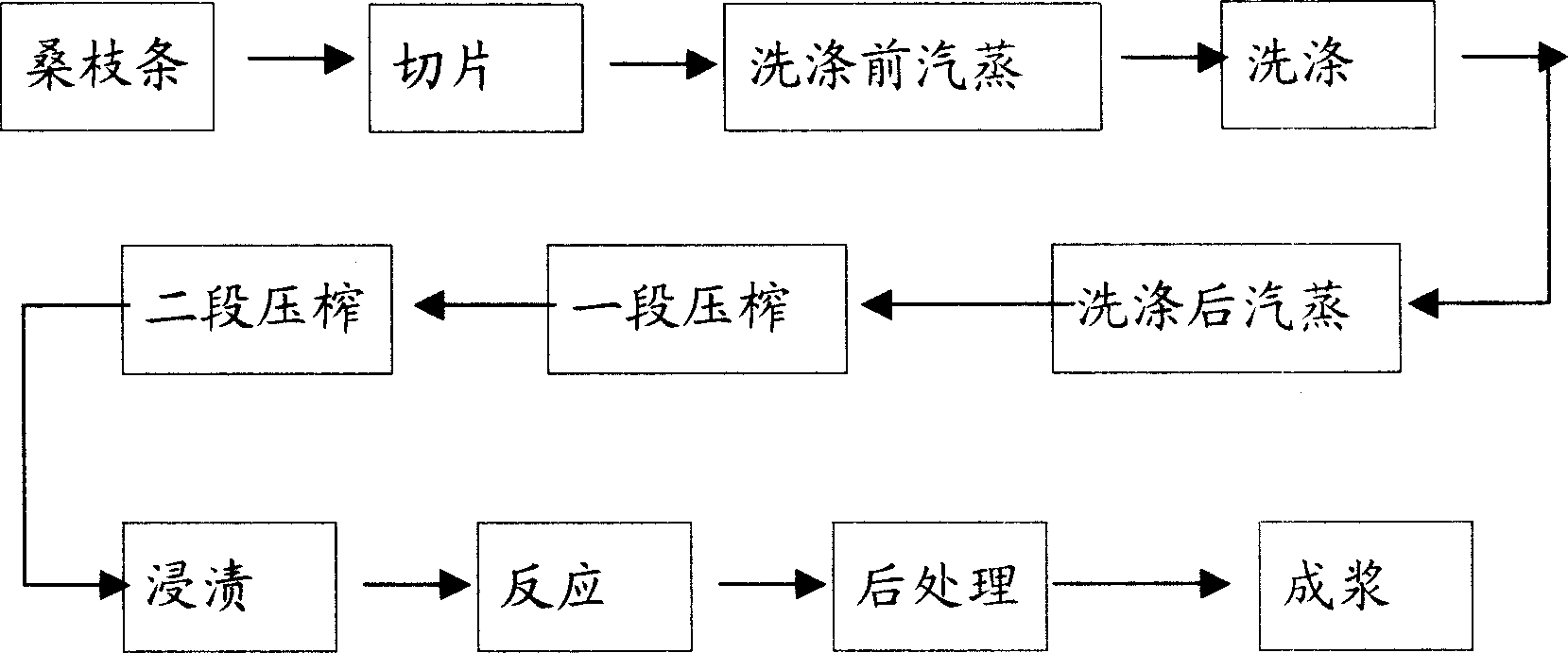
Chemical and machinery pulping process using complete white mulberry branch as raw material
InactiveCN1837458AImprove slicing pass rateLarge specific surface areaPretreatment with water/steamPretreatment with alkaline reacting compoundsFiberWhite Mulberry
This invention discloses a pulping process with mulberry bough as raw material, which comprises the following steps: slicing, steaming before scouring, scouring, steaming after scouring, first squeeze, second squeeze, steeping, reaction, post-treatment, and these steps are sequential. The invention improves percent of pass of slicing mulberry bough and availability ratio of pulp in the core, and has good dust collection efficiency. With mixing pulping of mulberry bough, the bore rod with short fibre and large content can be used fully, and the finished pulp can be used in top grade paper. With fully using resource is, the process settles said technical matters, and it is suit for use in commercial manufacture.
Owner:宜宾纸业股份有限公司
Advanced Methods for Sugar Production from Lignocellulosic Biomass and Fermenting Sugars to Microbial Lipids
InactiveUS20150184212A1Increase heightReduce crystallinityWashing/displacing pulp-treating liquorsBiofuelsCelluloseMicroorganism
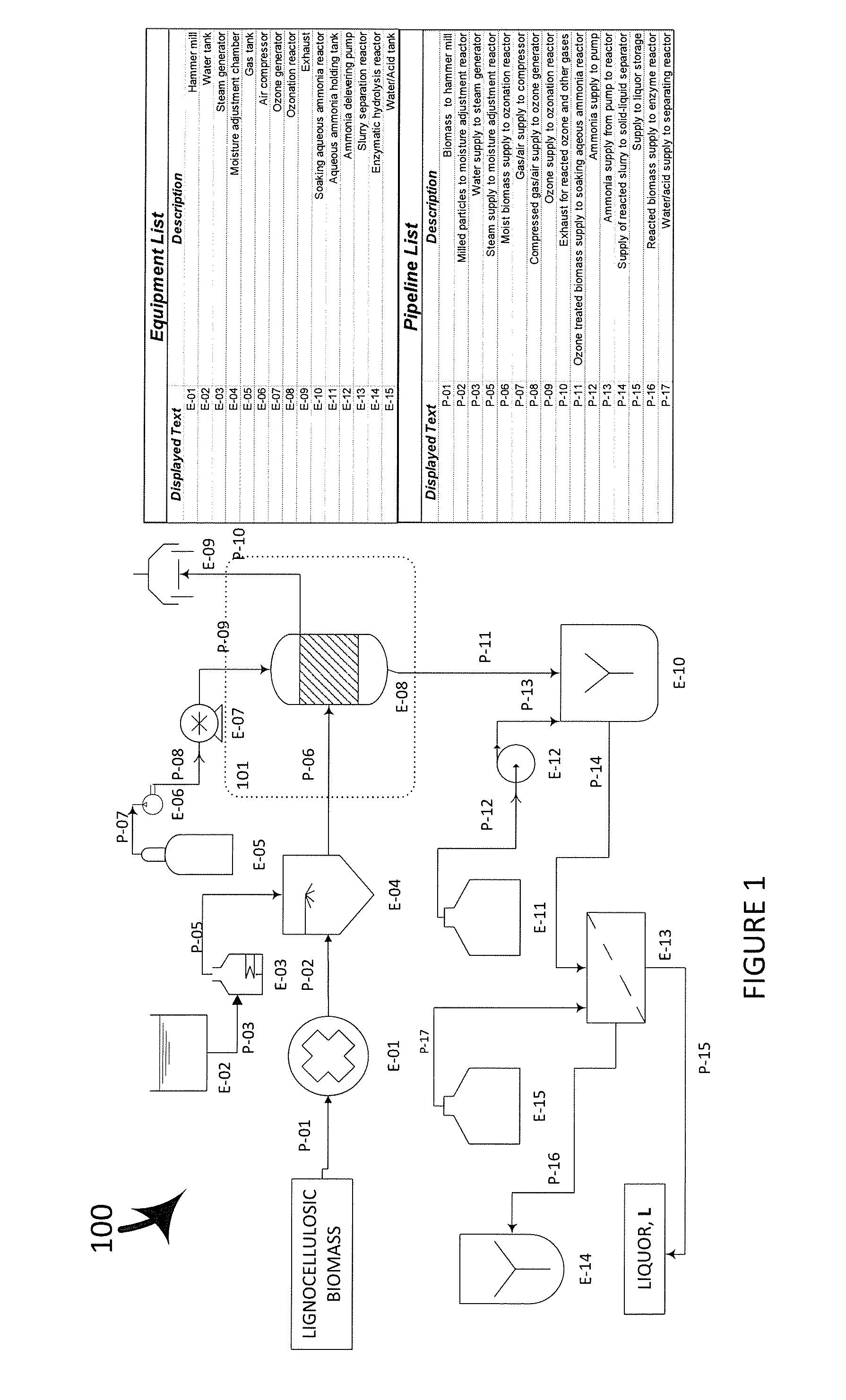
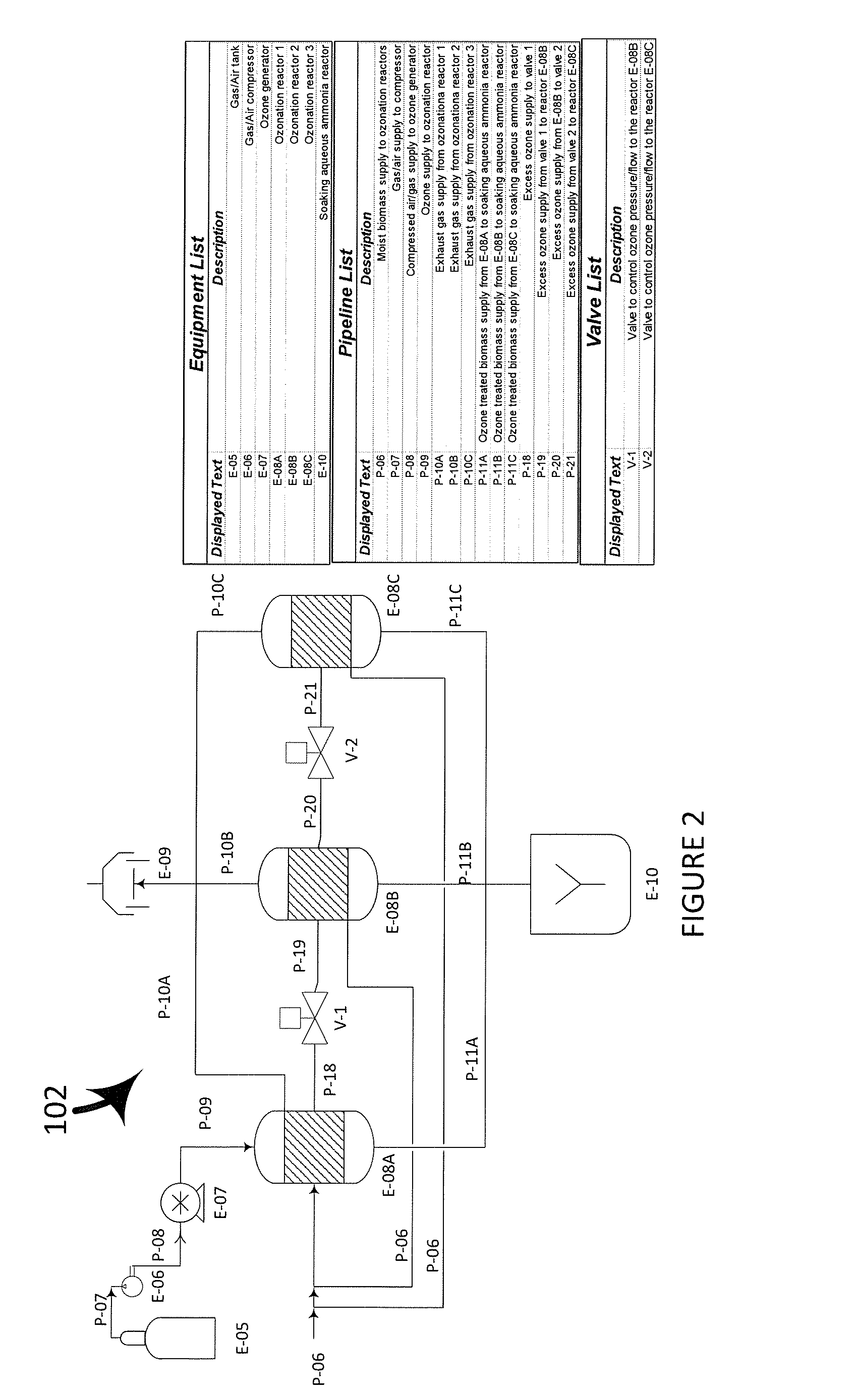
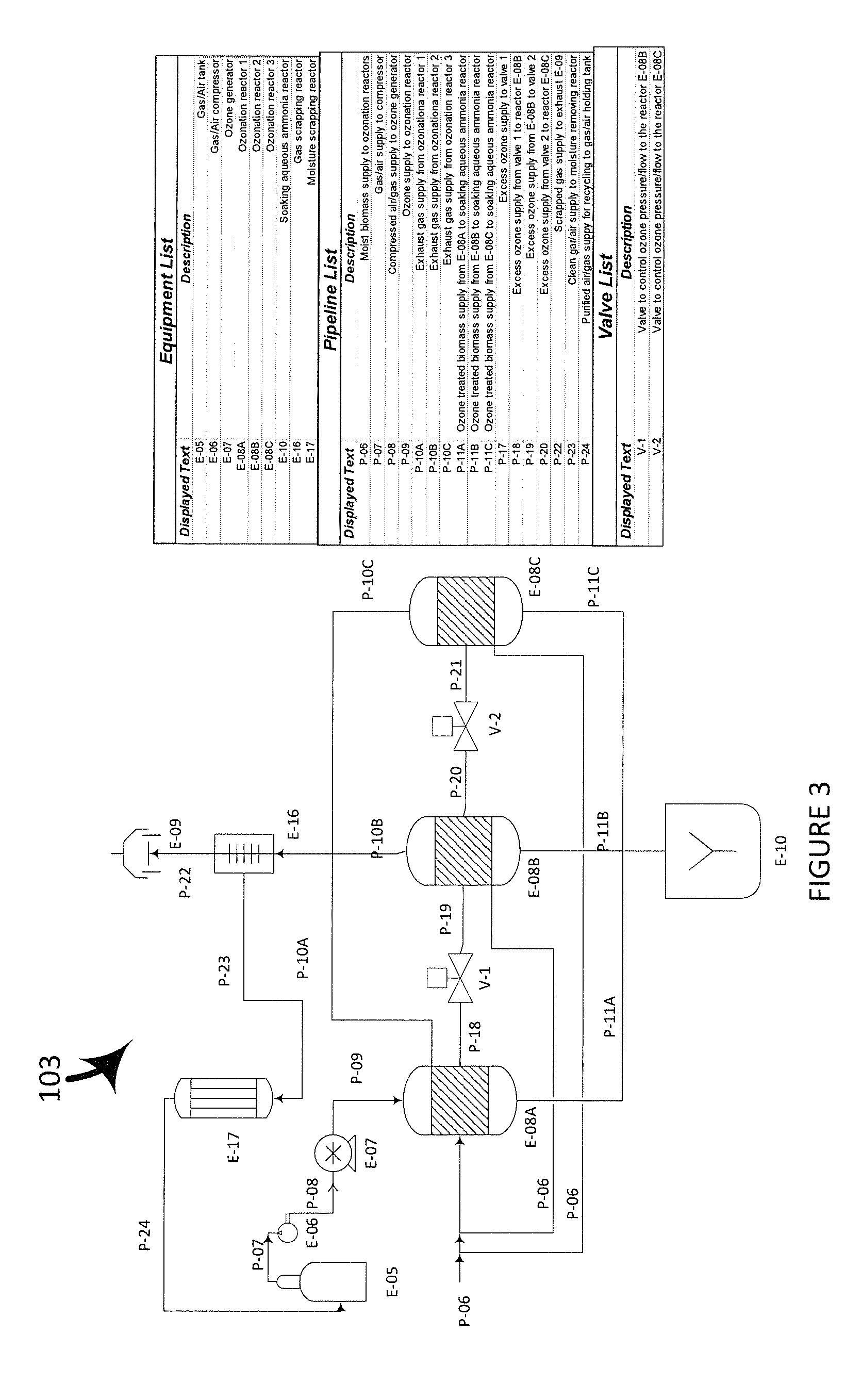
Methods for facilitating sugar release from lignocellulosic biomass and for utilizing the sugars for microbial lipid (e.g. biofuel) production are provided. The methods involve pretreating lignocellulosic biomass using various oxidizing agents (ozone, peroxone, etc.) at a temperature not higher than 50° C. and pressure no higher than 1.5 atm to render the biomass more accessible to enzymatic hydrolytic degradation into sugars and utilizing soluble sugars for fermenting oleaginous microorganism to produce microbial lipids.
Owner:WASHINGTON STATE UNIVERSITY
Wet oxidation of biomass
InactiveUS9458569B2Mitigate gas pocket formationEasy to unifyPretreatment with water/steamWater treatment parameter controlBioproductsFiber
The present disclosure comprises methods, apparatus, components, and techniques for pretreatment of biomaterials using targeted wet oxidation. The targeted wet oxidation pretreatment is an upstream method for converting solid biomass into fuels and / or specialty chemicals. Embodiments of the present disclosure comprise methods carried out on biomaterials to selectively oxidize lignin components of the biomass, thereby resulting in bio accessible / digestible biomass fibers. In embodiments of the present disclosure, such methods may comprise pretreatment processes to prepare the biomaterials for a subsequent fermentation or other like conversion may be carried out to result in useful bio fuels or other bioproducts.
Owner:CLEAN VANTAGE
Wet oxidation of biomass
InactiveUS20140199740A1Mitigate gas pocket formationEasy to unifyPretreatment with water/steamWater treatment parameter controlFiberBioproducts
The present disclosure comprises methods, apparatus, components, and techniques for pretreatment of biomaterials using targeted wet oxidation. The targeted wet oxidation pretreatment is an upstream method for converting solid biomass into fuels and / or specialty chemicals. Embodiments of the present disclosure comprise methods carried out on biomaterials to selectively oxidize lignin components of the biomass, thereby resulting in bio accessible / digestible biomass fibers. In embodiments of the present disclosure, such methods may comprise pretreatment processes to prepare the biomaterials for a subsequent fermentation or other like conversion may be carried out to result in useful bio fuels or other bioproducts.
Owner:CLEAN VANTAGE
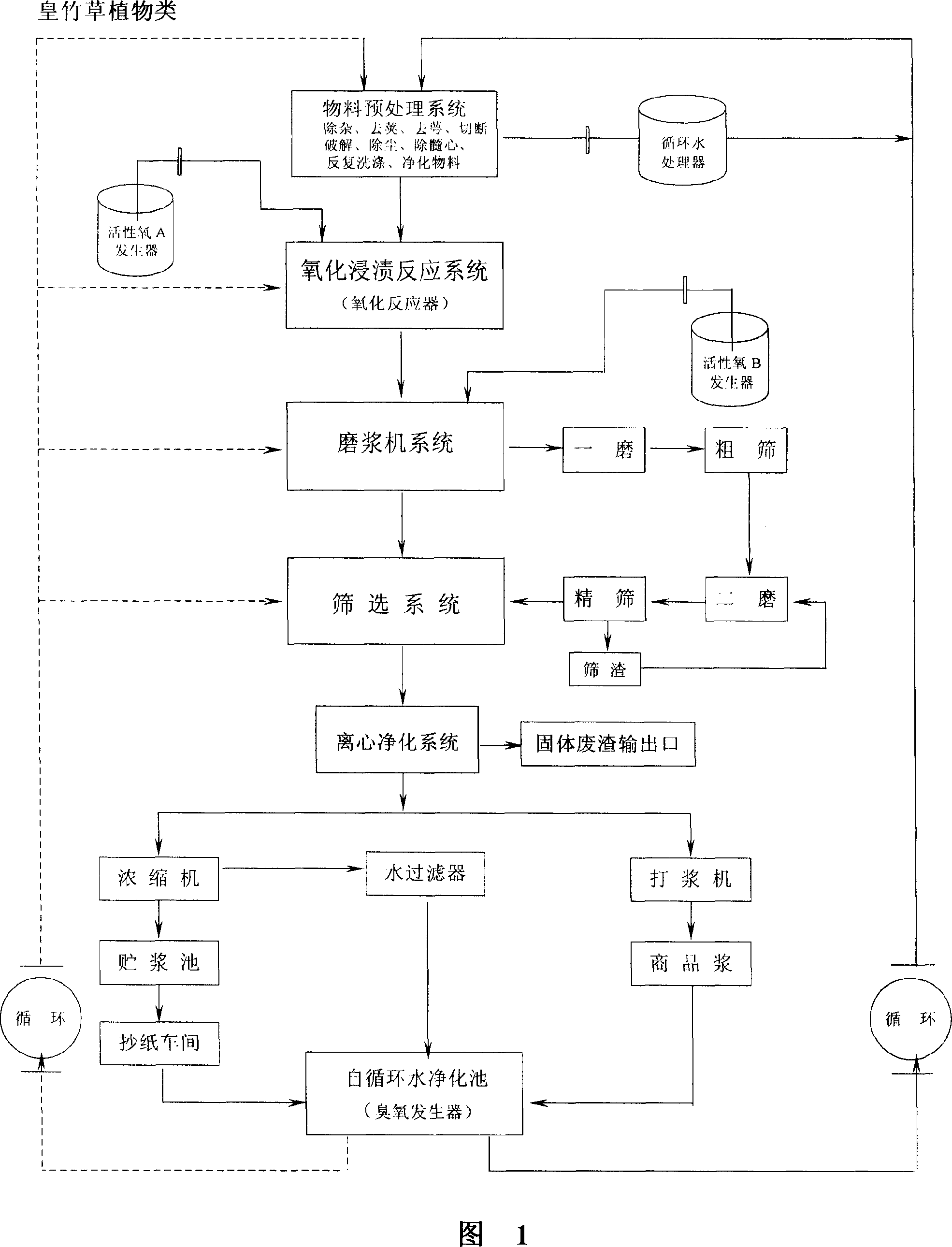
Method for hybrid giant napier producing in oxygen free radical doffing/bleaching integrated reactor with albefaction paper stuff
InactiveCN101063276ANo pollution in the processNo emissionsPretreatment with oxygen-generating compoundsPaper/cardboardBoiling processPlant cell
The invention discloses a method for producing poach paper slurry in an oxygen free radical remove / poach reaction kettle via bamboo grass, comprising that rotating an electric accelerator in the kettle to transmit electrons in an organic solution, to supply the electrons to basic oxygen, to generate the ultra-oxygen anion free radical (O2-. / HOO.) in the oxidization reaction kettle to transform and separate lignin, to change the color group of the plant cell layer, to obtain slurry. The invention can be applied on hard plants as bamboo, reed or the like. The invention completely changes the chemical slurry technique with serious pollutions as acid, alkali or the like, which avoids recycling alkali to save cost, and avoids boiling process and poaching tower with serious pollution, to utilize abundant resource, save water and reduce cost.
Owner:BEIJING GUOLIYUAN POLYMER SCI & TECH R & D CENT
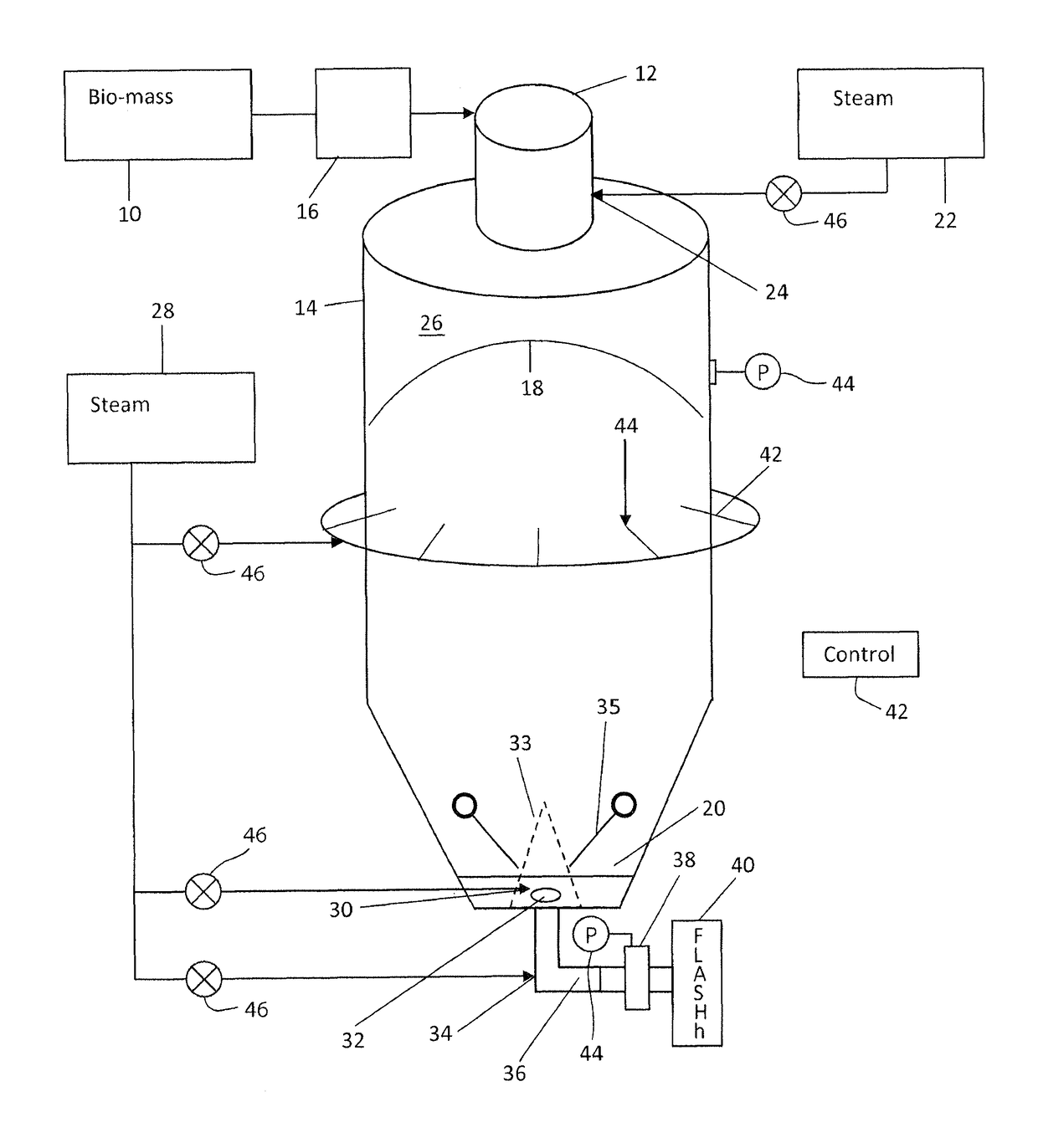
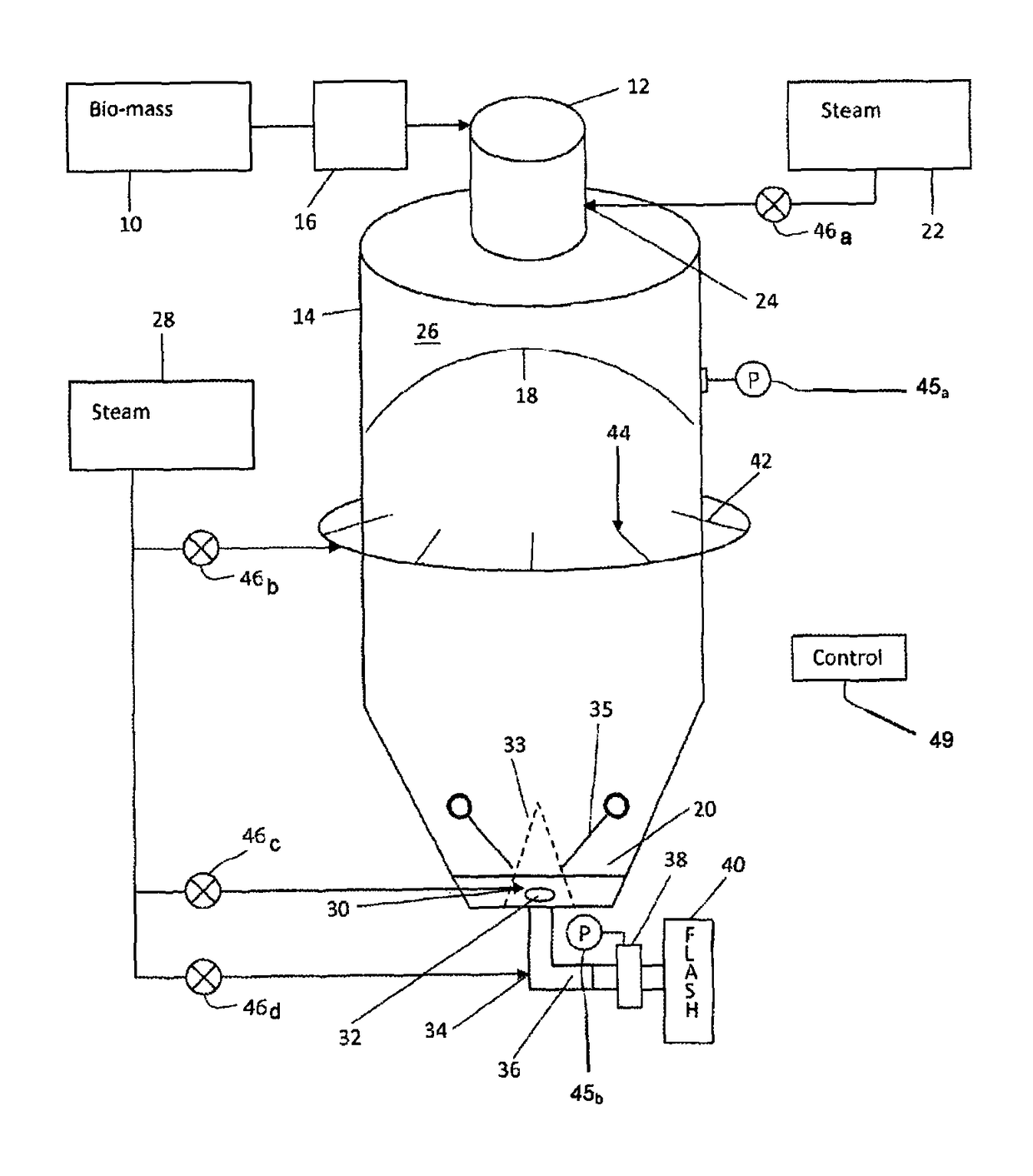
Method and apparatus for adding steam for a steam explosion pretreatment process
ActiveUS9856601B2Increase volumeReducing and eliminating rat-holesPretreatment with water/steamBiological substance pretreatmentsProcess engineeringBiomass
A method for treating cellulosic biomass feed stock including: feeding the feed stock to an upper inlet of a vertical reactor vessel, wherein the feed stock is deposited on a pile of feed stock within the vertical reactor vessel; adding heat energy to heat the feed stock by injecting steam to an upper region of the vertical reactor vessel; propelling the feed stock through an outlet in a lower region of the vertical reactor vessel by injecting steam into the biomass at, near or after the bottom outlet of the vertical reactor vessel, and moving the propelled feed stock through an expansion device, such as a steam explosion device, to subject the feed stock to a steam explosion process.
Owner:ANDRITZ INC
Short oxygen delignification method
InactiveUS20160122945A1Rapid and efficient mixingKeep energy smallPretreatment with water/steamTransportation and packagingOxygenMechanical engineering
A short oxygen delignification method employs a mixing assembly including a mixing chamber having an interior wall which is generally symmetrical about a central longitudinal axis. At least one inlet is used to introduce paper pulp, a basic compound, optional steam and an oxygen-containing gas into the mixing chamber. At least one axial baffle is connected to and extends along the interior wall. At least one transverse baffle is connected to and extends from the interior wall transverse to the axis. A rotatable agitator includes at least one agitator baffle extending transverse to the axis at a location in alignment with a respective transverse baffle. This forms at least one gap between the at least one agitator baffle and the at least one respective transverse baffle. The paper pulp fluid is forced to travel through the at least one gap. A short delignification reaction occurs inside the mixing chamber. Delignified paper pulp fluid leaves the mixing chamber through at least one outlet of the mixing chamber.
Owner:QUANTUM TECH INC
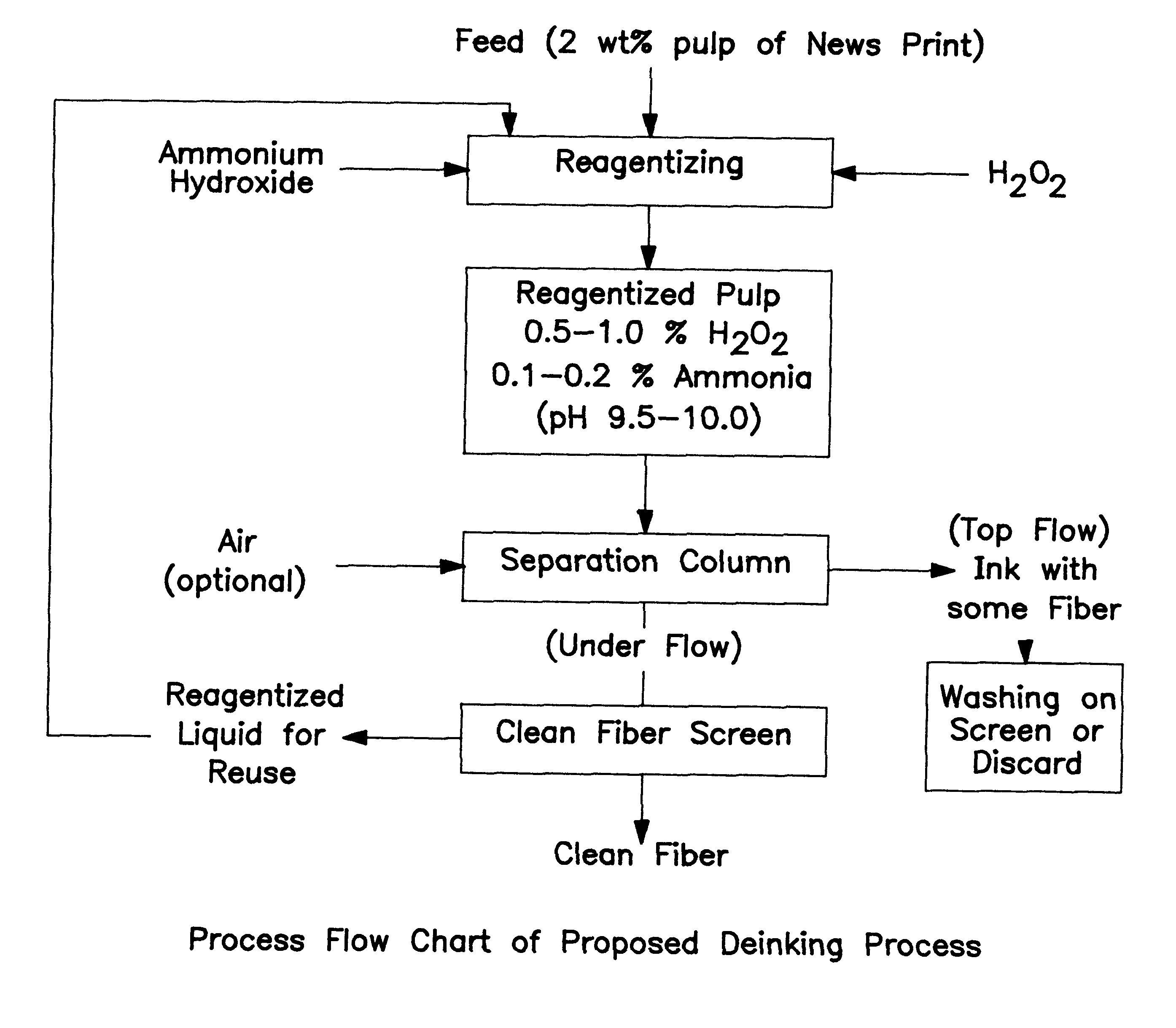
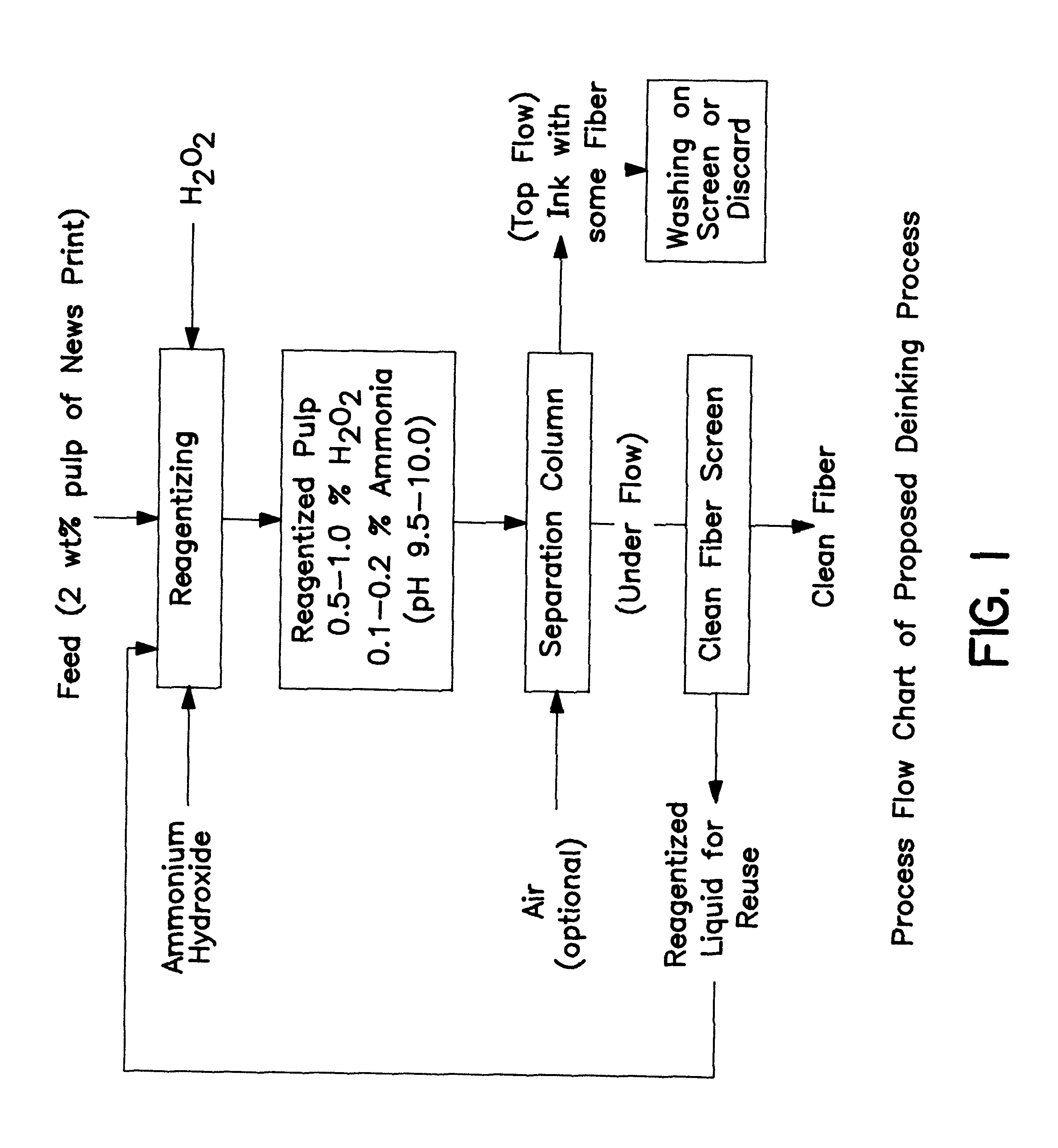
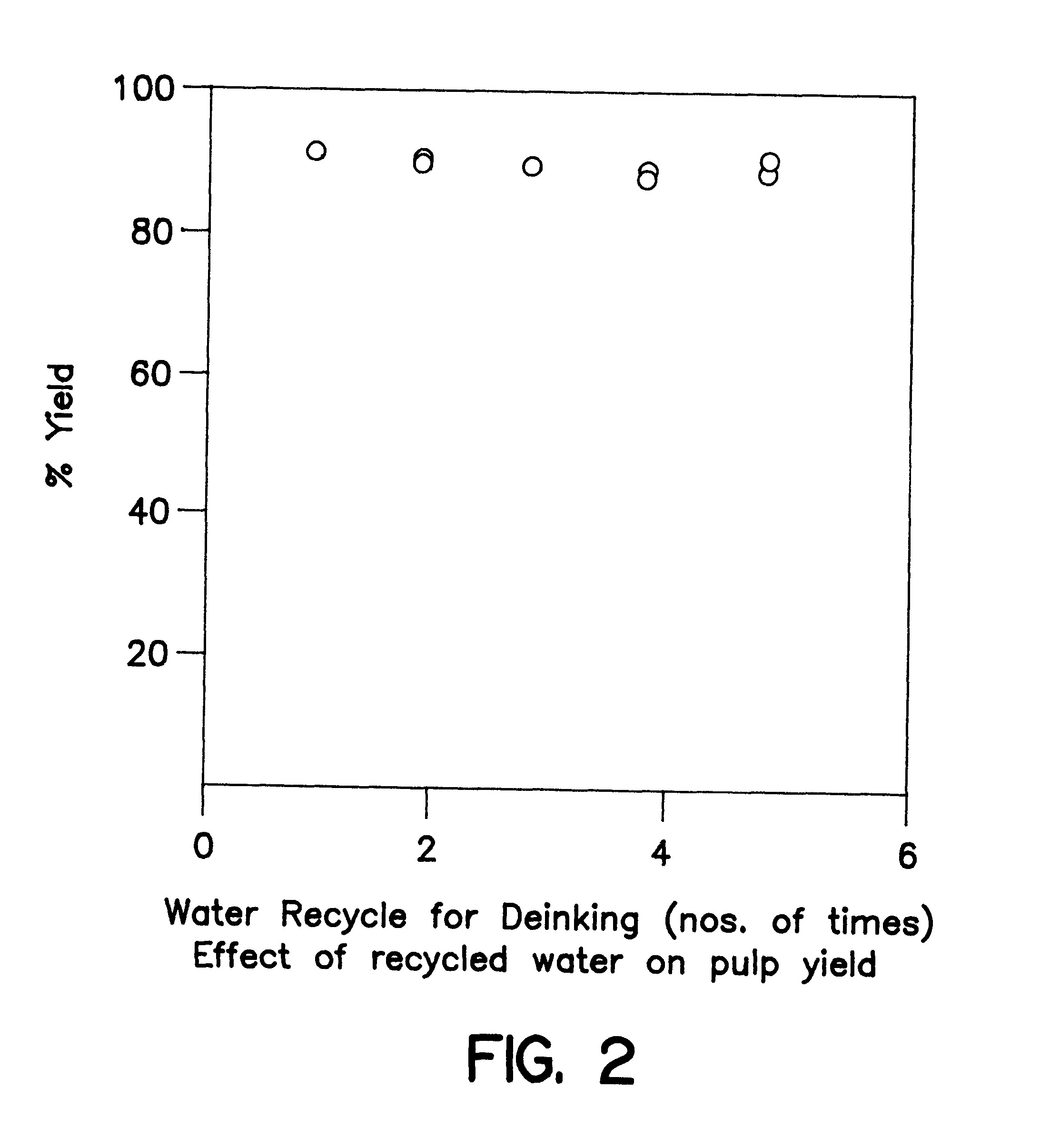
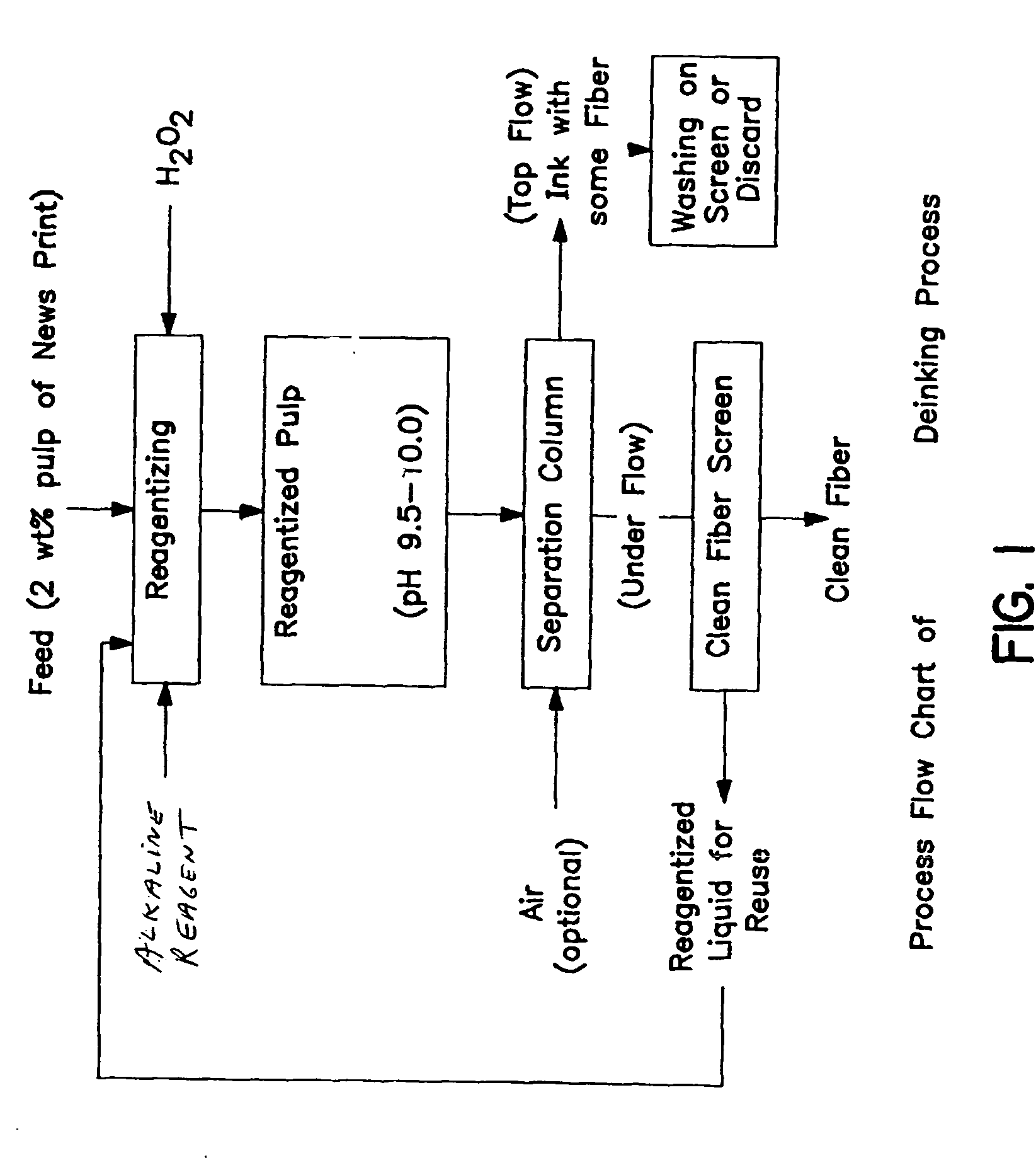
Method of de-inking paper and other cellulosic materials
InactiveUS6217706B1Pretreatment with alkaline reacting compoundsPaper recyclingCellulose fiberAmmonium hydroxide
A method of de-inking cellulosic fibrous materials comprising:a. admixing an alkaline reagent selected from the group consisting of ammonium hydroxide and hydrogen peroxide and mixtures thereof with an aqueous suspension of inked cellulosic fibrous material such that they react at the ink particle / cellulosic fiber interfaces to dislodge ink particles from the cellulosic materials; andb. removing the dislodged ink particles from the aqueous suspension.
Owner:FLORIDA UNIV OF A FLORIDA
Method for hybrid giant napier producing in oxygen free radical doffing/bleaching integrated reactor with dried bananas stalk
InactiveCN101063278AImprove reuseProtect environmentPulp liquor regenerationPretreatment with oxygen-generating compoundsBoiling processPlant cell
The invention discloses a method for generating poach paper slurry in an oxygen free radical remove / poach reaction kettle via dry banana stems, comprising that rotating an electric accelerator in the kettle to transmit electrons in an organic solution, to supply the electrons to basic oxygen, to generate the ultra-oxygen anion free radical (O2-. / HOO.) in the oxidization reaction kettle to transform and separate lignin, to change the color group of the plant cell layer, to obtain slurry. The invention can be applied on tropical plant as tropical plant or the like. The invention completely changes the chemical slurry technique with serious pollutions as acid, alkali or the like, which avoids recycling alkali to save cost, and avoids boiling process and poaching tower with serious pollution, to utilize abundant resource, save water and reduce cost.
Owner:BEIJING GUOLIYUAN POLYMER SCI & TECH R & D CENT
Method of de-inking paper and other cellulosic materials
InactiveUS20050145349A1Efficient processingPretreatment with alkaline reacting compoundsPaper recyclingSodium bicarbonateAmmonium hydroxide
A method of de-inking cellulosic fibrous materials comprising: 1) admixing an alkaline reagent with hydrogen peroxide and an aqueous suspension of inked cellulosic fibrous material in amounts whereby the alkaline reagent and hydrogen peroxide react at the ink particle / cellulosic fiber interfaces to dislodge the ink particles from the cellulosic materials; and, 2) removing the dislodged ink particles from the aqueous suspension, wherein the alkaline reagent comprises sodium carbonate or a mixture of sodium carbonate and a) ammonium hydroxide, b) sodium bicarbonate or c) mixtures of sodium carbonate and ammonium hydroxide.
Owner:FLORIDA UNIV OF A FLORIDA +1
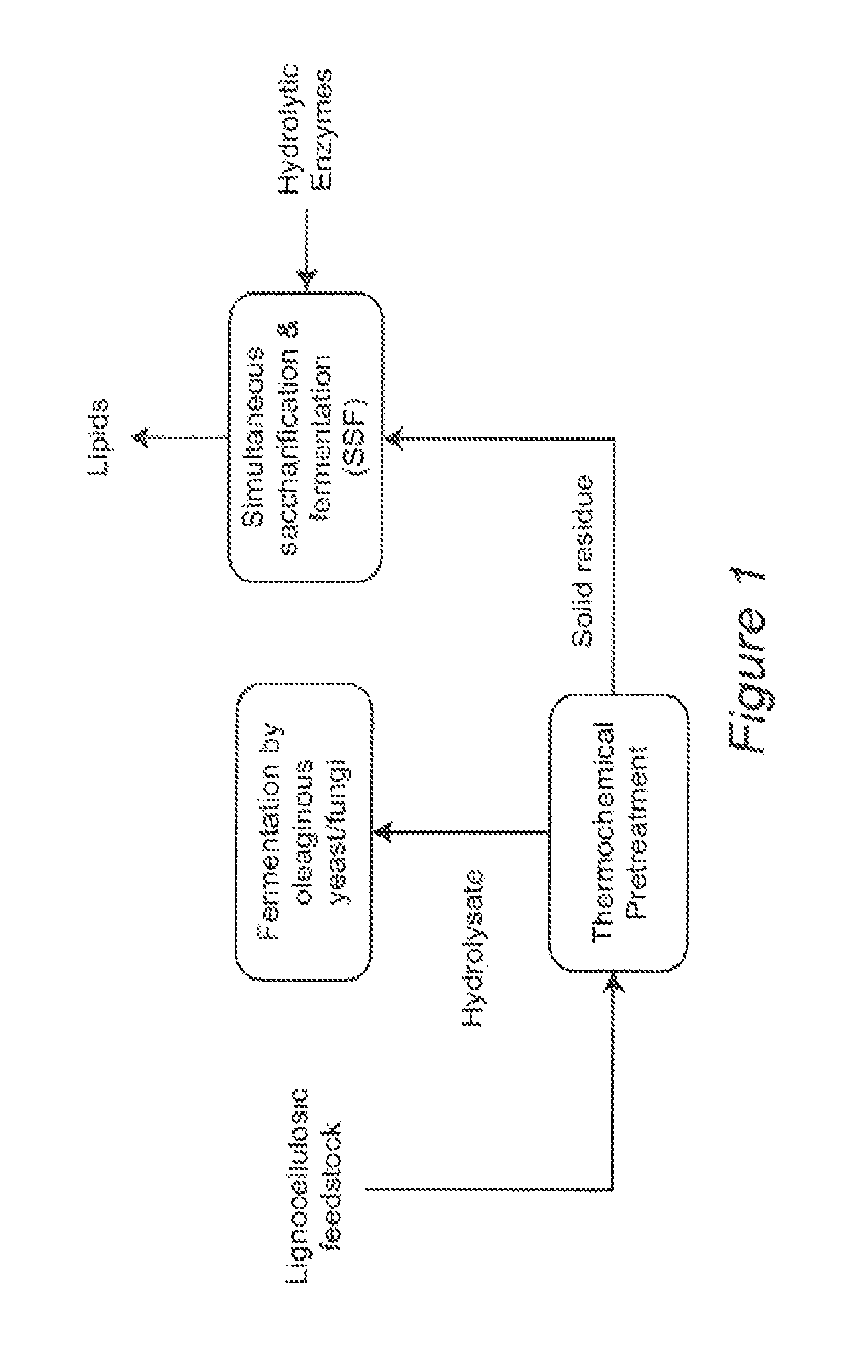
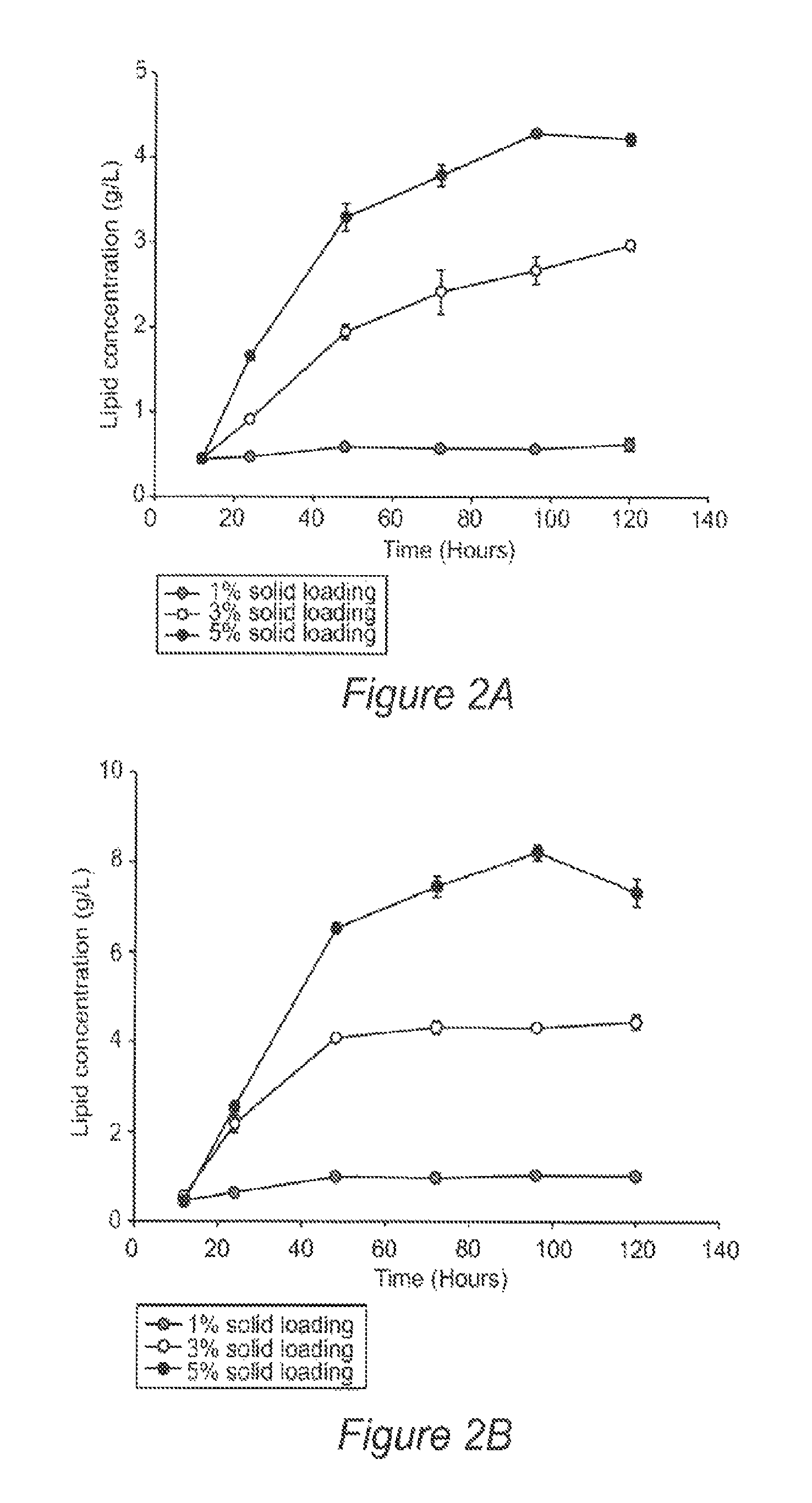
Simultaneous saccharification and fermentation(SSF) of lignocellulosic biomass for single cell oil production by oleaginous microorganisms
InactiveUS9322038B2Pretreatment with oxygen-generating compoundsWaste based fuelMicroorganismLignocellulosic biomass
Methods for producing lipids from lignocellulosic biomass are provided. Sugars produced by pretreatment of lignocellulosic biomass are utilized by heterotrophic oleaginous fungi or yeast to increase their biomass and to produce lipids without prior detoxification of the pretreated biomass. After the fungi / yeast are cultured with the sugars, solid residues from the pretreated biomass are combined with the fungi / yeast under conditions which allow simultaneous 1) enzymatic degradation of cellulose and / or hemicellulose to produce sugars and 2) fermentation of the sugars for further increases in biomass and lipid production.
Owner:WASHINGTON STATE UNIVERSITY
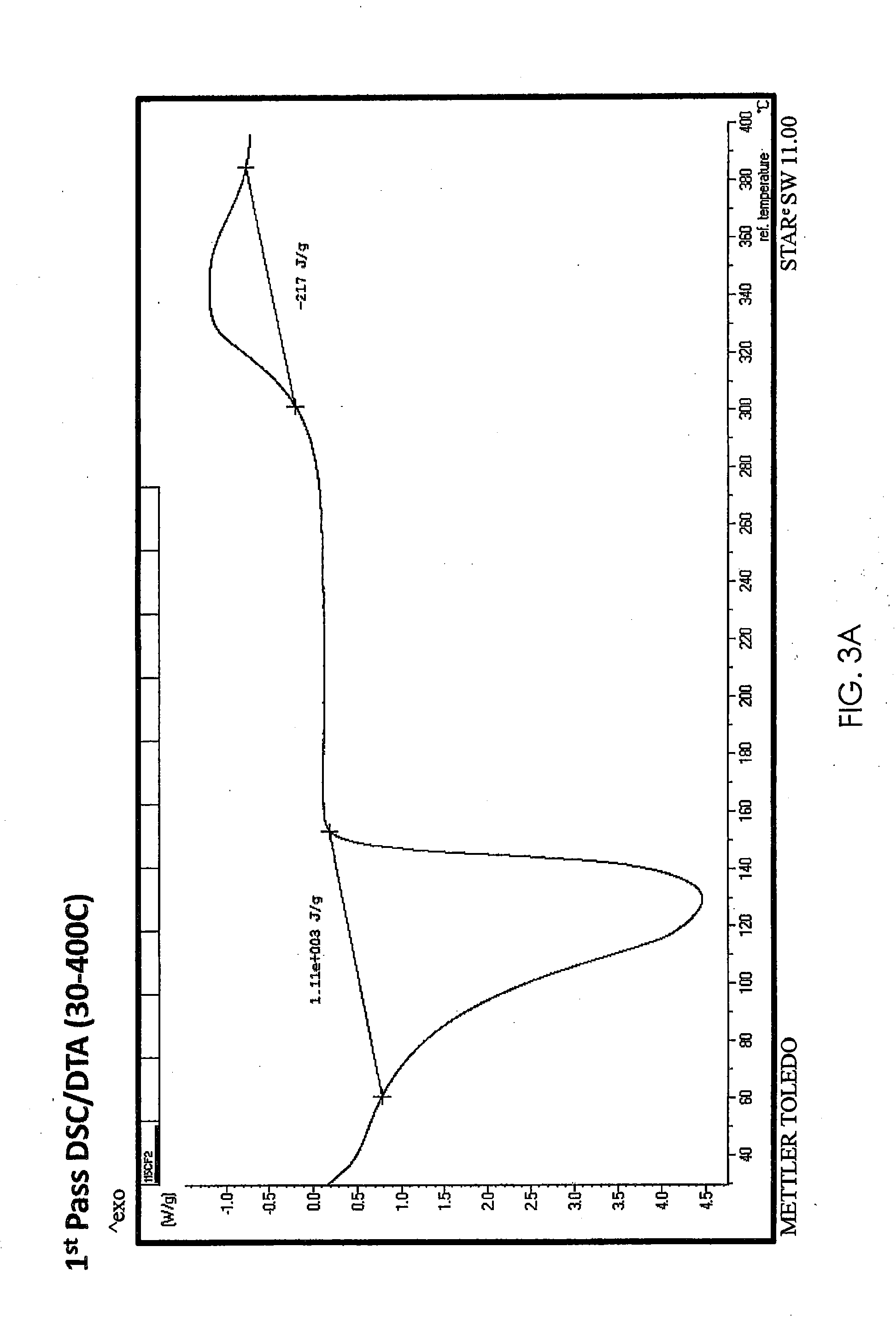
Cellulose solution manufacturing method, cellulose precipitate manufacturing method, cellulose saccharification method, cellulose solution, and cellulose precipitate
InactiveUS20130177948A1Improve hydrophilicityBig burden to solveOther chemical processesPaper recyclingCelluloseAqueous solution
The invention relates to a cellulose solution manufacturing method including: performing an ozonation treatment to bring a cellulose-containing material and ozone into contact with each other; and performing an alkali treatment to bring the obtained treated material and an alkali aqueous solution into contact with each other, thereby dissolving at least cellulose in the cellulose-containing material brought into contact with the ozone in the alkali aqueous solution. According to the invention, it is possible to provide a method of manufacturing a cellulose solution in which cellulose can be dissolved in a more simple manner, a method of manufacturing a cellulose precipitate in which cellulose can be recovered from the cellulose solution, and a method of saccharifying cellulose which uses the cellulose precipitate.
Owner:EHIME PREFECTURAL GOVERNMENT +1
Compositions comprising parenchymal cellulose particulate material
ActiveCN106795328AWorkmanship is effectiveSimple processPretreatment with oxygen-generating compoundsDrilling compositionCelluloseWater dispersible
The invention relates to a composition comprising a plant-derived cellulose particulate material comprising less than 30 wt% extractable glucose; and extractable xylose in an amount of at least 3 % of the amount of extractable xylose in the starting plant material, and an agent selected from the group comprising natural ionic polymersor natural non-ionic polymers; synthetic water dispersible polymers, and / or associative thickeners, and its various uses, including as a drilling fluid.
Owner:SELLYUKOMP LTD
Treated kraft pulp compositions and methods of making the same
ActiveCN104746375AImprove responseHigh yieldCellulosic pulp after-treatmentPretreatment with oxygen-generating compoundsFiberHemicellulose
Compositions including treated Kraft pulp, useful for making rayon fibers, having a lower degree of polymerization, a high R18, a low hemicellulose content, and high reactivity, are described. Methods of making the compositions are also described.
Owner:WEYERHAEUSER NR CO
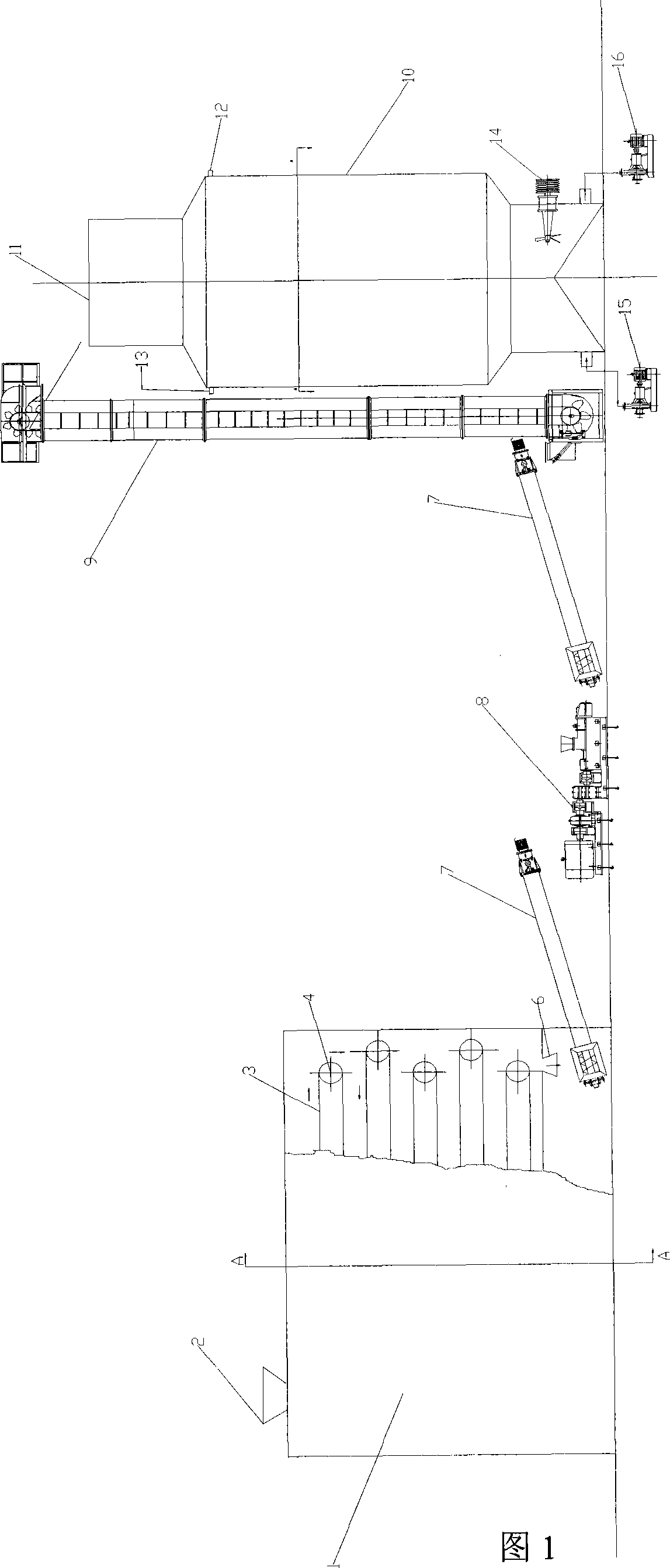
Method for preparing straw pulp with high yield by oxidation kneading and equipment used therefor
InactiveCN101161927AGuaranteed StrengthScientific and reasonableDigestersPretreatment with oxygen-generating compoundsOxygenHemicellulose
The invention discloses a method of oxidation rubbing high yield making straw pulp and equipment thereof, comprising the following process steps: firstly, straw is input into a feeding port (2) after being cut off and dust removed; secondly, promoter is prepared; thirdly, after the prepared promoter is diluted by water, material is injected when heated to 60-80 degree centigrade, then 2-4 percent of the total weight of the promoter and the material are stirred uniformly and input into an oxygen impregnating machine (1) for reacting; fourthly, the material after being oxygen impregnated is input into a rubbing machine (8) through a first feed screw (7) for vertically separating into wires; fifthly, the rubbed material is input into an oxygen dissolving machine (11) for oxygen dissolving. Processing equipment used by the method is orderly combined by the oxygen impregnating machine (1), the feed screw (7), the rubbing machine (8), a second feed screw (7), a hoist (10) and the oxygen dissolving machine (11). The invention can reserve most lignin, parenchyma cell and hemicellulose, has high pulp yield, and reduces environmental pollution.
Owner:朱晓平
Low energy consumption clean paper pulp extracting method and papermaking process thereof
InactiveCN101694075BAchieve recyclingGood flexibilityPretreatment with alkaline reacting compoundsPulp de-wateringFiberChemical solution
The invention relates to a low energy consumption clean paper pulp extracting method and a papermaking process thereof, solving the problems that fibrous raw materials need to be boiled at high temperature and pressure in the pulp preparing and papermaking processes and chemical solutions produce a large quantity of black or red liquid in the pulp preparing and papermaking processes to cause great waste to resources and great pollution to the environment in the prior art. The invention adopts the following technical scheme: the low energy consumption clean paper pulp extracting method is realized by removing impurities from biomass raw materials rich of fiber, crushing, softening and soaking, separating organic matters, grinding and pulping, wherein a softening and soaking solution contains the following components in percent by weight: 10-20 sodium oxide, 3-5 sodium carbonate, 0.5-2.5 penetrating agent T, 0.5 magnesium oxide and 0.05-0.15 chelating agent EDTA. The papermaking processmatched with the method comprises the following steps: getting materials ready, rubbing to devillicate, soaking to react, separating liquid medicine, spirally squeezing pulp, refining with high consistency, removing slag, coarsely screening and making paper. The pulp preparing process has simple course, no high requirements on environment and equipment condition, easily popularized technology, norequirement on the scale of production, low costs for building production lines and purchasing equipment and less running expense.
Owner:林宣禧
Process for fractionating sugarcane bagasse into high alpha-cellulose pulp, xylan and lignin
ActiveUS8529731B2Simple and efficientHigh yieldPretreatment with water/steamFats/resins/pitch/waxes removal in pulpXylanFractionation
Sugarcane bagasse consists of mainly three polymeric components, namely cellulose (40-45%), hemicellulose (xylan) (28-30%), and lignin (19-21%). A process is herein disclosed for fractionating sugarcane bagasse into cellulose, hemicellulose and lignin with high purity α-cellulose, which is a useful raw material for preparing cellulose esters like cellulose triacetate and other high value-added cellulose plastics. Co-production and recovery of hemicellulose (xylan) and lignin in high yields and high purities, along with α-cellulose, is another important feature of this process. Sugarcane bagasse consists of a material known as pith which constitutes 30-35% by weight of bagasse. Pith contains cellulose, hemicellulose, and lignin, in addition to various other ingredients and cell mass. The process described herein discloses the use of partially depithed bagasse as a preferred raw material for fractionation. Use of sugarcane bagasse containing pith leads to a product which is lower in yield as well as poorer in color.
Owner:COUNCIL OF SCI & IND RES
Fibrous cellulose composite resin and method for producing same
PendingCN114207007APretreatment with oxygen-generating compoundsVegetal fibresPolymer scienceResin-Based Composite
Owner:DAIO PAPER CORP
Advanced methods for sugar production from lignocellulosic biomass and fermenting sugars to microbial lipids
Methods for facilitating sugar release from lignocellulosic biomass and for utilizing the sugars for microbial lipid (e.g. biofuel) production are provided. The methods involve pretreating lignocellulosic biomass using various oxidizing agents (ozone, peroxone, etc.) at a temperature not higher than 50 DEC and pressure no higher than 1.5 atm to render the biomass more accessible to enzymatic hydrolytic degradation into sugars and utilizing soluble sugars for fermenting oleaginous microorganism to produce microbial lipids.
Owner:WASHINGTON STATE UNIVERSITY
Method for catalytic oxidation of cellulose and method for making a cellulose product
ActiveUS10767307B2Effectively and selectively oxidizing C-Improve efficiencyPulp properties modificationPretreatment with oxygen-generating compoundsPolymer sciencePtru catalyst
Owner:UPM-KYMMENE OYJ
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com