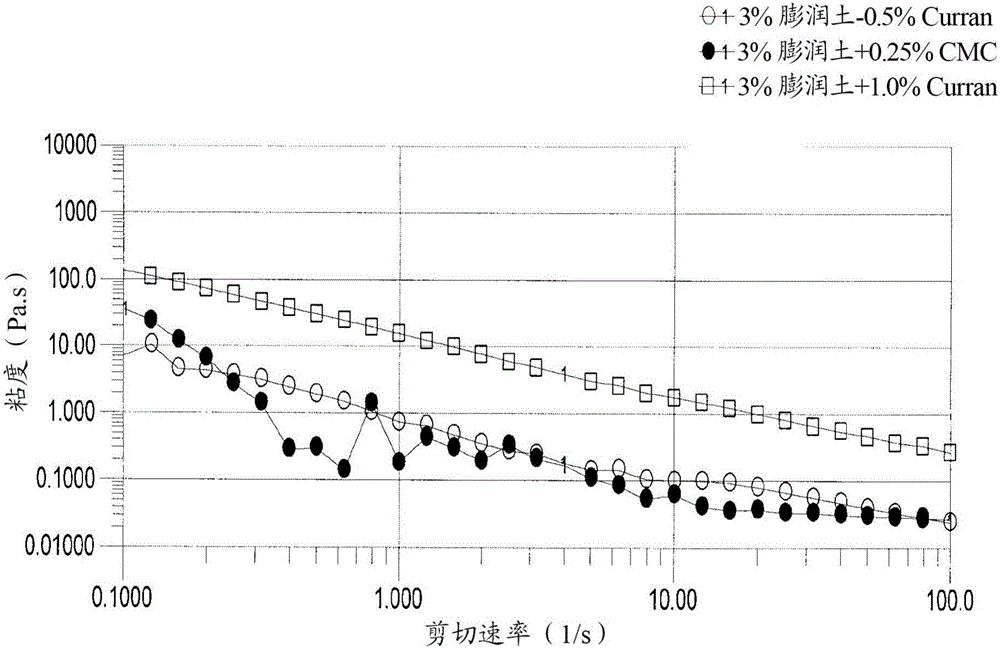
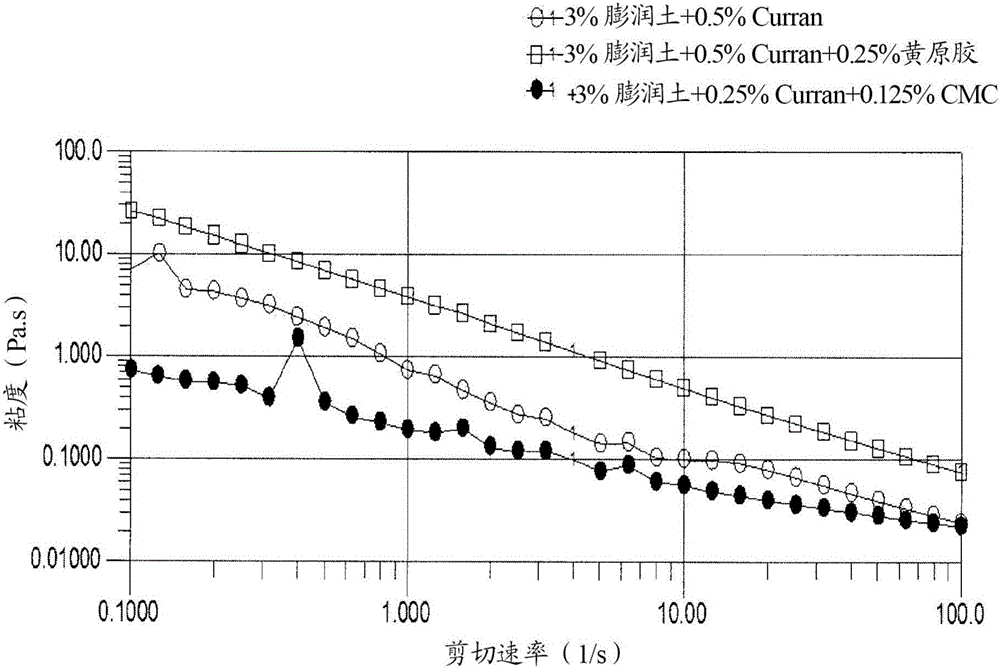
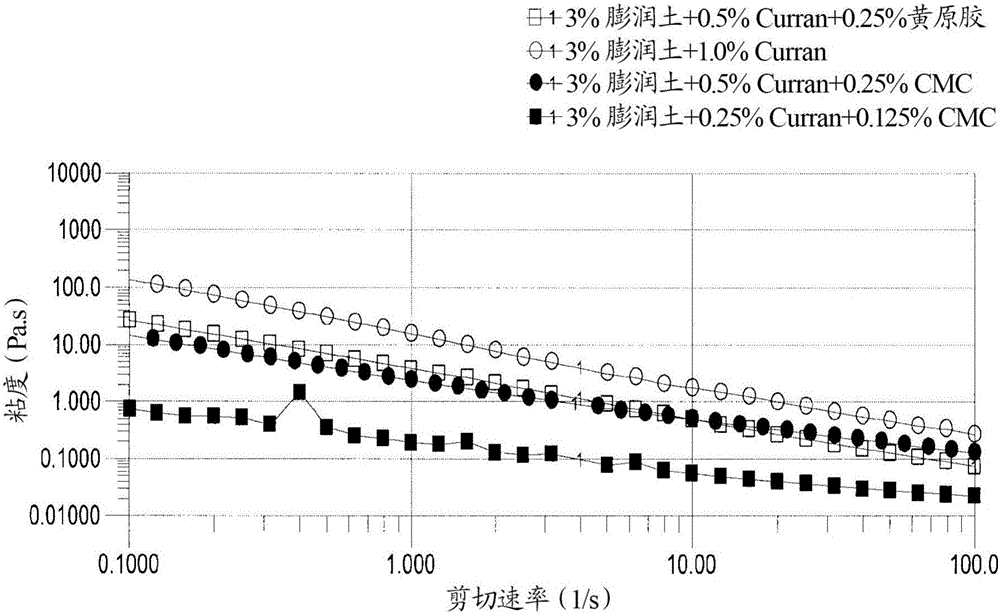
Compositions comprising parenchymal cellulose particulate material
一种颗粒材料、组合物的技术,应用在钻孔的组合物、用产生氧化合物预处理、化学仪器和方法等方向,能够解决组合物不适合应用、未示出滤饼形成特性等问题
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0151] Method for measuring viscosity and pH over reaction time for hydrogen peroxide treated root vegetable pulp
[0152] Fresh carrots were peeled, chopped and steamed at 90°C for 2 hours. The carrots were then homogenized in the cooking liquor using a Silverson FX homogenizer to form a slurry with particles less than 500 microns in diameter. The consistency of the slurry was measured as 5% solids in water using a moisture analyzer. The batch was then divided into a number of 1 liter samples, each contained in a polypropylene bottle with a tight fitting lid. Then, the bottles were placed in a water bath of hot water adjusted to 90°C. Check the internal temperature of the bottle periodically. When the temperature reached 90°C, 35% hydrogen peroxide was added to each bottle at a ratio of 1 part 35% peroxide to 1 part carrot solids. The bottles were then left in water at 90°C for varying lengths of time. The bottles were removed from the water bath at regular intervals and...
Embodiment 2
[0153] Example 2: Preparation of low-viscosity cellulosic granular material from sugar beets
[0154] 900 g of beet pellets were washed and hydrated by adding them to warm water, with the dirty water draining through a sieve. This beet hydrate is placed in a vat in excess water and agitated, then scooped out with a strainer and washed with water to ensure no stones / grit get into the next stage of processing.
[0155] The washed beets were then cooked at 100°C for 3 hours before being homogenized using a Silverson FX homogenizer fitted with an initially coarse stator screen and moving down to a small hole emulsifier screen (Process time 15 minutes for each sieve). Solids were measured using an Oxford solids meter and the mixture was adjusted to 2% solids by adding clean water.
[0156] Then, the mixture was placed in a 25 liter glass reaction vessel, and the dry solids content in the vessel was calculated. While the mixture was heating, peroxide was added based on a 0.25:1 r...
Embodiment 3
[0160] Example 3: Analysis of cellulose-containing particles for use in compositions
[0161] The dried material from three stages of the process (beginning; after peroxide treatment; after sodium hypochlorite treatment) was analyzed for extractable monosaccharide / polysaccharide content. The starting plant materials tested were beets and carrots.
[0162] The test procedure was carried out according to the standard two-step protocol below, which is based on the separation of polysaccharides from mono- and oligosaccharides by boiling the samples in 80% alcoholic solution. Monosaccharides and oligosaccharides are soluble in alcoholic solutions, while polysaccharides and fibers are insoluble. Soluble components can be separated from insoluble components by filtration or centrifugation. Both fractions (soluble and insoluble) can then be dried and weighed to determine their concentration.
[0163] The dried material can then be used for HPLC analysis after acid hydrolysis.
[0...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com