Method and apparatus for ALD on a rotary susceptor
a susceptor and rotary technology, applied in the field of method and apparatus for atomic layer deposition or epitaxy, can solve the problems of unwanted gas phase reaction, and low production rate of ald processes, and achieve the effect of minimizing gas cross-contamination
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
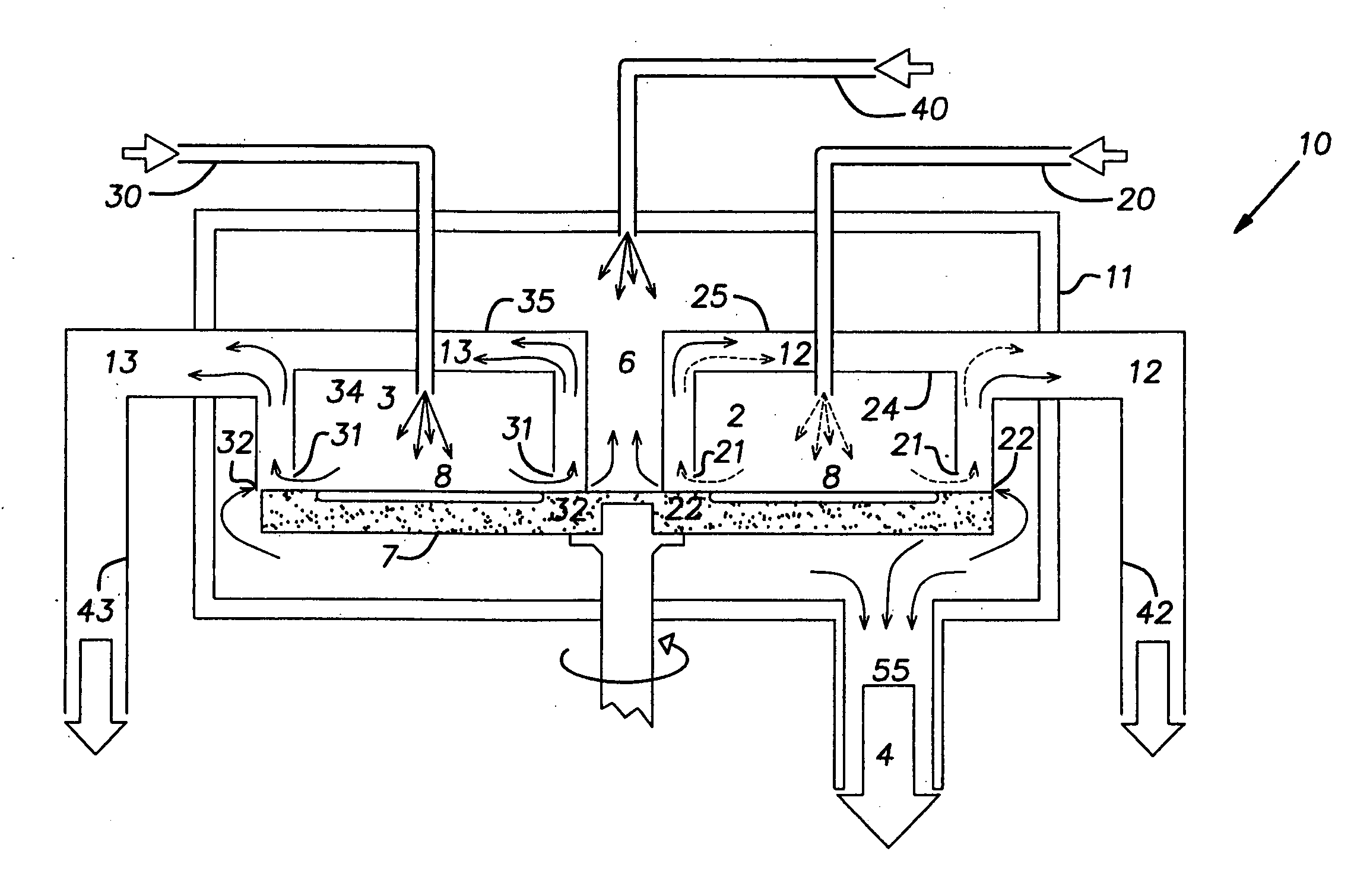
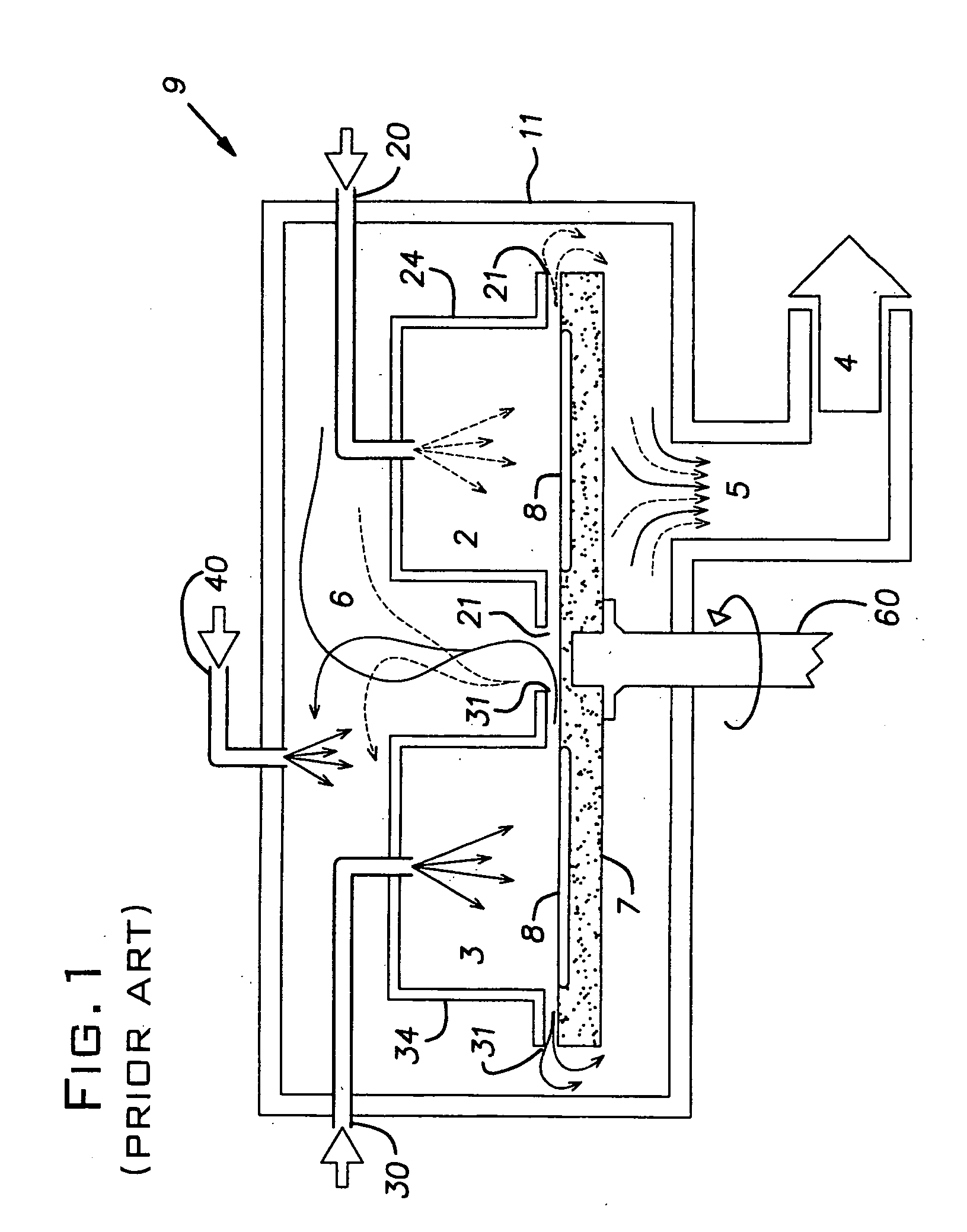
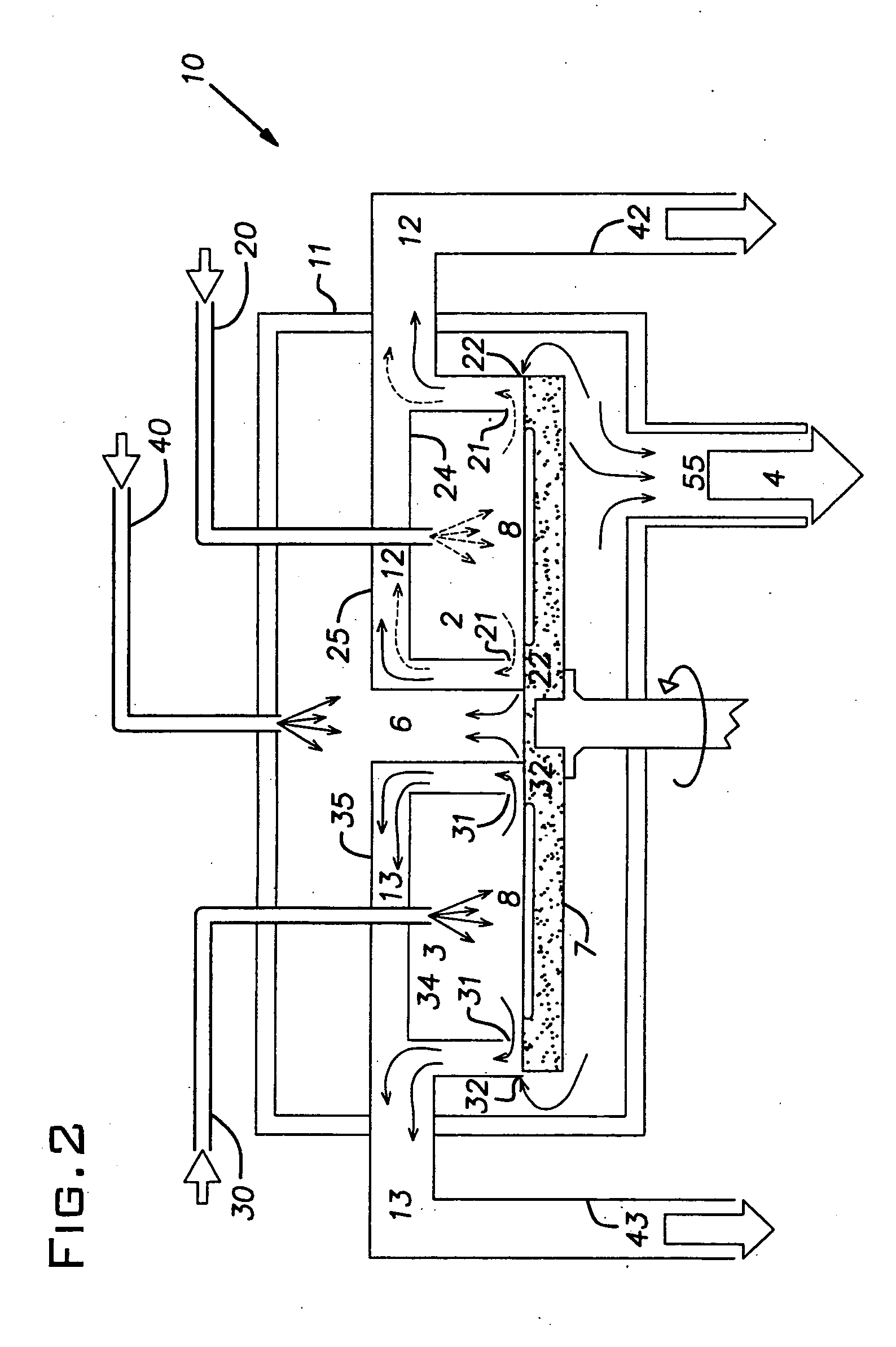
[0024] The present invention relates to an apparatus for use in CVD or ALD, using a rotary turntable susceptor. In the following description, the same numbers are used generally to refer to the same or similar parts.
[0025] The present invention is designed to avoid intermixing of non-compatible gases in any place close to the substrate environment. Referring to FIG. 2, the apparatus 9 has an outer enclosure 11. The outer enclosure contains reactive enclosures 24 and 34 having reactive zones 2 and 3 that are supplied by reactive gas inlet pipes 20 and 30 respectively. A neutral gas inlet 40 supplies a neutral flush gas to the buffer zone 6 in the outer enclosure. A pipe 55 leads to a pump 4. The substrates 8 rest on the susceptor, a rotary turntable 7. The reactive enclosures 24 and 34 are surrounded by ring-shaped channels 25 and 35 respectively. The ring-shaped channels 25 and 35 are connected to separate exhaust pipes 42 and 43 respectively.
[0026] In operation, the turntable car...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| deposition rate | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| distance | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| distance | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com