High performance composite tubular structures
a tubular structure, composite technology, applied in the direction of golf clubs, sport apparatus, fishing, etc., can solve the problems of reducing the diameter and reducing the performance of the tubular structure. , to achieve the effect of enhancing performance, reducing buckling, and being lighter and/or more resistant to buckling
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
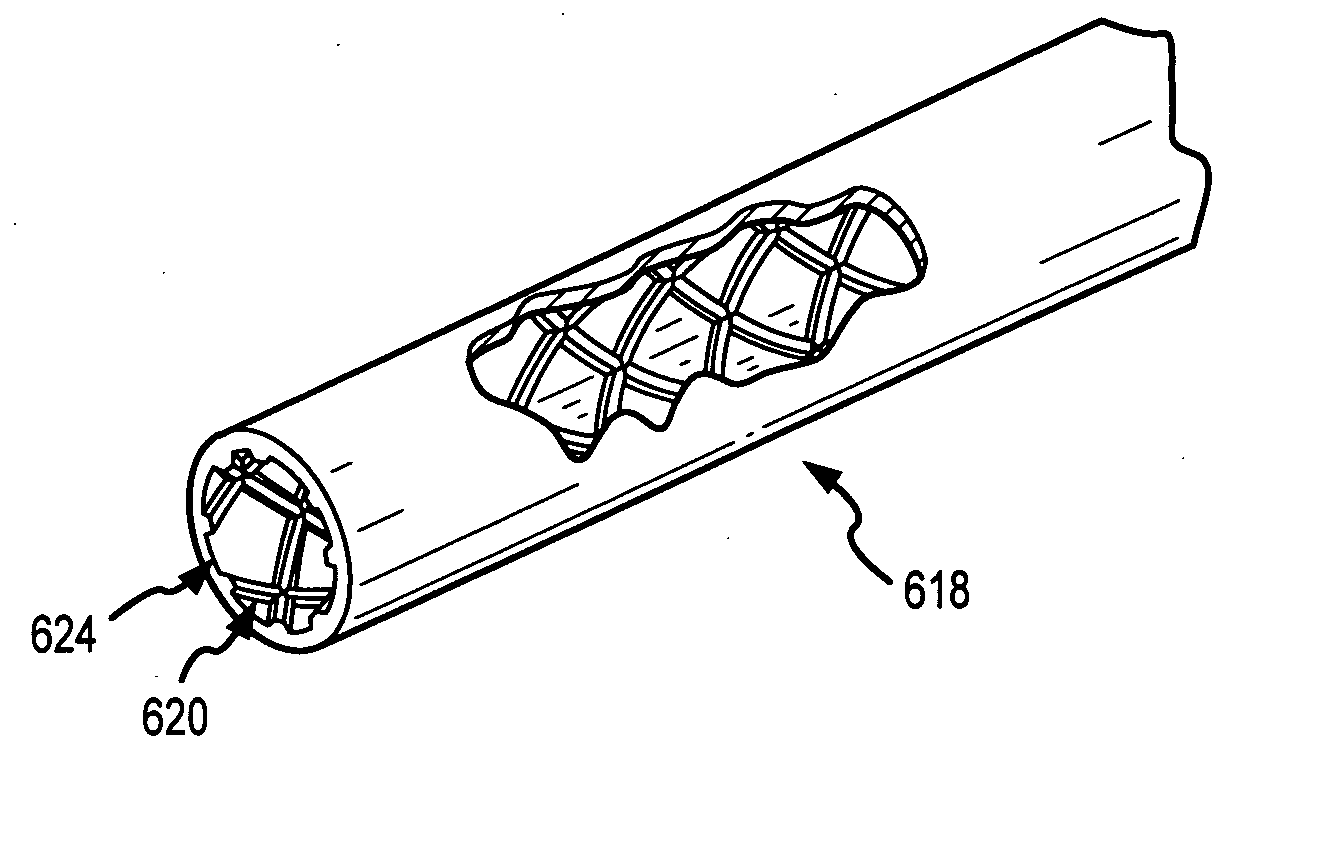
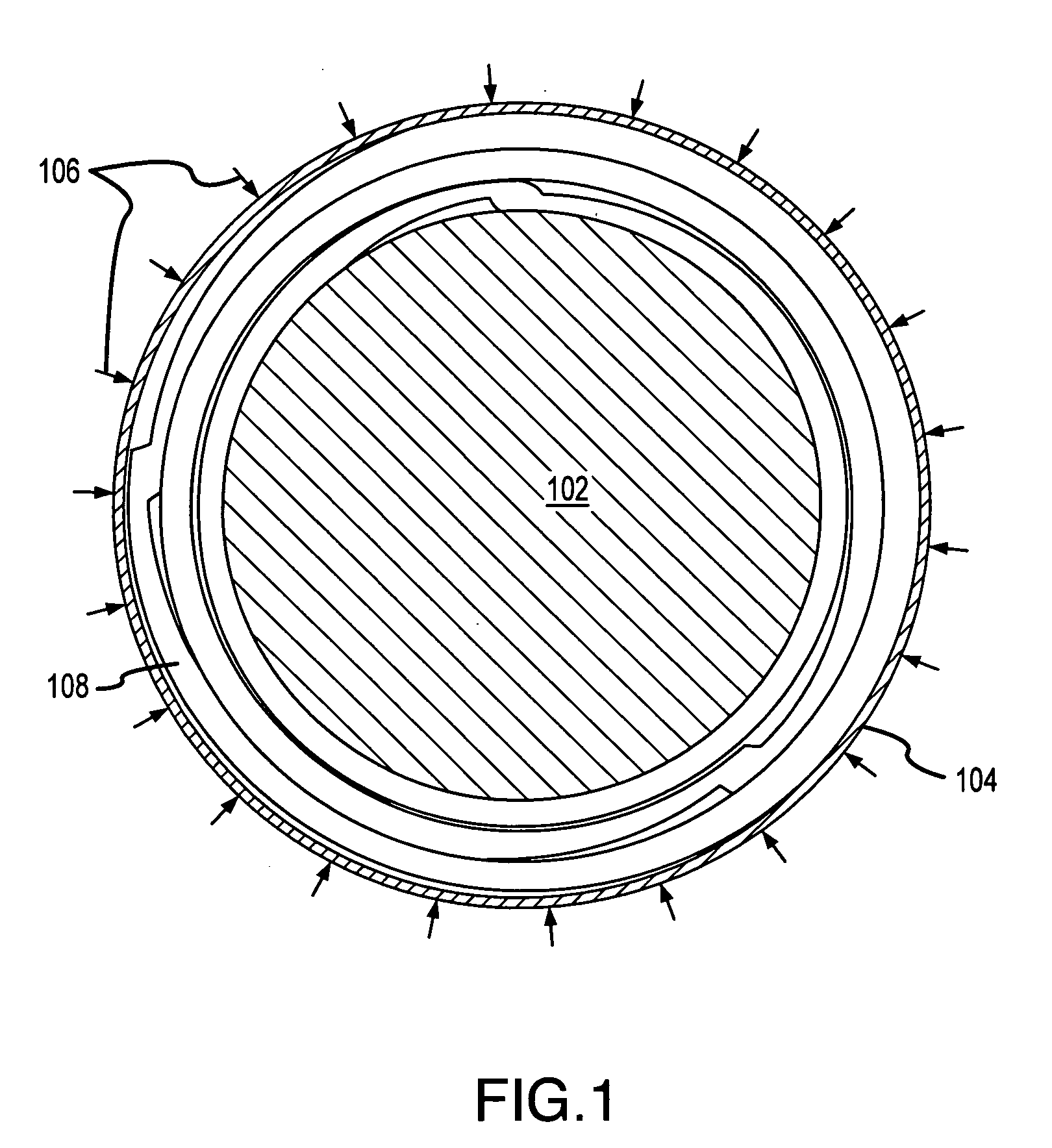
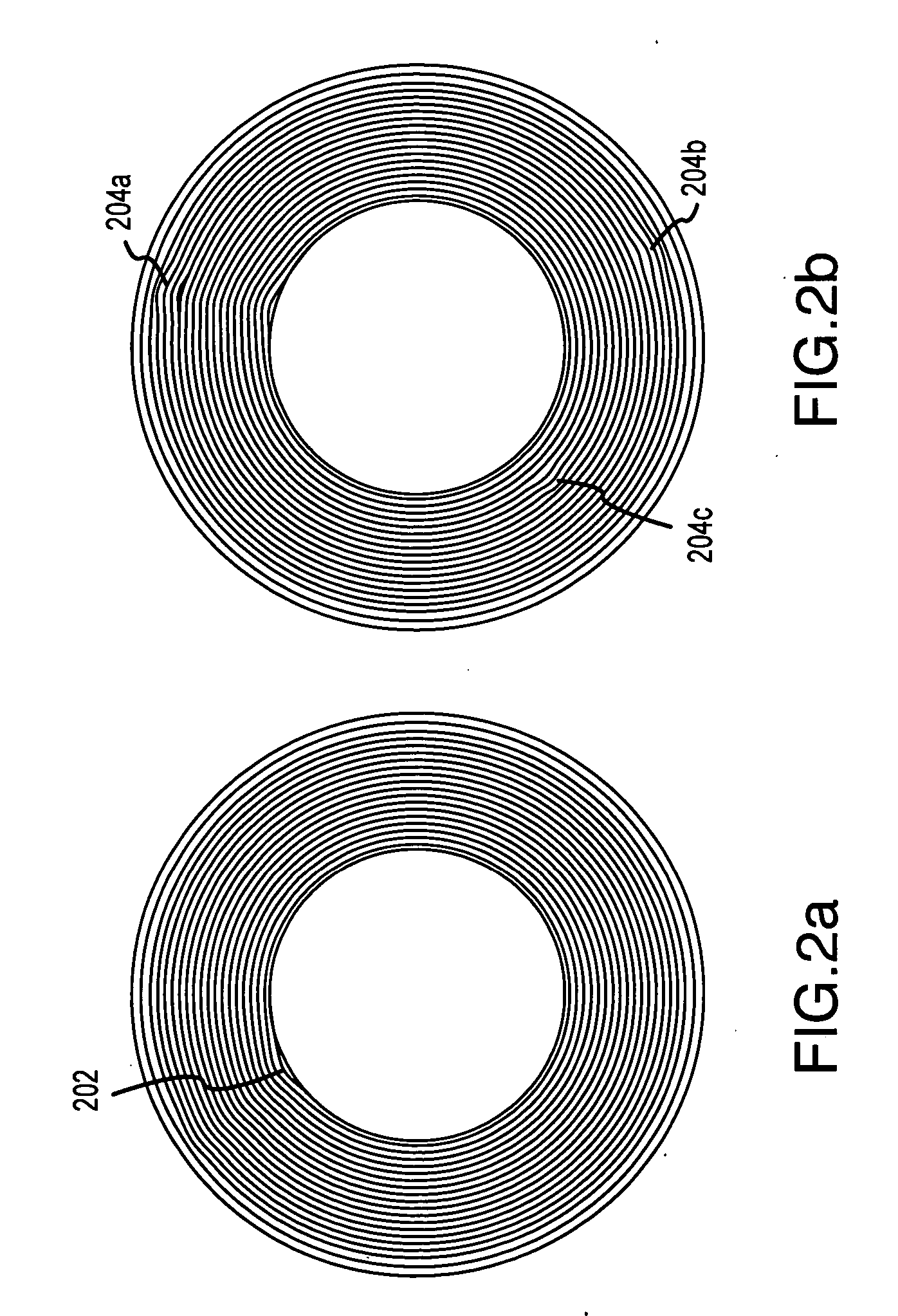
[0023] The following descriptions are of exemplary embodiments of the invention only, and are not intended to limit the scope, applicability or configuration of the invention in any way. Rather, the following description is intended to provide convenient illustrations for implementing various embodiments of the invention. As will become apparent, various changes may be made in the function and arrangement of the elements described in these embodiments without departing from the sprit and scope of the invention. For example, as described herein, integral ribs in accordance with the present invention are described as having a helical configuration, though, as mentioned above, various alternative configurations of ribs may likewise be used and still fall within the ambit of the appended claims.
[0024] That being said, with reference to FIGS. 4a-4c and 5a-5c and in accordance with one exemplary embodiment of the present invention, an expandable, elastomeric tube 408, with an outer surfa...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Angle | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Angle | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Angle | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com