Embolic protection device
a protection device and embolism technology, applied in the field of embolism protection devices, can solve the problems of neurological impairment, patient experiencing a loss of function, brain impairment either temporarily or permanently, etc., and achieve the effect of facilitating the maintenance of the filter position
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
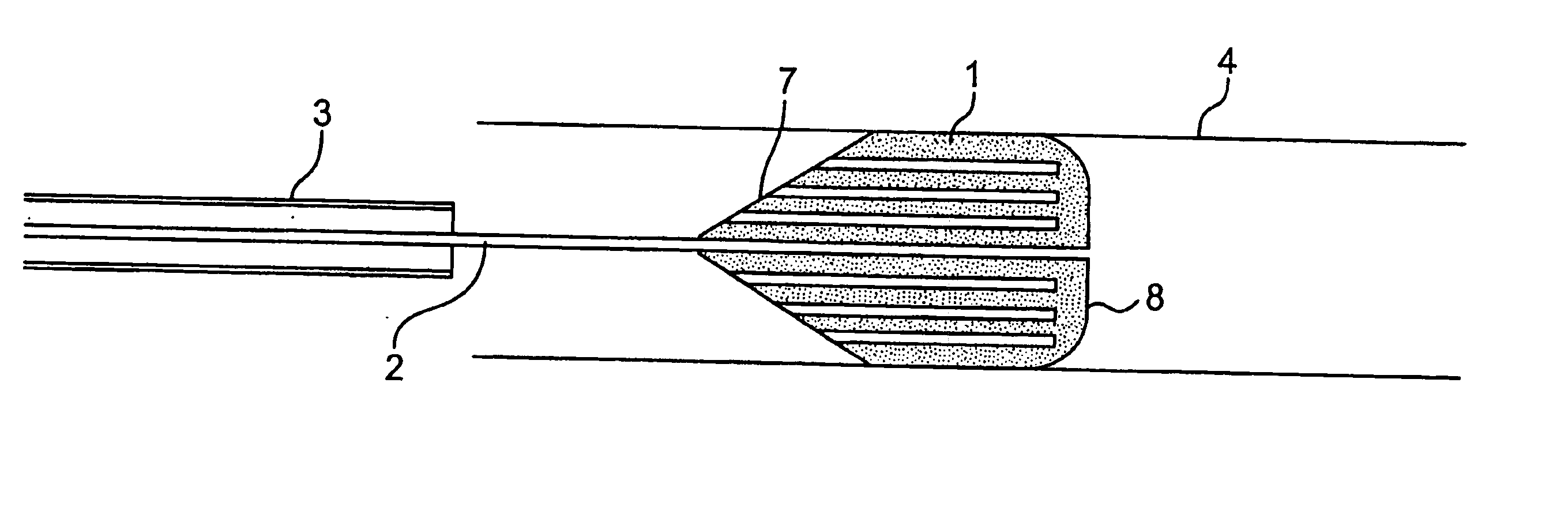
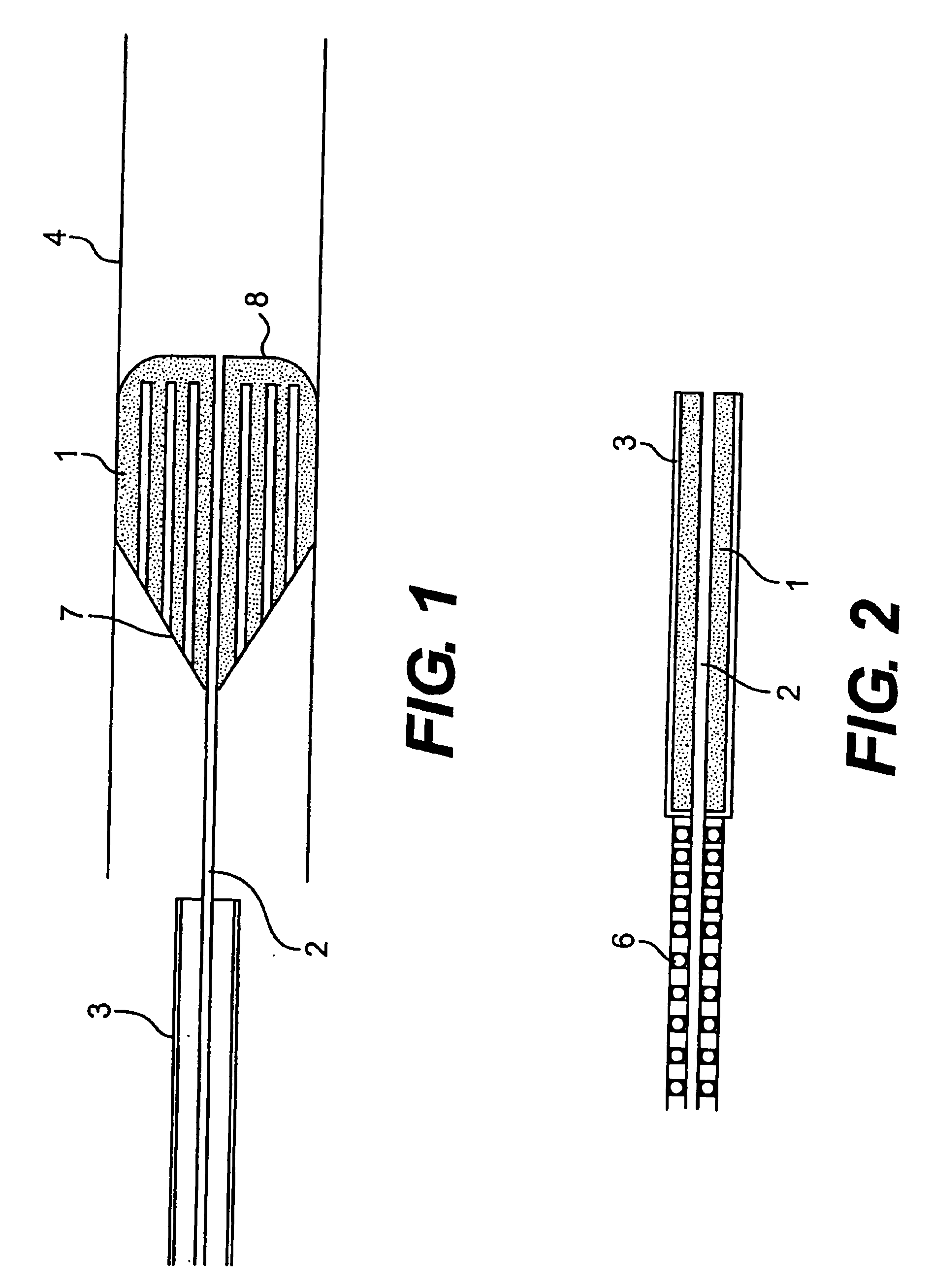
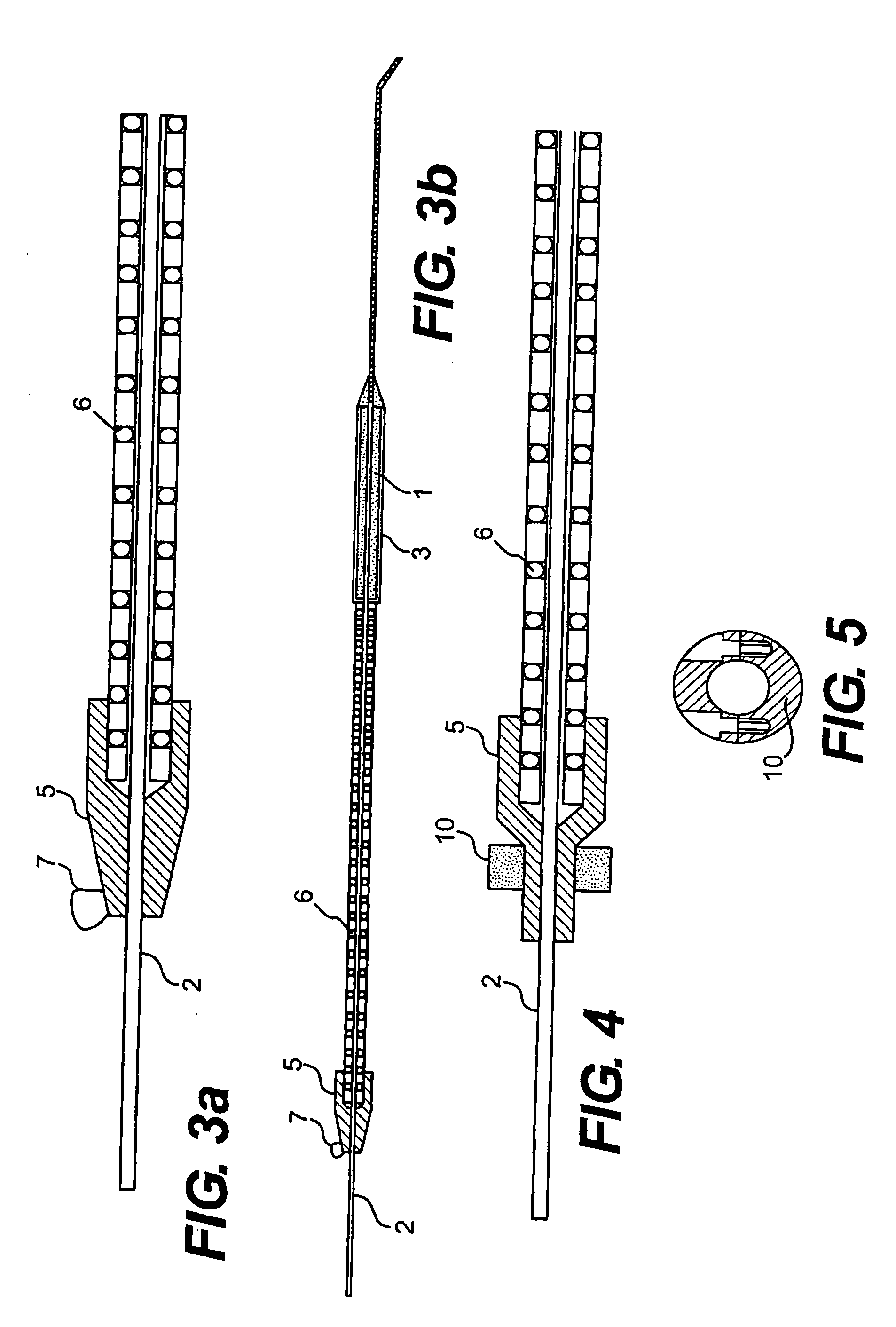
[0130] Referring to the drawings there are illustrated various embolic protection devices according to the invention. The devices, in general, comprise a filter element for temporary placing in a desired position during a surgical or interventional procedure typically using a guidewire and catheter. The filter element provides a pathway for blood and has means for capturing and retaining undesired embolic material released during the surgical procedure. The filter element containing the retained embolic material is removed when the interventional procedure is completed. In this way the patient is protected against the risk of stroke or other complications caused by the release of undesired embolic material during the procedure.
[0131] In one embodiment of the device it will be used in an over the wire transcatheter configuration. The clinician will cross the lesion with a steerable guidewire. The cerebral protection device will then be threaded over the guidewire and will be placed ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com