Composite model construction and method
a composite model and construction method technology, applied in the direction of toys, remote-control toys, toy aircrafts, etc., can solve the problems of high cost, high degree of scale fidelity, and difficult to achieve the effect of improving the solution of model construction and use, quick and easy construction of a model
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
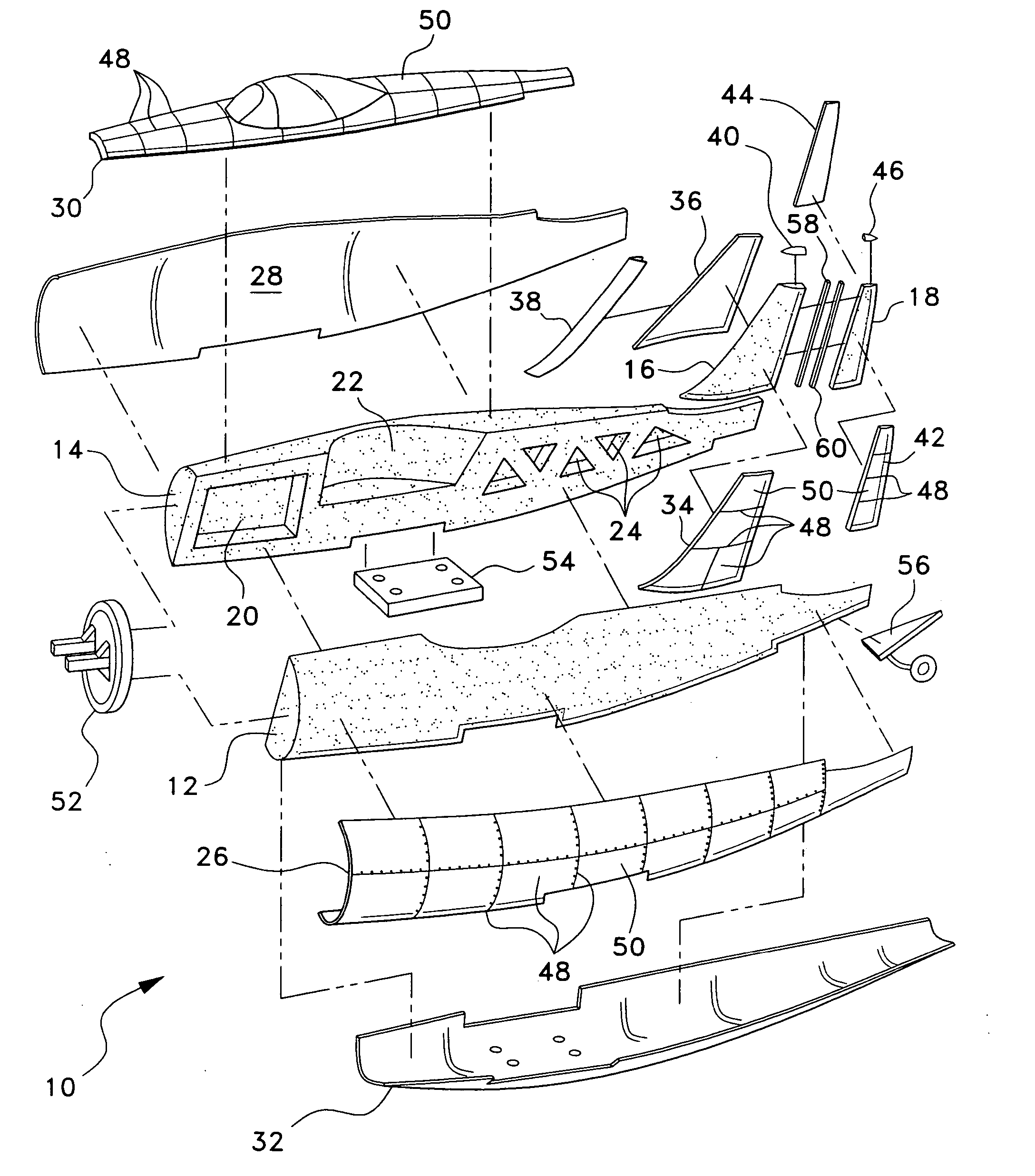
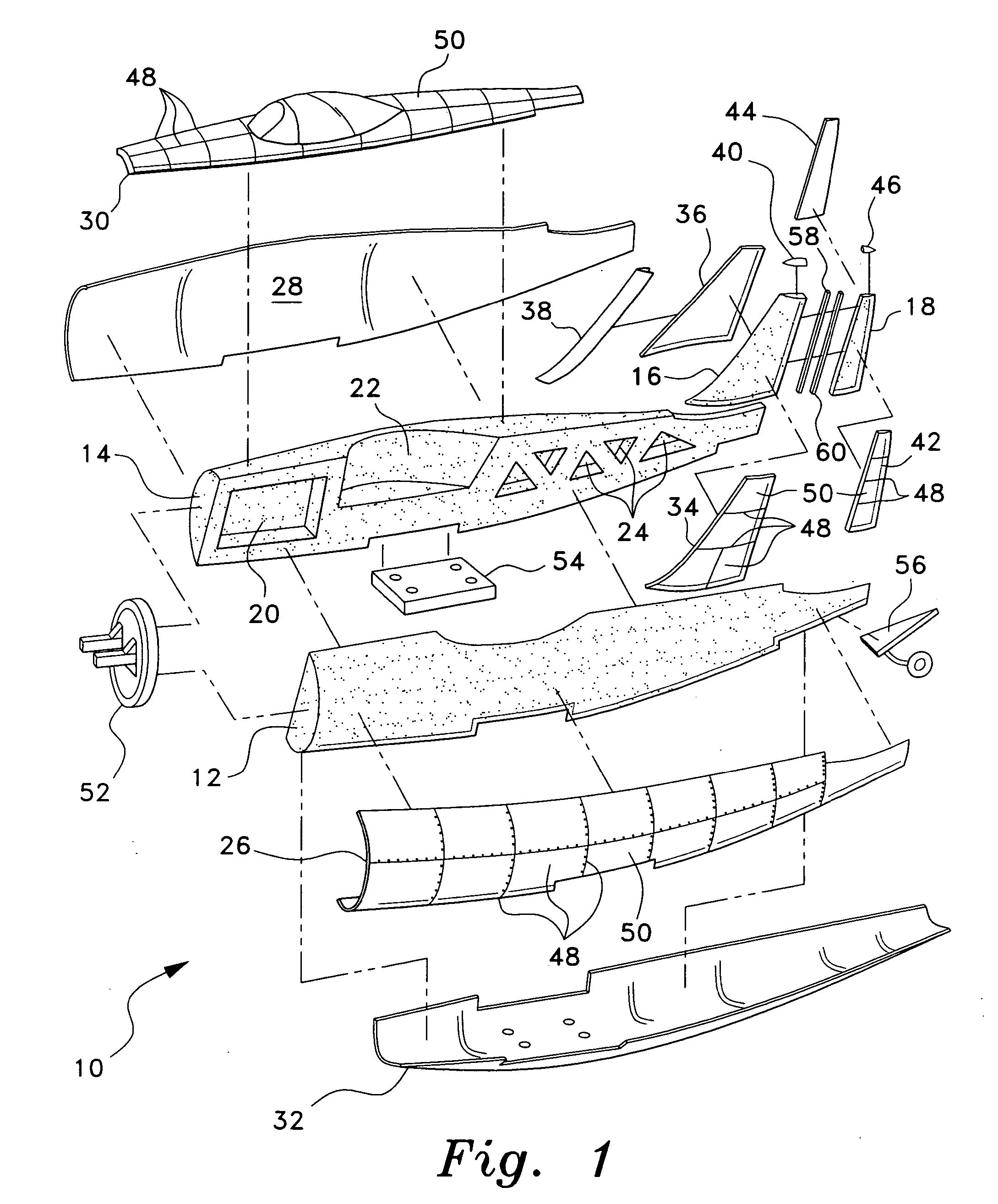
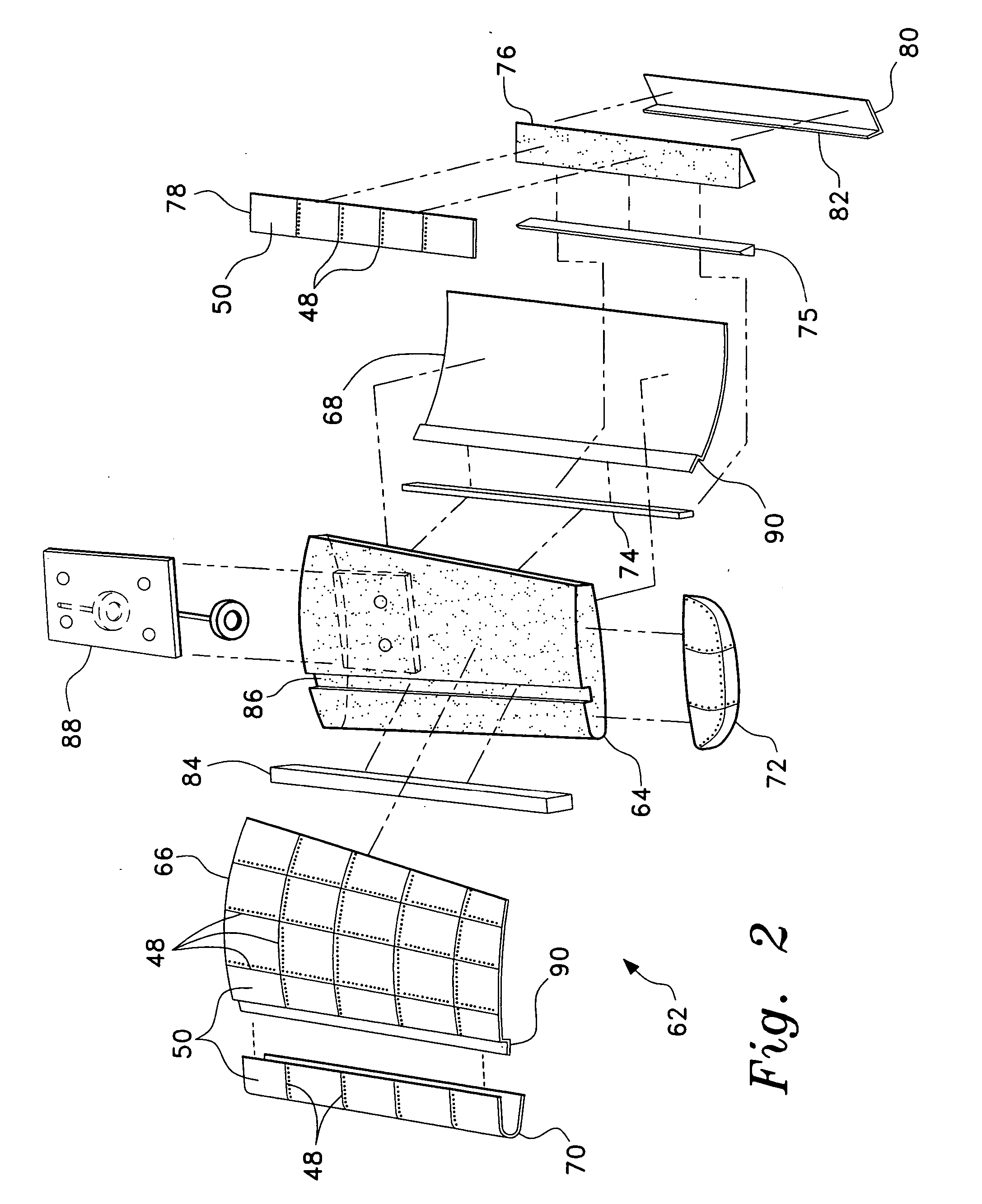
[0021] The present invention comprises various embodiments of a model or miniature vehicle, a kit for the assembly thereof, and a method of manufacturing such a kit. While the miniature vehicle may be a model aircraft, as shown in FIGS. 1 through 5, it will be seen that the present invention lends itself to application to miniature or model boats and cars as well.
[0022]FIG. 1 of the drawings provides an exploded perspective view of the fuselage and vertical empennage structure 10 of a model airplane kit or assembly according to the present invention, with FIG. 4 providing an elevation view in section of the completed fuselage structure 10 and FIG. 5 providing a perspective view of an exemplary model or miniature aircraft constructed in accordance with the present invention. The composite model construction provides for the use of a resilient foam plastic material, e.g., expanded polypropylene (EPP) foam, for the core components, i.e., left and right fuselage halves 12 and 14, the v...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com