Semiconductor manufacturing apparatus and chemical exchanging method
a technology of semiconductors and manufacturing equipment, applied in the direction of chemistry apparatus and processes, lighting and heating equipment, cleaning using liquids, etc., can solve the problems of method not being applied to a system of supplying new chemicals,
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
first embodiment
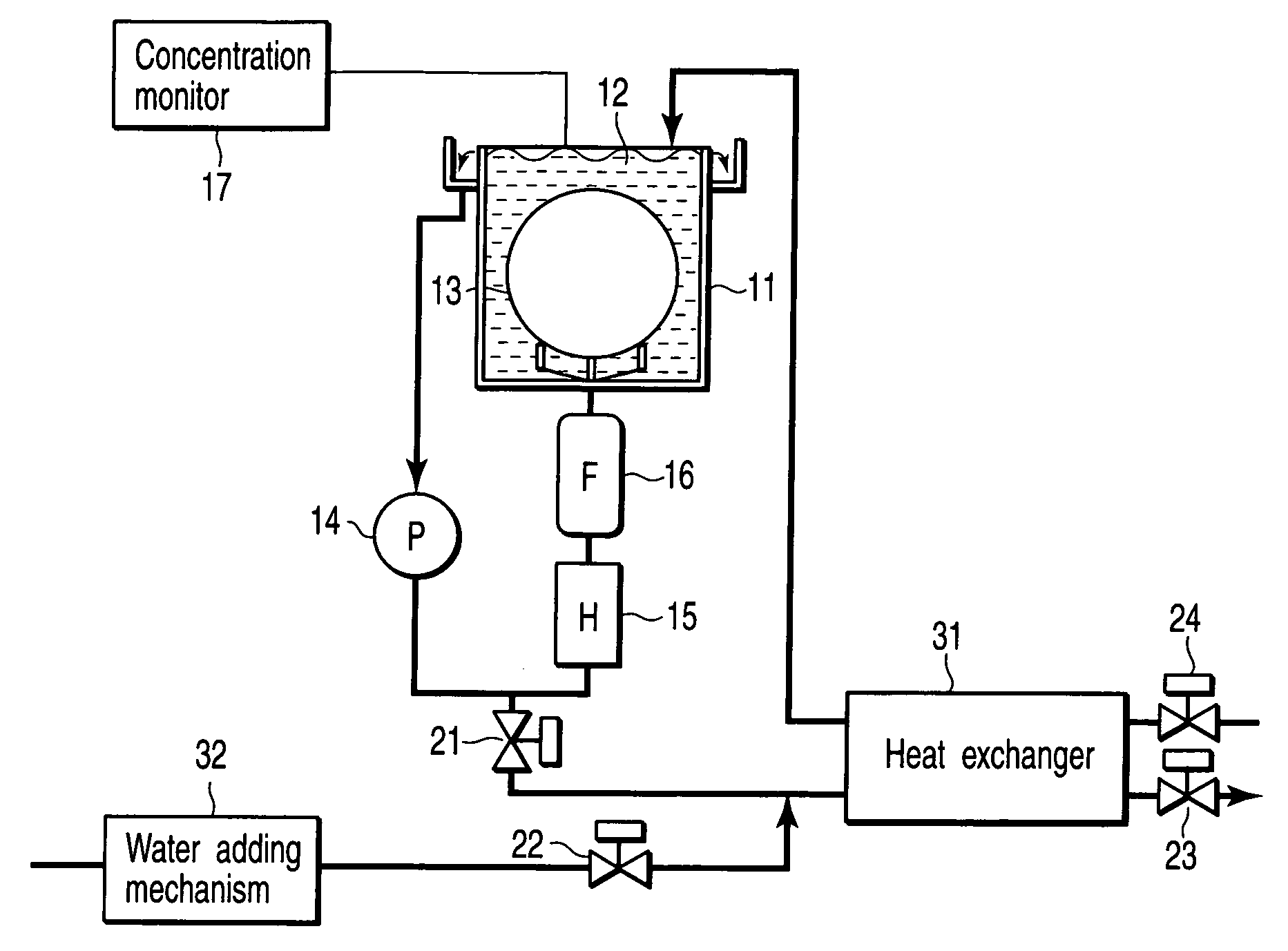
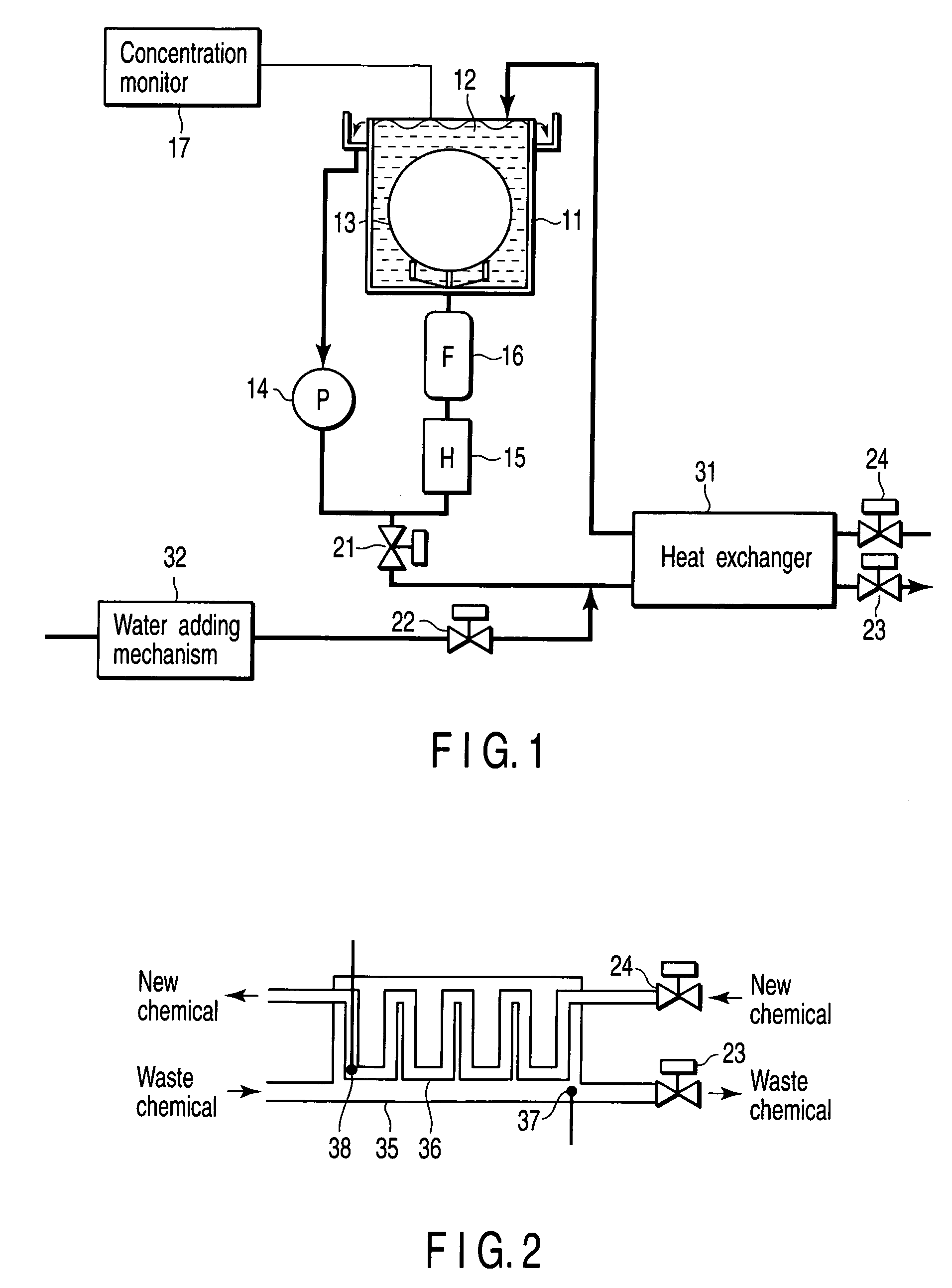
[0021]FIG. 1 is a schematic diagram showing a semiconductor manufacturing apparatus according to a first embodiment of the present invention.
[0022] Reference numeral 11 denotes a processing bath (high-temperature circulation type chemical bath) employed for cleaning of a semiconductor substrate such as a Si wafer or the like. The processing bath 11 is filled with, for example, a sulfuric acid based high-temperature chemical 12. A semiconductor substrate 13 is dipped into the chemical 12 in the processing bath 11 and then cleaned.
[0023] The chemical 12 in the processing bath 11 is circulated by a pump (P) 14. In other words, the chemical is supplied from a bottom portion of the processing bath 11 by the pump 14, and the chemical spilling from a top portion of the processing bath 11 is supplied again from the bottom portion of the processing bath 11 through a chemical circuit. A heater (H) 15 which controls a temperature of the chemical and a filter (F) 16 through which particles ar...
second embodiment
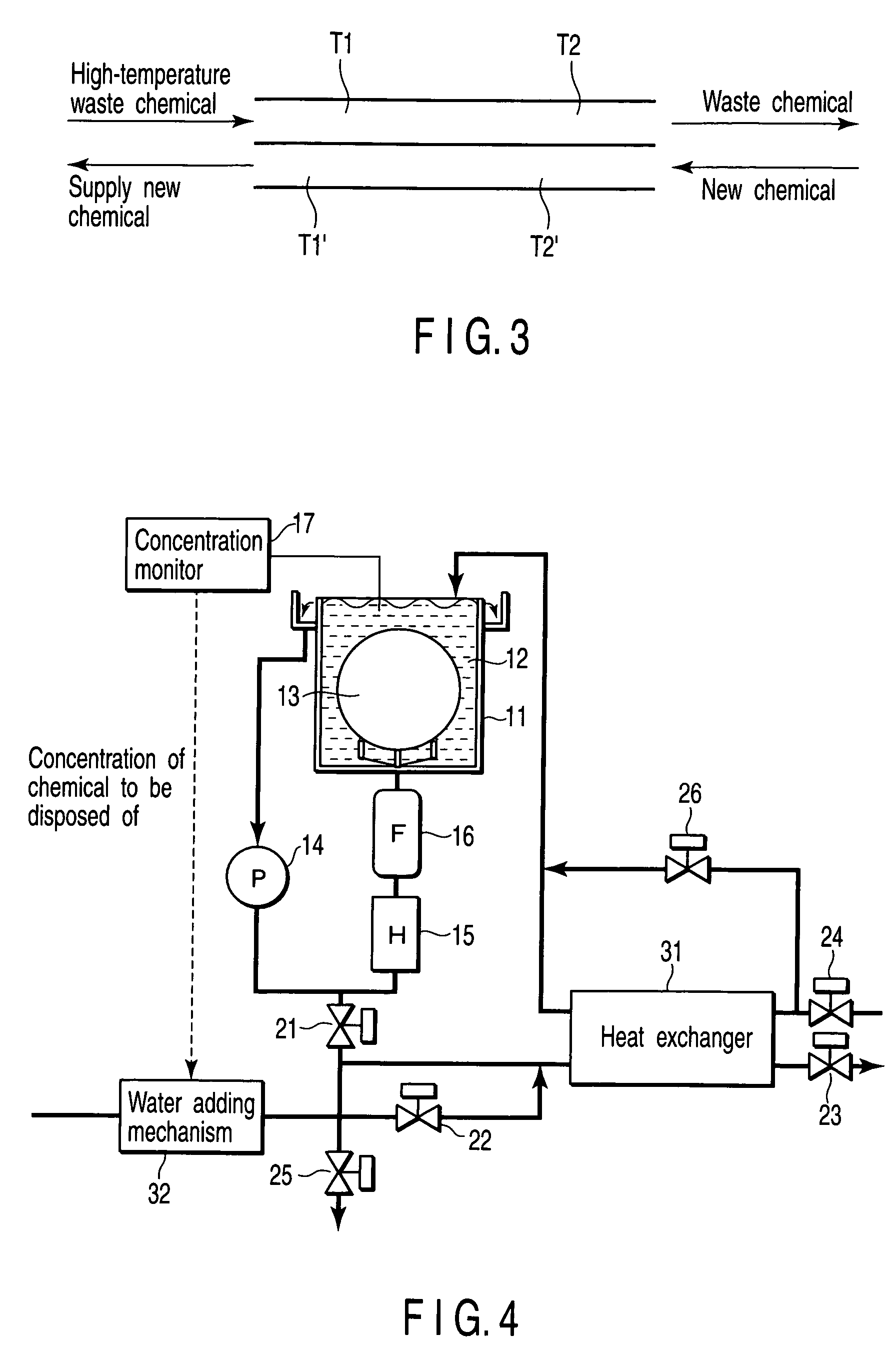
[0044]FIG. 4 is a schematic diagram showing a semiconductor manufacturing apparatus according to a second embodiment of the present invention. Elements like or similar to those disclosed in the first embodiment are denoted by similar reference numbers and are not described in detail here.
[0045] The present embodiment is different from the first embodiment in view of setting an addition amount of water by the water adding mechanism 32 on the basis of the measurement result of the concentration monitor 17. In addition, a valve 25 which does not allow the waste chemical to partially pass through the heat exchanger 31, but allows the waste chemical to be directly discharged, is provided between the waste chemical valve 21 and the heat exchanger 31. A valve 26 which does not allow the new chemical to partially pass through the heat exchanger 31, but allows the new chemical to be directly supplied to the processing bath 11, is provided at a new chemical side pipe of the heat exchanger 31...
modified embodiment
[0053] The present invention is not limited to the above-described embodiments. In the embodiments, water is used as an auxiliary fluid for the sulfuric acid based chemical used as a cleaning fluid and the waste chemical is heated by heat of dilution. However, combination of the chemical and the auxiliary fluid can be arbitrarily changed. For example, a chloric acid based chemical can be heated with heat of neutralization generated by adding an organic alkali thereto. An ammonium based chemical can be heated with heat of reaction generated by adding an organic acid thereto. However, a substance which is not deposited or precipitated inside the heat exchanger when the temperature is lowered, needs to be selected.
[0054] A position where the auxiliary fluid is added may be the pipe to enter the heat exchanger or in the heat exchanger. A relief valve (not shown) may be provided at the waste chemical side of the processing bath as a safety device. FIG. 2 shows only one chemical. However...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Concentration | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Volume | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com