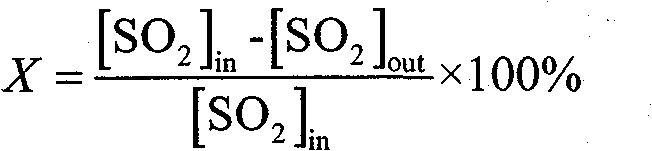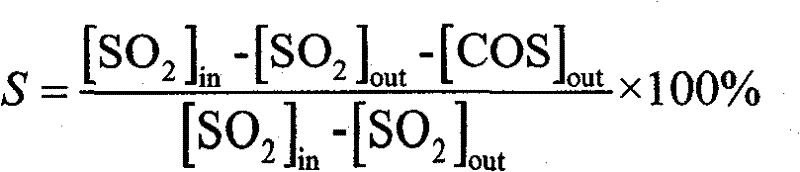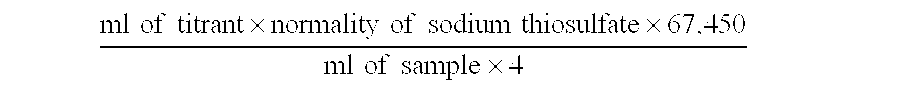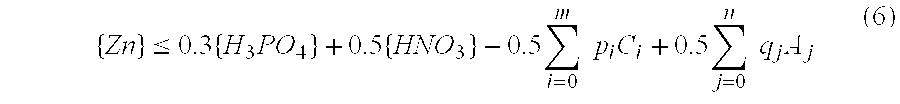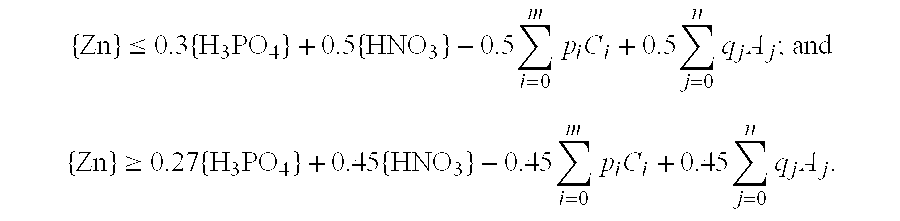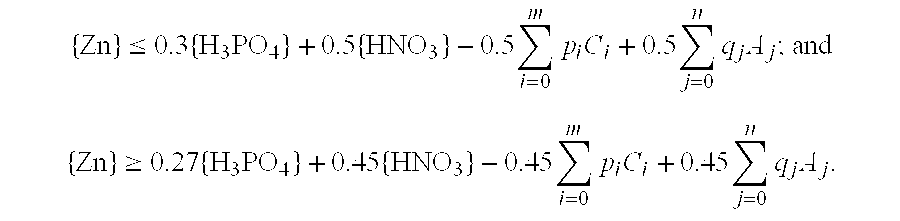Patents
Literature
188 results about "Chloric acid" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Chloric acid, HClO₃, is an oxoacid of chlorine, and the formal precursor of chlorate salts. It is a strong acid (pKₐ ≈ −1) and oxidizing agent.
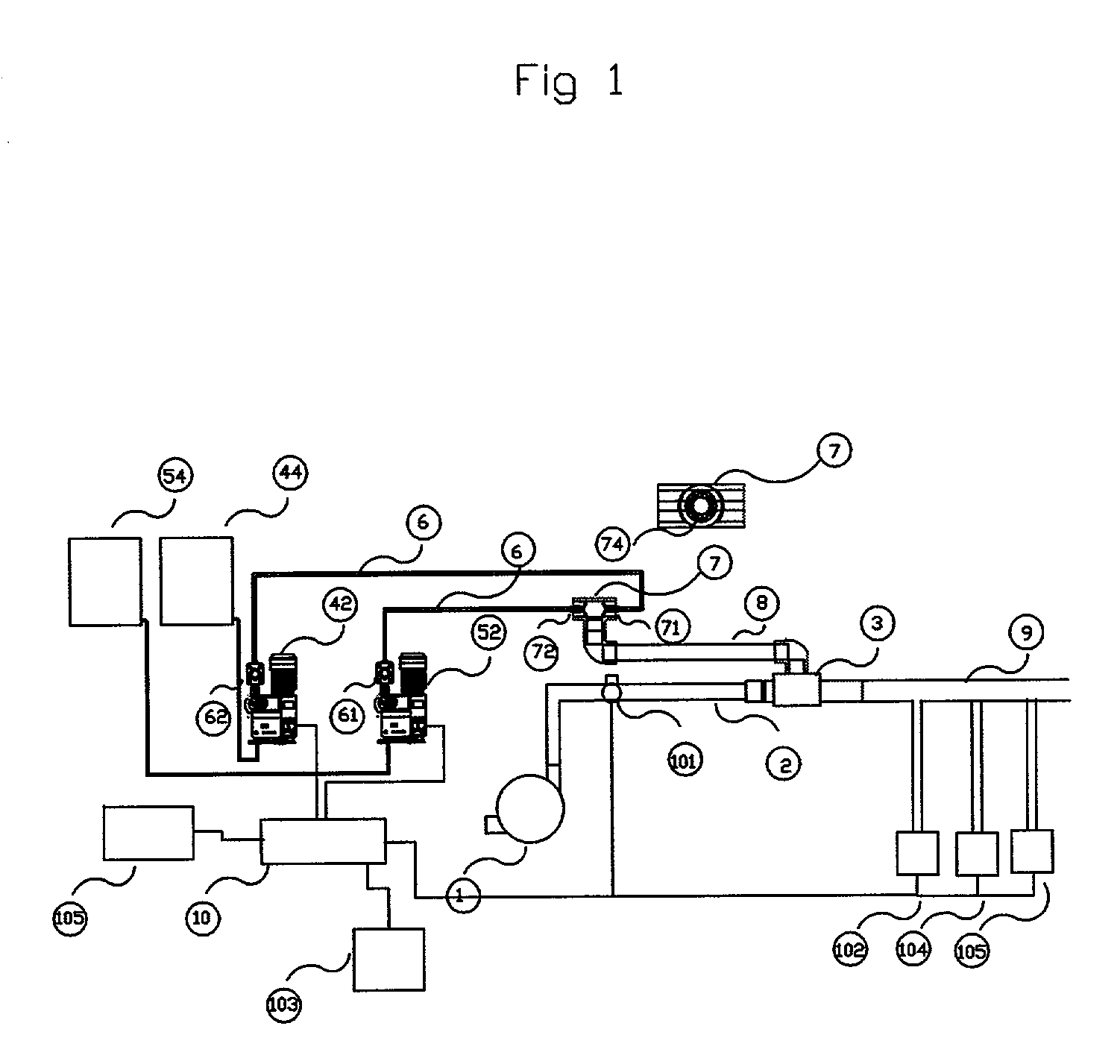
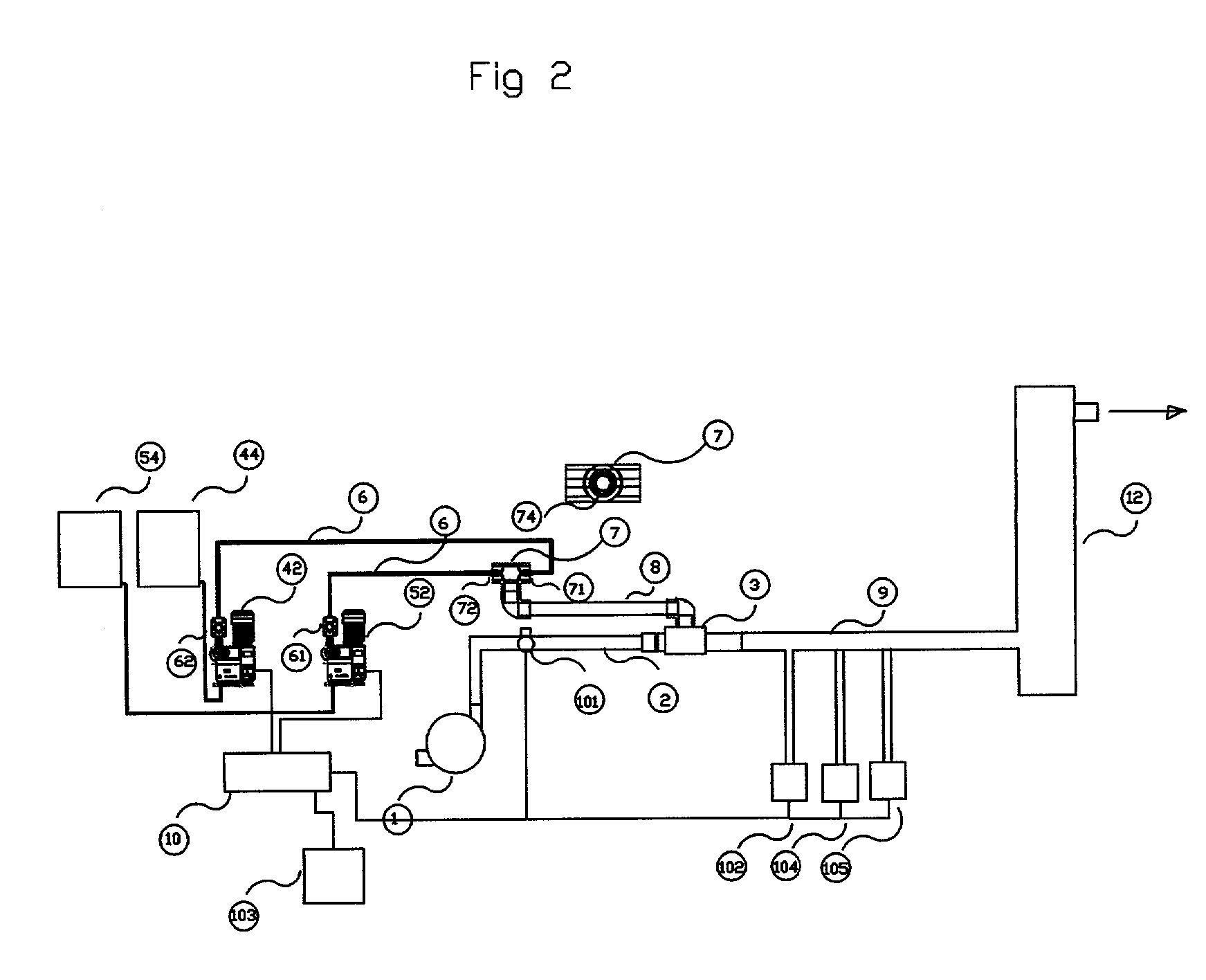
Process and apparatus for the generation of chlorine dioxide using a replenished foam system
InactiveUS20030031621A1Reduce operating costsReadily availableChlorine dioxideChlorine dioxideAlkali metal
An aqueous solution of metal chlorate, mineral acid and a reducing agent are continuously or intermittently sprayed, in a pattern to achieve intimate mixing, into a spherical chamber creating an aqueous foam reaction mixture generating chlorine dioxide which is removed in a direction 90 degrees to the axis of the spray nozzles. A baffle plate may be used to reduce the open cross sectional area of the exit port to increase reaction efficiency. The reactants are a mineral acid and an alkali metal chlorate or chloric acid and a reducing agent such as hydrogen peroxide. The mineral acid is either diluted or concentrated sulfuric acid, hydrochloric acid, acetic acid, nitric acid or a blend thereof. The ratio of acid is greater than one and less than 3 kg acid per kg of ClO2 formed. The chlorine dioxide may be removed with a stripper column.
Owner:GRAVITT ALAN +1
Super paramagnetic ferric oxide composite nanometre particle preparation method
InactiveCN1736881AReduce nucleationReduced growth rateNanostructure manufactureFerric oxidesSal ammoniacNanoparticle
The invention discloses a preparation method for composite nano particcle of superparamagnetic ferric oxide. Wherein, adding ammonia and sodium citrate synchronously and speed controlled to make ions of Fe3+ and Fe2+ coprecipitate and form Fe3O4 nano particle with water-phase dispersion surface adsorbed by citric acid radical that can be substituted by multi chemical functional group on basic condition as crystal seed for sodium citrate-goden chloric acid reduction reaction and form SPION nano particle.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Etching liquid composition and etching method
The invention relates to an etchant composition and an etching method, wherein, the etchant composition comprises any two components of oxidants, acid and salt, and the pH value of the etchant composition is between 1 and 7. The oxidant components are selected from hydrogen peroxide, ammonium persulfate, potassium persulfate and ceric ammonium nitrate; the acid components are selected from chloric acid, perchlorate, acetic acid, nitric acid, hydrofluoric acid, sulfuric acid and oxalic acid, and the salt components are selected from ammonium fluoride, ammonium bifluoride, diammonium phosphate, ammonium phosphate, ammonium chloride and perfluorinated octyl sulfanilic acid (C8F17SO3NH4).
Preparation of activated carbon-based catalyst used for selective reduction desulphurization of flue gas
ActiveCN102357364AImprove activity stabilityGood dispersionDispersed particle separationMetal/metal-oxides/metal-hydroxide catalystsCoalPollution
Belonging to the technical field of sulfur recovery, the invention relates to a catalyst for selective reduction desulphurization, its preparation method and application. The catalyst is characterized in that: a catalyst active component is loaded on a carrier by means of an isometric immersion method, a multiple immersion method and an immersion precipitation method so as to obtain the catalyst; the catalyst carrier consists of coconut-shell activated carbon, fruit-shell activated carbon and coal-based activated carbon; the oxidation modifier of the catalyst carrier is one or a mixture of any of chloric acid, nitric acid, hydrogen peroxide or concentrated sulfuric acid; the active component of the catalyst is one or a mixture of any of CuO, NiO, Fe2O3, ZnO, Cr2O3, Co2O3, MnO2, and V2O5. The desulfurizer of the invention employs a selective reduction desulphurization technology to convert SO2 in flue gas into elemental sulfur. The preparation technology of the catalyst has the advantages of simplicity, easy control, low cost and long service life. Adoption of the activated carbon-based catalyst prepared in the invention for selective reduction desulphurization not only realizes high efficiency SO2 conversion rate and sulfur selectivity, but also effectively prevents secondary pollution.
Owner:SHANDONG QINGYUAN GROUP CO LTD
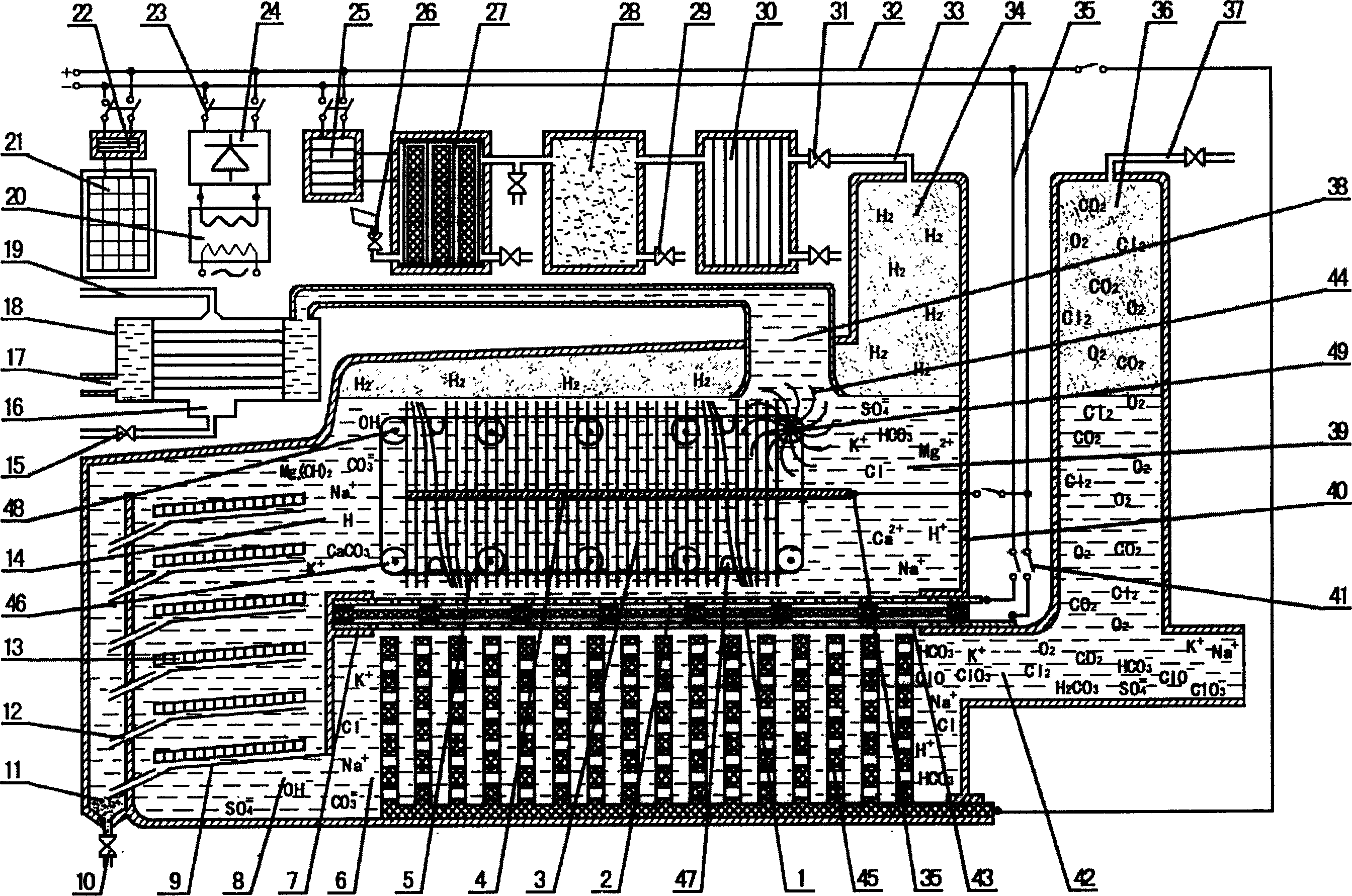
Apparatus for water treatment by electrolysis method
InactiveCN1623918AAchieve softeningRealize disinfectionDispersed particle separationScale removal and water softeningElectrolysisHypochlorous acid
An apparatus for treating water by electrolysis method is composed of DC power supply controller, water supply-discharge unit, two electrolyzing cathode bathes, electrically isolating plate unit, water scale depositing unit, and two electrolyzing anode bathes. The electrolytic reaction of water can make the calcium carbonate and the hydroxide of heavy metals to be deposited in anode bathes and the Cl2, O2, the radicals of hypochlorous acid and chloric acid, and ozone to be generated in cathode bathes.
Owner:BEIJING HIKEEN TECH +1
Method for preparing crystal whisker of gypsum
This invention describes a process for producing gypsum whiskers, which includes the the following processes: a)purification of chemical gypsum into dihydrate gypsum; b)levigation of the purified chemical gypsum, and then injection of the slurry thus obtained into an enamelled reactor; c)adding chloric acid or salts into the reactor, and boiling to the dissolution of the gypsum; d)stirring and cooling the solution to the recrystallization into dihydrate gypsum whiskers; e)swing-drying the recrystallization product; and f)neutralizing the swing-dried dihydrate gypsum to obtain a first product of wet dihydrate gypsum whiskers. In this invention the estimated production cost of the gypsum whiskers produced is 800-1900 RMB per ton, only 1 / 40-1 / 200 the price of the whiskers in the market. Besides, the overall process of this invention is easy to operate, and all the equipment utilized is common chemical equipment. The produced gypsum whiskers are mainly used for paper manufacturing and the corresponding paper products, while a minor part of them are used for reinforced materials of rubber and plastic products.
Owner:SHANGHAI DONGSHENG NEW MATERIALS
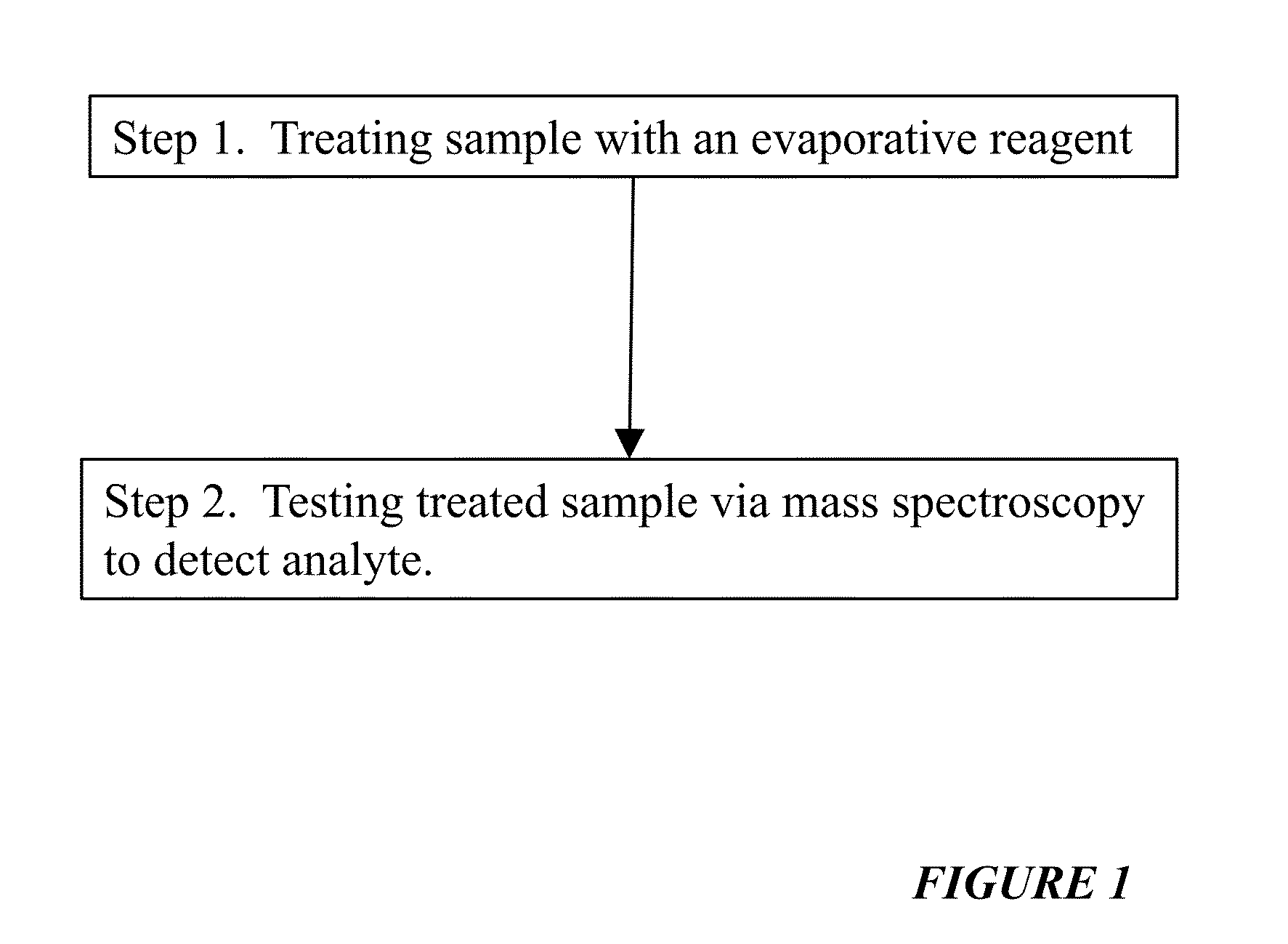
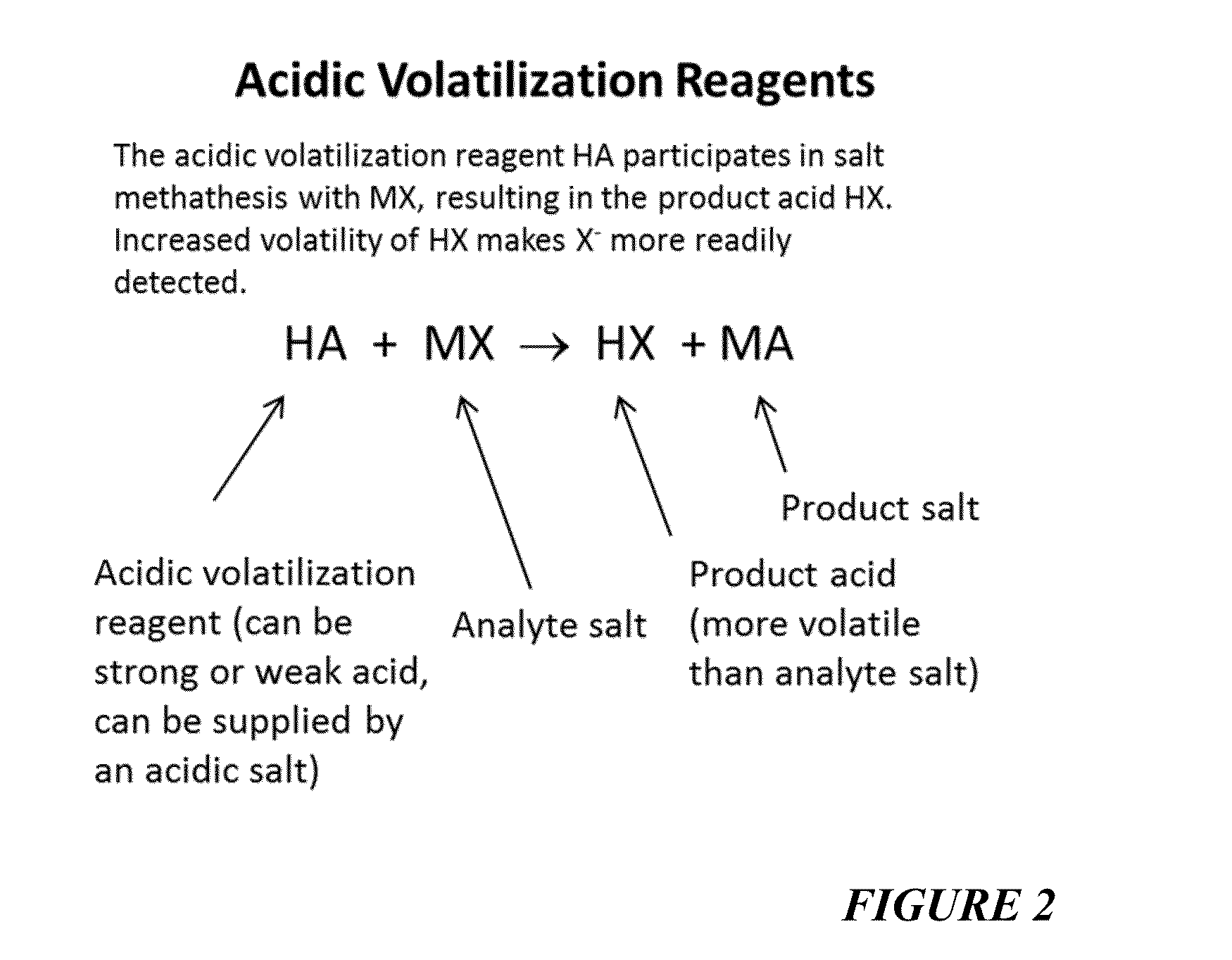
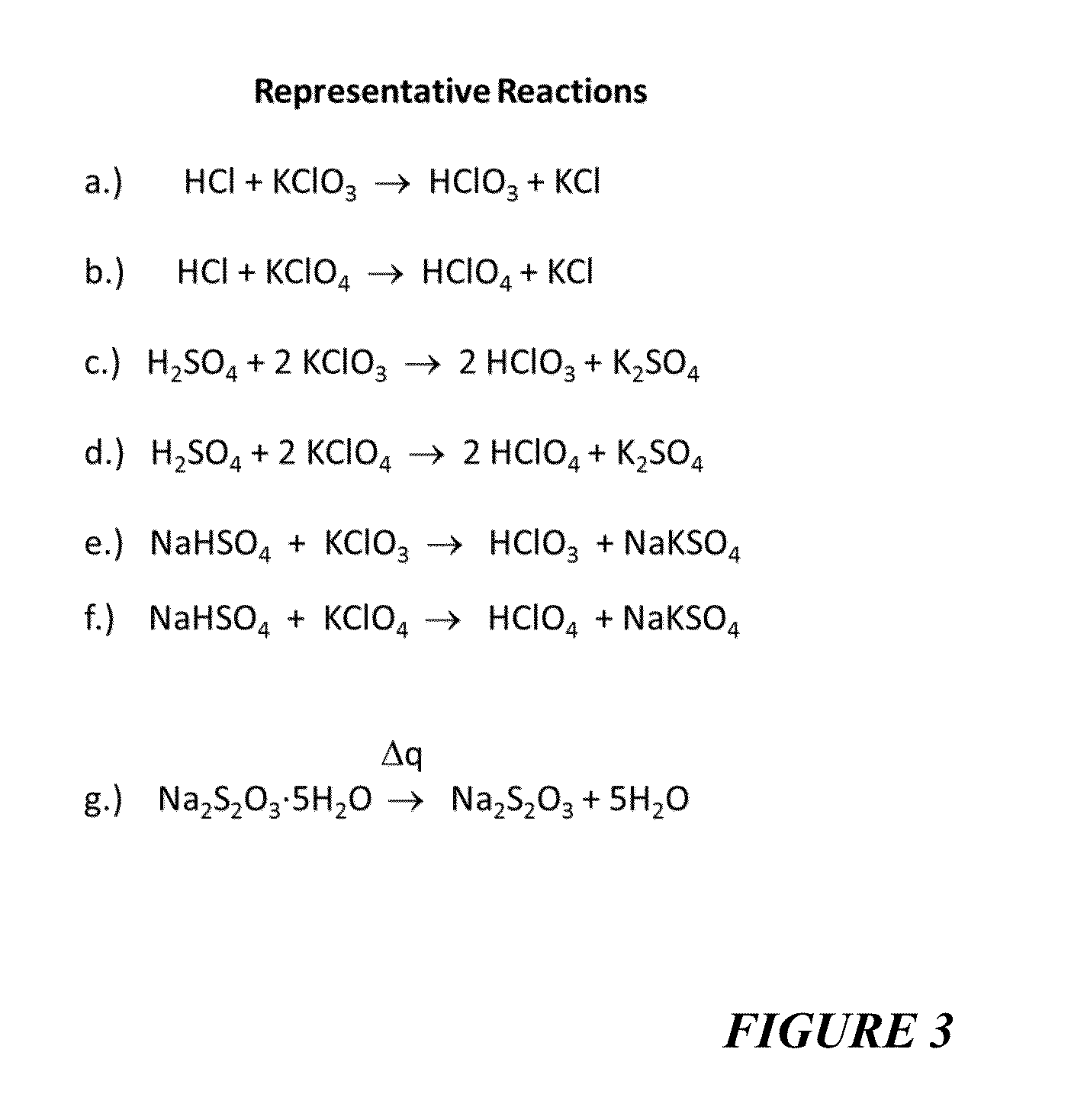
Reagents For Enhanced Detection Of Low Volatility Analytes
ActiveUS20150285780A1Easy to detectEasy to evaporateFuel testingMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansOrganic acidInorganic salts
The use of volatilization reagents is disclosed for improved detection of inorganic oxidizers such as, but not limited to, chlorates and perchlorates. Detection methods are disclosed whereby a reagent can transfer a proton to the anion (i.e., chlorate, perchlorate, etc.) of an inorganic salt analyte, forming an acid (i.e., chloric acid, perchloric acid) that is easier to detect by a mechanism whereby the acidified reagent is more easily vaporized, and hence, more easily detected. Concurrently, the anion of the acid forms a new salt with the cation released from the salt that was acidified. The reagents can also include acidic salts or cation-donators, more generally. In some embodiments, hydrated reagents or co-reagents that can release water can be employed. In another aspect of the invention, a class of reagents including polmeric acids, polymeric organic acids and polymeric sulfonic acids are disclosed that can carry out this method. In various embodiments, these reagents can be embedded in a swipe or other substrate, delivered as a liquid infused via nebulizer, or otherwise introduced to a sample to be tested for the presence of a target analyte.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
Colloidal gold immunity percolation sensitization method for detecting avian influenza virus and its reagent kit
The invention provides a colloidal gold immunity infiltration sensitivity raising method for checking avian influenza virus and a reagent kit therefore. The colloidal gold immuno infiltration sensitivity raising method comprises: (1) preparing an immunity infiltration test strip; (2) fixing influenza virus multi-clonal antibody on the immunity infiltration test strip; (3) preparing avian influenza virus gold marking probes; 4) preparing sensitivity raising agent; (5) detecting avian influenza virus. The invention utilizes the oxidation reduction reaction between chloric acid and ac=scorbic acid, to generate gold atoms which can be absorbed by colloidal gold, to position the deposition part of the colloidal gold to develop and enhance color, thereby improving the detection sensitivity on object antigen by 8 to 50 times. Based on colloidal gold spot immunity infiltration test method (double-antibody sandwich), the invention adopts nanometer gold particle sensitivity raising technique, to improve the detection sensivity on avian influenza virus, screen sample of high flux, and adapt avian influenza virus detection in basic layer or in-situ field.
Owner:CHINESE ACAD OF INSPECTION & QUARANTINE
Simple and fast preparing process for Au-Ag complex nanometer particles
The invention discloses a simple and rapid method for preparing Au-Ag complex nanometer particles, which adopts one-step liquid phase deoxidizing method at room temperature to prepare Au-Ag complex nanometer particles. The specific method is that: sequentially add gold chloric acid solution and sodium citrate solution into colorimetric tube; then, respectively add silver nitrate solution into the colorimetric tube, making that Au3+: Ag+ in the tube is 1:9 to 9:1; then add ascorbic acid and shake, thus the Au-Ag complex nanometer particles is obtained. The method has the advantages that: 1) comparing with the current method, the preparation method is simple with mild reaction conditions, and does not need the assistant means of laser induction and ultrasonic processing; the Au-Ag complex nanometer particles can be prepared at room temperature, and the diameter of nanometer particles can be regulated by regulating the proportion of Au and Ag; 2) the deoxidizing agent of ascorbic acid and the stabilizing agent of sodium citrate solution are easily obtained with low cost.
Owner:GUANGXI NORMAL UNIV
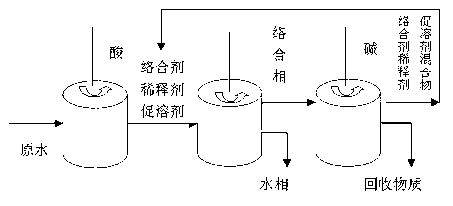
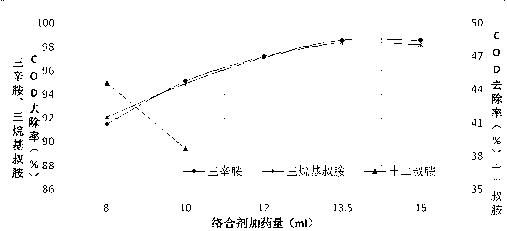
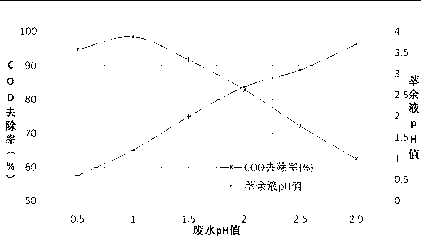
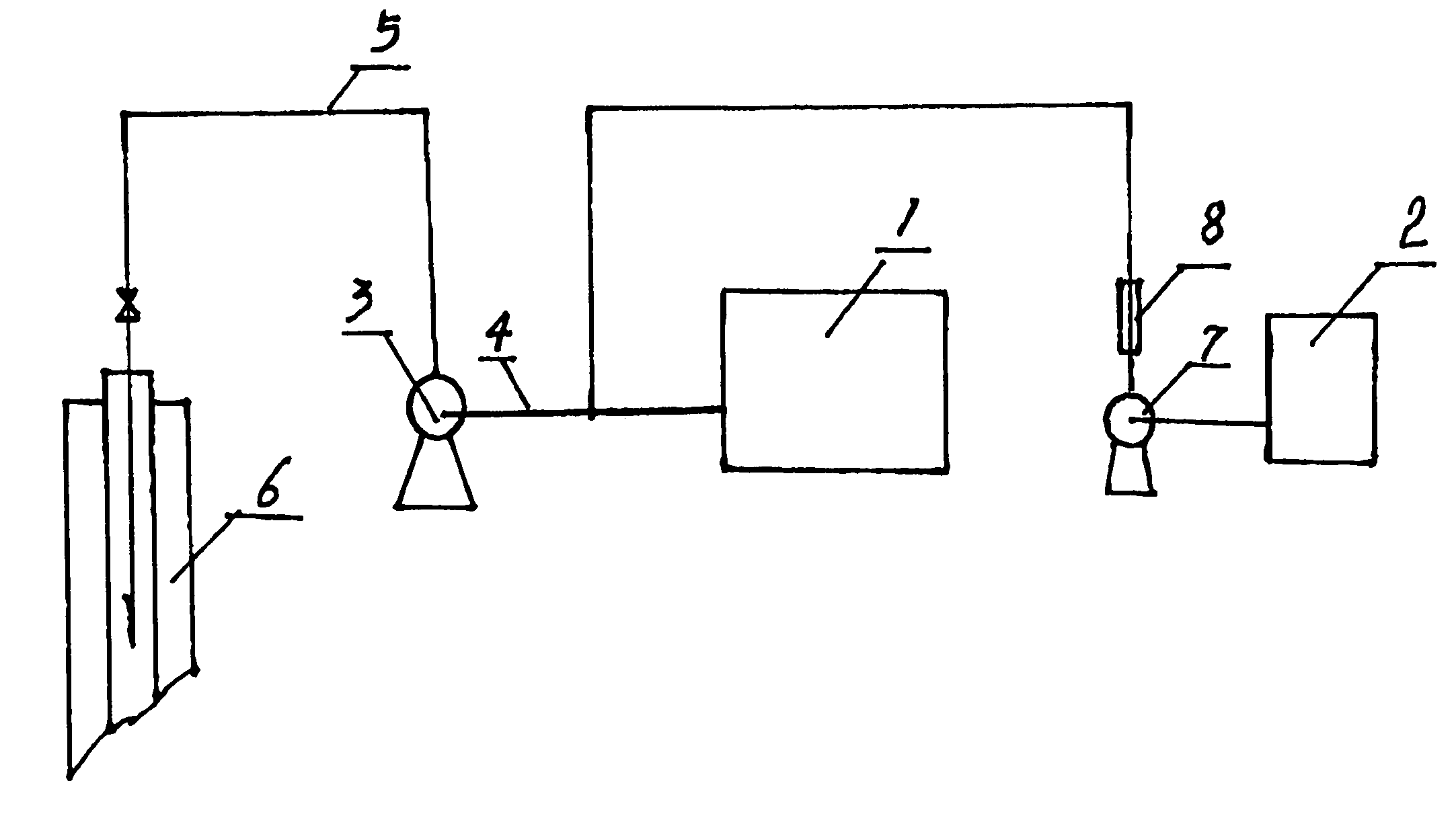
Process for treating dinaphthol wastewater by using complexation extraction method
InactiveCN102936051AImplement full automationCan run continuouslyMultistage water/sewage treatmentWater/sewage treatment by extractionKeroseneOil phase
The invention discloses a process for treating dinaphthol wastewater by using a complexation extraction method. A process core includes that trioctylamine or trialkyl tertiary amine serves as a complexing agent, sulfonated kerosene serves as a diluent, and chloric acid tributyl ester serves as a chaotropic agent to be mixed according to a certain ratio into an extraction agent, the extraction agent comprises, by volume, 20% to 30% of the complexing agent, 60% to 70% of the diluent and 5% to 15% of the chaotropic agent. Dinaphthol production wastewater is extracted when the temperature is in a range of 20 DEG C to 30 DEG C and the pH is 1, aqueous phase: oil phase is 1: 1 (volume ratio), the removal rate of first extraction CODcr can reach 97%, naphthalene sulfonate in wastewater can be extracted through multistage extraction, and simultaneously water is discharged up to standard. Water phases of back extraction can be recycled as production materials; and organic phases are mixtures of the extraction agent and the diluent and can be recycled.
Owner:SHANGHAI BIOFIT ENVIRONMENTAL TECH
Preparation method of nanoscale stannic oxide hollow sphere
InactiveCN102583266ANo pollution in the processRaw materials are cheap and easy to getNanotechnologyElemental selenium/telluriumGas detectorPotassium hypochlorite
The invention belongs to the field of nano materials and relates to a preparation method of a nanoscale stannic oxide hollow sphere. The method is characterized in that stannous salts and oxidants serve as reaction materials and a hydro-thermal method is used for preparation under the acidic condition at the PH value between 1.0 and 4.0; the stannous salts consist of at least one of stannous sulfate, stannous chloride and stannous oxalate; the oxidants consist of at least one of hydrogen peroxide, chloric acid, hypochlorous acid, potassium chlorate, sodium chlorate, potassium hypochlorite and sodium hypochlorite; and PH value of solutions is adjusted by one of sulphuric acid, hydrochloric acid, oxalic acid and sodium hydroxide. The preparation method does not use any sacrificial templates and organic solvents and is environmentally friendly, simple in process, mild in reaction condition, low in energy consumption, easy to control, high in product purity, and suitable for large-scale industrial production. The nanoscale stannic oxide hollow sphere can be applicable to gas sensors, lithium ion batteries, catalysts and photoelectronic devices.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
Method for preparing a chlorine dioxide block-removing agent in oil wells
InactiveUS7131495B2Low viscosityFlows out easily and quickly kills variousSurveyCleaning apparatusChlorine dioxideAcid substances
A method to synthesize a chlorine dioxide block remover in a well is described. The method includes dissolving a chlorate aqueous solution and some acidic substances in water and to produce a hydrogen ion. The chlorate aqueous solution and acidic substances are quickly injected into the well by an injection pump, so they react with each other and produce chlorine dioxide. The synthesis of the chlorine block remover in the well removes oil layer blocks induced by polymers and microbes, while reducing the risk of explosion caused by leaked chlorine dioxide, and reducing the corrosion of equipment and pipes caused by chlorine dioxide.
Owner:HAO ZHANYUAN +1
Etching liquid for conductive polymer, and method for patterning conductive polymer
InactiveUS20100089872A1Improve etching effectDecorative surface effectsPrinted circuit aspectsHydrogen halidePermanganic acid
The object is to provide an etching liquid for a conductive polymer having excellent etching capability toward a conductive polymer, and a method for patterning a conductive polymer employing the etching liquid for a conductive polymer. The conductive etching liquid of the present invention is selected from the group consisting of (1) an etching liquid comprising greater than 0.5 wt % but no greater than 70 wt % of (NH4)2Ce(NO3)8 or at least 0.5 wt % but no greater than 30 wt % of Ce(SO4)2, (2) an etching liquid comprising greater than 0.5 wt % but no greater than 30 wt % of (NH4)4Ce(SO4)4, (3) an etching liquid comprising a hypochlorous acid salt aqueous solution having an effective chlorine concentration of at least 0.06 wt % and a pH of greater than 3 but less than 8, (4) an etching liquid comprising nitrosyl chloride which comprises at least 5 wt % of hydrochloric acid and at least 20 wt % of nitric acid, a (hydrochloric acid concentration+0.51×nitric acid concentration) value being no greater than 35 wt %, and a (hydrochloric acid concentration+0.5×nitric acid concentration) value being at least 30 wt %, (5) an etching liquid comprising at least 3 wt % but no greater than 40 wt % of a bromic acid compound and at least 4 wt % of an inorganic acid, (6) an etching liquid comprising at least 6 wt % but no greater than 40 wt % of a chloric acid compound and at least 7 wt % of a hydrogen halide, (7) an etching liquid comprising at least 0.001 wt % but no greater than 20 wt % of a permanganic acid compound, and (8) an etching liquid comprising at least 3 wt % but no greater than 30 wt % of a hexavalent chromium compound.
Owner:TSURUMISODA +1
Detection method of heavy metal in soil
ActiveCN105784864AIncrease concentrationHigh sensitivityComponent separationAlkaline hydrolysisSeparate sample
The invention discloses a detection method of heavy metal in soil. The detection method comprises the following steps: weighing soil, adding an alkali solution containing an ammonia solution, performing shaking and microwave treatment, adding an acid solution containing chloric acid, adjusting a pH valve, and performing ultrasonic extraction and centrifugation so as to obtain a crude extract; then performing concentration and microfiltration, and setting volumes so as to obtain a sample solution; preparing a blank solution; performing quantitative determination on the obtained sample solution by an extra-high efficient liquid chromatography. According to the detection method disclosed by the invention, an alkaline hydrolysis acid extraction method is adopted for pre-treating samples, so that losses and air pollution of heavy metal elements are avoided. Besides, the detection method has the advantages of being high in recovery rate, precision, and treatment speed, simple and convenient to operate, wide in application range and the like. According to the detection method disclosed by the invention, after the samples are pretreated, the determination of varied heavy metal elements can be performed on the pretreated samples, and performing separate sample pretreatment on each heavy metal element is not needed, so that the workload is reduced. The detection method disclosed by the invention is very acute for determining the content of the heavy metal in the soil, and has a relatively high detection efficiency.
Owner:SHANDONG WUZHOU DETECTION
Method for observing epidermal and internal microstructures of leaf by using transparent leaf
InactiveCN102095730ALess materialLow costPreparing sample for investigationMaterial analysis by optical meansCuticleDimethyl benzene
The invention relates to a method for observing the epidermal and internal microstructures of a leaf by using a transparent leaf, which has low cost and can accurately observe the microstructures of leaf. The technical scheme in the method comprises the following steps: firstly, processing the leaf, and cleaning and soaking the leaf in ethanol to remove chlorophyll; then soaking in alkaline solution to break the mesophyll cells; decolorizing in sodium hypochlorite; rinsing with flowing water; placing in hydrated chloric acid; taking out the leaf; rinsing with flowing water; dewatering with alcohol solutions with gradient concentrations; placing in xylene solution to enable the leaf to be transparent; and sealing with neutral balsam or water; and observing and picking images with optical microscope to observe the internal and external structure at different levels of the leaf. The method has the advantages of less material selection, low cost, less work load, high success rate and good effect, and is suitable for observation of various leaves.
Owner:HENAN UNIV OF CHINESE MEDICINE
Method for preparing expandable graphite by using ozone
The invention relates to a method for preparing expandable graphite by using ozone. Concentrated sulfuric acid, fuming nitric acid, perchloric acid or mixed acid is adopted to oxidize crystalline flake graphite, together with oxidant, the temperature of the oxidation reaction is 5-50 DEG C, the oxidation reaction lasts for 30 min-100 hours, and then the pH value is adjusted to be 6-7 through suction filtration and water scrubbing, the oxidized graphite is dried for 10-72 hours at the temperature of 40-60 DEG C, and the expandable graphite is obtained. The mixed acid at least contains concentrated sulfuric acid, fuming nitric acid or perchloric acid; and the oxidant is ozone or mixed oxidant containing ozone. The method provided by the invention has the following advantages: the oxidative products of ozone are oxygen and water, no other residual materials are produced, and the secondary pollution is not caused; the ozone is easy to prepare, and the equipment and technique are simple; and the source of ozone is easy to obtain and is not limited by transportation conditions. Ozone is adopted to oxidize the graphite, so that the environmental protection is reduced, and the instability and insecurity of peroxides are also avoided, and meanwhile, the recycling of intercalation solution is facilitated.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
Optical resin monomer material and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN101319024AGood refractive indexQuality improvementOptical elementsRefractive indexChloric acid
The invention discloses an optical resin monomer material and a preparation method thereof. The optical resin material takes the shape of an easily processed colorless transparent thick liquid, and the refractive index of copolymers consisting of the material can reach 1.56, thereby the optical resin material is used for producing a resin lens with a refractive index of 1.56; and the quality is high and the moulding processing of the lens is convenient. The method for preparing the optical resin material is easy and feasible and convenient to control; and offensive odor such as sulfuric isopropyl chlorate, isopropyl sulfuric chlorate and so on and toxic volatile chemical products can not be generated during the preparation process, thereby the environmental pollution is reduced.
Owner:山东鲁源化工科技有限公司
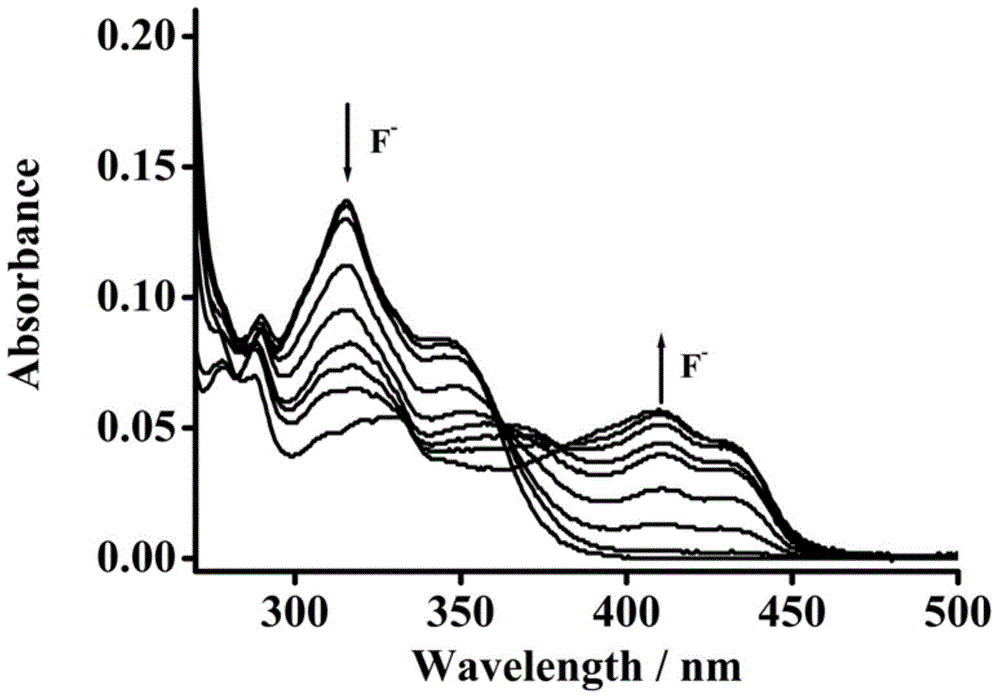
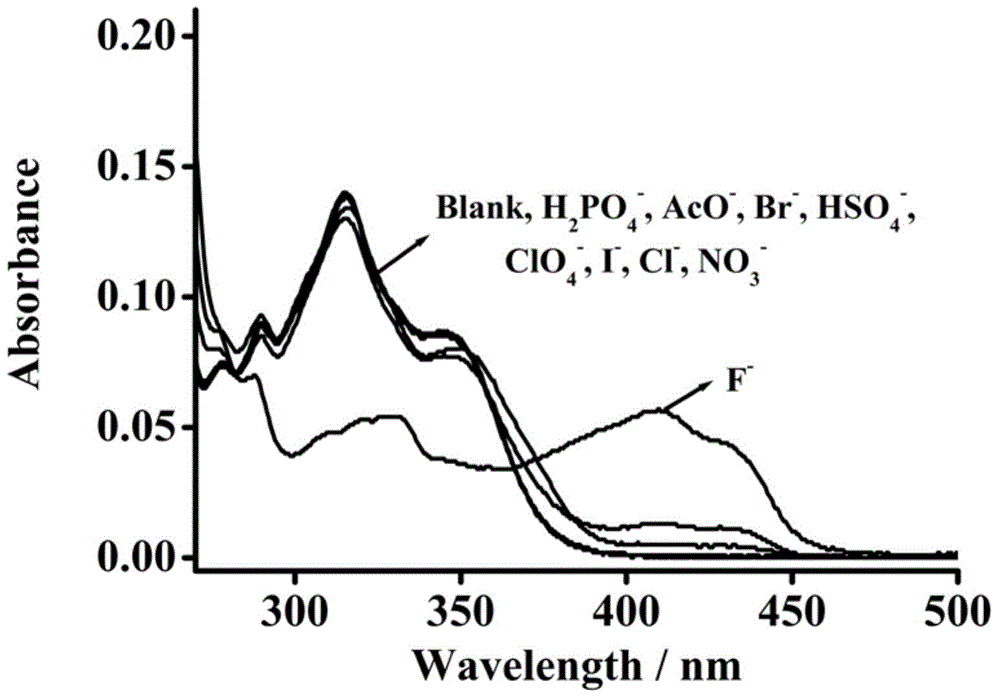
Fluorescent molecular probe for detecting fluoride ions as well as synthesis method and application thereof
InactiveCN104418875AHigh sensitivityStable fluorescenceGroup 4/14 element organic compoundsMaterial analysis by observing effect on chemical indicatorHigh fluoridePhosphate
The invention relates to a preparation method of a fluorescent molecular probe for detecting fluoride ions through colorimetric detection and fluorescence enhancement and an application of the fluorescent molecular probe to detecting fluoride ions. The fluorescent molecular probe is prepared by protecting 2-hydroxyl-1-naphthaldehyde taken as a raw material with silane and then condensing the raw material and malononitrile. The fluorescent molecular probe is simple and convenient to synthesize, and reaction conditions are mild. The fluorescent molecular probe has the specific characteristics that the probe molecule has stable optical properties and higher synthetic yield; the probe molecule has high fluoride ion detection sensitivity and low lower limit of detection, and the limit of detection is 0.52mu M; the response range is 0-100mu M and the detection range is wide; the probe molecule has good selectivity and has no responses to anions, such as dihydrogen phosphate radicals, acetate radicals, bromide ions, hydrosulfate radicals, chlorate radicals, iodide ions, chloride ions and nitrate radicals; the probe molecule is suitable for colorimetric detection; the fluorescent molecular probe has practical application values in the fields of biochemistry, environmental sciences and the like.
Owner:SUZHOU ROWLAND BIOTECH
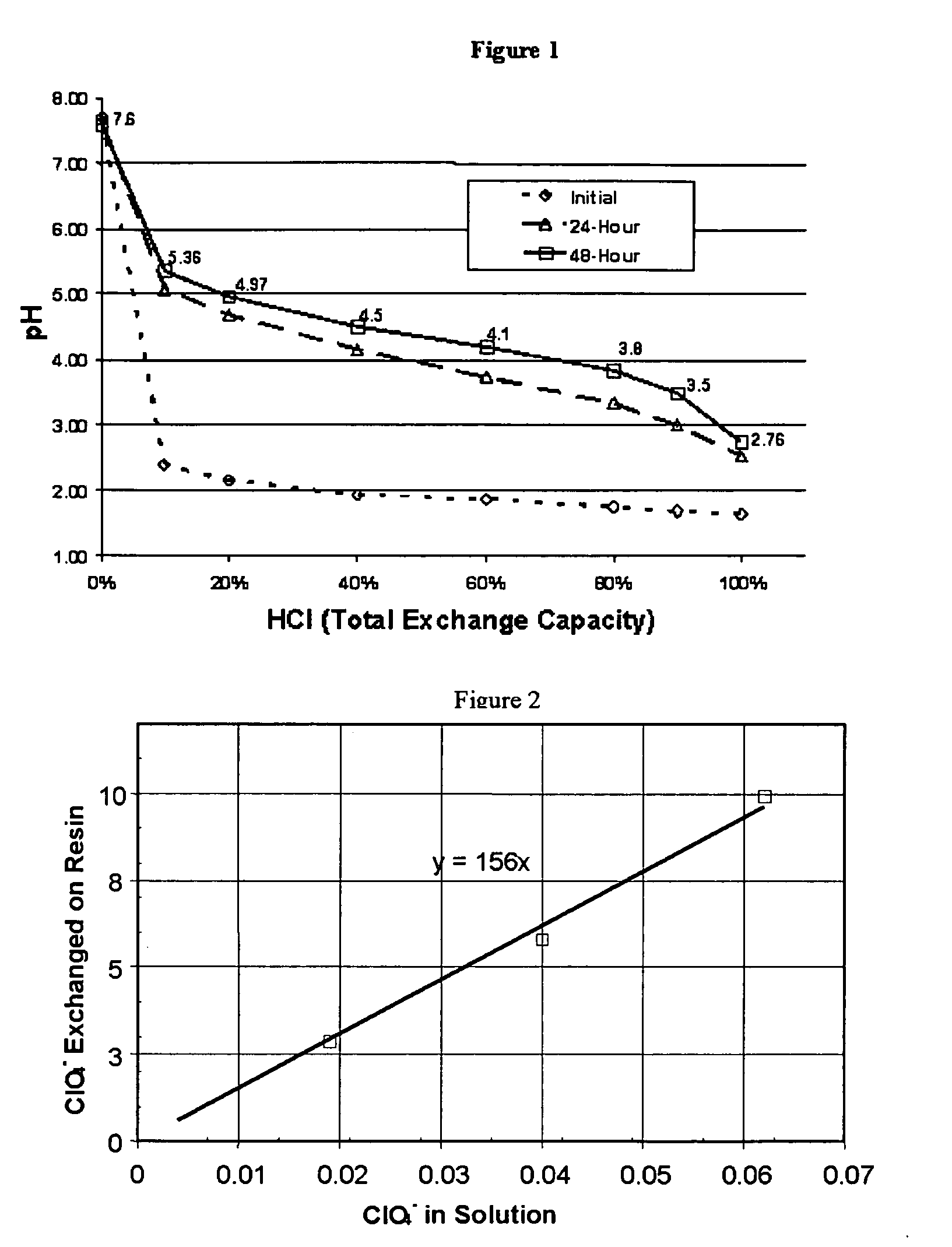
Process for regenerating and protonating a weak-base anion exchange resin
ActiveUS7875186B2Low costEasy disposalIon-exchanger regenerationOrganic anion exchangersSelenateIon exchange
The invention consists of a water treatment process using selective and regenerable weak base anion exchange resins to remove any number of complex anions, especially oxyanions including perchlorate, nitrate, chlorate, arsenate, selenate, and chromate, from aqueous solutions. The treatment process is comprised of three key processes including 1) pretreatment to lower pH, 2) ion exchange, and 3) post treatment to adjust pH and alkalinity. The invention also includes processes for regenerating weak base anion resins and treatment of the residuals generated. This invention employs pressurized treatment, carbon dioxide management, and reuse of regenerating solution to minimize pumping and treatment costs.
Owner:APPLIED RES ASSOCS INC +1
Method for preparing conductive textile fibre
Owner:江苏正本净化节水科技实业有限公司
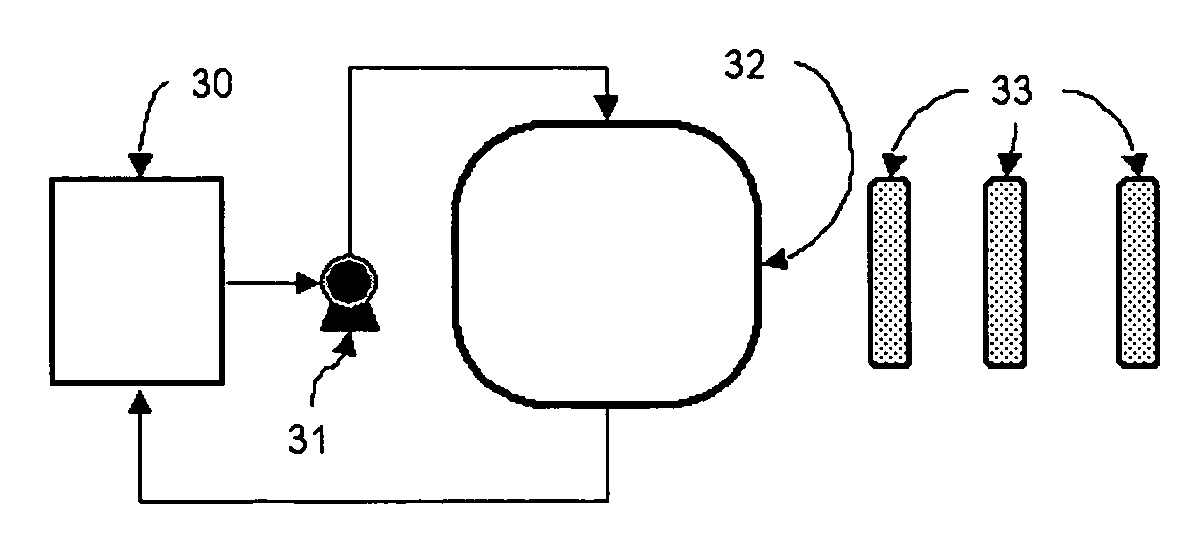
Methods for making chlorous acid and chlorine dioxide
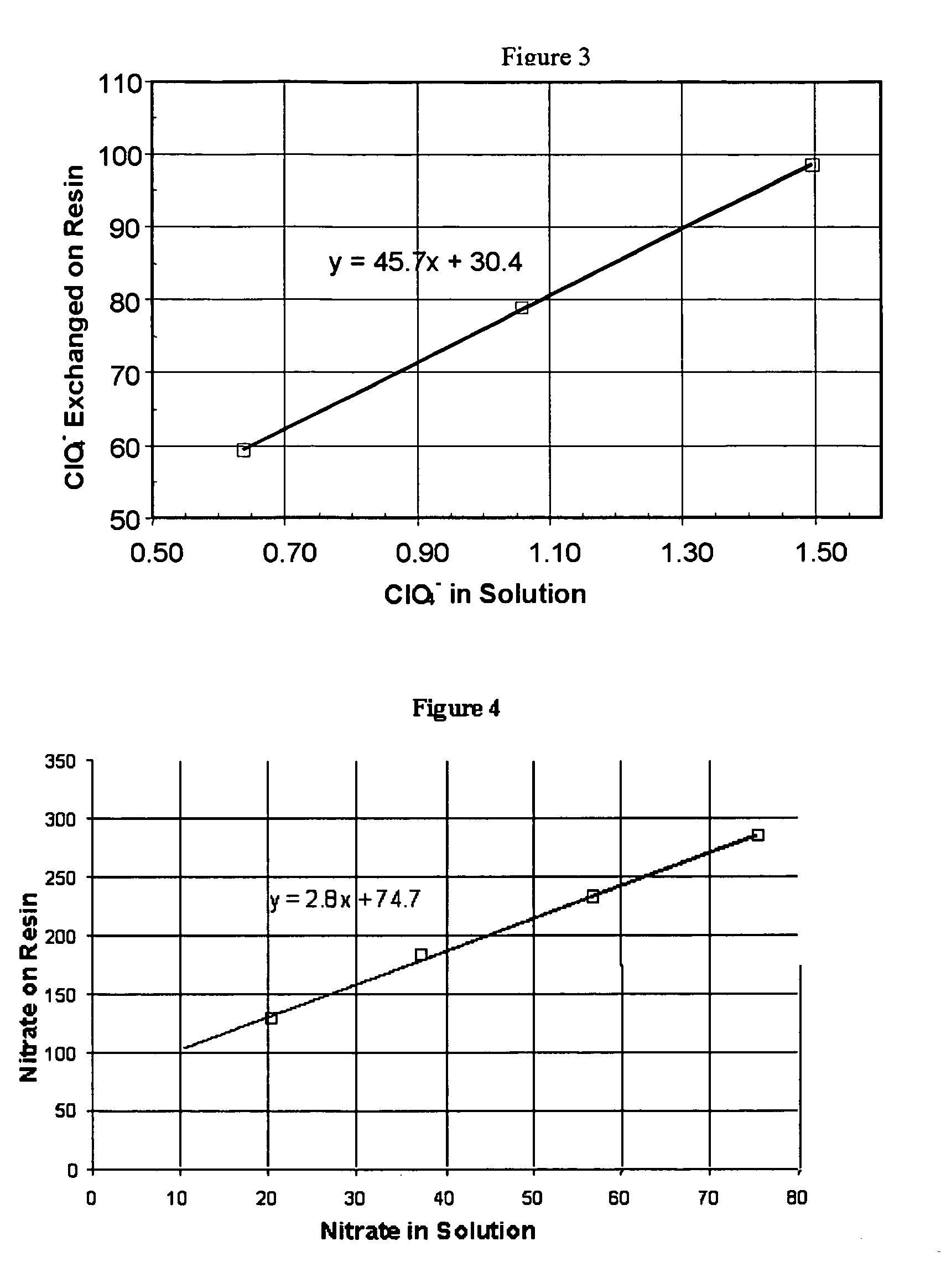
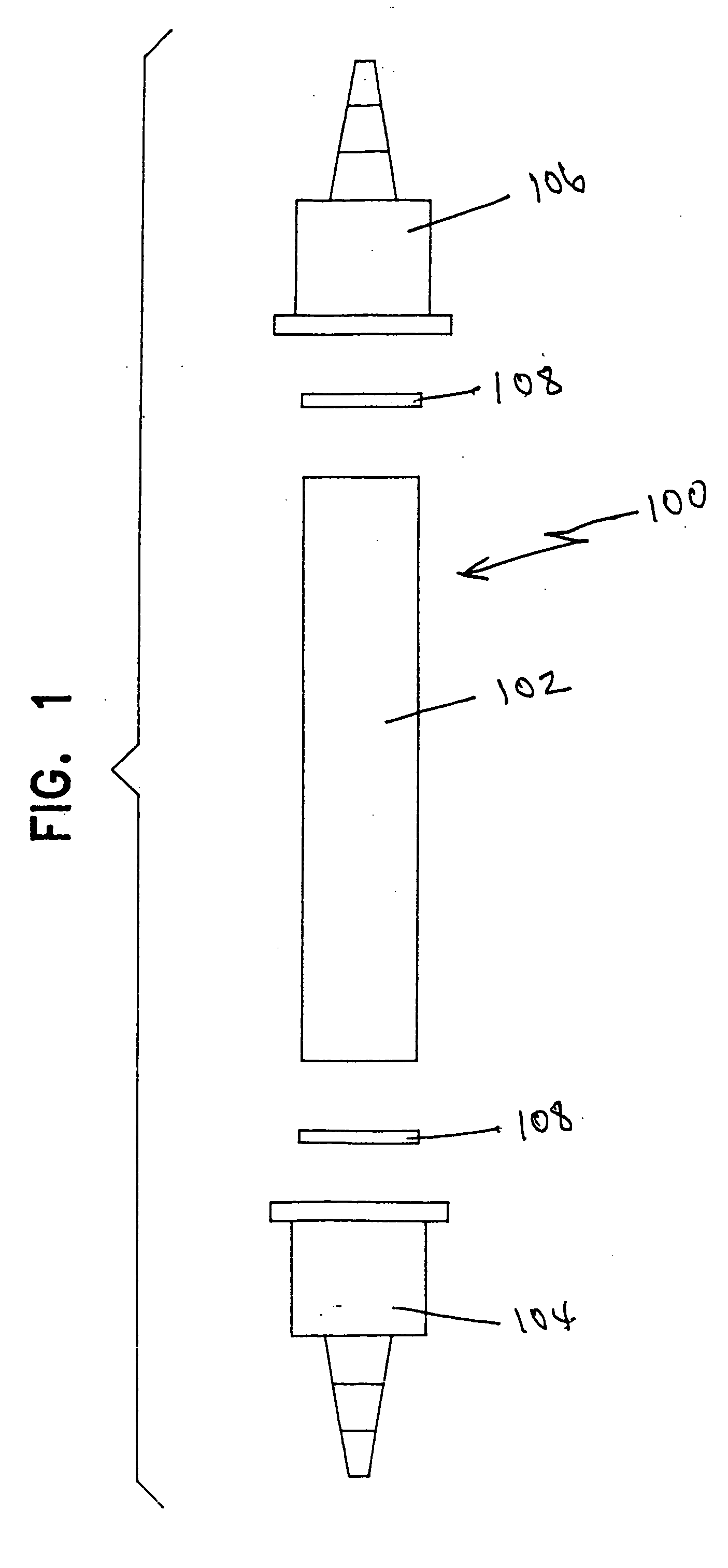
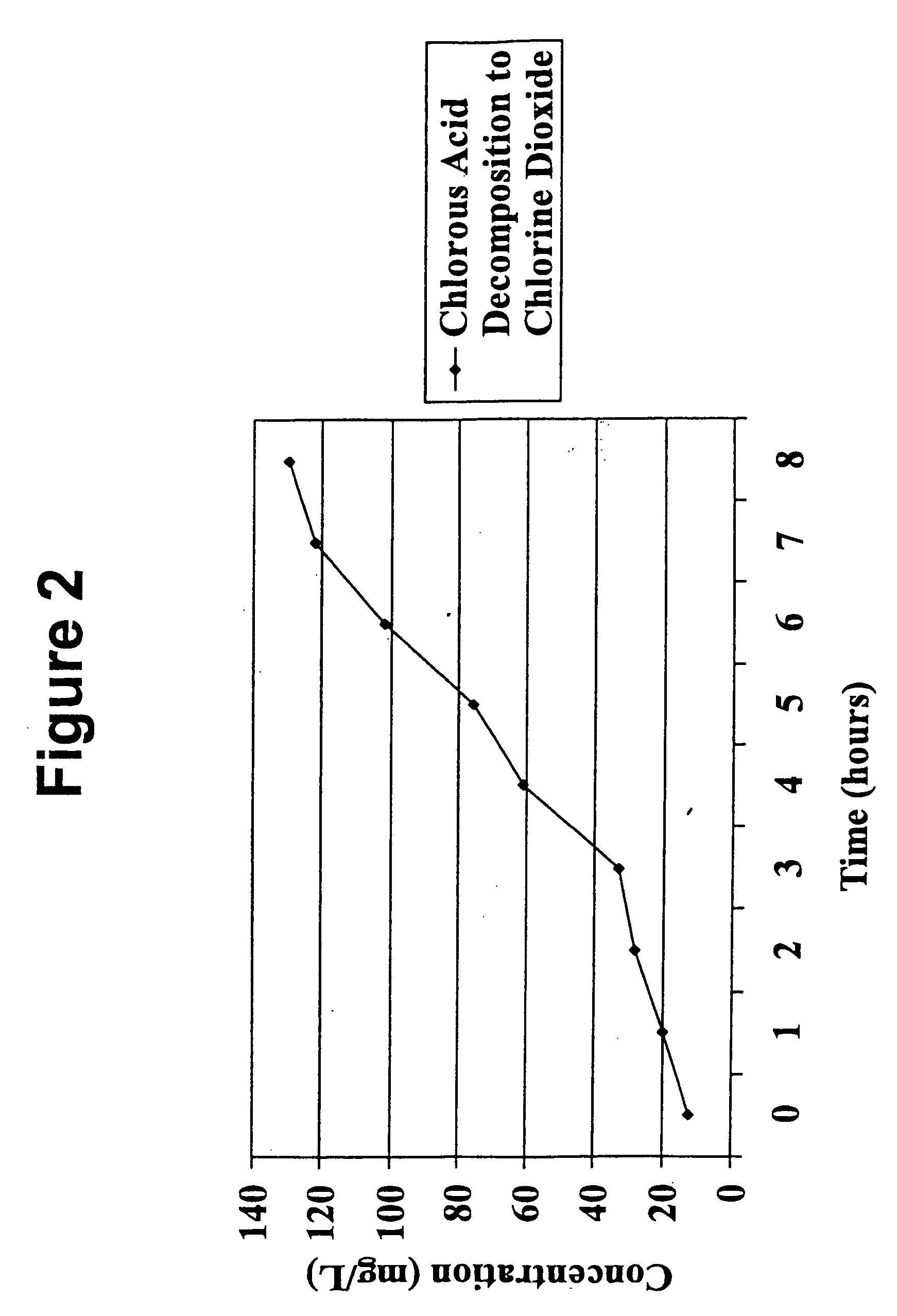
Chlorous acid is generated from a chlorite salt precursor, a chlorate salt precursor, or a combination of both by ion exchange. The ion exchange material facilitates the generation of chlorous acid by simultaneously removing unwanted cations from solution and adding hydrogen ion to solution. Chlorine dioxide is generated in a controlled manner from chlorous acid by catalysis. Chlorine dioxide can be generated either subsequent to the generation of chlorous acid or simultaneously with the generation of chlorous acid. For catalysis of chlorous acid to chlorine dioxide, the chlorous acid may be generated by ion exchange or in a conventional manner. Ion exchange materials are also used to purify the chlorous acid and chlorine dioxide solutions, without causing degradation of said solutions, to exchange undesirable ions in the chlorous acid and chlorine dioxide solutions with desirable ions, such as stabilizing ions, and to adjust the pH of chlorous acid and chlorine dioxide solutions.
Owner:SAMPSON ALLISON H +1
Aluminum and aluminum alloy film removing agent and application thereof
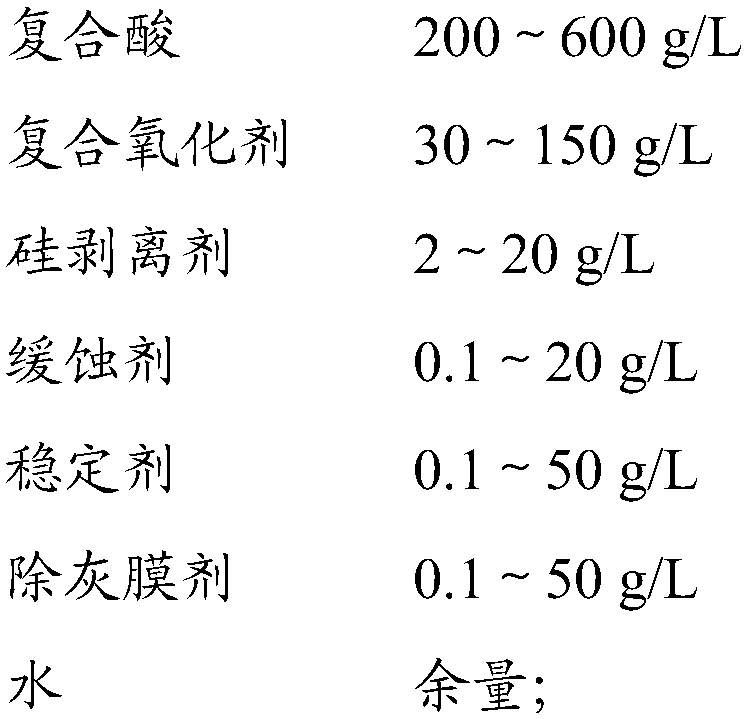
The invention relates to an aluminum and aluminum alloy film removing agent. The aluminum and aluminum alloy film removing agent comprises the following components: 200-600g / L of composite acid, 30-150g / L of a composite oxidant, 2-20g / L of a silicon remover, 0.1-20g / L of corrosion inhibitor, 0.1-50g / L of a stabilizer, 0.1-50g / L of an ash removal film agent and water, wherein the composite acid isselected from at least two of sulfuric acid, aminosulfonic acid, fluoboric acid and chloric acid; and the composite oxidant is selected from at least two of hydrogen peroxide, persulfate, perborate and percarbonate. On the premise of guaranteeing the film removal effect of the aluminum and the aluminum alloy, the aluminum and aluminum alloy film removing agent reduces treatment difficulty of industrial waste gas and industrial wastewater after aluminum and aluminum alloy electroplating.
Owner:GUANGZHOU SANFU NEW MATERIALS TECH
Cobalt copper sulfide ore processing method
ActiveCN102465202AImprove leaching efficiencyLow costProcess efficiency improvementChloric acidSulfite
The invention which is suitable for the technical field of mineral processing provides a cobalt copper sulfide ore processing method. The method comprises the following steps: 1, grinding the cobalt copper sulfide ore, mixing the cobalt copper sulfide ore with sulfurous acid or a sulfite according to a ratio of the total mass of cobalt and copper in the cobalt copper sulfide ore to the mass of sulfurous acid or the sulfite of 1:1-3, adding an acidic solution to adjust the pH value of the obtained system to 0.5-1, and reacting for more than 1h at 65-80DEG C; and 2, maintaining the pH value andthe temperature of the system, adding chloric acid or a chlorate according to a ratio of the total mass of residual cobalt and residual copper in the system to the mass of chloric acid or the chlorate of 1:1-3, and continuously reacting for more than 1h. The cobalt copper sulfide ore processing method of the invention, which allows cobalt and copper in the cobalt copper sulfide ore to be fully leached by carrying out primary leaching with sulfurous acid or the sulfite and carrying out secondary leaching with chloric acid or the chlorate, allows the leaching efficiency of cobalt and copper in the cobalt copper sulfide ore to be substantially improved. Sulfurous acid or the sulfite is used as an oxidant and a reductant in the primary leaching process, and chloric acid or the chlorate is used as an oxidant in the secondary leaching process, so the processing cost is substantially reduced.
Owner:GEM CO LTD +1
Chemical carbon dioxide gas generator
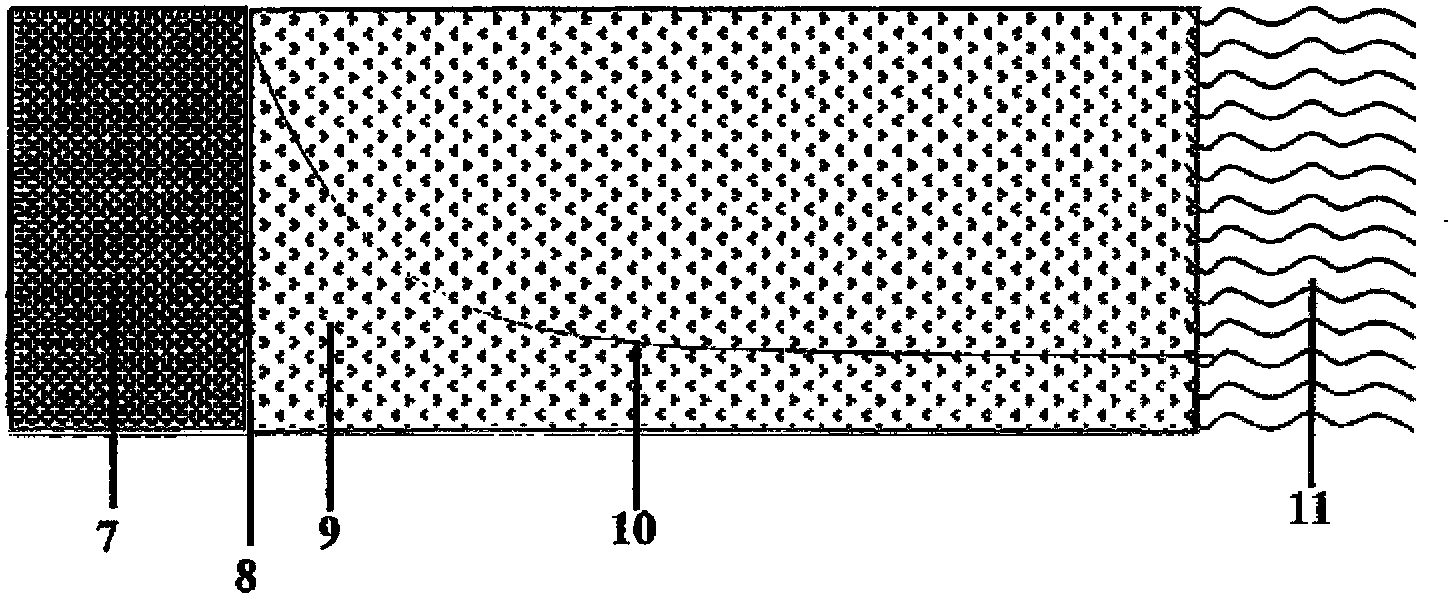
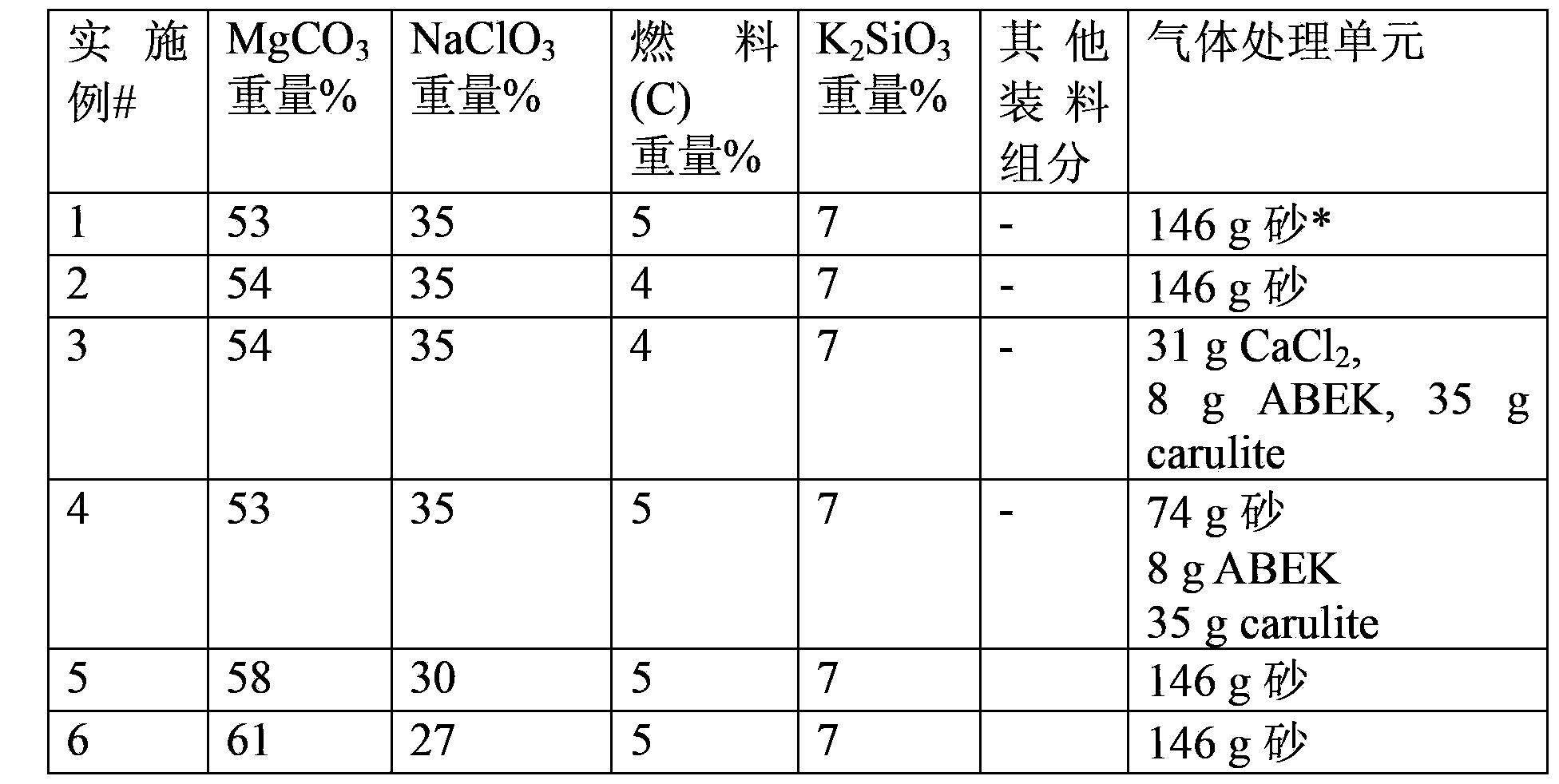
A chemical carbon dioxide gas generator comprising: - a charge housing; - a carbon dioxide gas penetrable charge, contained in the said housing, the charge comprising a) 40-60 wt. % of a substance which upon decomposition generates carbon dioxide, which substance is selected from the group of magnesium carbonate, other carbonates, magnesium oxalate and other oxalates, b) 20-50 wt. % of an oxidiser selected from the group of sodium chlorate, potassium chlorate, lithium chlorate, other metal chlorates, sodium perchlorate, potassium perchlorate, lithium perchlorate, and other metal perchlorates, c) 1-20 wt. % of carbon or another fuel, d) 1-10 wt. % binder, said components a), b), c) and d) together forming 90-100 wt. % of the total weight of the charge; - an ignition device for igniting the charge; - a carbon dioxide gas treatment unit for reducing the content of one or more side-products - which may have been formed by the charge - in the generated carbon dioxide, and / or for cooling carbon dioxide gas generated by the charge; and - an outlet for carbon dioxide gas generated by the charge.
Owner:荷兰应用自然科技研究组织TNO
Nonsludging zinc phosphating composition and process
InactiveUS7422629B1Electrolytic inorganic material coatingOther chemical processesPhosphoric Acid EstersElectrolysis
Electrolysis using a suitable electrolyte provides a completely nonsludging zinc phosphate conversion coating process that produces a high quality conversion coating in a very short time. The suitable electrolyte contains at least water, dissolved nitric acid, and dissolved zinc cations and optionally also contains m chemically distinct species of cations other than zinc and n chemically distinct species of anions other than anions derivable by ionization of phosphoric and nitric acids, each of m and n independently being zero or a positive integer. Preferably, the liquid composition contains as additive at least one selection from nitrous acid, permanganic acid, peroxysulfuric acid, hydrogen peroxide, chloric acid, perchloric acid, nitrobenzenesulfonic acid, hydroxylamine, starch / phosphoric acid esters, fluorine compounds, and salts of the preceding; and / or the metal substrate is subjected to cathodic electrolysis after the workpiece has been brought into contact with a weakly basic aqueous colloidal solution that contains titanium oxide, titanium hydroxide, and zinc phosphate.
Owner:HENKEL KGAA
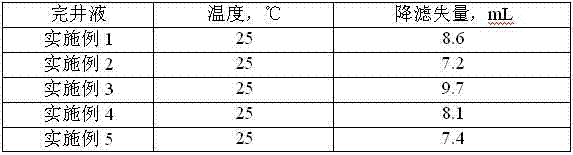
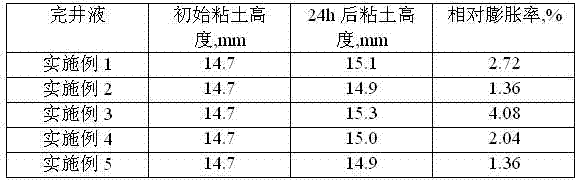
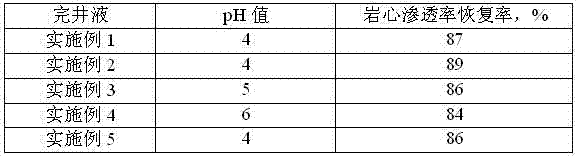
Low-permeability solid-free completion fluid
Owner:DAQING HUAYING CHEM IND
New low-cost oxidation denitrating technology
ActiveCN103191634ALow operating costSimple processDispersed particle separationEngineeringNitric oxide
The invention provides a new low-cost oxidation denitrating technology aiming at the problem that the denitrating technology in the prior art is high in cost. The new low-cost oxidation denitrating technology comprises the specific steps as follows: A) preparing aqueous solution with chlorate ion concentration of 50-500g / L by taking lime water and chlorine as raw materials; B) in oxidation section, diluting the prepared aqueous solution to serve as an oxidant, and spraying into the oxidation section from the upper part, so as to contact with smoke entering from the lower part reversely and enable nitric oxide in the smoke to have oxidation reaction; and C) in an absorption section, spraying alkali liquor as an absorbent into the absorption section from the upper part to absorb the oxidized nitric oxide in the smoke to produce corresponding nitrite dissolved in water, thereby achieving the denitration purpose. The new low-cost oxidation denitrating technology has the advantages of being simple in technological flow, low in operation cost and the like.
Owner:陈洪会 +2
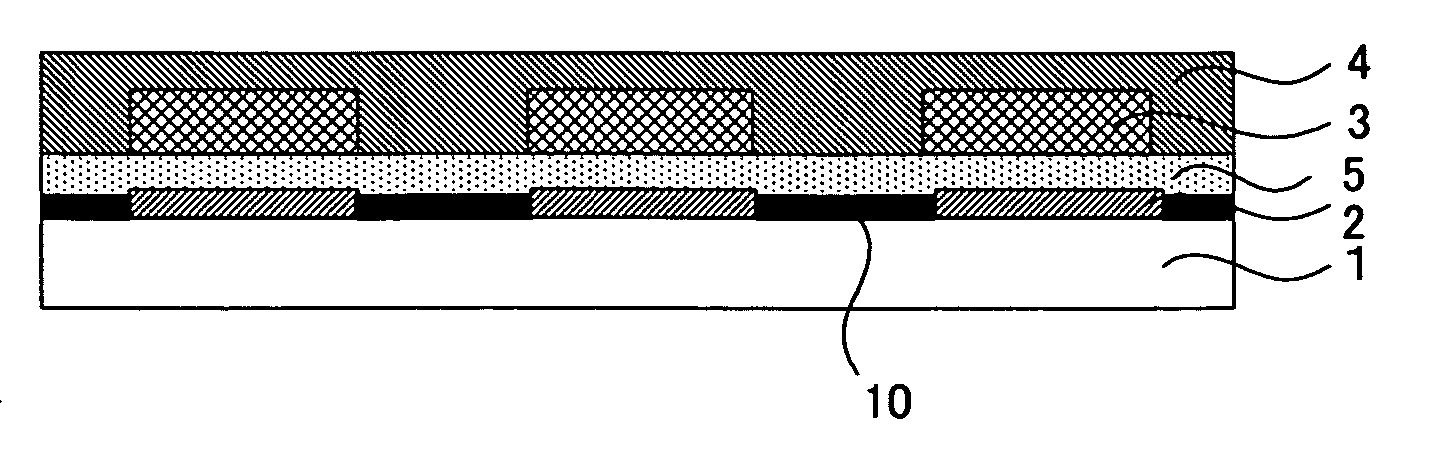
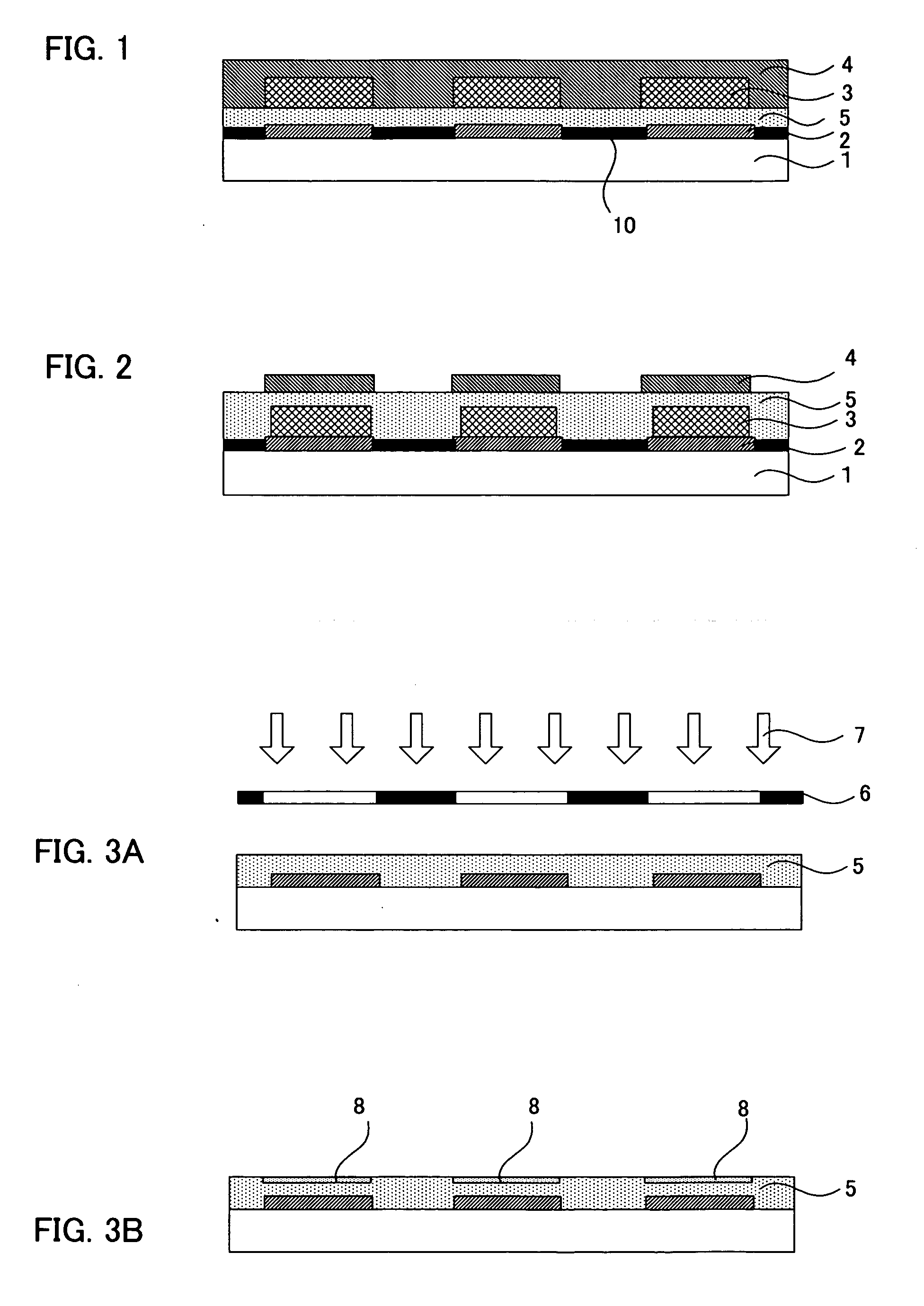
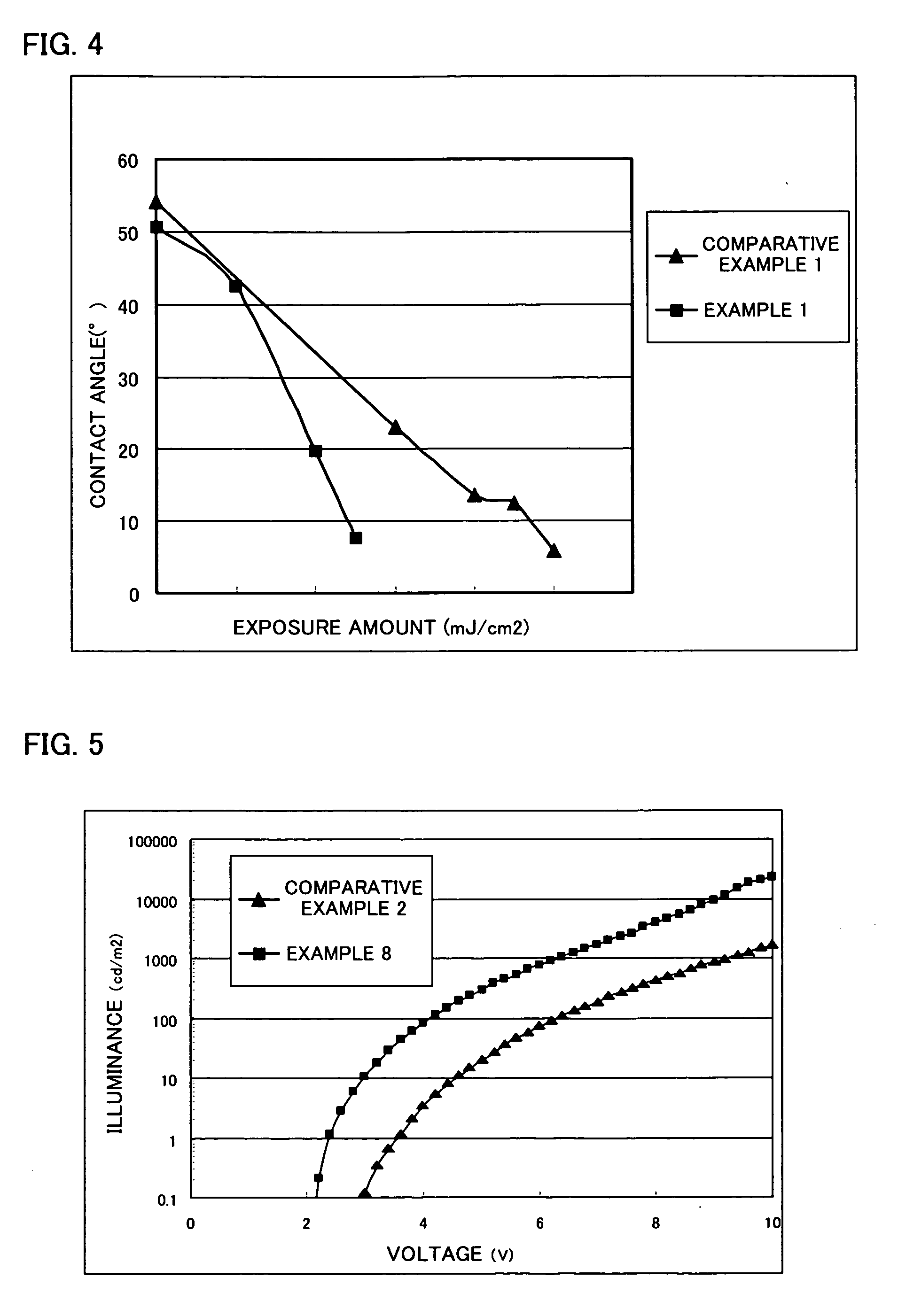
Organic electroluminescent element and photocatalyst containing coating solution for organic electroluminescent element
InactiveUS20070059555A1Made tallerHigh activationSolid-state devicesNatural mineral layered productsNitro compoundCarboxylic acid
A main object of the present invention is to provide an organic EL element having members such as an organic EL layer formed highly precisely in a pattern with preferable light emission characteristic of the organic EL layer, and a photocatalyst containing coating solution to be used for the production thereof. To achieve the object, the present invention provides an organic electroluminescent element comprising: a substrate; a first electrode layer formed on the substrate; an organic electroluminescent layer formed on the first electrode layer; and a second electrode layer formed on the organic electroluminescent layer, wherein a photocatalyst containing layer containing a photocatalyst, a characteristic providing agent, and a light emission characteristic improving material having the function of improving the activation of the photocatalyst and the light emission characteristic of the organic electroluminescent layer so as to have the characteristic of the characteristic providing agent changed by the action of the photocatalyst accompanied by the energy irradiation is formed at any position between the substrate and the second electrode layer; and the light emission characteristic improving material is a silver salt of a fluorine or an acid selected from the group consisting of carboxylic acids, sulfonic acids, sulfinic acids, phenols, enols, thiophenols, imides, oximes, primary or secondary nitro compounds, clathrate compounds, a chloric acid and a perchloric acid.
Owner:DAI NIPPON PRINTING CO LTD
Method for regenerating precious-metal mercury-free catalyst for acetylene hydrochlorination
InactiveCN106732827AExtended service lifeReduce use costCatalyst regeneration/reactivationCooking & bakingElemental mercury
The invention discloses a method for regenerating a precious-metal mercury-free catalyst for acetylene hydrochlorination. The method comprises the following steps: (1) carrying out drying treatment; (2) carrying out treatment by using regeneration reagents such as an acid mixture of hypochlorous acid, chloric acid, perchloric acid, hydrogen peroxide and hydrochloric acid, formic acid, acetic acid and tartaric acid; and (3) carrying out water washing and baking. According to the method, the performance of the deactivated precious-metal mercury-free catalyst can be restored, and the precious-metal mercury-free catalyst can be recycled, so that the use cost is greatly reduced; and the implementation process is environmentally friendly, so that a foundation is laid for non-mercurization of calcium-carbide-process PVC industry.
Owner:XINJIANG CORPS MODERN GREEN CHLOR ALKALI CHEM ENG RES CENT LTD +1
Electrolysis cell for synthesizing perchloric acid compound and method for electrolytically synthesizing perchloric acid compound
The present invention provides an electrolysis cell for synthesizing a perchloric acid compound, the electrolysis cell having: a feedstock solution containing a chloride or a chloric acid compound; a cathode; and an anode having an electroconductive diamond as an anode substance, the anode electrolytically oxidizing the chloride or the chloric acid compound to synthesize the perchloric acid compound, and a method for electrolytically synthesizing a perchloric acid compound.
Owner:DE NORA PERMELEC LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com