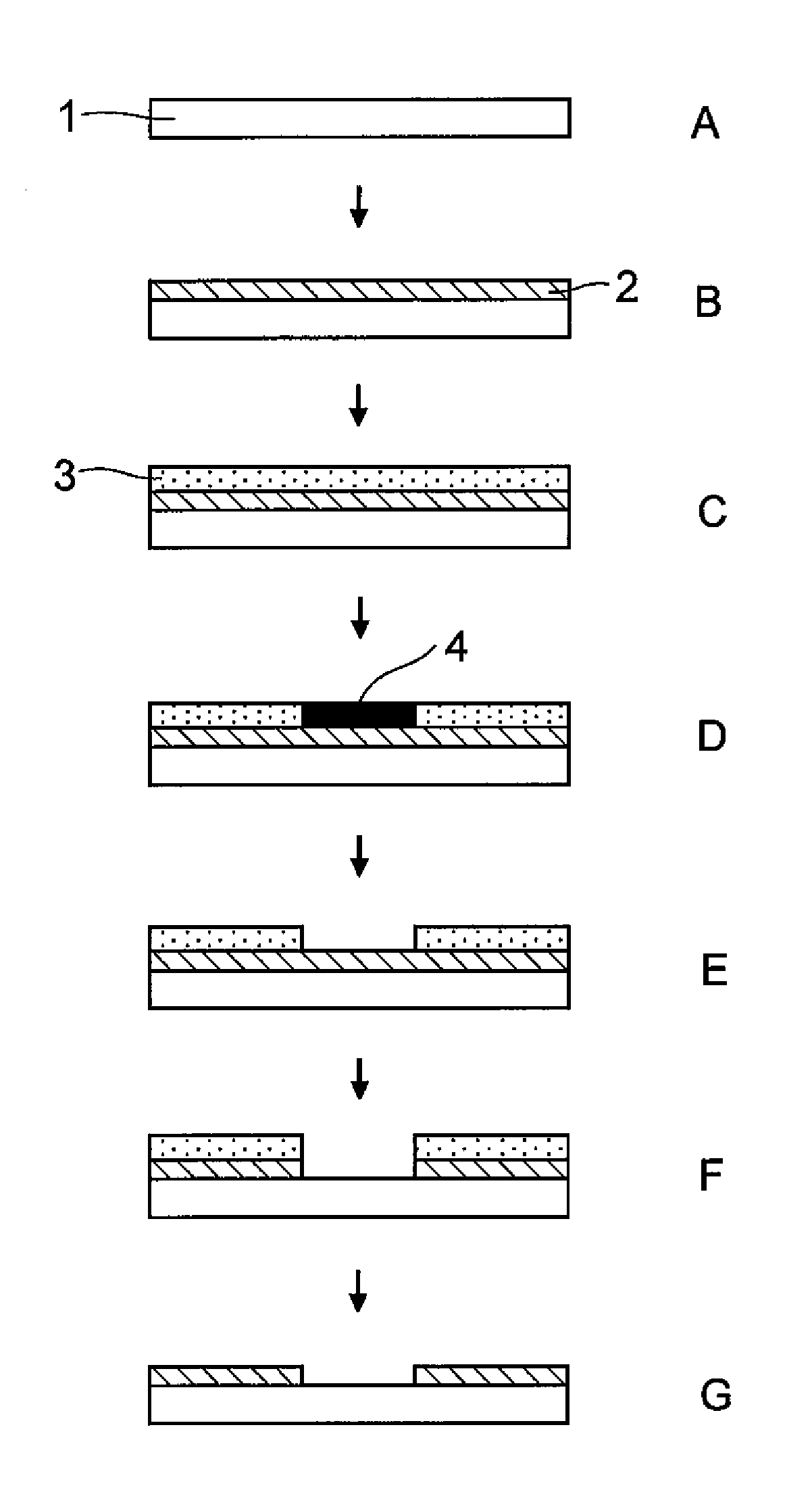
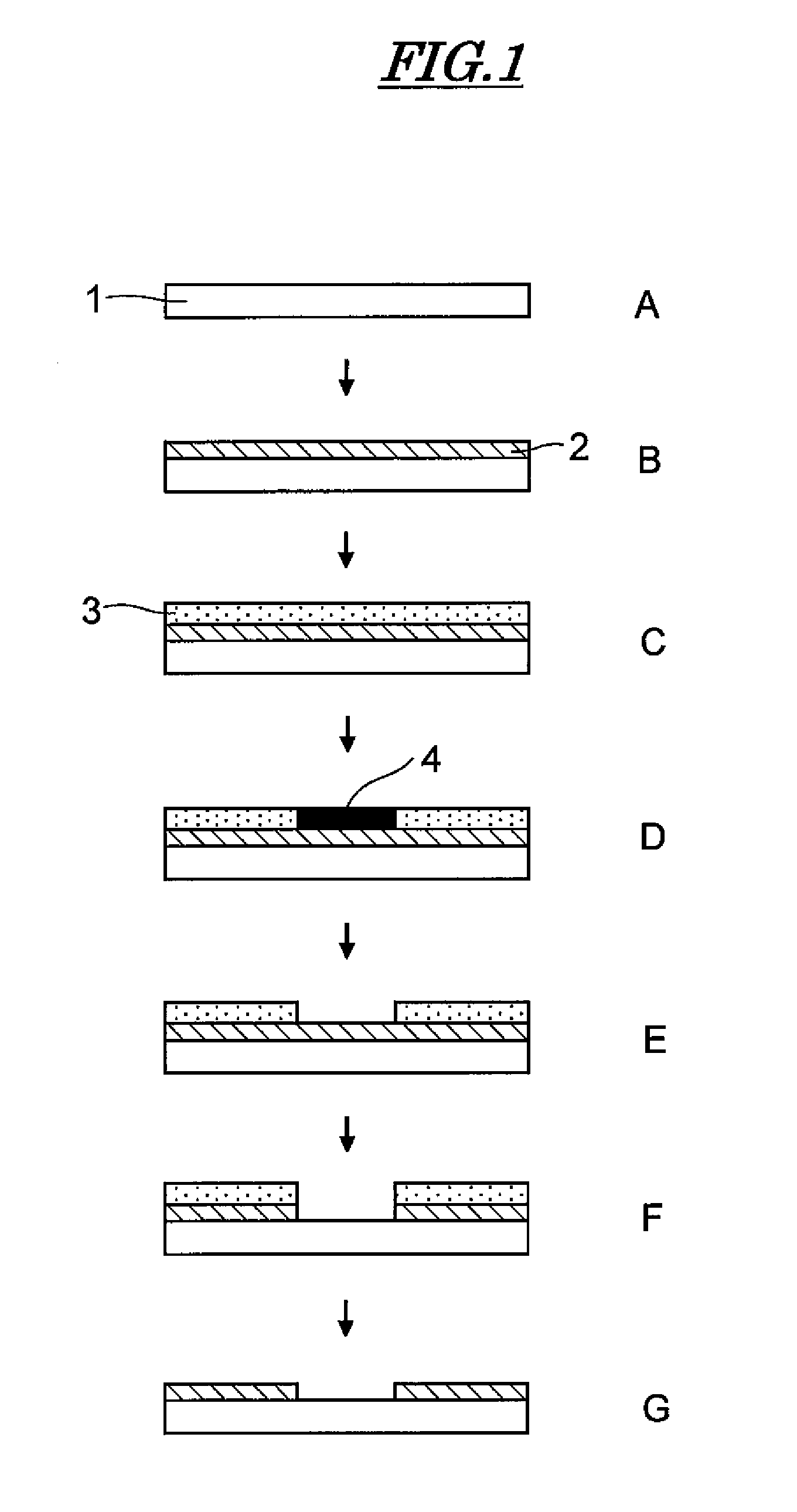
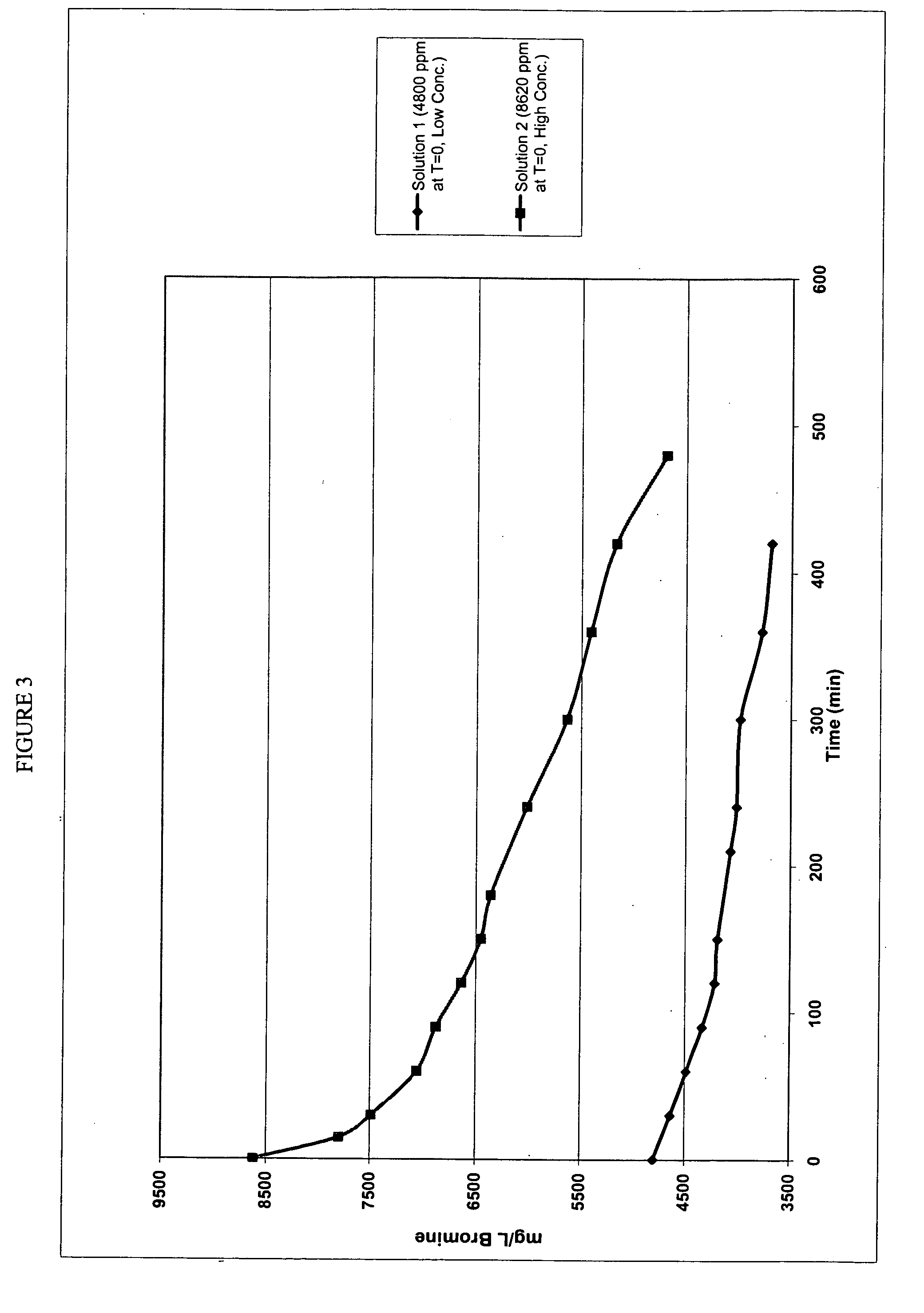
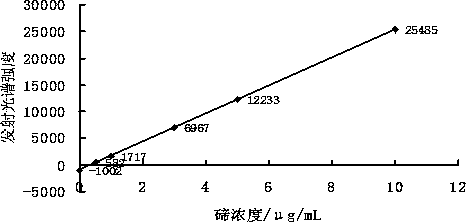
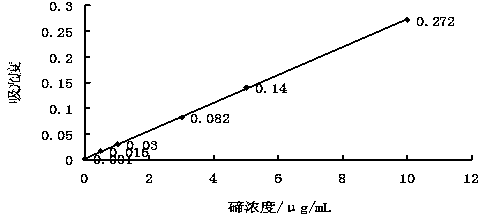
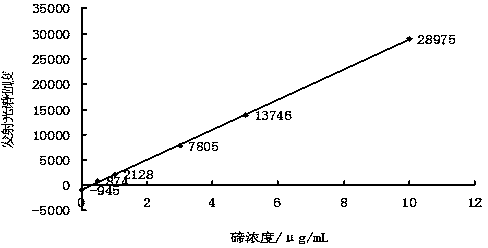
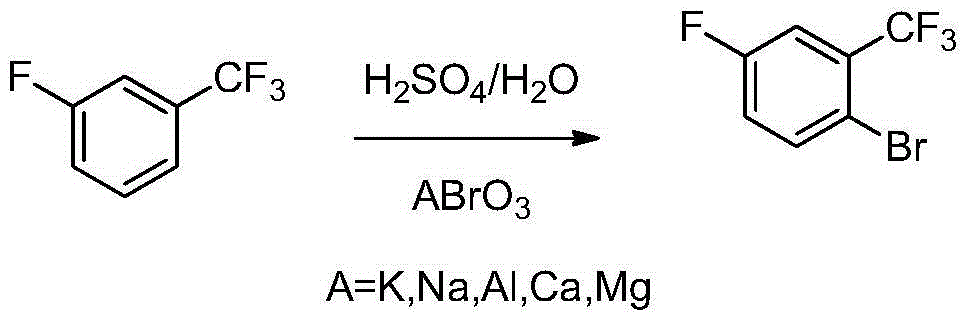Patents
Literature
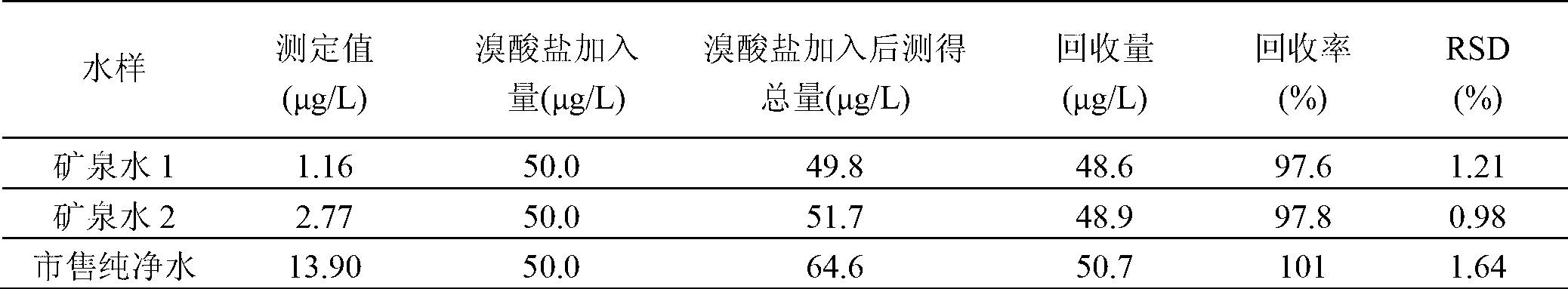
105 results about "Bromic acid" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Bromic acid, also known as hydrogen bromate, is an oxoacid with the molecular formula HBrO₃. It only exists in aqueous solution. It is a colorless solution that turns yellow at room temperature as it decomposes to bromine. Bromic acid and bromates are powerful oxidizing agents and are common ingredients in Belousov-Zhabotinsky reactions. Belousov-Zhabotinsky reactions are a classic example of non-equilibrium thermodynamics.
Color changing lipstick and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN107595679AEffective penetrationGood conditioning effectCosmetic preparationsMake-upColor changesMoisture
The invention relates to the field of cosmetics, in particular to color changing lipstick. The color changing lipstick is prepared from the following raw materials in percentage by weight: 20 to 30 percent of plant conditioning grease, 20 to 30 percent of skin moisturizing agents, 20 to 30 percent of wax, 0.5 to 1 percent of additives, 1 to 5 percent of polyglycerol 2-isostearate / dilinoleic estercopolymers, 1 to 5 percent of hydrogenated castor oil dilinoleic ester, 5 to 10 percent of castor oil and 0.01 to 2 percent of bromic acid haematochrome. The color changing lipstick has the advantagesthat relatively good color luster and touch sense are realized; the conditioning effect is good; the moistening and moisture preserving effects are achieved; the coating is fine and smooth, and the like.
Owner:OPAL COSMETICS HUIZHOU
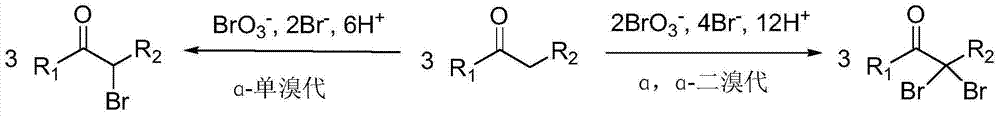
Method for preparing alpha-monobrominated ketone and alpha, alpha-dibrominated ketone compounds by selectively brominating ketone compounds
InactiveCN104119211AIncrease profitHigh selectivity for brominationOrganic compound preparationCarboxylic acid esters preparationKetoneSolvent
The invention discloses a method for preparing alpha-monobrominated ketone and alpha, alpha-dibrominated ketone compounds by selectively brominating ketone compounds. The method comprises the steps of by taking ketone compounds as reactants, taking bromated and metal bromides in the presence of bromic acid or inorganic acid as brominating reagents and taking alcohol as a solvent, selectively brominating the ketone compounds into corresponding alpha-monobrominated ketone. The reaction has effects of high brominating selectivity, gentle reaction condition, high reaction velocity and high yield; the selected brominating reagents are cheap, easily available and low in toxicity; moreover, the method is high in bromine rate which is close to requirements of green chemistry, and therefore, the method is easy for industrial production and has good application prospect.
Owner:HUANGSHAN UNIV
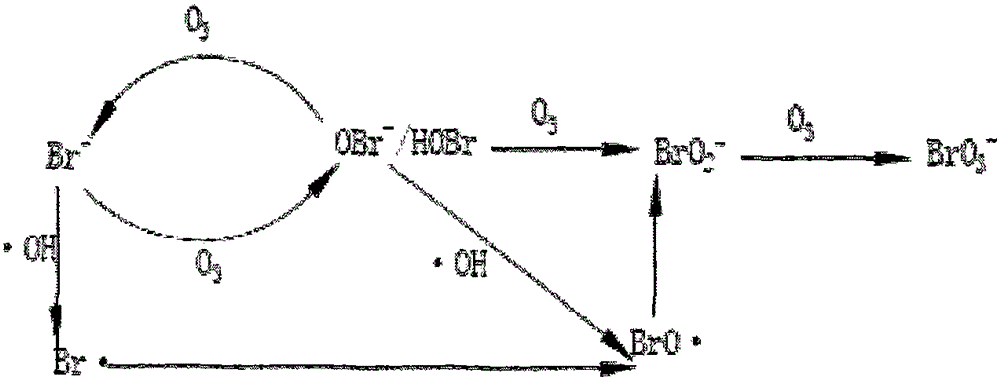
Method for controlling generation quantity of bromic acid radicle in treating procedure for oxidizing drinking water by ozone
InactiveCN101050036AGeneration of controlInhibitionMultistage water/sewage treatmentWater/sewage treatment using germicide/oligodynamic-processCatalytic oxidationWater quality
This invention relates to a method for controlling the quantity of bromate ions produced during treatment of ozone-oxidized drinking water. The method solves the problems of consuming residual chlorine, eroding pipes and meshes, and generating toxic substances by present techniques. The method controls the quantity of bromate ions by introducing cerium oxide, transition metal oxide-doped cerium oxide or supported cerium oxide catalyst for catalytic oxidation. The quantity of produced bromate ions is decreased by 80% when the bromic ions concentration is 100-200 mu.g / L and the consumption of cerium oxide is 100 mg / L. The method has a high efficiency in inhibiting the generation of bromate ions, and the yield of byproducts is 20-30% lower than that produced by pure ozone oxidation.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
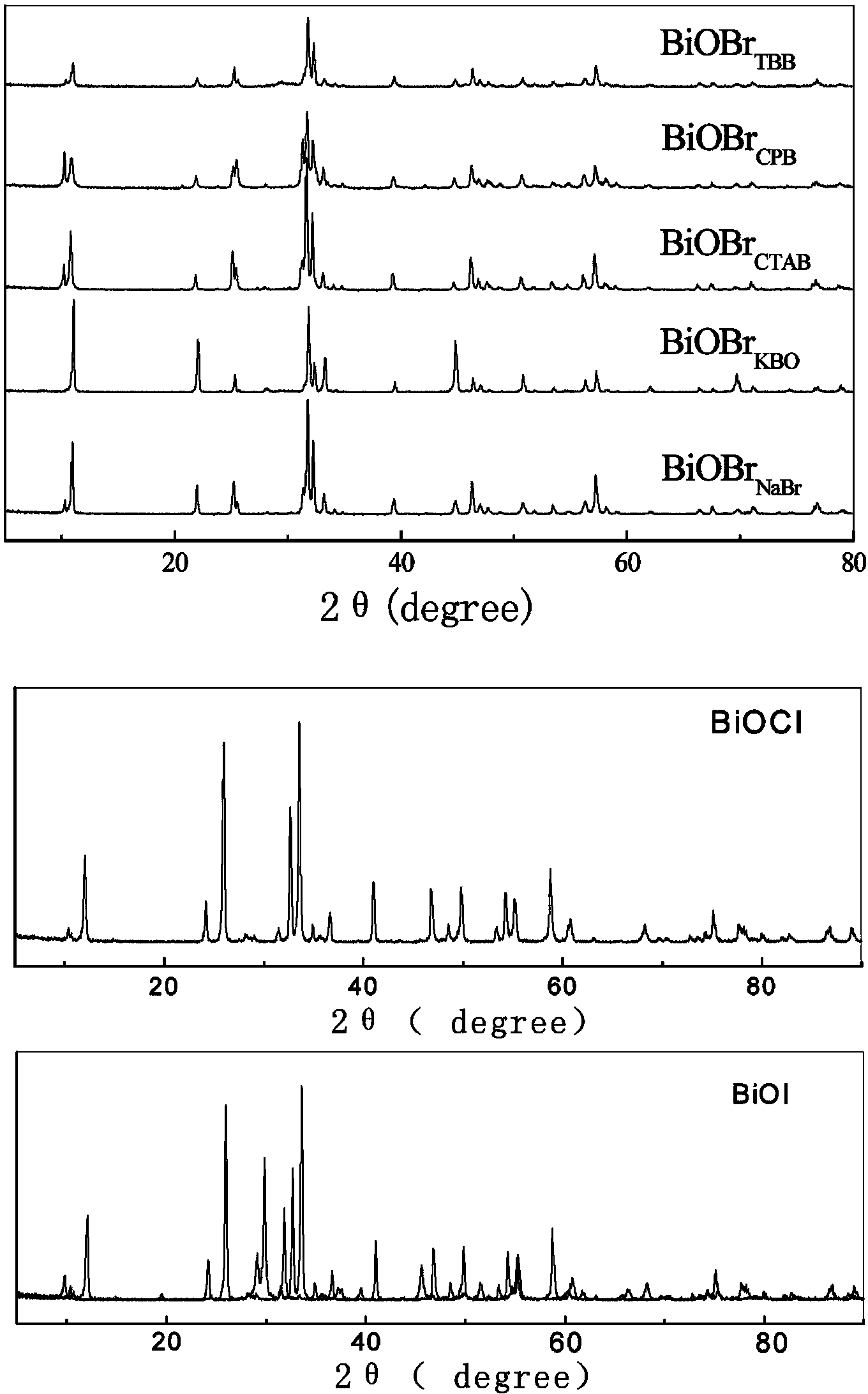
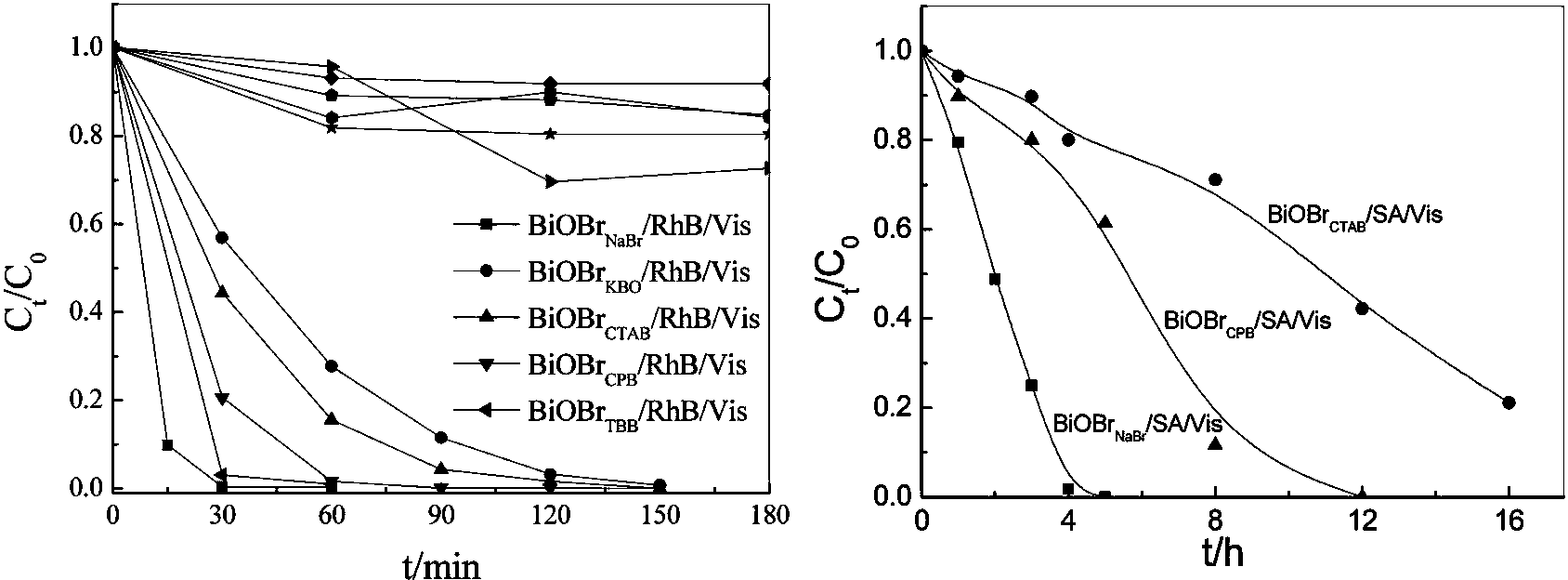
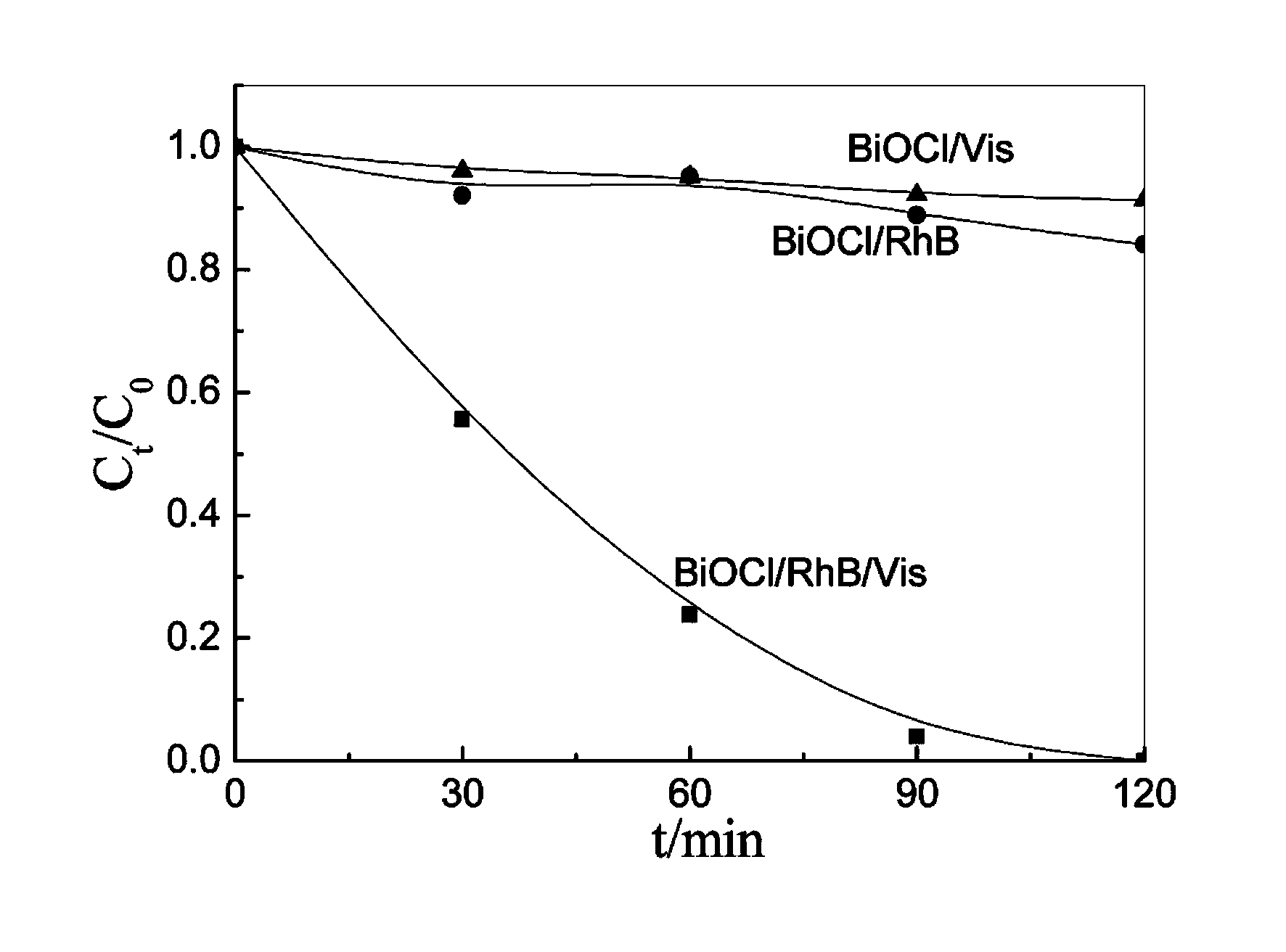
Bismuth oxyhalide photocatalyst and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN103878000AAvoid disadvantagesPhysical/chemical process catalystsBismuth compoundsCetylpyridiniumPhotochemistry
The invention relates to a bismuth oxyhalide photocatalyst. According to a method for preparing bismuth oxyhalide photocatalyst, sodium bismuthate is used as the bismuth source, and sodium halide or potassium bromate or cetyl trimethyl ammonium chloride or halogenated cetylpyridinium or tetrabutyl ammonium halide is used as the halogen source; the halogen source is added into deionized water and mixed for 20 minutes for dissolution under the ultrasonic condition, and then sodium bismuthate is added into the halogen source for pH adjustment; the mixed solution is put into a reaction kettle for reaction, and the halogen source is marked as follows according to the bromine source: sodium halide (BiOBrNaBr), potassium bromated (BiOBrKBrO3), cetyl trimethyl ammonium chloride (BiOBrCTAB), halogenated cetylpyridinium (BiOBrCPB) and tetrabutyl ammonium halide (BiOBrTBB). The bismuth oxyhalide photocalyst is applied to visible light sensitization or degradation of rhodamine B (RhB) and salicylic acid (SA); the bismuth oxyhalide photocalyst has good stability and photocatalytic activity, and meanwhile, the preparation process is simple and the cost is low.
Owner:CHINA THREE GORGES UNIV
Etching liquid for conductive polymer, and method for patterning conductive polymer
InactiveUS20100089872A1Improve etching effectDecorative surface effectsPrinted circuit aspectsHydrogen halidePermanganic acid
The object is to provide an etching liquid for a conductive polymer having excellent etching capability toward a conductive polymer, and a method for patterning a conductive polymer employing the etching liquid for a conductive polymer. The conductive etching liquid of the present invention is selected from the group consisting of (1) an etching liquid comprising greater than 0.5 wt % but no greater than 70 wt % of (NH4)2Ce(NO3)8 or at least 0.5 wt % but no greater than 30 wt % of Ce(SO4)2, (2) an etching liquid comprising greater than 0.5 wt % but no greater than 30 wt % of (NH4)4Ce(SO4)4, (3) an etching liquid comprising a hypochlorous acid salt aqueous solution having an effective chlorine concentration of at least 0.06 wt % and a pH of greater than 3 but less than 8, (4) an etching liquid comprising nitrosyl chloride which comprises at least 5 wt % of hydrochloric acid and at least 20 wt % of nitric acid, a (hydrochloric acid concentration+0.51×nitric acid concentration) value being no greater than 35 wt %, and a (hydrochloric acid concentration+0.5×nitric acid concentration) value being at least 30 wt %, (5) an etching liquid comprising at least 3 wt % but no greater than 40 wt % of a bromic acid compound and at least 4 wt % of an inorganic acid, (6) an etching liquid comprising at least 6 wt % but no greater than 40 wt % of a chloric acid compound and at least 7 wt % of a hydrogen halide, (7) an etching liquid comprising at least 0.001 wt % but no greater than 20 wt % of a permanganic acid compound, and (8) an etching liquid comprising at least 3 wt % but no greater than 30 wt % of a hexavalent chromium compound.
Owner:TSURUMISODA +1
Laminated material for reclaiming bromine and bromine-containing water treatment method
InactiveCN1765516AAchieve regenerationFull recoveryInorganic anion exchangersWater/sewage treatment by ion-exchangeSingle elementBromine
The invention provides a layered material for recycling the bromine and the method for treating water with bromine, belonging to the water treatment technique. The inventive layered material is the layered bi-hydroxy composite metallic oxide LDHs whose chemical formula is [M2+1-xM3+x (OH) 2] x+ (An-) x / 2*yH2O), and its sintered product CLDH. The invention has the advantages that the LDHs and its sintered product CLDH can be used in the treatment of industry acid waste water with bromine and the bromine recycle, while said material can treat the drinking water with bromine to avoid the hurt on the human body caused by the bromic acid ion produced in the water purification disinfection process. The bromine ion absorbed by said treatment agent exchanged by sodium carbonate or sodium-hydroxide solution in a certain concentration can be recycled via being prepared into bromine single element by a certain oxidant.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF CHEM TECH
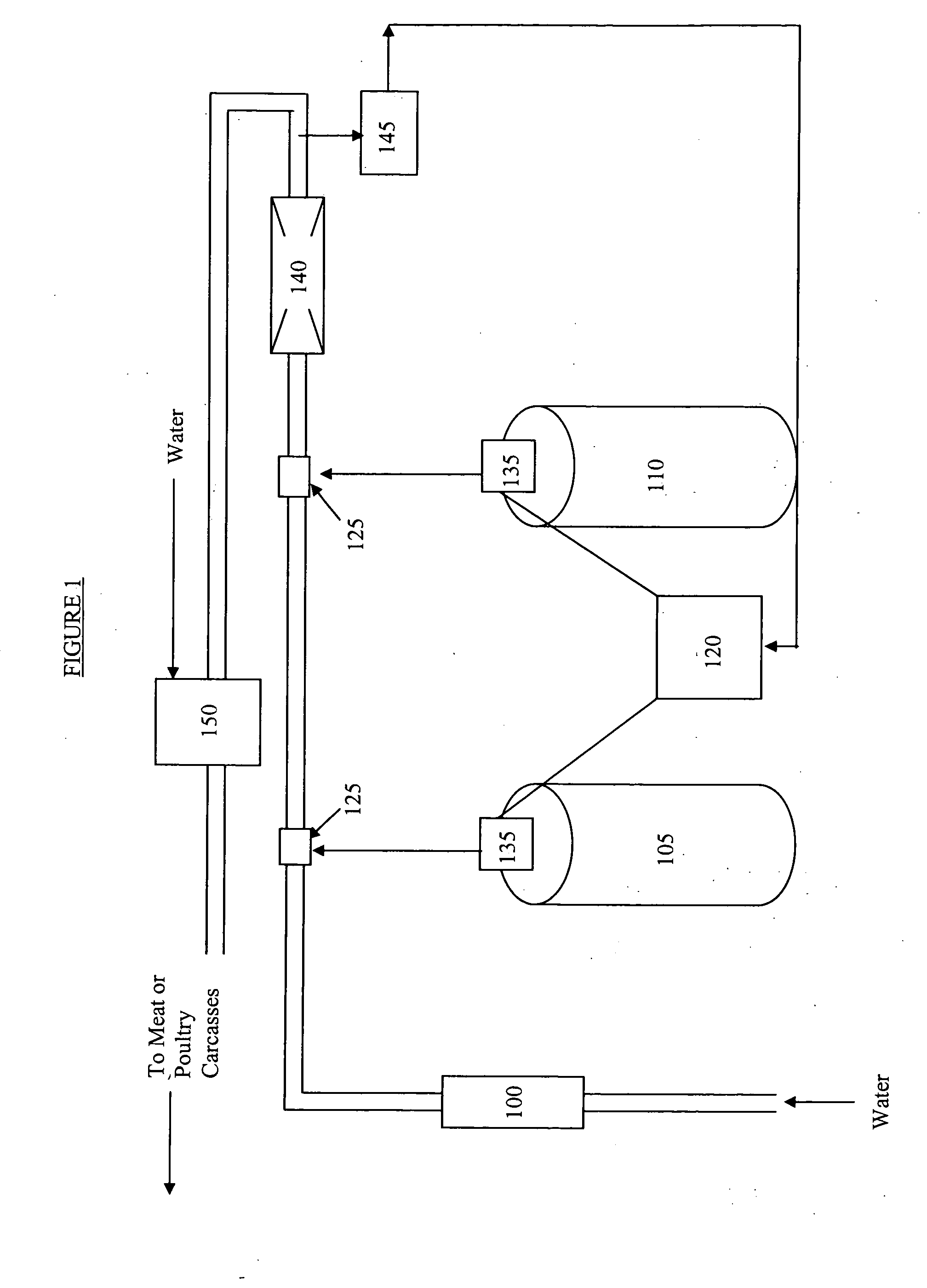
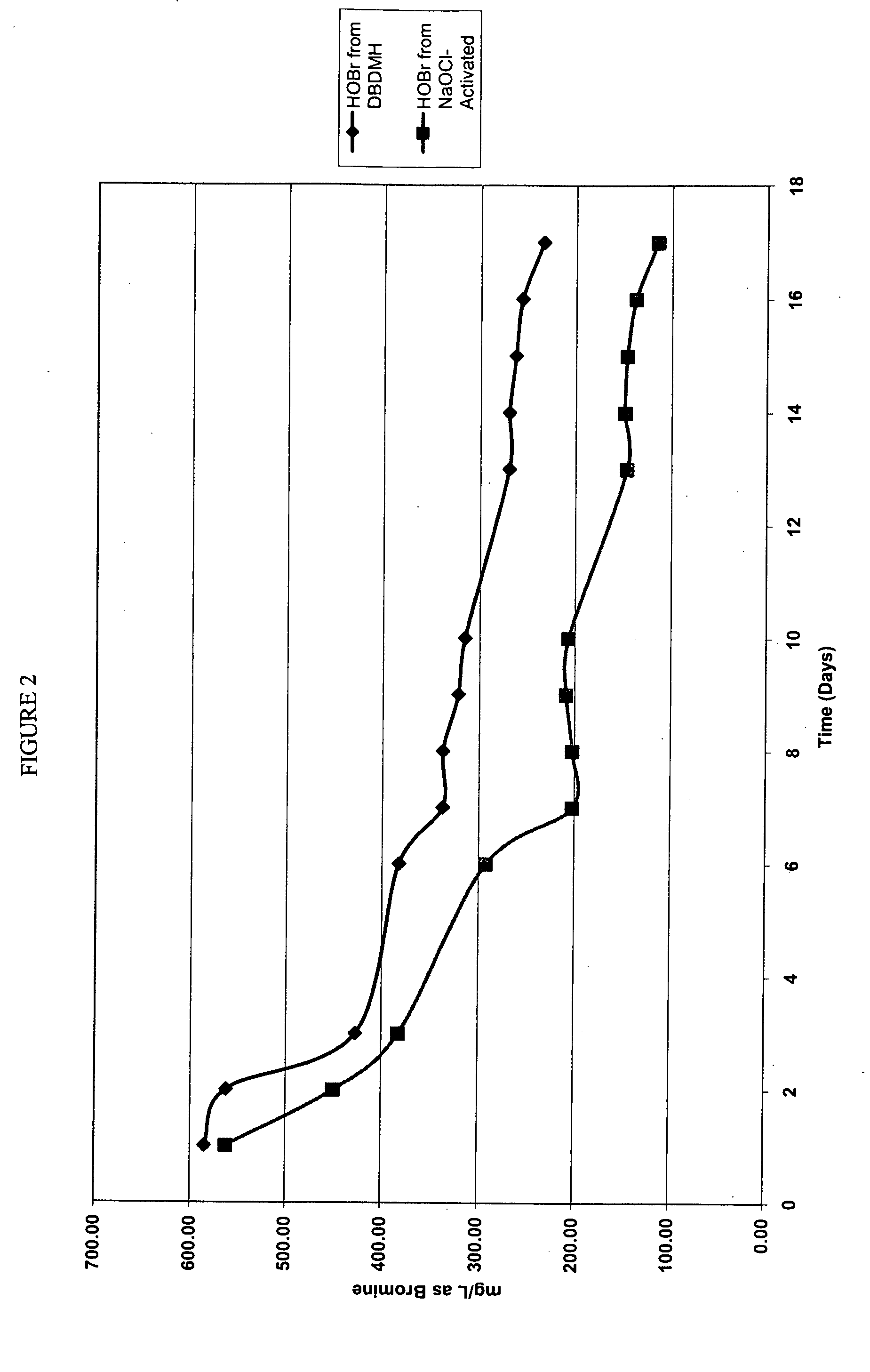
Methods and compositions for the reduction of pathogenic microorganisms from meat and poultry carcasses, trim and offal
InactiveUS20110200688A1Reducing cleaning chemicalReduce cleanup timeInorganic/elemental detergent compounding agentsBiocideMicroorganismHypobromous acid
The invention includes a method of preparing hypobromous acid by mixing an aqueous solution of hydrogen bromide and a source of hypochlorite with water. The invention also includes a method of using the hypobromous acid prepared by this method to wash animal carcasses, trim, and offal to reduce microorganisms, in particular, human pathogenic bacteria, on and in the carcasses, trim, or offal. Compositions of hypobromous acid are also described. The hypobromous acid of the invention may also be used to reduce fat, oil, and grease build-up on equipment and hard surfaces used in the processing of animal carcasses, trim, and offal.
Owner:ENVIRO TECH CHEM SERVICES
Lipophilic personal care composition
InactiveCN107669516AEffective penetrationGood conditioning effectCosmetic preparationsMake-upMyristic acidPersonal Care Product
The invention relates to the field of personal care products, in particular to a lipophilic personal care composition and use thereof. The lipophilic personal care composition comprises, by weight percentage, 1-10% of polyglyceryl 2-isostearate / dimer dilinoleic acid copolymer, 1-10% of hydrogenated castor oil dimer linoleate, 25-50% of isopropyl myristate, 10-50% of castor oil, 0.01-2% of bromic acid red pigment and 5-35% of conditioner. The composition has excellent dispersibility and stability in lipstick and excellent moisturizing and conditioning effects, is bright and beautiful in appearance and color, and is friendly and non-irritating to the human body.
Owner:OPAL COSMETICS HUIZHOU
Method for measuring content of tellurium in antimony and antimonous oxide
ActiveCN104034668AFast measurementSimple and fast operationPreparing sample for investigationColor/spectral properties measurementsAcid dissolutionAntimony trioxide
The invention relates to a method for measuring the content of tellurium in antimony and antimonous oxide. The method comprises the steps of dissolving antimony through chloroazotic acid or dissolving antimonous oxide through hydrochloric acid, then adding sulfuric acid and hydrobromic acid for volatilizing antimony under the temperature of 200-340 DEG C, repeatedly adding hydrochloric acid and bromic acid, heating under low temperature to volatilize and remove antimony, adding hydrochloric acid to dissolve residues, and performing dilution to make up to the volume; measuring a standard tellurium solution through an electric inductance coupling plasma emission spectrometer or a flame atom absorption spectrometer and drawing a working curve, then measuring the emission spectrum intensity or the absorbancy of an impurity, namely tellurium in a test sample, and constructing methods for analyzing tellurium in antimony and antimonous oxide in sequence according to a linear relation between concentration of tellurium and the emission spectrum intensity or the absorbancy in a certain concentration range; and calculating the concentration of tellurium in test liquid according to the working curve of the measured standard tellurium solution, and further calculating the mass percentage of tellurium. The method disclosed by the invention has the advantages of high sensitivity, high precision, high accuracy, wide linear range, high analysis efficiency and the like.
Owner:锡矿山闪星锑业有限责任公司
Water-based paint
InactiveCN104277687AImprove uniformityHigh mechanical strengthPolyester coatingsIsooctyl acrylateWater based
The invention discloses a water-based paint. The paint comprises alkyd resin, hydroxypropyl bromic acid resin, 2-hydroxyethyl acrylate, 2-ethylhexyl acrylate, diethyl malonate, methyl methacrylate, acrylic acid, talcum powder, calcite, titanium white, dibutyltin dilaurate, 10% silicon oil, magnesium stearate, N,N-dimethylethanolamine, organobentonite, lecithin, diluter, assistant, propylene glycol monomethyl ether and deionized water. The paint has the advantages of uniformly dispersed raw materials in the paint preparation process, favorable uniformity, high mechanical strength, favorable impact resistance, weather resistance, low energy consumption, favorable adhesive force, favorable scratch and abrasion resistance, low cost and no environment pollution.
Owner:QINGDAO JIASHANG CREATIVE CULTURE
Production process for controlling generation of ozonized bromate
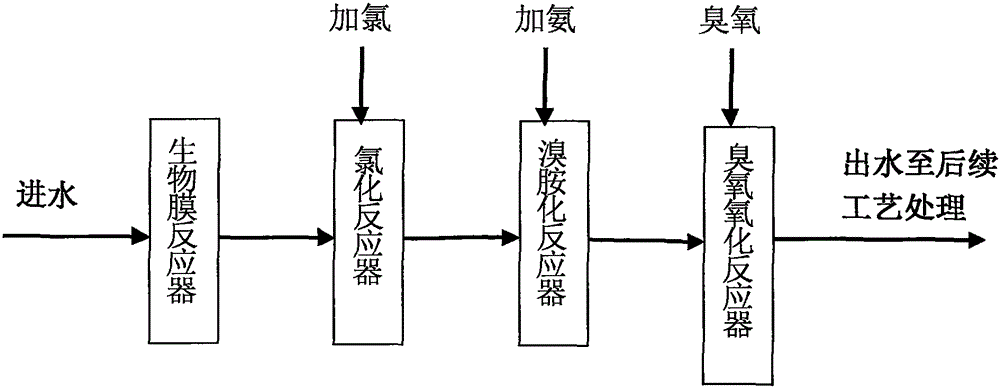
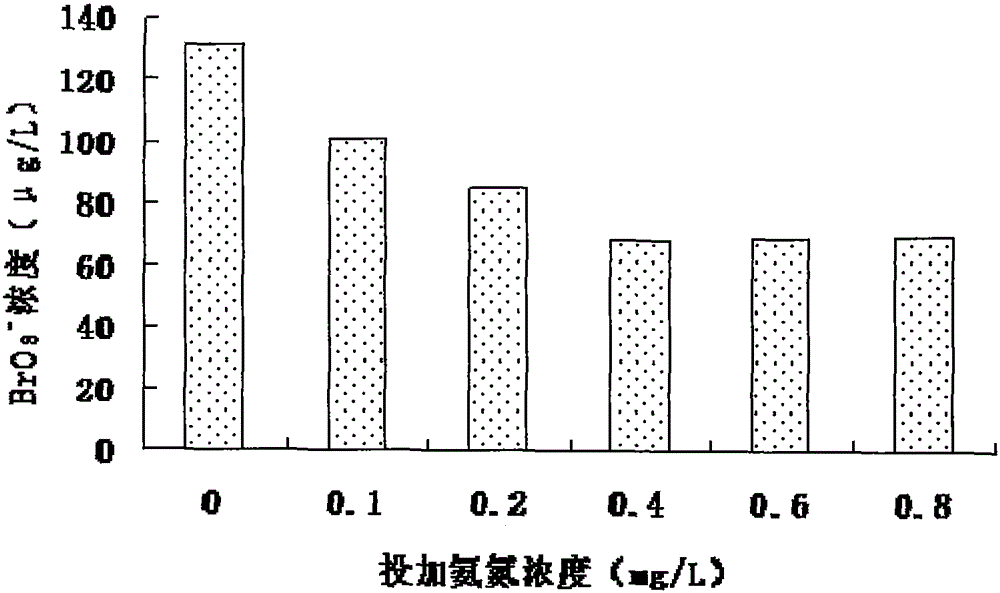
InactiveCN105236691AControl generationReduce concentrationWater contaminantsMultistage water/sewage treatmentHypobromous acidEngineering production
The invention discloses a production process for controlling generation of ozonized bromate. A biological film reactor is used for removing ammonia nitrogen in water before ozone is in contact with a pool, sodium hypochlorite is added to water for reacting, bromide ions in water are oxidized into hypobromous acid through hypochlorous acid, then ammonium chloride is added to water, hypobromous acid and the ammonium ions react to generate ammonium bromide, most of bromide ions in water are converted into ammonium bromide to reduce the concentration of the bromide ions in water, ozone is added to water to react with water, and due to the fact that the concentration of the bromide ions is low, the generation amount of bromate is effectively restrained in the ozonization process. The process is simple, operation is convenient, generation of bromate can be effectively controlled in practical engineering production, and therefore the concentration of bromate in water is reduced.
Owner:SHANDONG JIANZHU UNIV
Flux paste special for unleaded tin-bismuth solder and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN106001998AHigh activityImprove wettabilityWelding/cutting media/materialsSoldering mediaPolyamideSuccinic acid
The invention discloses flux paste special for unleaded tin-bismuth solder. The flux paste special for the unleaded tin-bismuth solder comprises, by weight, 10-20 parts of hydrogenated rosin, 5-10 parts of disproportionated rosin, 10-15 parts of dimer rosin, 5-10 parts of tetrahydrofurfuryl alcohol, 5-10 parts of pentaerythritol, 5-8 parts of butyl cellosolve, 5-8 parts of octyl ether, 5-8 parts of dibasic acid esters, 2-5 parts of phthalic acid dibutyl esters, 2-3 parts of oleyl alcohol polyoxyethylene ether, 3-6 parts of polyamide modified hydrogenated castor oil, 2-4 parts of succinic acid, 1-2 parts of pyridine hydrochloride, 1-2 parts of bromic acid tributylamine, 4-8 parts of DIACID 1550 and 1-3 parts of N,N,N,N'',N''-pentamethyldiethylenetriamine. The flux paste special for the unleaded tin-bismuth solder is good in wettability, the welding defect is lower than that of existing flux paste for the unleaded tin-bismuth solder, organic acid and polyamine decompose and volatilize in the welding process, the amount of residues generated after welding is small, and protective films can be formed on the surfaces of welding points through the used rosin.
Owner:丘以明
Process for eco-friendly synthesis of bromobenzene
ActiveUS6956142B2High atomic substitutionEliminate needPreparation by halogen additionBenzeneHypobromous acid
A new eco-friendly process is described in the present invention for the preparation of bromobenzene through substitution of one of the C—H proton of benzene ring with a highly reactive hypobromous acid generated in situ, said process comprises the steps of activating a water soluble, easy to handle, brominating reagent with a mineral acid at elevated temperature and atmospheric pressure to generate active bromine species which in turn reacts with benzene.
Owner:CENT SALT & MARINE CHEM RES INST +1
Color-changing lipstick
InactiveCN102366354AStrong and long-lasting colorPleasant aromaCosmetic preparationsMake-upColor changesVaseline
The invention provides a color-changing lipstick which contains the following components in parts by weight: 40 parts of glycerol monostearate, 4 parts of carnauba wax, 5 parts of vaseline, 36 parts of castor oil, 3 parts of wool grease, 7 parts of white oil, 5 parts of bromic acid red, 0.01 part of propylparaben and 0.01 part of essence. The lipstick is prepared by adopting the following steps of: S1, adding the castor oil into a blender and adding the bromic acid red; blending and heating to disperse and dissolve the bromic acid red into the castor oil; S2, fusing other raw materials except the essence and then blending uniformly; S3, mixing the material in the step S1 with the material in the step S2 and adding the essence; milling the mixture by utilizing a three-roller machine and repeatedly milling the mixture for five times; and after milling, carrying out vacuum degassing on the milled mixture; and S4, casting the treated mixture into a mould to be molded at a temperature of 40-50 DEG C. The invention aims to provide the color-changing lipstick which can be used for preventing lips from being chapped; after the lipstick is coated on the lips, the color of the lipstick is changed due to the change of the pH value; and the color-changing lipstick has the advantages of durable colors, pleasant fragrance and capabilities of moisturizing and softening skins.
Owner:SHANTOU JIANGYUAN CHEM
Treatment method of bromine-containing organic wastewater
PendingCN111087047AIncrease ion concentrationAvoid contactWater contaminantsWater/sewage treatment using germicide/oligodynamic-processHypobromous acidElectrolysis
The invention discloses a treatment method of degradation-resistant bromine-containing organic wastewater. The method comprises the following steps: adding bromine-containing organic wastewater into an electrolytic reactor; switching on the power supply connected to positive electrode and negative electrode of the electrolytic reactor, carrying out reactions for a while so that bromine ions in thewastewater are oxidized into bromine, and quickly carrying out reactions between bromine and water to generate strongly oxidative hypobromous acid. Hypobromous acid can oxidize and degrade refractoryorganic matters in the wastewater, so that COD of wastewater is reduced, and biodegradability of wastewater is improved. After the wastewater is treated by the method, refractory organic matters in the wastewater are greatly reduced, B / C is improved, the treated wastewater can independently enter a biochemical system or the treated wastewater can be mixed with other wastewater before entering a biochemical system.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
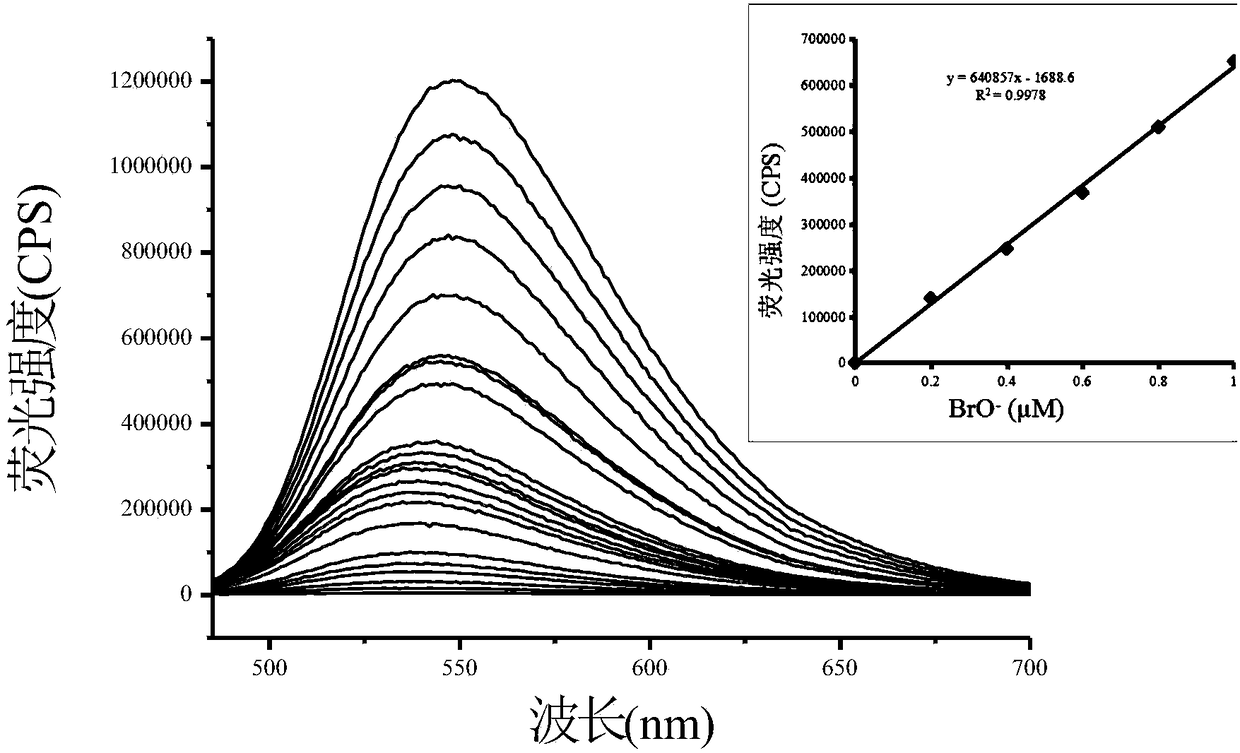
Quick, highly selective and ultra-sensitive hypobromous acid fluorescence probe
InactiveCN108610289AAchieving selective recognitionFacilitate instant detectionOrganic chemistryFluorescence/phosphorescenceInterference resistanceHypobromous acid
The invention relates to a quick, highly selective and ultra-sensitive hypobromous acid fluorescence probe. In particular, the probe is a 4-amino-1,8-naphthalimide compound and can serve as the hypobromous acid fluorescence probe for hypobromous acid detection. The probe can achieve at least one of the following technical effects that probe can highly selectively identify hypobromous acid, quicklyrespond to hypobromous acid, highly sensitively analyze hypobromous acid and achieve hypobromous acid analysis, is stable in property, can be stored and used for a long term, and has higher interference resistance.
Owner:李新元
Normal temperature leather diaphragm passivating agent before periodically spraying and coating cast iron and steel workpiece and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN101671826AReliable adsorptionReliable adhesionMetallic material coating processesChemical reactionPhytic acid
The invention relates to a normal temperature leather diaphragm passivating agent before periodically spraying and coating a cast iron and steel workpiece, comprising the raw materials by mass percent: 3-9% of phytic acid, 0.1-0.6% of tartaric acid, 0.5-1.5% of citric acid, 0.1-0.4% of bromic acid, 4-8% of sodium benzoate, 0.1-0.3% of benzotriazole, 5-9% of triethanolamine, 0.1-0.2% of industrialalcohol and the rest of tap water. A preparation method comprises: adding the tap water into a reaction kettle and stirring; then, sequentially adding the tartaric acid, the citric acid, the bromic acid, the sodium benzoate, the triethanolamine, the phytic acid, the industrial alcohol and the dissolved solution of the benzotriazole; and finally, stirring the mixed solution until the solution is even light purple transparent water-soluble liquid. The passivating agent can be used under the condition of normal temperature, leads the continuous, complete and conpact leather diaphragm passivationreaction to be carried out on the surface of the cast iron and steel workpiece, and generates a diaphragm with strong adsorbability, adhesiveness, rust-proof property and bonding property; the passivating agent needs no heating treatment, simplifies the equipment, has low cost, and is non-toxic and harmless; furthermore, the preparation method is simple in technique, easy to control and convenientfor operation.
Owner:DALIAN SANDAAOKE CHEM
Preparation method of 2-bromine-5-fluorine trifluorotoluene
ActiveCN104610015ALow priceFew reaction stepsHalogenated hydrocarbon preparationOrganic synthesisBromine
The invention discloses a method for preparing 2-bromine-5-fluoro-benzo-trifluoride, and belongs to the field of organic synthesis. The method comprises the following steps: firstly, mixing sulfuric acid with fluorobenzotrifluoride, and further adding bromated into the obtained mixture at 0-80 DEG C to react, thereby obtaining 2-bromine-5-fluorobenzotrifluoride. Through the adoption of the method, the yield can be greater than 90.0%, the purity is greater than 99.0%, the raw materials are easy to obtain, and the reaction condition is mild and easy to control.
Owner:ADAMA HUIFENG (JIANGSU) LTD
Process for prepn of non-hazardous brominating agent
A cost-effective process is described for the preparation of a stable and non-hazardous brominating reagent containing 2:1 stoichiometric ratio of alkali bromide to alkali bromate. The process comprises of reacting alkaline bromine intermediate mixture, obtained from bromine recovery plant, with chlorine gas in the presence of a strong alkali to oxidize the bromide ions to bromate ions. This brominating reagent is useful for the bromination of aromatic compounds by substitutions.
Owner:COUNCIL OF SCI & IND RES
Synthetic method of 2-Bromo-9-fluorenone
ActiveCN104774141ASimple and safe operationControl concentrationOrganic compound preparationCarbonyl compound preparationSimple Organic CompoundsFluorenone
The invention discloses a synthetic method of 2-Bromo-9-fluorenon and belongs to the technical field of synthesis of organic compounds. The synthetic method of the 2-Bromo-9-fluorenon includes the following steps that firstly, 9-fluorenone and a phase transfer catalyst are mixed with an ammonium bromide aqueous solution and then are heated to 40 DEG C to 95 DEG C, the mixed solution is added to potassium bromate for reaction in batches, and the mole ratio of the 9-fluorenone, the ammonium bromide and the potassium bromate is 1:2-4:1-1.25;secondly, the mixed solution is cooled to the indoor temperature after reaction is completed, bromine removal fluid is added, and then the 2-Bromo-9-fluorenon is obtained through filtering and washing. The synthetic method of the 2-Bromo-9-fluorenon is easy and safe to operate, good in reaction selectivity and high in yield.
Owner:HENAN BUSINESS SCI RES INST
Water treatment method and water treatment apparatus
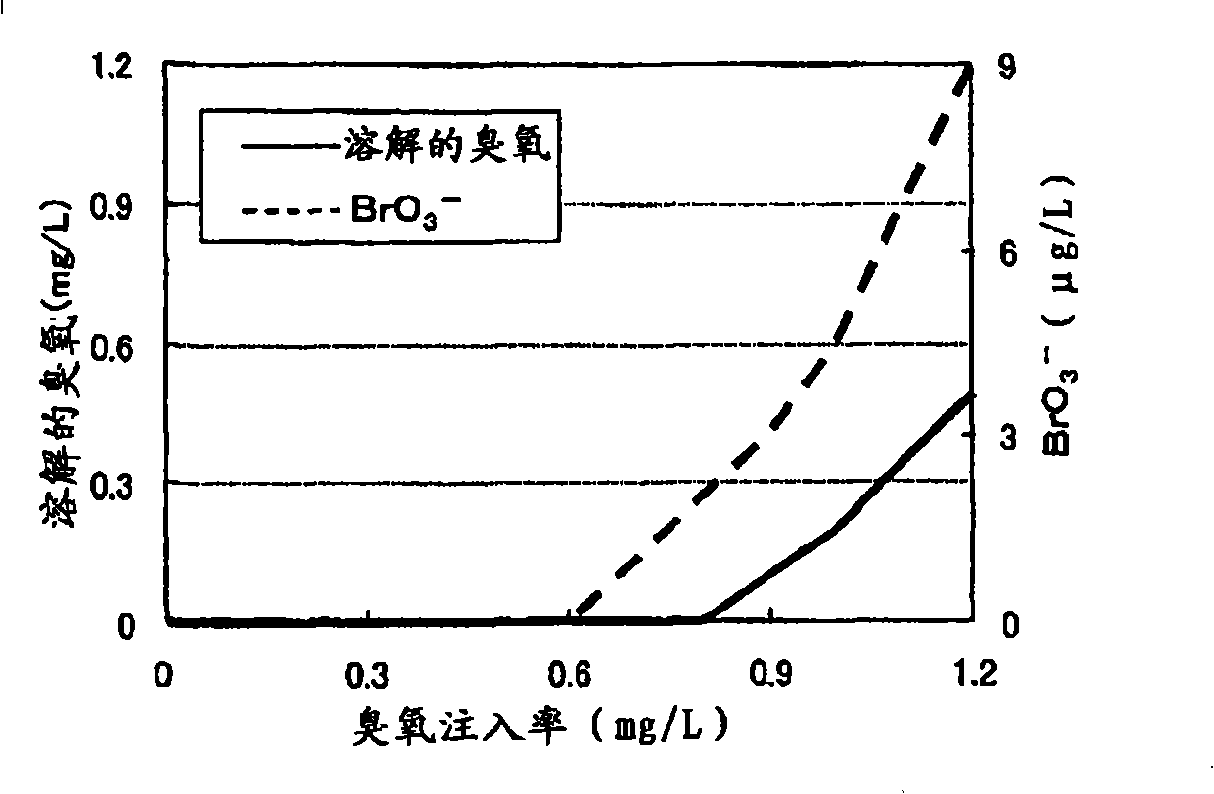
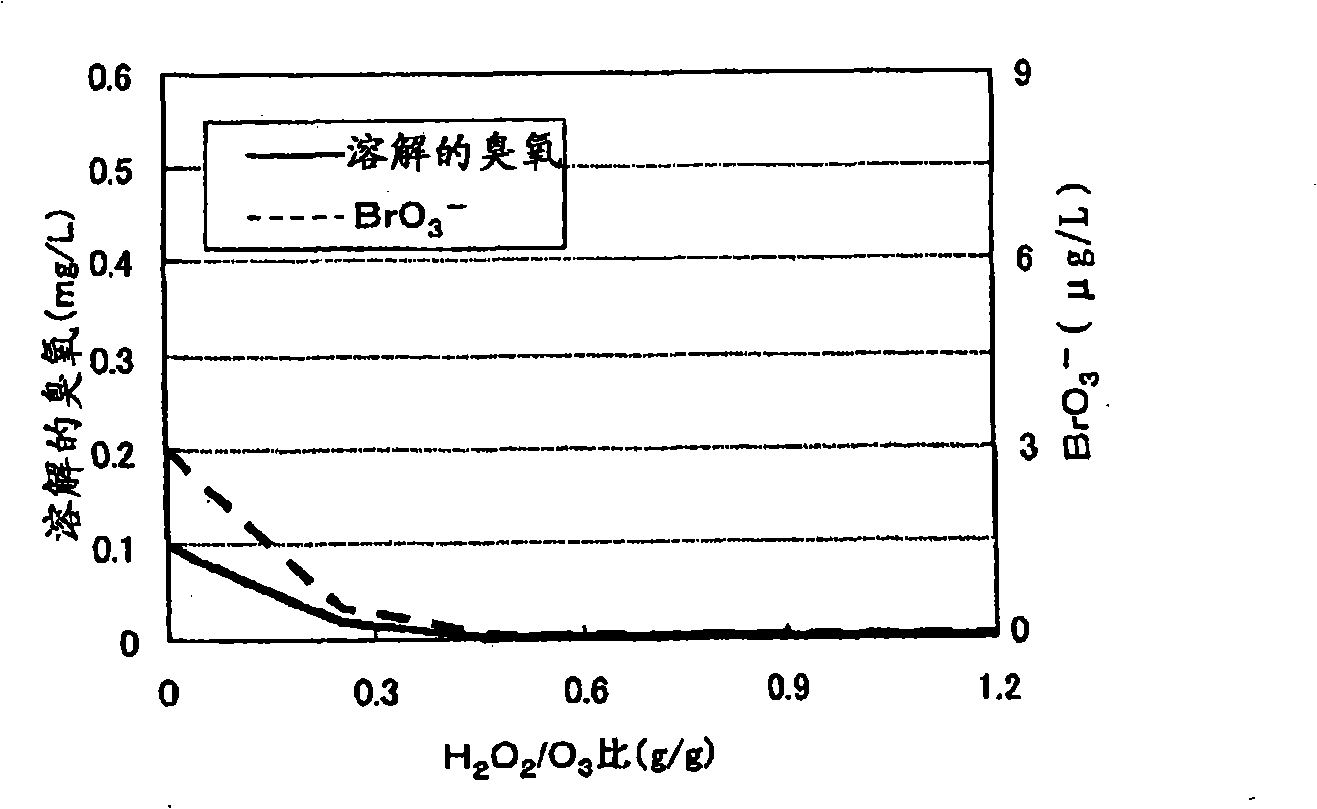
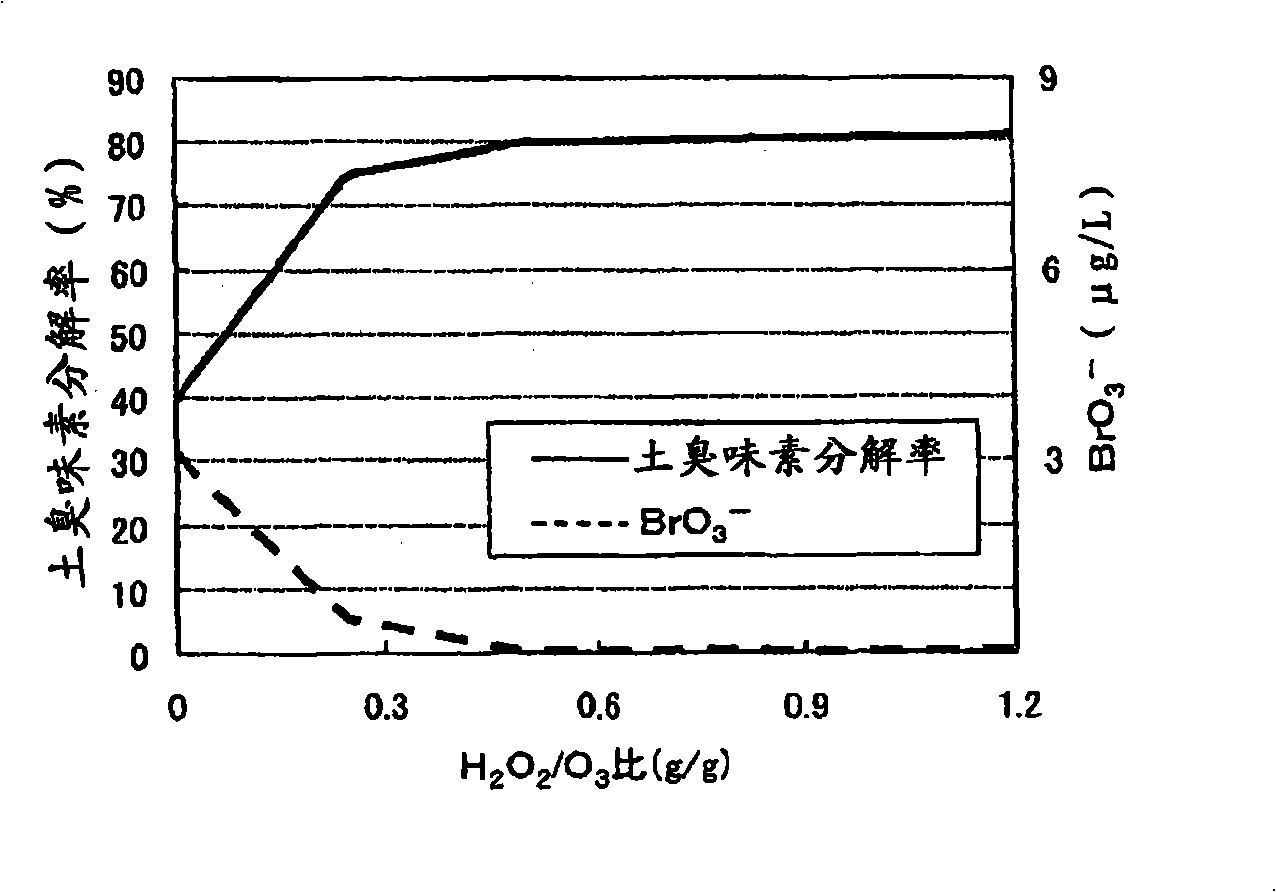
InactiveCN101254972ASuppress generationReduce processing loadWater treatment parameter controlWater contaminantsLength waveAbsorbance
To minimize an amount of hydrogen peroxide required for controlling the production of bromic acid in an ozone / hydrogen peroxide treatment. The ozone / hydrogen peroxide treatment is performed at an ozone injection rate by which a predetermined dissolved ozone concentration of the water subjected to an ozone treatment alone can be maintained or at an ozone injection rate by which a specific ratio of absorbance at a specific wavelength of the water to absorbance at a specific wavelength of the water subjected to the ozone treatment alone can be achieved. It is preferable that the injection rate of hydrogen peroxide is 0.01 to 5 times the ozone injection rate on a mass basis.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC CORP
Method for producing stabilized hypobromous acid composition, stabilized hypobromous acid composition, and slime inhibition method for separation membrane
ActiveUS20160198721A1Good storage stabilitySatisfactory slime inhibitory effectBiocideMembranesHypobromous acidBromate
Provided is a method for producing a one-liquid stabilized hypobromous acid composition which contains substantially no bromate ions, has excellent sterilization performance, exhibits almost no corrosiveness relative to metals, and displays excellent storage stability. This method for producing the stabilized hypobromous acid composition includes a step in which a reaction is induced by adding, under an inert gas atmosphere, bromine to a mixed solution including water, an alkali hydroxide, and sulfamic acid, wherein the proportion of bromine added is not more than 25 wt % relative to the total weight of the composition.
Owner:ORGANO CORP
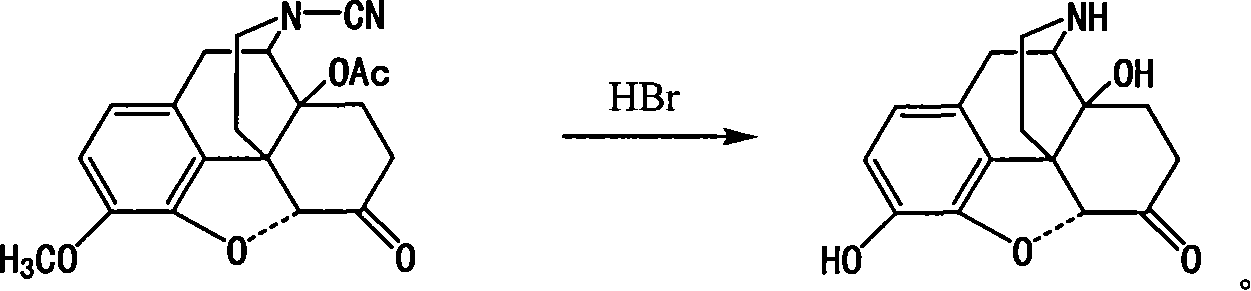
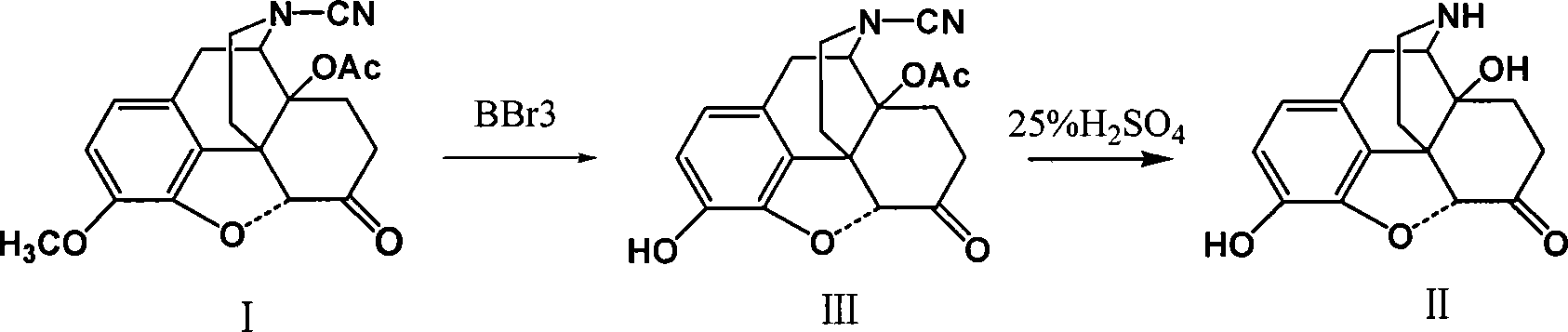
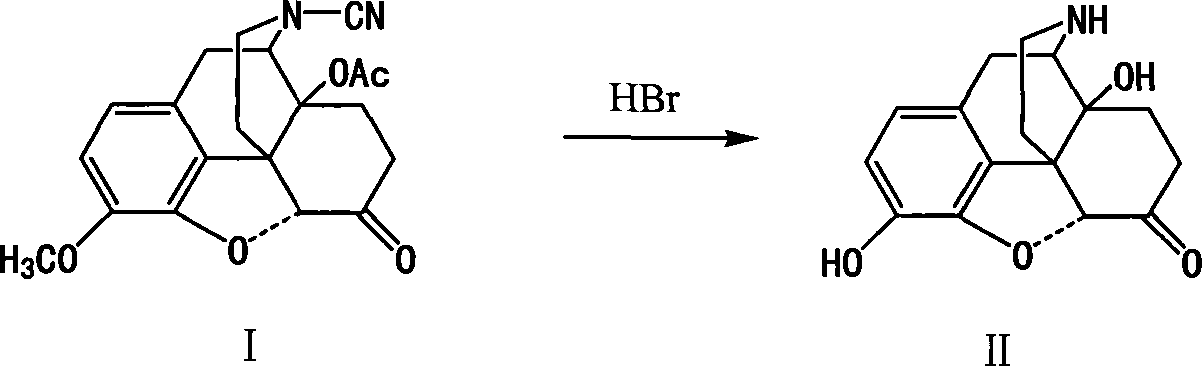
Method of preparing 14-hydroxy-7,8-dihydromorphone
This invention discloses a method for preparing 14-hydroxide-7, 8-One drop of morphine dihydro, which takes 14-acyloxy-17- Cyano-7, 8-dihydro - codeine drop one as the raw material, hydro-bromic acid as the deoxidation methyl and hydrolyzation reaction reagent to process14-acyloxy-7, 8-dihydro-morphia ketone.
Owner:FUDAN UNIV
Iodate preparation method
InactiveCN105271126AImprove solubilityObvious superiorityIodine oxygen compoundsHalogenReaction temperature
The invention relates too an iodate preparation method, which comprises: A, iodic acid preparation, wherein hydrogen peroxide is used as an oxidant, small amounts of nitric acid and halogen acid such as chloric acid, bromic acid and iodic acid are adopted as catalysts of an oxidation reaction, refined iodine is oxidized into the iodic acid, the addition amount of the used nitric acid is 1-10% of the added refined iodine, the addition amount of the used halogen acid is 0.5-50% of the added refined iodine, the reaction temperature is 50-100 DEG C, and the reaction time is 4-8 h; and B, iodate preparation, wherein the pure iodic acid solution obtained through the step A is neutralized directly with a carbonate solution of a hydroxide or alkali metal, the neutralization reaction temperature is controlled at 20-50 DEG C, and the neutralization PH value is 7.
Owner:谈丽娜
High-gloss color-changing lipstick and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN110559214AHigh glossImprove color saturationCosmetic preparationsMake-upIsostearyl alcoholStearic acid
The invention belongs to the technical field of cosmetics, and discloses a high-gloss color-changing lipstick and a preparation method thereof, wherein the color-changing lipstick comprises the following components by the mass percentage: 25 to 60% of liquid grease, 10 to 20% of solid wax, 1 to 3% of stearic acid, 5 to 20% of bis-behenyl alcohol / isostearyl alcohol / phytosterol dimer linoleate, 2 to8% of diisostearyl malate, 10 to 20% of phenyl silicone oil, 0.05 to 2% of bromic acid red pigment, 0.01 to 1% of an auxiliary coloring agent, 0.05 to 0.5% of anhydrous citric acid, 0.1 to 0.7% of anauxiliary component, and the balance being isopropyl myristate. The high-gloss color-changing lipstick has the advantages of being stable in color and obvious in color changing in use.
Owner:SHANGHAI ZHONGYI DAILY CHEM CO LTD
Preparation method of iodate
InactiveCN105329856AObvious superiorityAdvancedBromine oxygen compoundsReaction temperatureIodic acid
A preparation method of iodate is characterized by comprising the following two steps: 1, iodic acid preparation: oxidizing refined iodine into iodic acid by using hydrogen peroxide as an oxidant, and using a small amount of nitric acid and hydracids such as chloric acid, bromic acid, and iodic acid as the catalyst for the oxidation reaction, wherein the amount of nitric acid is 1-10% of the fined iodine, the amount of hydracids is 0.5-50% of the refined iodine, the reaction temperature is 50 DEG C to 100 DEG C, and the reaction time is 4-8 h; and 2, iodate preparation: directly neutralizing the pure iodate solution obtained by step 1 by using hydrogen oxide or carbonate solution of alkali metal, wherein the reaction temperature of neutralization reaction is controlled in the range of 50-100 DEG C and the neutralization pH value is equal to 7.
Owner:马井芳
Method for measuring trace amount of bromate in water
InactiveCN103018184AHigh sensitivityImprove anti-interference abilityMaterial analysis by observing effect on chemical indicatorColor/spectral properties measurementsPhosphoric acidAbsorbance
The invention relates to a method for measuring trace amount of bromate in water, and particularly relates to a method which utilizes victoria brilliant blue BO (VPBBO) containing an emulsifying agent OP as a color-developing agent and utilizes a spectrophotometric method to measure trace amount of bromate in water. The method comprises the following steps of successively adding 25.0mL of a water sample to be measured, 3.0mL of 0.1mol.L-1 of hydrochloric acid solution and 2.0mL of 0.05 mol.L-1 of solution KI, successively adding 5.0mL of phosphoric acid-sodium dihydrogen phosphate buffer solution with the pH value being 1.9+ / -0.1 and 5.0mL of 2.0*10-4mol.L-1 victoria blue BO containing 0.4g.L-1 of emulsifying agent OP after 5min; carrying out constant volume by utilizing distilled water, shaking up, using a color comparison dish being 1cm after 2min, adopting a reagent blank as a reference, and measuring the absorbance of a solution at 580nm wavelength; and calculating the concentration of the bromate ion by using a regression equation according to a standard work curve, namely A=1.40*10-3C (mu g.L-1)-7.11*1.0-4 (r is equal to 0.9995, the linear range is 0-260 mug.L, A is optical density, and C is concentration of bromate ion). The method provided by the invention has the advantages that the sensitivity is high, the result is exact, the operation is simple and convenient, and the cost is low.
Owner:UNIV OF SHANGHAI FOR SCI & TECH
Process for preparation of non-hazardous brominating agent
InactiveUS20040242939A1Maximize bromine atom efficiencyRaise the ratioOther chemical processesOrganic compound preparationBromineBromate
A cost-effective process is described for the preparation of a stable and non-hazardous brominating reagent containing 2:1 stoichiometric ratio of alkali bromide to alkali bromate. The process comprises of reacting alkaline bromine intermediate mixture, obtained from bromine recovery plant, with chlorine gas in the presence of a strong alkali to oxidize the bromide ions to bromate ions. This brominating reagent is useful for the bromination of aromatic compounds by substitutions.
Owner:COUNCIL OF SCI & IND RES
Treatment method of organic nitrogen wastewater
PendingCN111087049AIncrease ion concentrationAvoid contactWater contaminantsWater/sewage treatment using germicide/oligodynamic-processHypobromous acidWastewater
The invention discloses a treatment method of degradation-resistant organic nitrogen wastewater. The method comprises the following steps: adding wastewater containing degradation-resistant organic nitrogen and bromine-containing wastewater into an electrolytic cell according to a certain ratio, carrying out an electrolytic reaction for a certain period of time, oxidizing bromide ions in the wastewater into bromine, rapidly reacting bromine with water to generate hypobromous acid with a very strong oxidizing performance, and oxidizing and degrading organic nitrogen in the wastewater by hypobromous acid. After being treated by the method, more than 90% of degradation-resistant organic nitrogen can be removed. According to the method, waste is treated with waste, the treatment cost is low, the pH application range is wide, and the method can be widely applied to treatment of various degradation-resistant organic nitrogen-containing wastewater.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
Modified activated carbon, preparation method thereof and method for removing bromate in water
The invention relates to the field of water treatment, in particular to modified activated carbon, a preparation method thereof and a method for removing bromate in water. The method comprises the following steps: reacting the epoxidized quaternary ammonium salt solution with activated carbon to prepare the modified activated carbon; mixing the modified activated carbon with an aqueous solution containing bromate, and adsorbing to remove bromate. According to the method, the epoxidized quaternary ammonium salt is adopted to modify activated carbon, so that epoxidized functional groups and oxygen-containing functional groups on the surface of the activated carbon are subjected to a cationization reaction, quaternary ammonium salt functional groups and activated carbon chemical bonds are combined, the connection strength is improved, and the activated carbon is not prone to falling off in the water treatment process. After the modified activated carbon is in contact with bromate ions inwater, on one hand, nitrogen-containing functional groups with positive charges in quaternary ammonium salt have a strong electrostatic adsorption effect on bromate with negative charges; and on theother hand, alkyl long chains in the quaternary ammonium salt have strong adsorption attraction on the surface of the modified activated carbon, so that the removal effect on bromate is greatly improved under the dual effects.
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF MINING & TECH (BEIJING)
Popular searches
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com