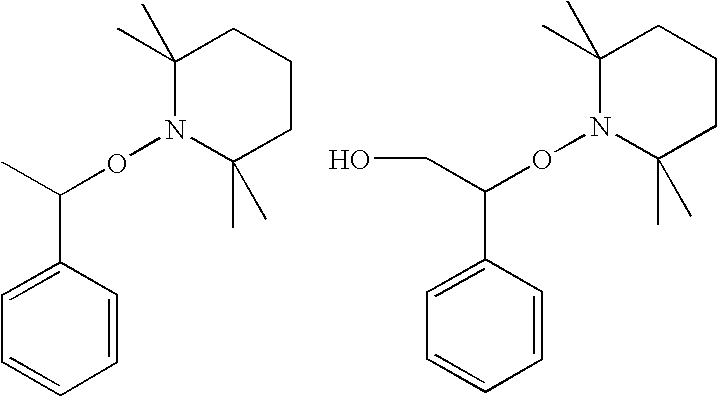
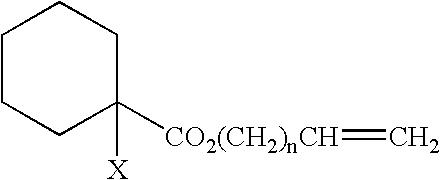
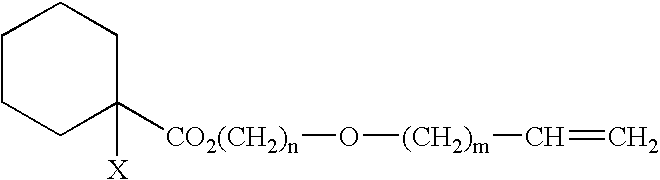Process for producing branched polymer and polymer
a polymer and branched polymer technology, applied in the field of branched polymer production methods, can solve the problems of inability to achieve chain extension or stellar structure, and the stellar structure has scarcely been put to practical use, and the method for constructing a stellar structure has not yet been successfully developed
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
production example 1
Synthesis of Br-Terminated poly(butyl acrylate)—(1)
[0221] A 2-L separable flask equipped with a reflux condenser and stirrer was charged with CuBr (5.54 g, 38.6 mmol) and the reaction vessel was purged with nitrogen. Acetonitrile (73.8 mL) was added, and the contents were stirred on an oil bath at 70° C. for 30 minutes. Thereto were added butyl acrylate (132 g), methyl 2-bromopropionate (14.4 mL, 0.129 mol) and pentamethyldiethylenetriamine (4.69 mL, 0.022 mol), and the reaction was started thereby. While heating at 70° C. with stirring, butyl acrylate (528 g) was added dropwise continuously over 90 minutes and thereafter heating was continued with stirring for 80 minutes.
[0222] The reaction mixture was diluted with toluene and passed through an activated alumina column, and the volatile matter was distilled off under reduced pressure to give poly(butyl acrylate) having a Br-containing group at one terminus (hereinafter referred to as polymer [1]). The polymer [1) had a number ave...
production example 2
Synthesis of Potassium Acrylate
[0223] A flask was charged with methanol (500 mL) and the contents were cooled to 0° C. Thereto was added tert-butoxypotassium (78 g) in several divided portions. This reaction mixture was maintained at.0° C. and a methanol solution of acrylic acid (50 g) was added dropwise thereto. After completion of the dropping, the temperature of the reaction mixture was returned from 0° C. to room temperature and then the volatile matter was distilled off from the reaction mixture under reduced pressure to give potassium acrylate (hereinafter referred to as carboxylic acid salt [1]) represented by the following formula: [0224] CH2═CHCO2K.
production example 3
Synthesis of Potassium Methacrylate
[0225] A flask was charged with methanol (800 mL) and the contents were cooled to 0° C. Thereto was added tert-butoxypotassium (130 g) in several divided portions. This reaction mixture was maintained at 0° C. and a methanol solution of methacrylic acid (100 g) was added dropwise thereto. After completion of the dropping, the temperature of the reaction mixture was returned from 0° C. to room temperature and then the volatile matter was distilled off from the reaction mixture under reduced pressure to give potassium methacrylate (hereinafter referred to as carboxylic acid salt [2]) represented by the following formula: [0226] CH2═C(CH3)CO2K.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| molecular weight distribution | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com