Toroidal rotary damper apparatus
a rotary damper and rotary damper technology, which is applied in the direction of shock absorbers, liquid based dampers, mechanical instruments, etc., can solve the problems of limited dynamic range, inherent characteristics of traditional van type rotary dampers, frictional losses, etc., and achieve excellent sealing properties, low internal static pressure, and reduce internal friction and hysteresis
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
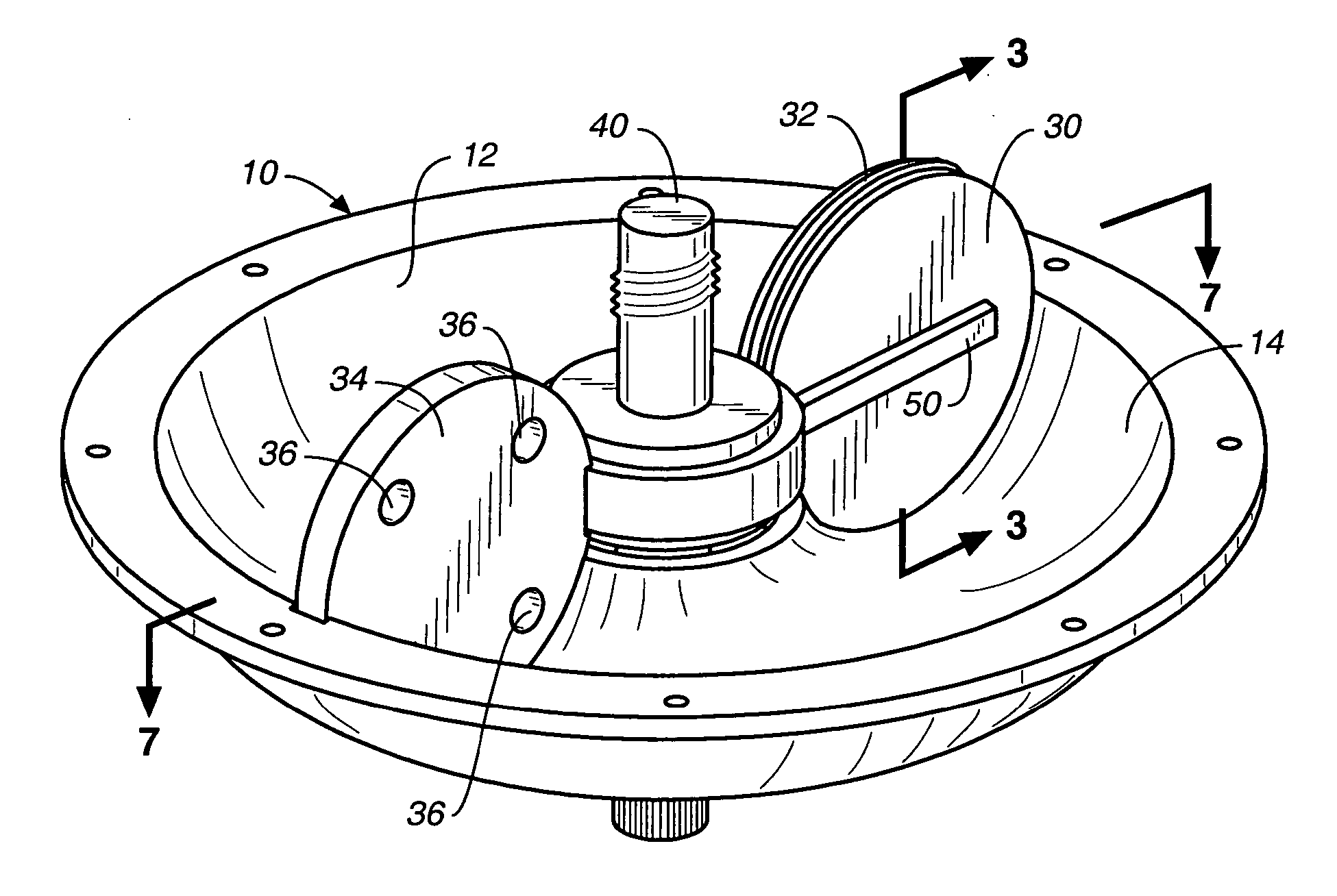
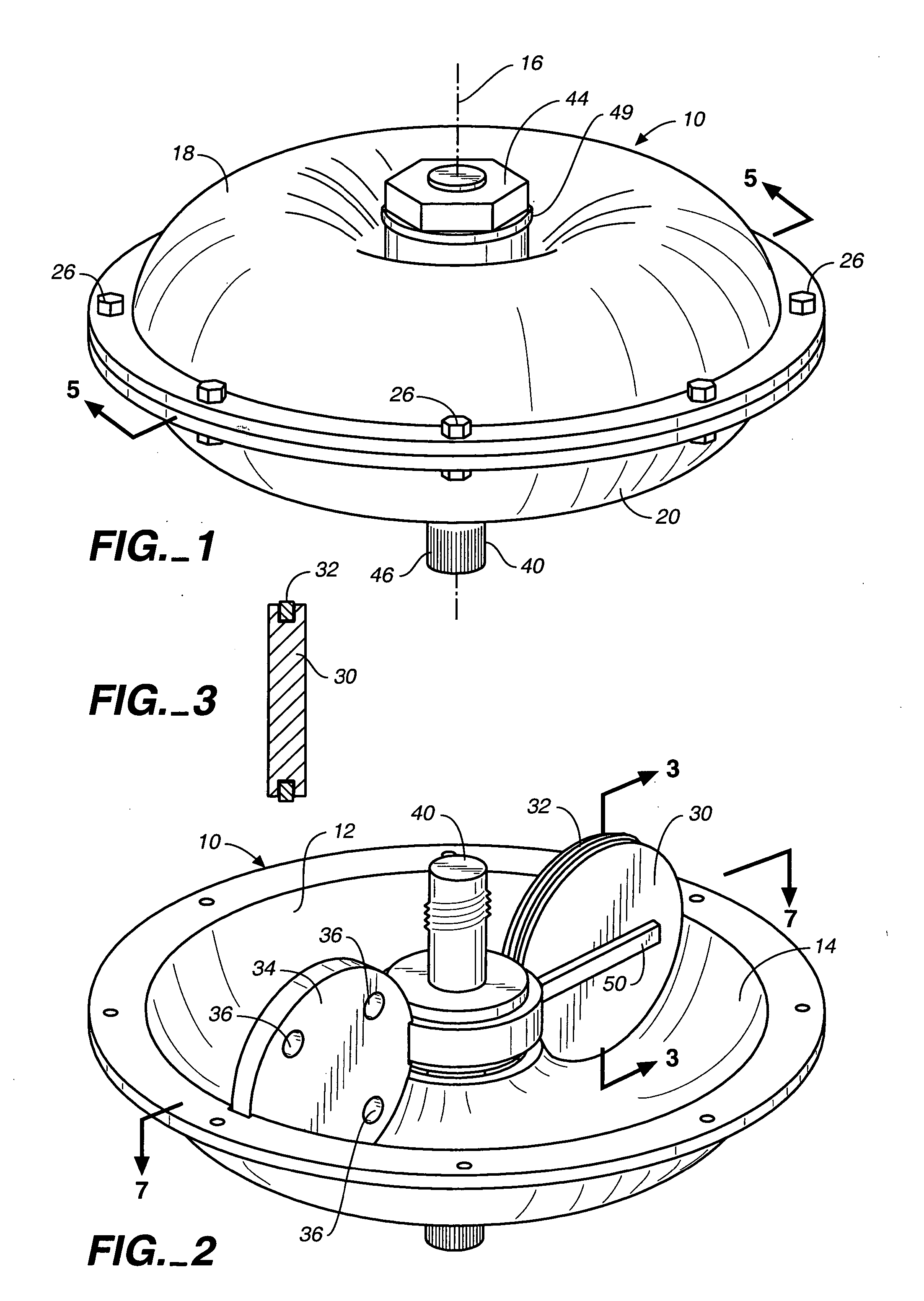
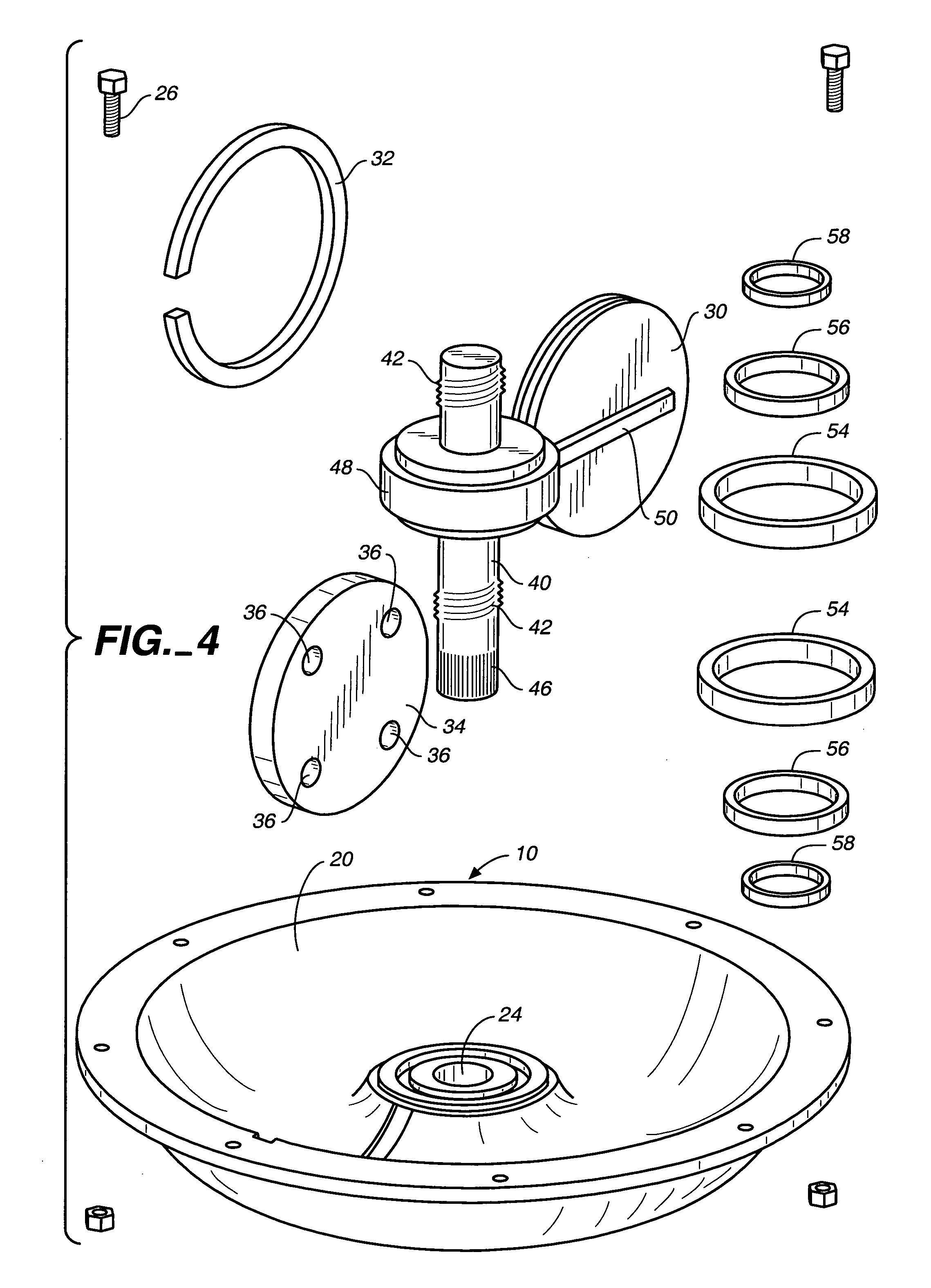
[0049] Referring now to FIGS. 1-6, a toroidal rotary damper apparatus constructed in accordance with the teachings of the present invention is illustrated. The apparatus includes a housing 10 defining a housing interior 12 for containing damper fluid (not shown) of any conventional nature. The housing interior has a substantially circular cross section and is formed by a toroidal inner housing surface 14 disposed about and spaced from a central axis 16.
[0050] The housing 10 includes two adjoining housing members 18, 20, each housing member defining a portion of the housing interior and further defining openings 22, 24, respectively, at the centers thereof. Threaded fasteners 26 extending through holes in outer flanges of the housing members are utilized to releasably secure the housing members together.
[0051] A piston 30 having a substantially circular-shaped outer peripheral piston surface at which is located an outer seal 32 is in substantially fluid-tight, slidable engagement w...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com