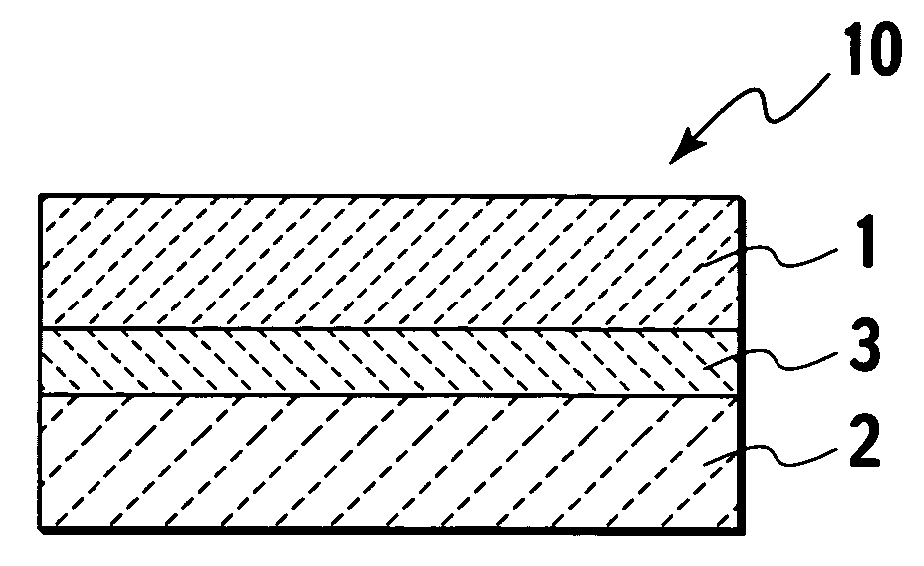
Bonding agent, aluminum nitride composite body, and manufacturing method of the same
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
examples
[0074] Next, the present invention is described in more detail with examples, but the present invention is not limited to the following examples.
examples 1 to 11
, Comparative Examples 1 to 3
(Aluminum Nitride Sintered Body)
[0075] 95 wt % of the aluminum nitride powder was added to 5 wt % of yttrium oxide as a sintering auxiliary agent and then mixed using a ball mill. The obtained powder mixture was added to the binder and granulated by spray granulation. The obtained granulated powder was molded into a plate and a pipe by die molding and CIP. The obtained plate compact and pipe compact were baked at 1860° C. for 6 hours in nitrogen gas by hot pressing and in nitrogen gas by atmospheric sintering, respectively.
[0076] In terms of size of the obtained aluminum nitride sintered bodies, the plate sintered body had 60 mm length×60 mm width and 20 mm thickness, and the pipe sintered body had 58 mm outer diameter, 20 mm inner diameter, and 20 mm length. The aluminum nitride sintered bodies were processed such that the flatness was 10 μm or less.
(Bonding Conditions)
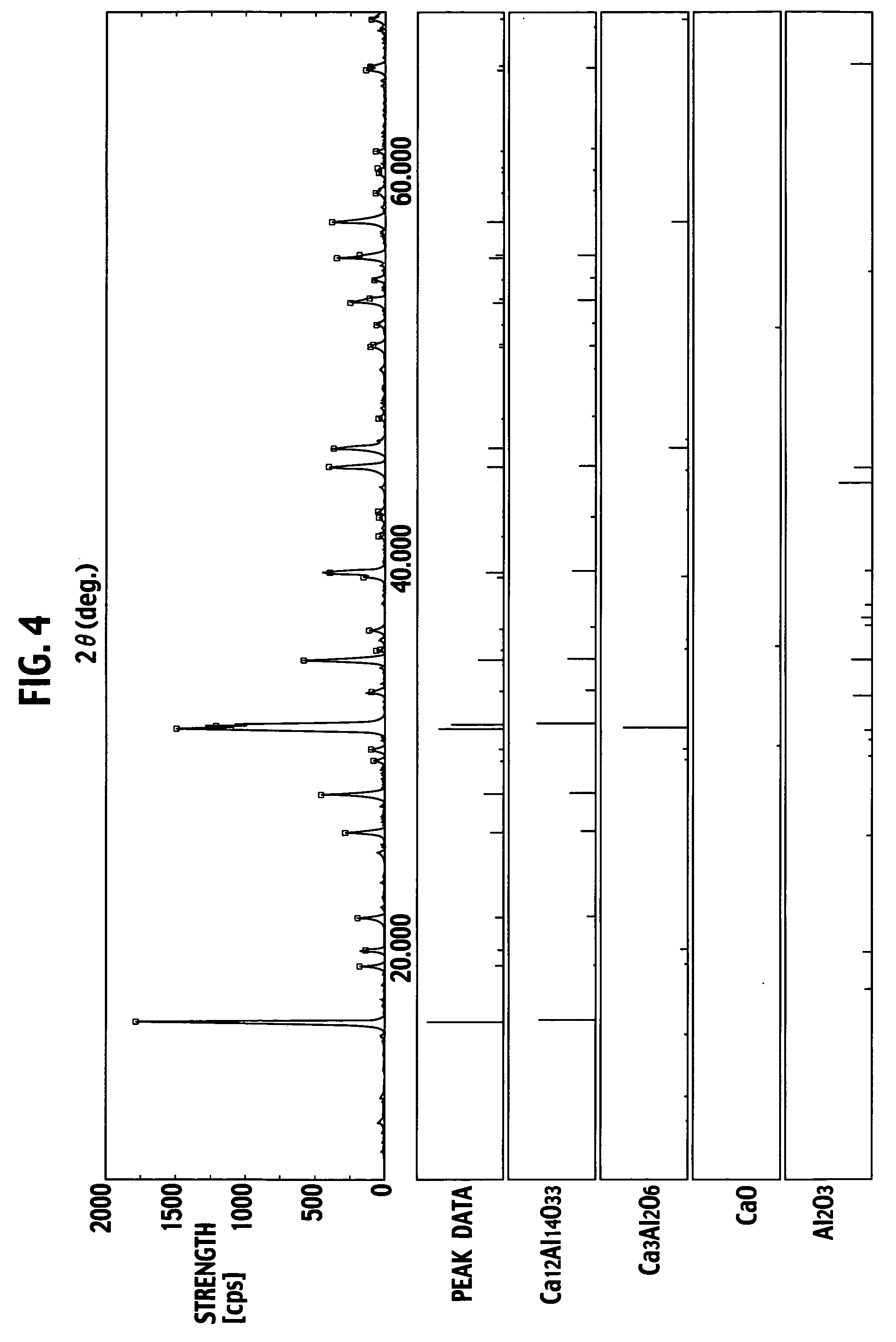
[0077] Bonding agents shown in Tables 1 and 2 were uniformly applied to the bon...
example 12
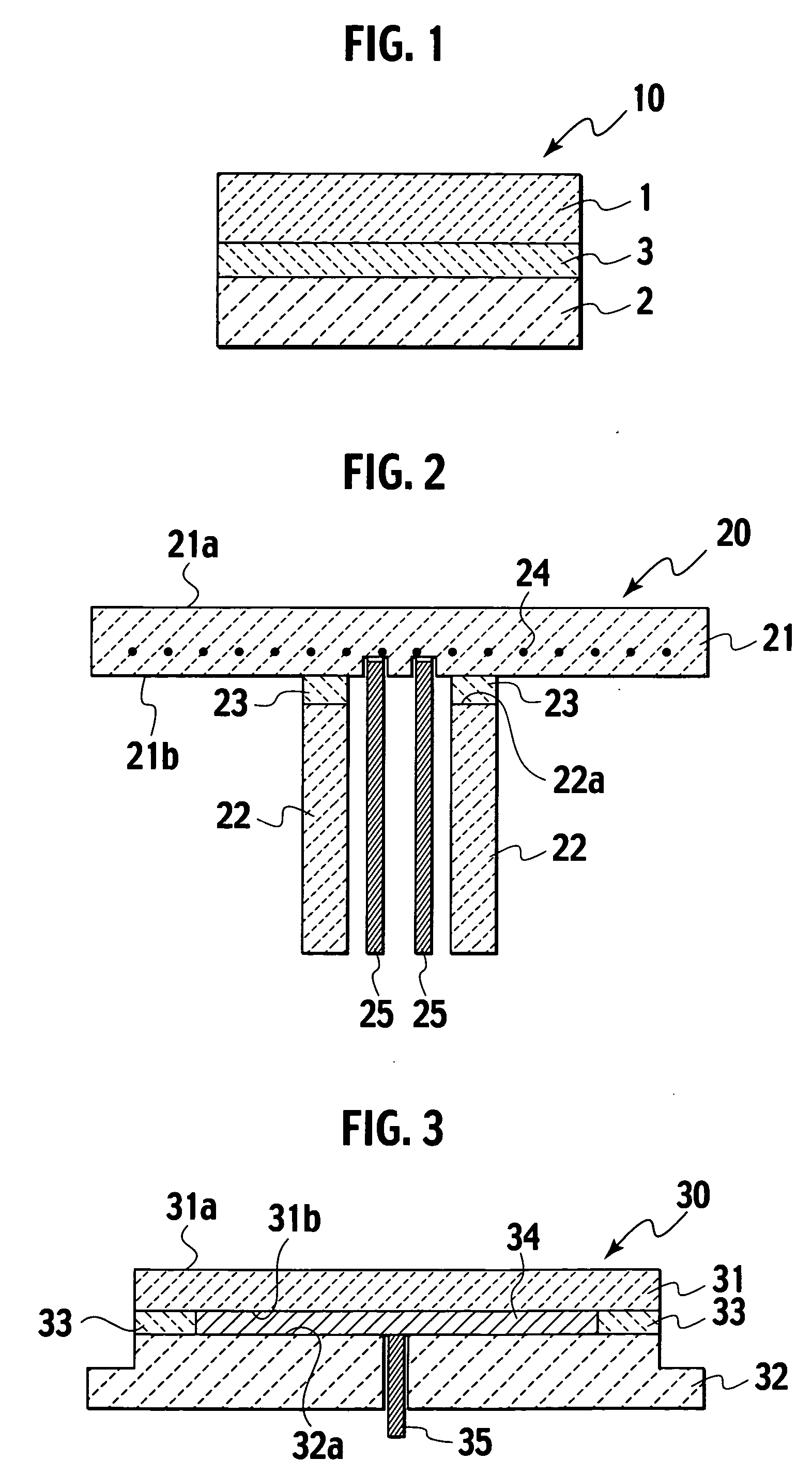
[0098] The heater 20 shown in FIG. 2 was manufactured. A compact for the disk member 21 was formed using the granulated powder obtained in the same way as that of Examples 1 to 11 by die molding, and a compact for the pipe member 22 was formed by CIP. In the compact for the disk member 21, the heating element 24 which was coil-shaped and made of molybdenum was embedded. The obtained compact was baked at 1860° C. in nitrogen gas by hot pressing for 6 hours. In terms of size of the obtained aluminum nitride sintered bodies, the disk member 21 had 340 mm diameter and 20 mm thickness, and the pipe member 22 had 70 mm outer diameter, 60 mm inner diameter, and 180 mm length. The placement surface 21a of the disk member 21 was processed to have a flatness of 10 μm or less.
[0099] The bonding agent of Example 1 shown in Tables 1 and 2 was uniformly applied to the end surface 22a of the pipe member 22 such that the density of the bonding agent was 18 g / cm2. The back surface 21b of the disk m...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Current | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com