Complete user datagram protocol (CUDP) for wireless multimedia packet networks using improved packet level forward error correction (FEC) coding
a multimedia packet network and complete user datagram protocol technology, applied in the field of wireless packet networks, can solve the problems of packet loss, degraded quality, and packet loss of wireless packet networks between base stations, and achieve the effect of reducing unnecessary packet discarding
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
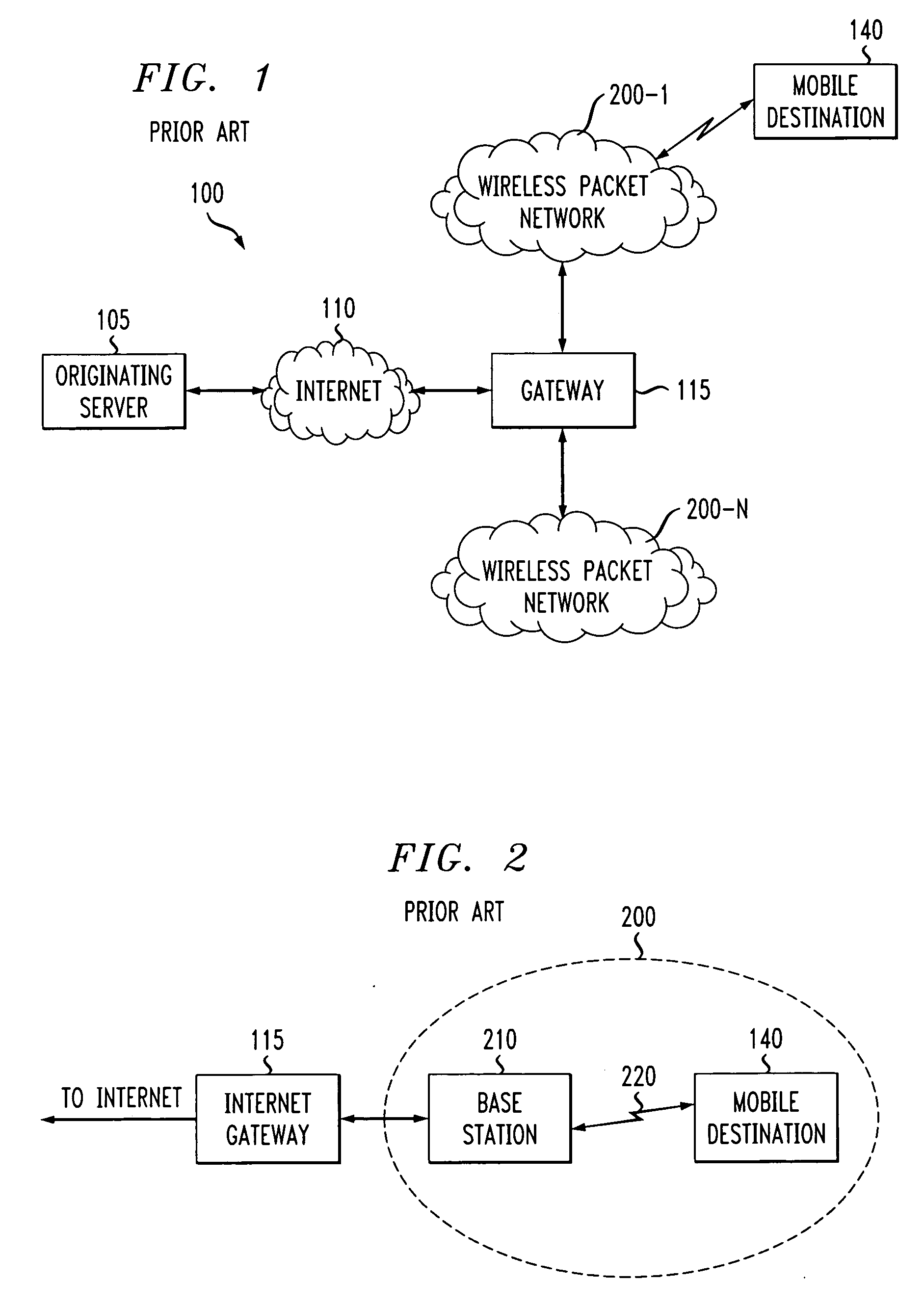
[0018]FIG. 1 illustrates a conventional heterogeneous network environment 100 that supports IP-Wireless multimedia communications. As shown in FIG. 1, the end-to-end path of many wireless multimedia sessions, such as an Internet-to-mobile communication, involves a number of heterogeneous network technologies, with the multimedia packets being sent from an originating server 105, through the Internet 110 and then over one or more wireless packet networks 200-n, shown in further detail in FIG. 2, to the mobile destination 140.
UDP and FEC in Wireless Packet Networks
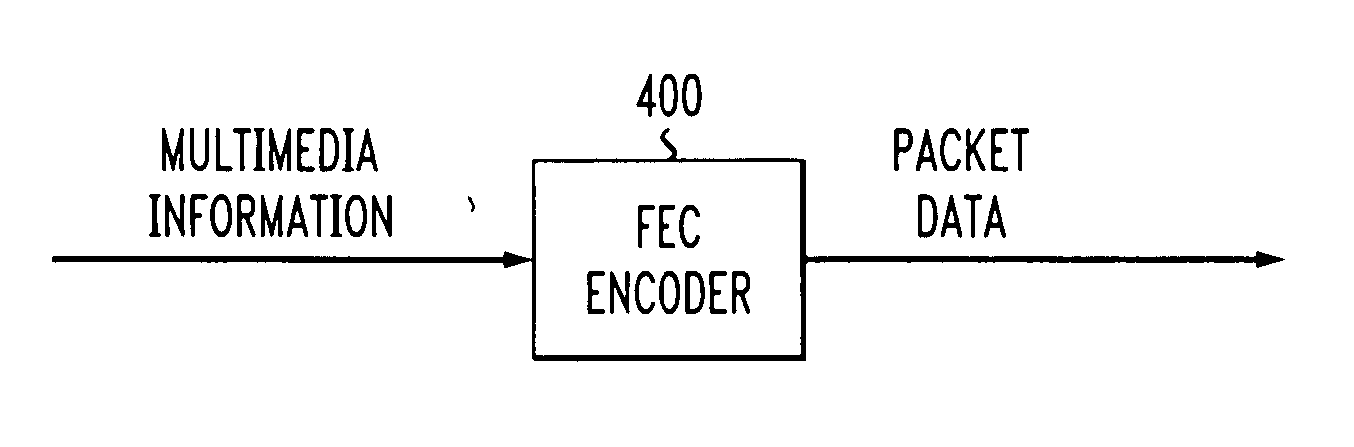
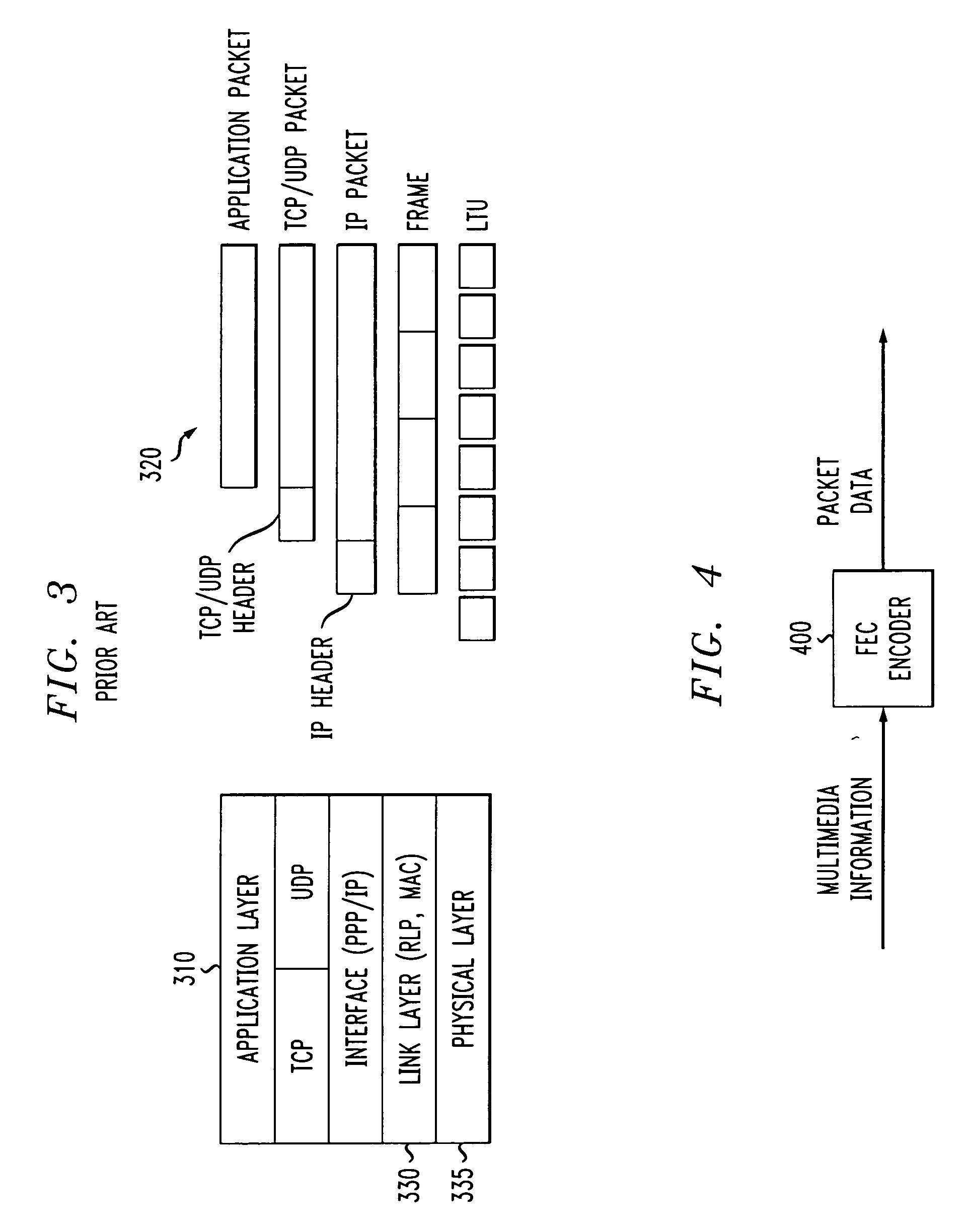
[0019]FIG. 3 illustrates a general wireless protocol stack 310 and packet structure 320. The link layer 330 partitions each single data packet into multiple units to accomplish physical layer transmission. The unit size depends on the radio link protocol (RLP), medium access control (MAC) and physical layer (PHY) 335, but is usually much smaller than the packet size. In 3G wireless systems, for example, each physical layer...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com