Cushion material formed of spring-structured resin-molded product, manufacturing method for the cushion material, and mold used for the manufacturing method
a technology of spring structure and resin molded products, which is applied in the field of cushion materials composed of resin molded articles, can solve the problems of difficult to obtain a product of which parts are modified in density and strength, unstable balance, fatigue, etc., and achieves the effects of easy production, simple molding process, and excellent shock resistance and load resistan
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
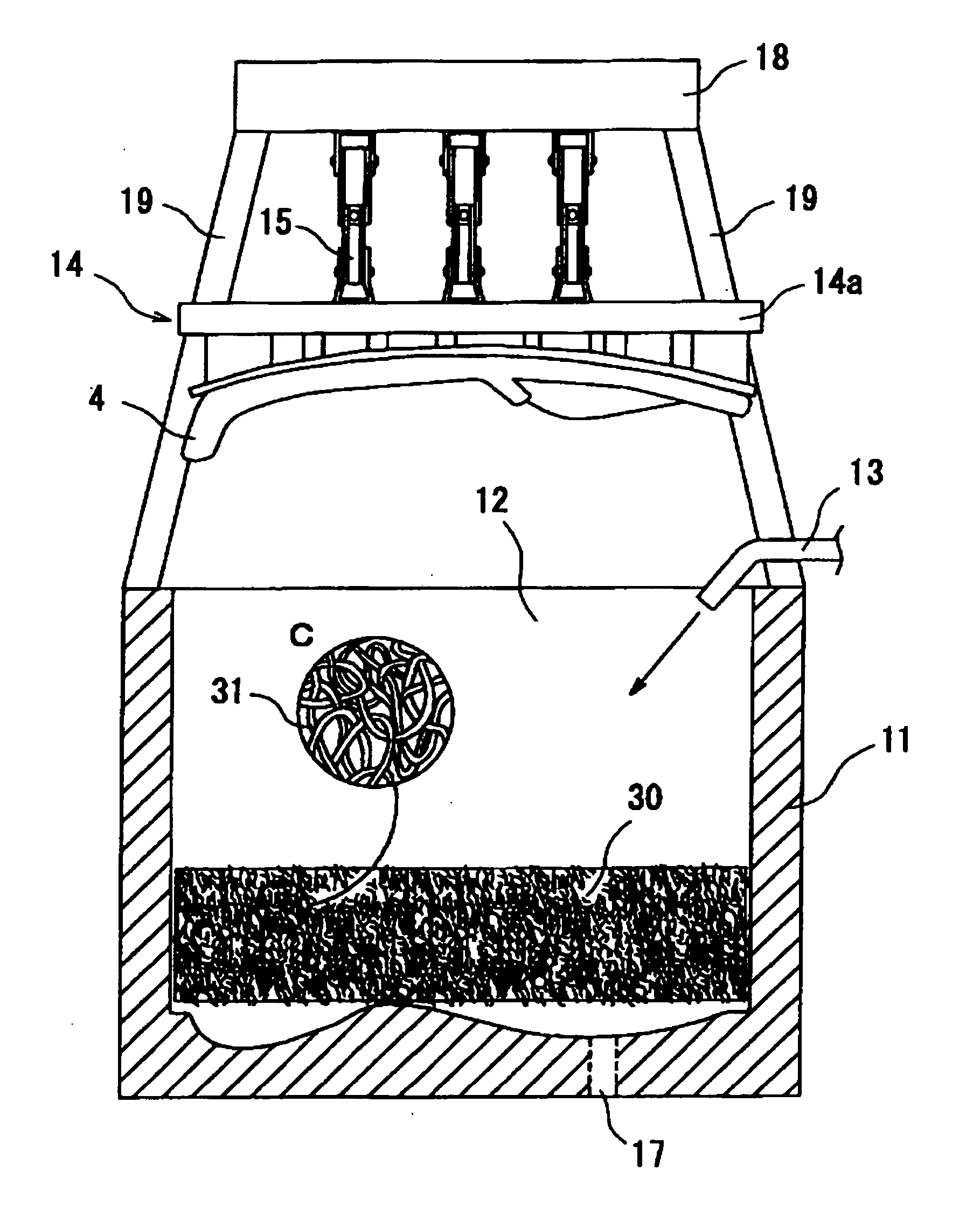
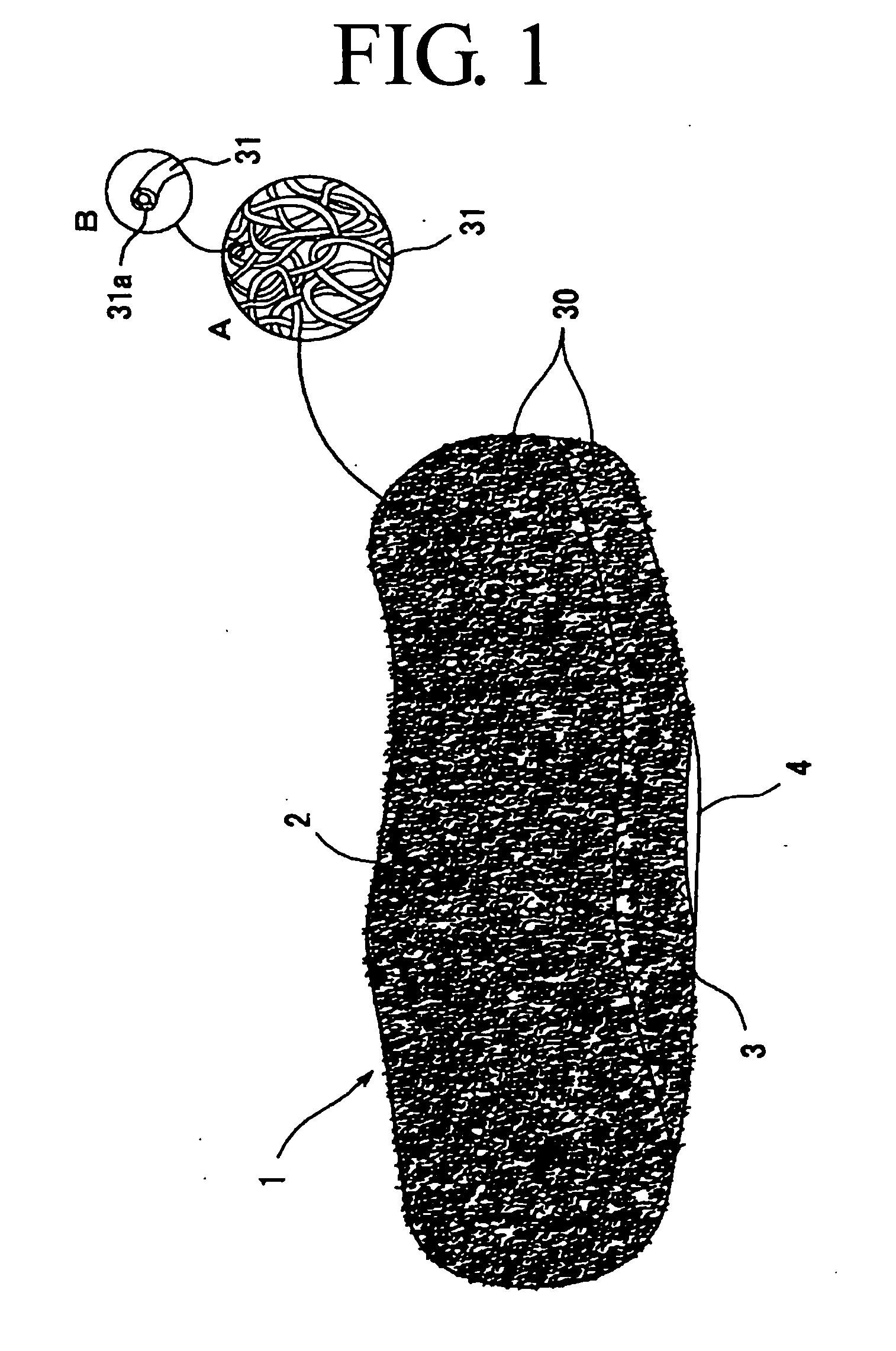
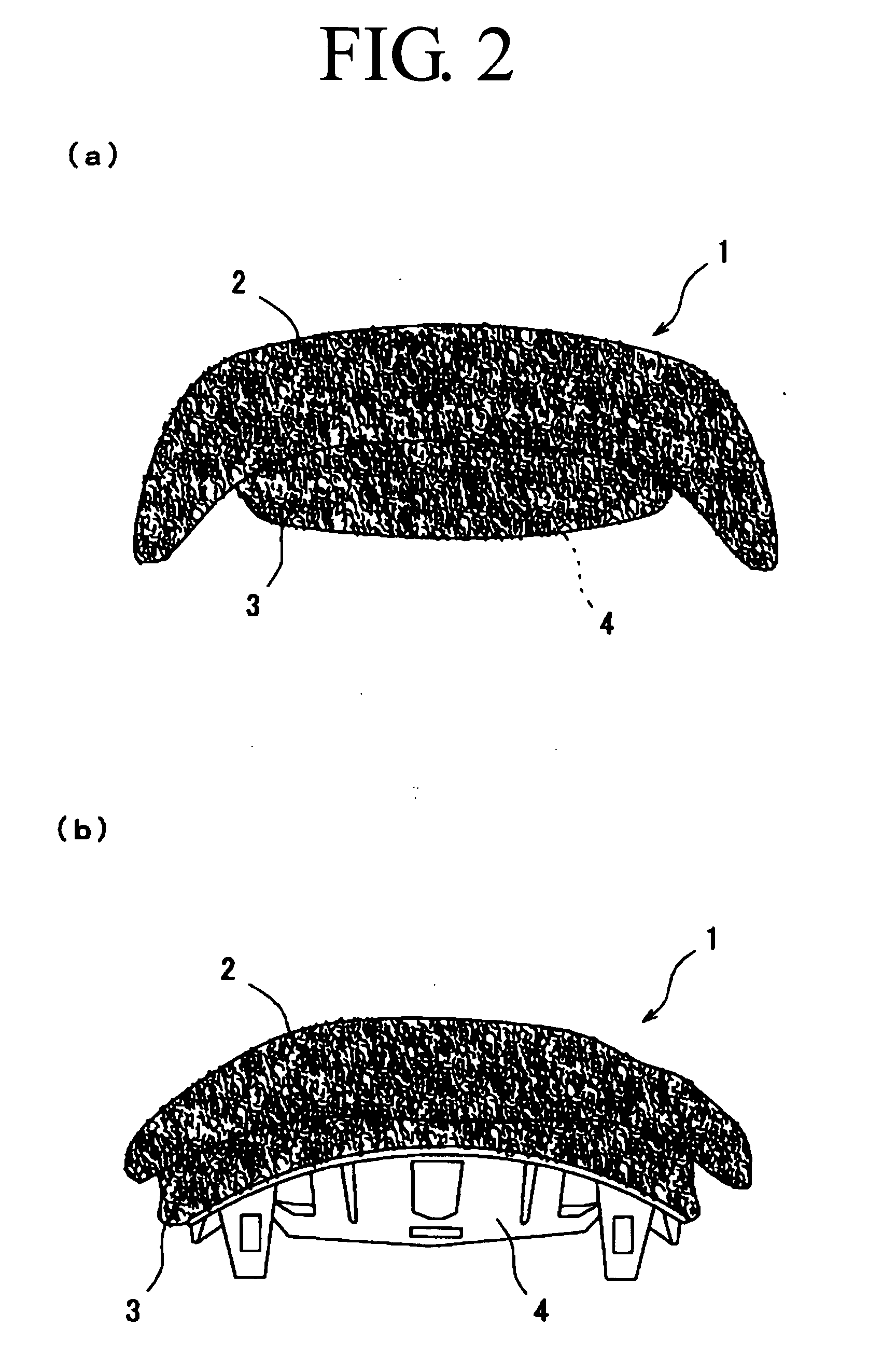
[0055] As is obvious from the reference to a perspective view shown in FIG. 1, and frontal and rear views shown in FIGS. 2a and 2b, the cushion material 1 is obtained by preparing a thermoplastic resin (e.g., thermoplastic elastomer) such as a blend obtained by mixing, for example, a polyolefin resin such as PE, PP, etc., with VAC, EVA or SBS, and by processing the blend into a resin molded article 30 with a spring structure or a three-dimensional structure, and subjecting the article or the structure to compression molding.
Explanation of a Resin Molded Article 30 with a Spring Structure
[0056] Firstly, the resin molded article 30 with a spring structure will be described.
[0057] The resin molded article 30 with a spring structure used in this embodiment of the invention is a three-dimensional structure having voids which is obtained by contacting, entwining, and gathering adjacent ones of random loops or curls of continuous and / or short filaments (simply filaments 31 hereinafter)...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| density | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com