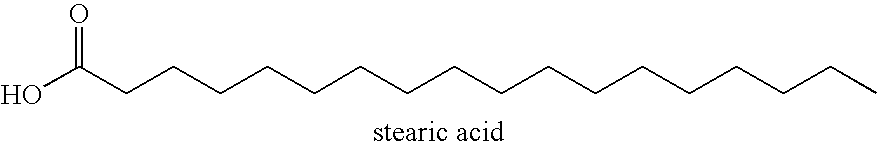
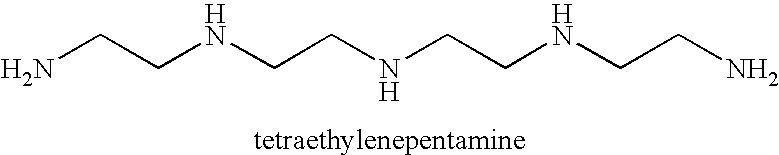
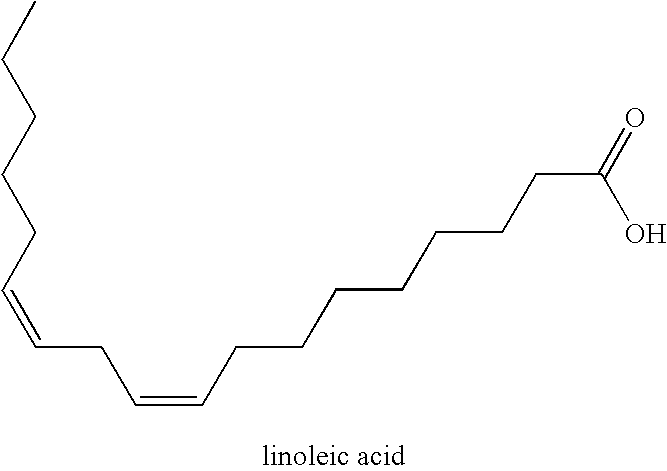
Method for producing a wet-laid fiber mat
a technology of wet-laid fiber and mat, which is applied in the direction of non-fibrous pulp addition, paper-making, coating, etc., can solve the problems of increasing the uniformity of the weight of the air-laid process mat, the distribution of fibers is uneven, and the uniform weight of the mat is not uniform. , to achieve the effect of uniform weigh
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0020] The process of the present invention provides many advantages over prior art mats which are formed by a dry-laid process. The wet-laid process of the present invention provides a highly porous, thin, non-woven glass fiber mat which has greater uniformity of fiber distribution than mats produced in dry-laid processes. Further, the mat of the present invention can be produced at lower cost because it uses low-cost wet chopped fibers which are formed into bundles by altering the components of the slurry used in a normal wet-laid process. In addition, the slurry components may be modified so as to produce mats comprising either bundles of fibers or dispersed fibers without having to replace the entire slurry.
[0021] The wet-laid mat of the present invention may be processed with the use of papermaking-type machines such as Fourdrinier, wire cylinder, Stevens Former, Roto Former, Inver Former and Venti Former machines. The general procedure for preparing the glass fiber mat of the...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| length | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| length | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com