Electroplated abrasive tools, methods, and molds
a technology of abrasive tools and molds, which is applied in the direction of gear teeth, grinding devices, gear teeth, etc., can solve the problems of hammering the performance and usable life of many known superabrasive tools, the height to which a superabrasive particle extends above the tool substrate, and the placement and retention of superabrasive particles remain problemati
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
Manufacture of a CMP Pad Dresser
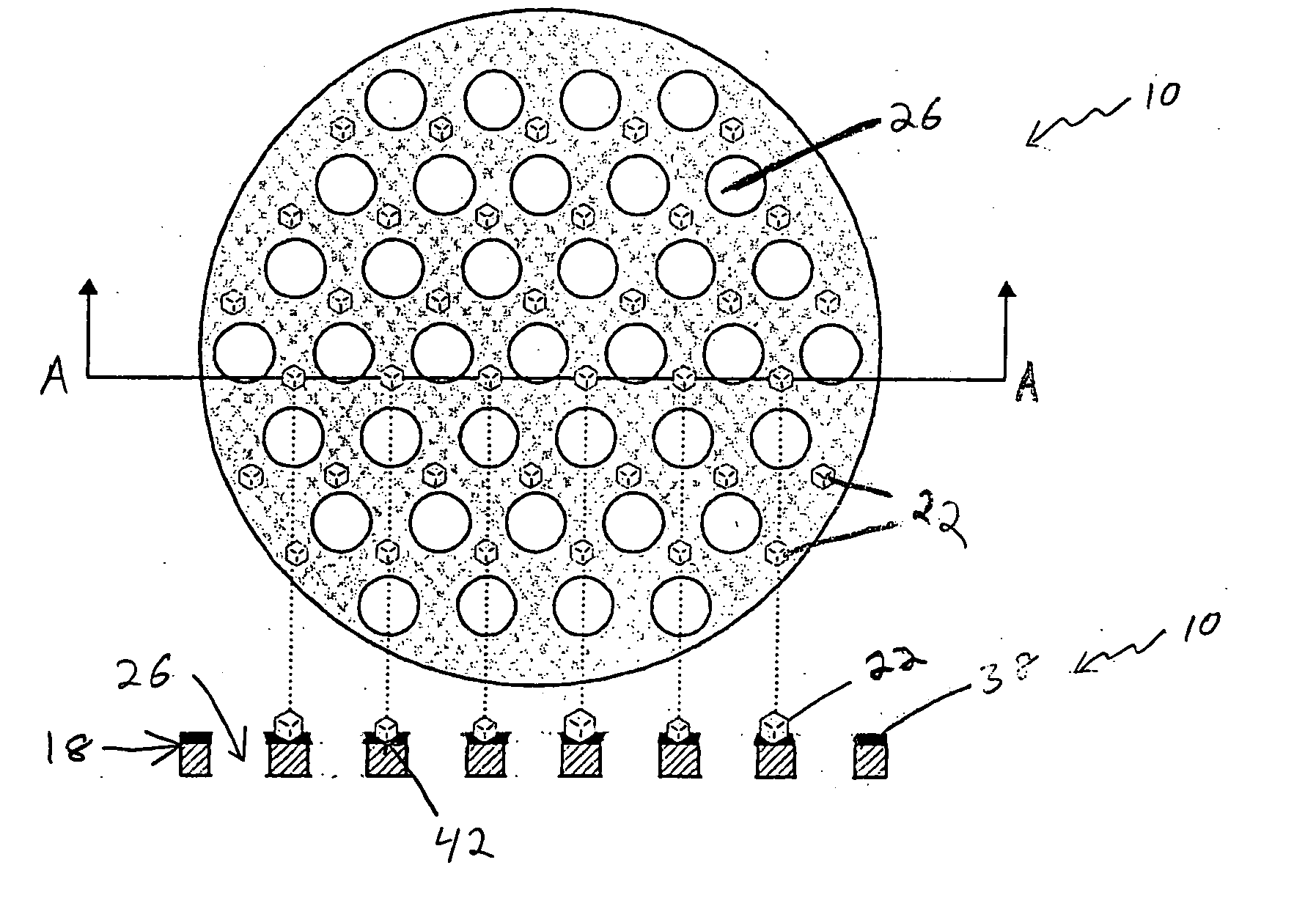
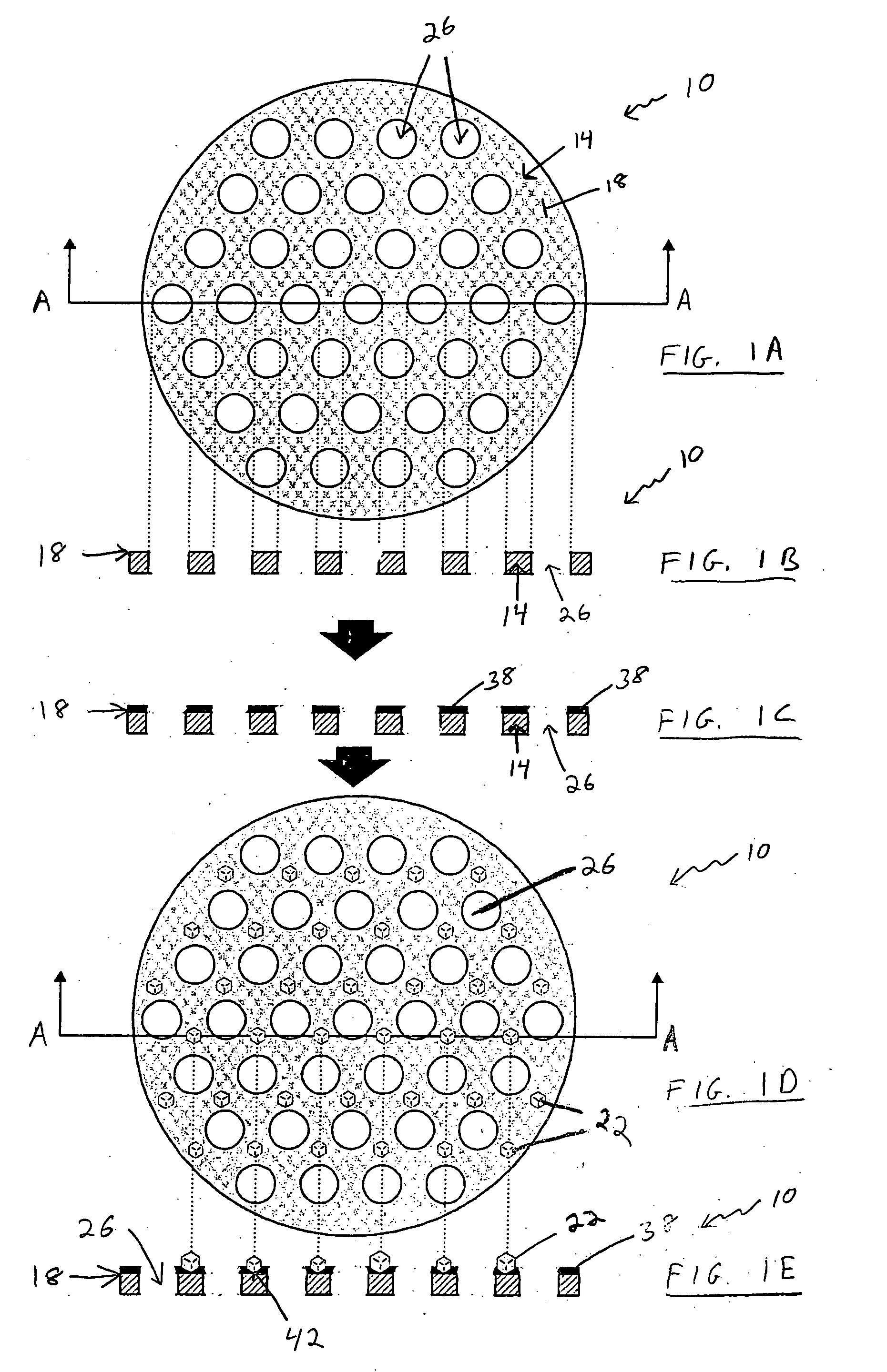
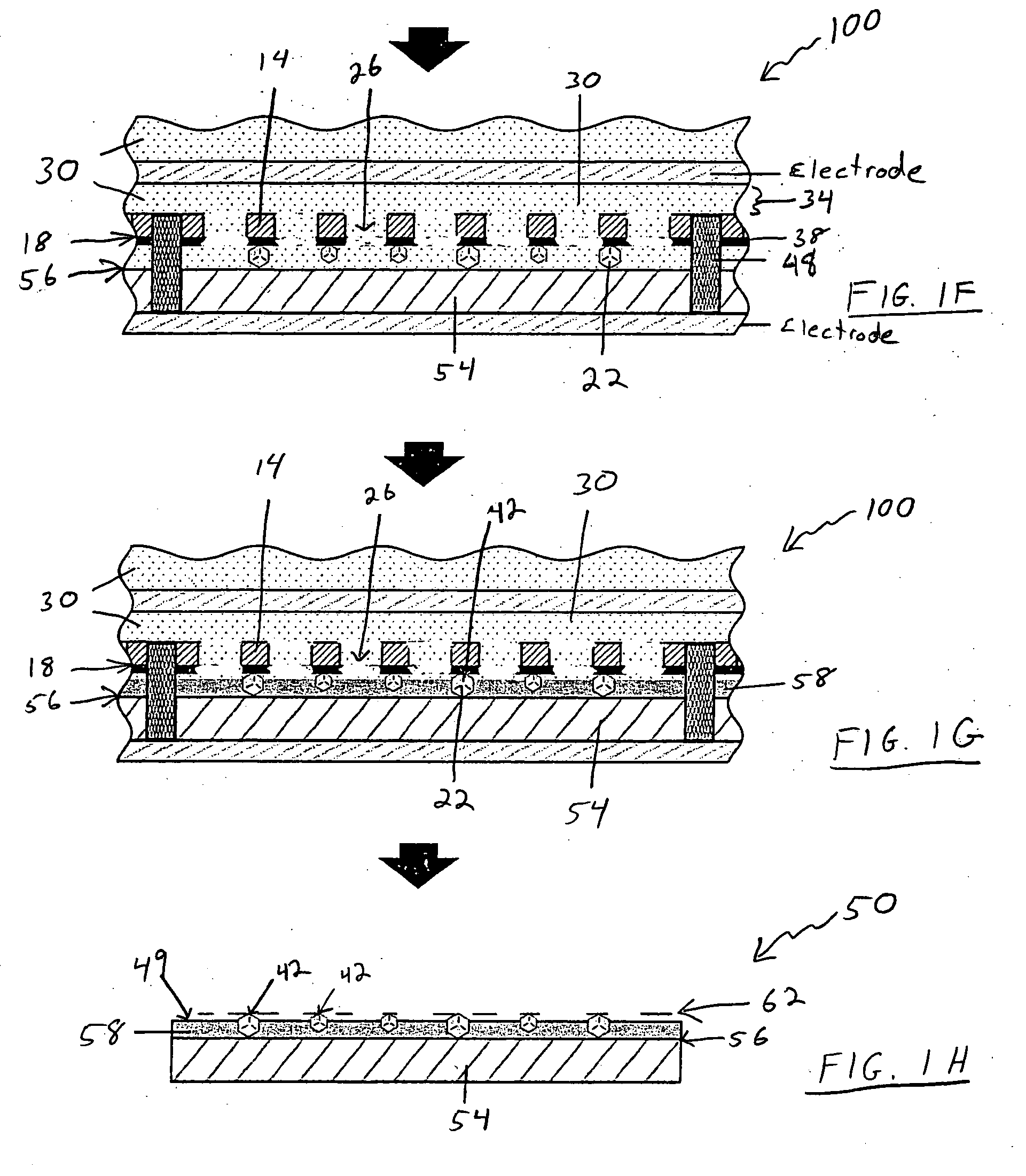
[0069] A mold of a polyimide layer (1 mm thick) that is stamped to contain a plurality of apertures arranged in a lattice pattern. The center of each aperture is separated from the center of neighboring apertures by a distance of 0.7 mm, and each aperture has a 0.5 mm diameter. One surface of the polyimide layer (i.e. the molding surface) is coated with an acrylic adhesive (50 microns thick). Diamond grits of 100 / 120 mesh are attached to the molding surface with each diamond grit located in the center of the four surrounding apertures. The diamond covered molding surface is placed against a disc-shaped stainless steel substrate (being 108 mm in diameter by 6.5 mm in thickness). The diamond grits are between the molding surface and the stainless steel substrate. The mold and the substrate are located in a plastic (PVC) ring 48 to hold them together during electrolytic process. The substrate is placed in contact with a cathode. NiSO4 solution is used a...
example 2
[0070] Thirty molds are made as follows:
[0071] Each mold is formed of a stainless steel disc that is about 120 mm in diameter and about 120 microns in thickness. Each disc is lithographically etched to form a plurality of apertures thereon distributed in a lattice pattern as described below. The apertures cover a generally circular area on a central portion of each disc of about 100 mm in diameter, leaving a width of about 20 mm around the perimeter of each disc without any apertures. Measuring from the approximate center points of adjacent apertures, (the “aperture separation”), a number of discs are formed with the following aperture separations:
[0072] 1. Ten discs with an aperture separation of about 800 microns, each aperture about 400 microns in diameter;
[0073] 2. Ten discs with an aperture separation of 600 microns, each aperture about 300 microns in diameter;
[0074] 3. Ten discs with an aperture separation of 400 microns, each aperture about 200 microns in diameter.
[0075]...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com