Expandable emboli filter and thrombectomy device
a filter and thrombosis technology, applied in the field of expanding emboli filter and thrombosis devices and systems, can solve the problems of emboli being released into the circulatory system, affecting the patient's health, and causing significant health problems for the patient,
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
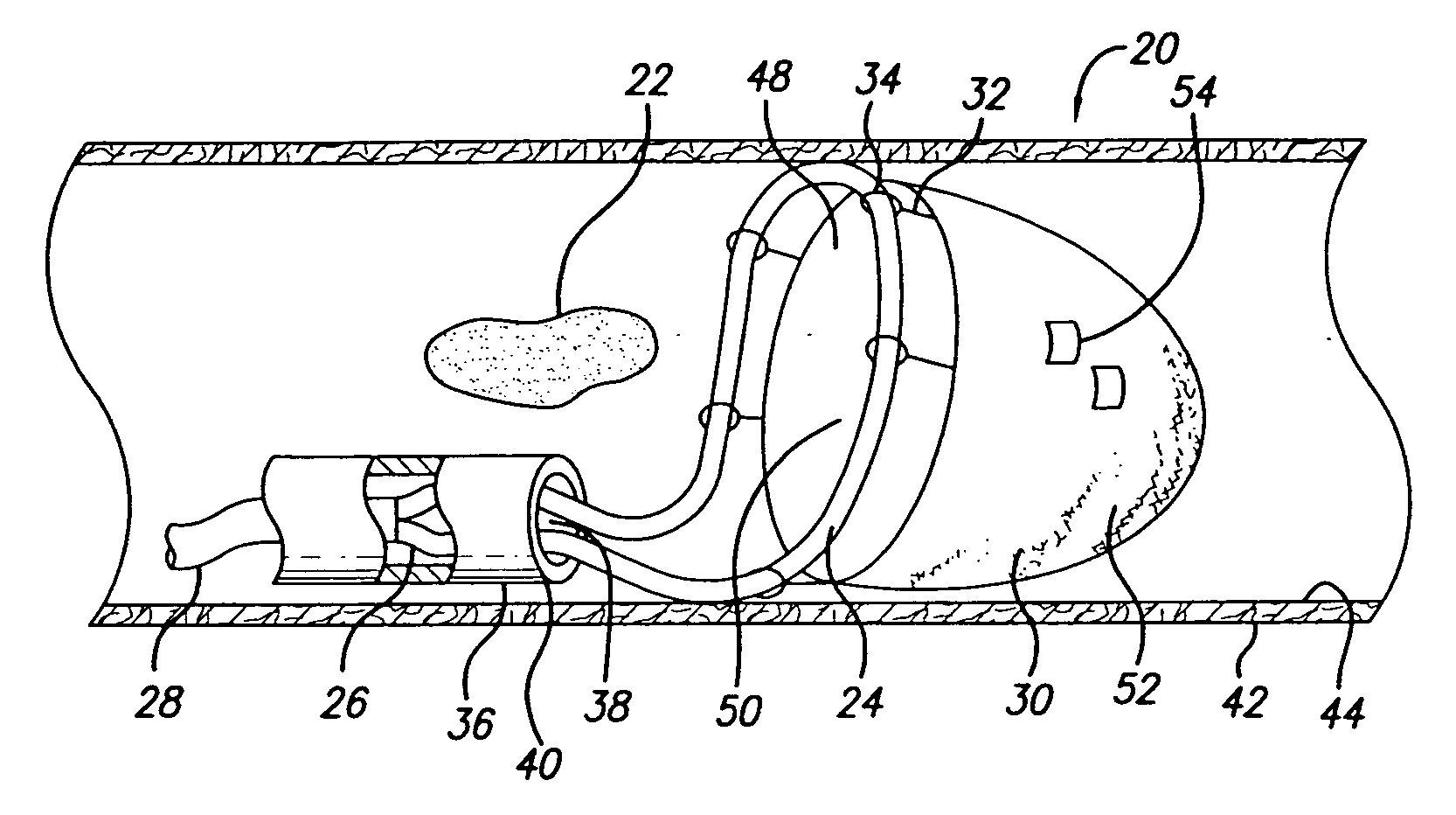
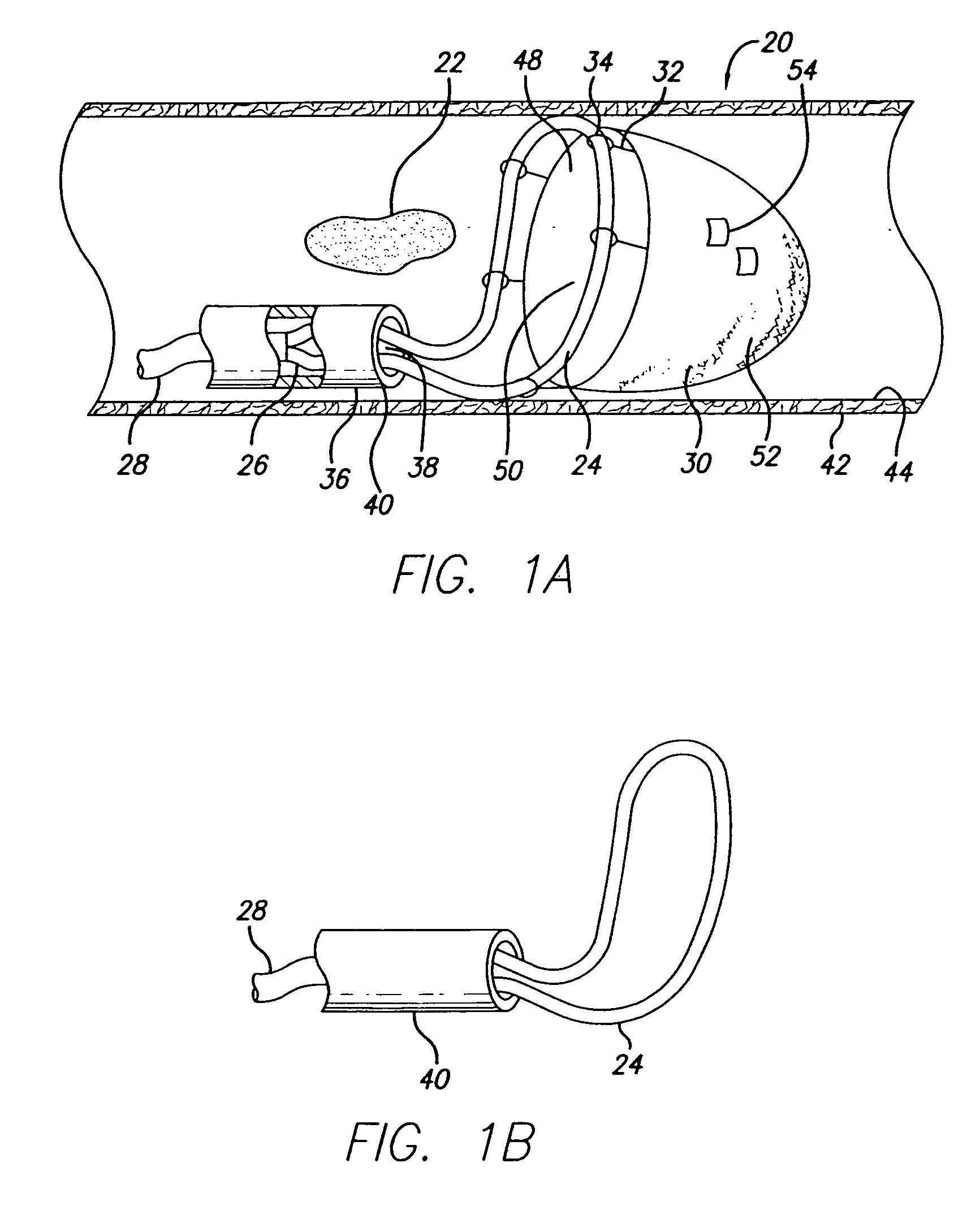
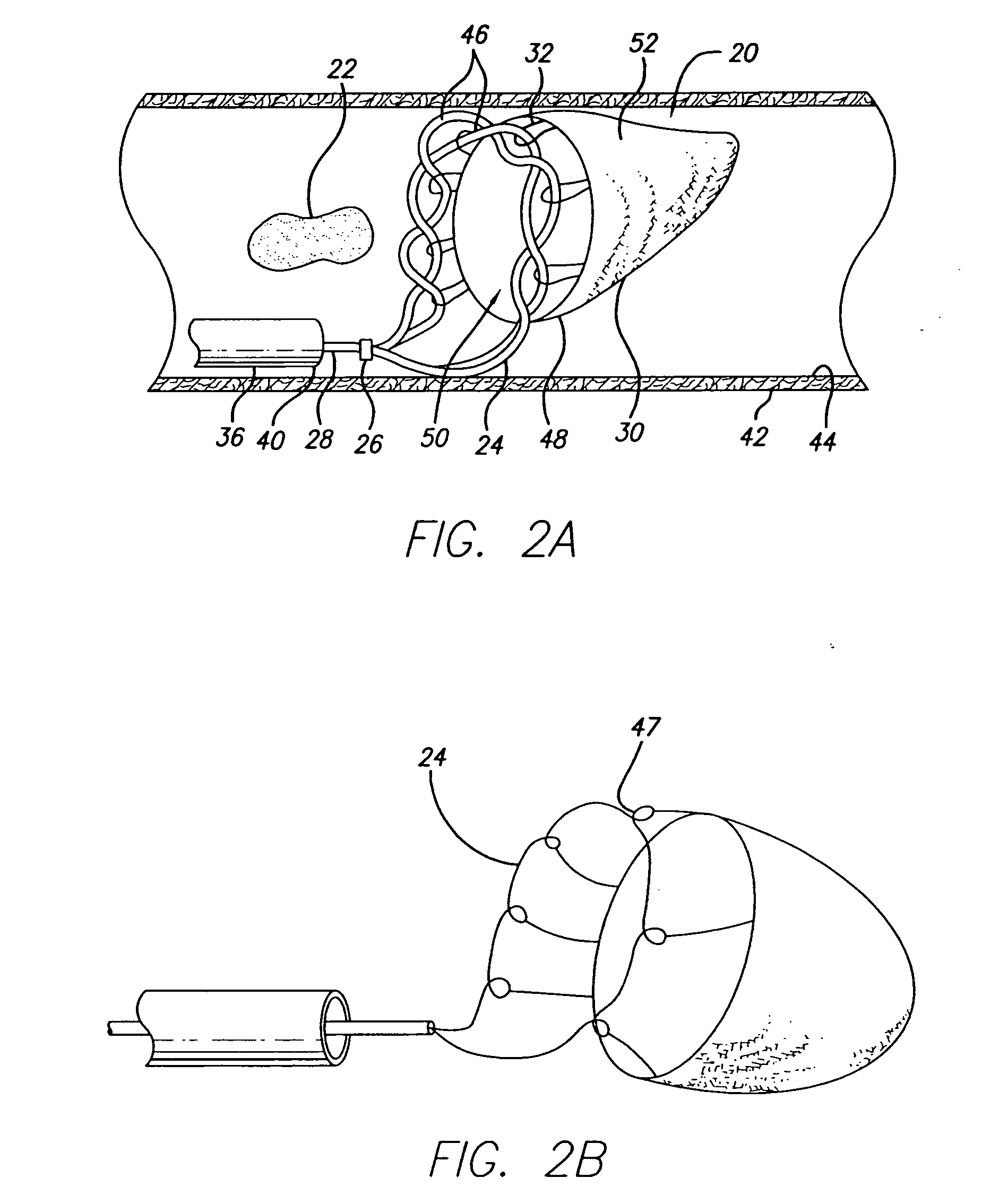
[0032] Turning now to the drawings, and particularly to FIG. 1A, there is shown an expandable device 20 of the present invention. The expandable device 20 is suited for repairing vessels and in particular, for capturing emboli 22 found in the bloodstream of a patient. Due to its novel structure, the repair device 20 embodies an expanded profile that is highly effective in filtering unwanted material from vasculature and is capable of being deployed within very narrow and distal vasculature, including the cerebral vasculature.
[0033] In one presently preferred embodiment, the expandable device 20 includes a loop 24 attached by conventional means to a distal end 26 of an elongate member 28. Attached to the loop 24 is an emboli filter 30. The loop 24 can be soldered to the elongate member 28 or can be affixed thereto using epoxy or other forms of adhesive. Alternatively, the loop 24 can be an integral part of the elongate member 28 (See FIG. 1B). A band or other mechanical fixation dev...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com