Persistent Dynamic Payment Service
a dynamic payment and persistent technology, applied in the field of persistent dynamic payment services, can solve the problems of security, privacy, anonymity, complex schemes, etc., and achieve the effect of protecting the credit card number but not the privacy of the cardholder himsel
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
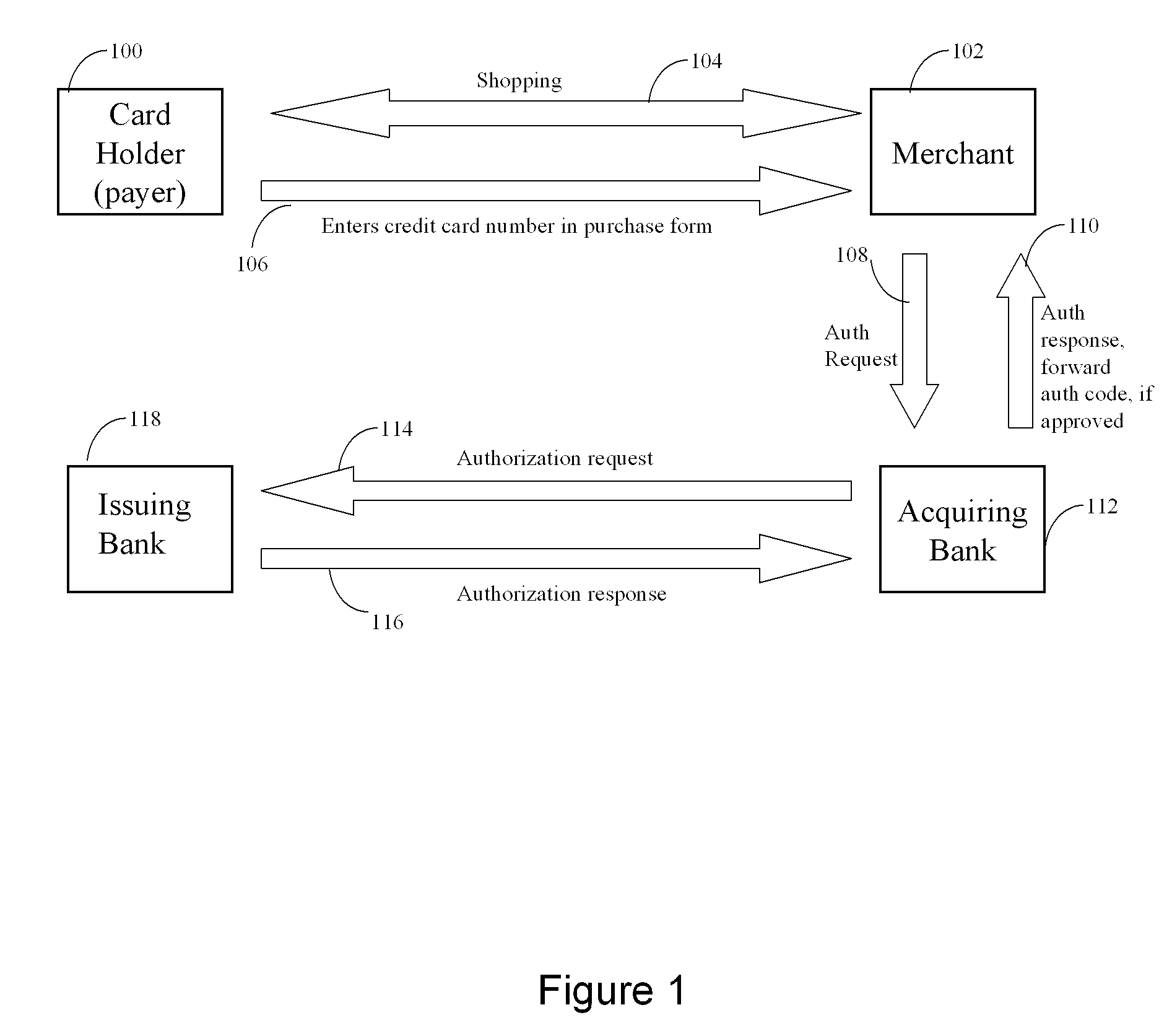
[0117] Referring to FIG. 3, a preferred embodiment of a method according to the invention is illustrated showing processing a payment transaction using a PDPS.
[0118] In process 123 a cardholder (payer) 100 completes an enrollment process with the PDPS which in this case is achieved by contacting the PDPS portal through its web address using a browser operating on the payer's computer system. If the cardholder is not a member (does not have credentials to authenticate to the PDPS) the enrollment process is initiated by which the PDPS extracts personal information, account information and preferences from the payer. In alternative options the enrollment process could be carried out off line by mail or telephone. The cardholder is assigned at least one proxy account number. Each proxy account number is associated with at least one actual financial account of some type. The proxy account number looks like a credit card number and is partly composed of random looking numbers, as well as...
example 2
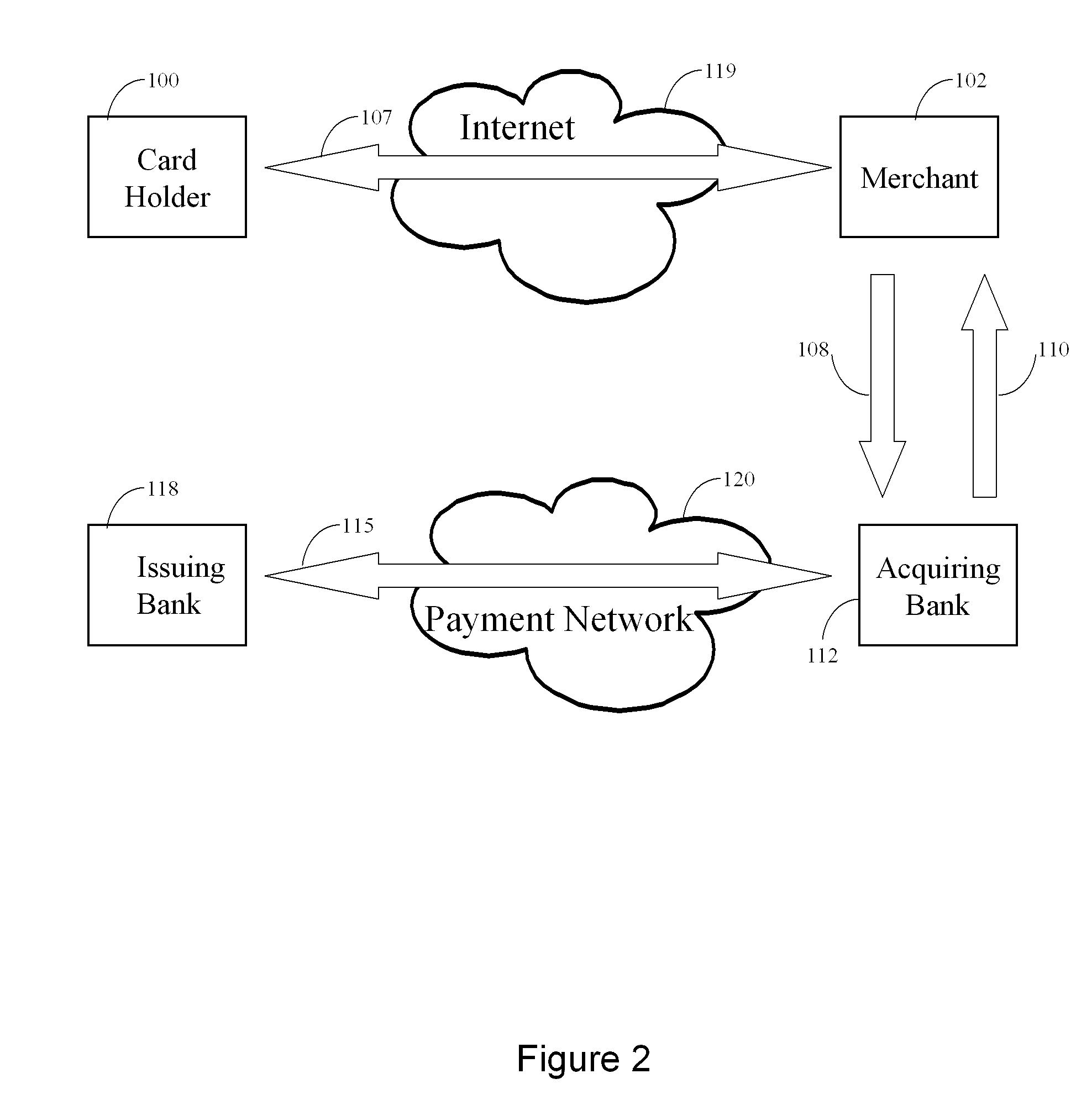
[0128] In another embodiment of the invention, the Payment Processor is also an issuer (issuing bank) for a secure credit card using a PDPS. In this embodiment, several options are possible. In one option, a bank which has an affiliated PDPS, issues secure credit cards to its clients. In this option, the card is capable of use both as a physical card as when the cardholder is physically present at a merchant or alternatively for an online e-commerce transaction. It would not be necessary to use a proxy account number in order to gain the security benefits of the invention. Since the Payment Processor Bank is also the issuer of the credit card the routing information contained in the credit card number will cause a transaction to be routed to the Payment Processor / PDPS in due course when the Acquiring bank presents a transaction for payment. FIG. 5 shows that one step is eliminated in this option because the issuing bank and the payment Processor coincide. This option illustrates tha...
example 3
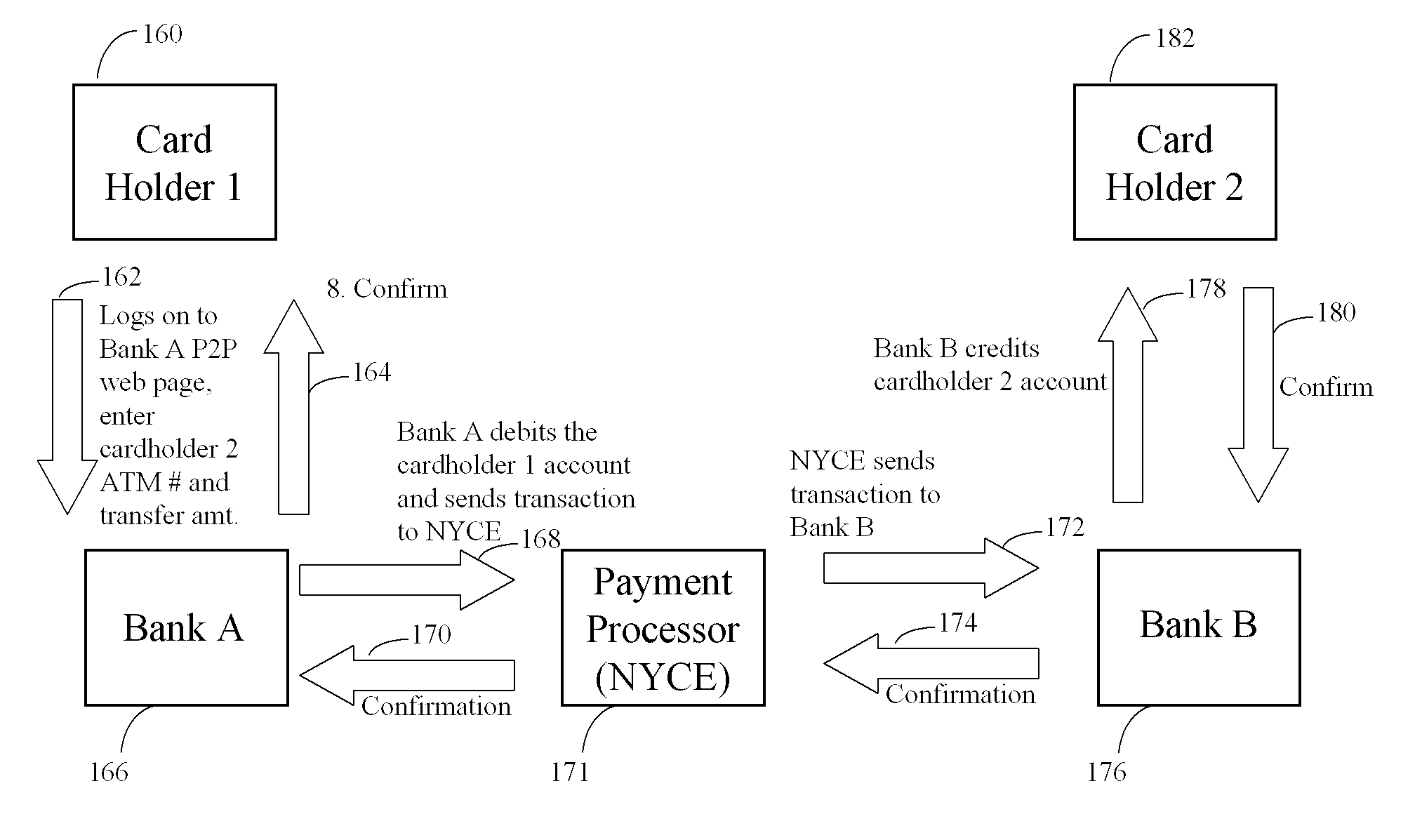
[0132] Another embodiment of the invention involves processing peer to peer payments between two debit card holders. There is an existing web based service offered by banks to their customers whereby an essentially real time transfer of funds is made from a first card holder's account to a second account holder's account. The transfer is effected between the first cardholder's bank and the second cardholder's bank over a shared ATM / debit card payment network such as the NYCE network. FIG. 7 shows the existing NYCE peer to peer process as an example. Referring to FIG. 7, Cardholder 1160 wishes to transfer funds to Cardholder 2182. The first cardholder has an account in Bank A 166. The second cardholder has an account in Bank B 176. In process 162 Cardholder 1 logs on to the peer to peer web page and enters Cardholder 2's ATM card number and the amount to be transferred. Bank A debits cardholder 1's account and sends the transaction to the Payment Processor 171, in this case NYCE, for...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com