Polyethylene terephthalate filament having high tenacity for industrial use
a polyethylene terephthalate, high tenacity technology, applied in the direction of geotextiles, yarn, transportation and packaging, etc., can solve the problems of poor post-processing properties, increase in production costs and product quality, and difficulty in obtaining high-tenacity yarns therefrom, so as to increase the draw ratio
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
examples 1 to 3
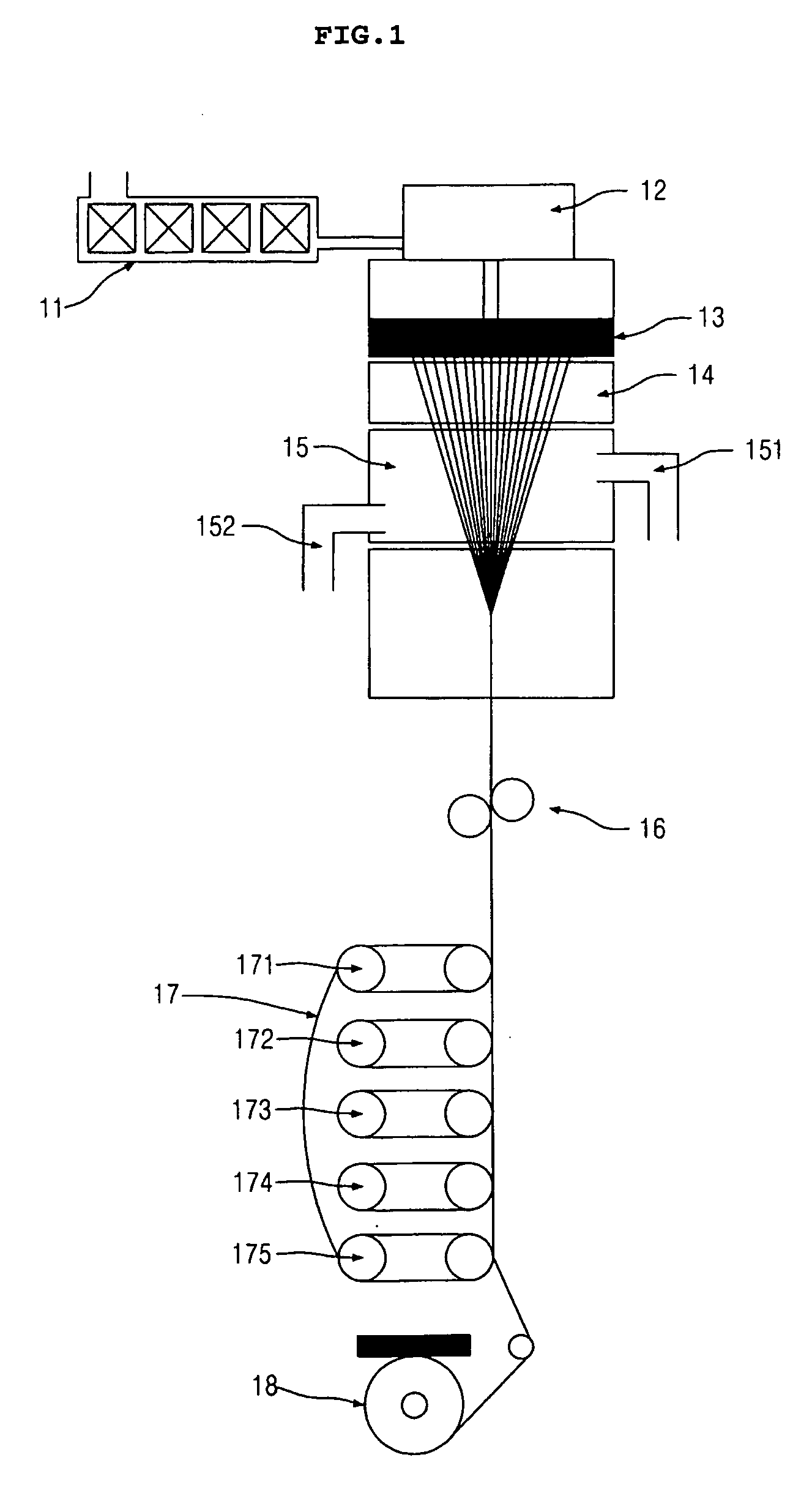
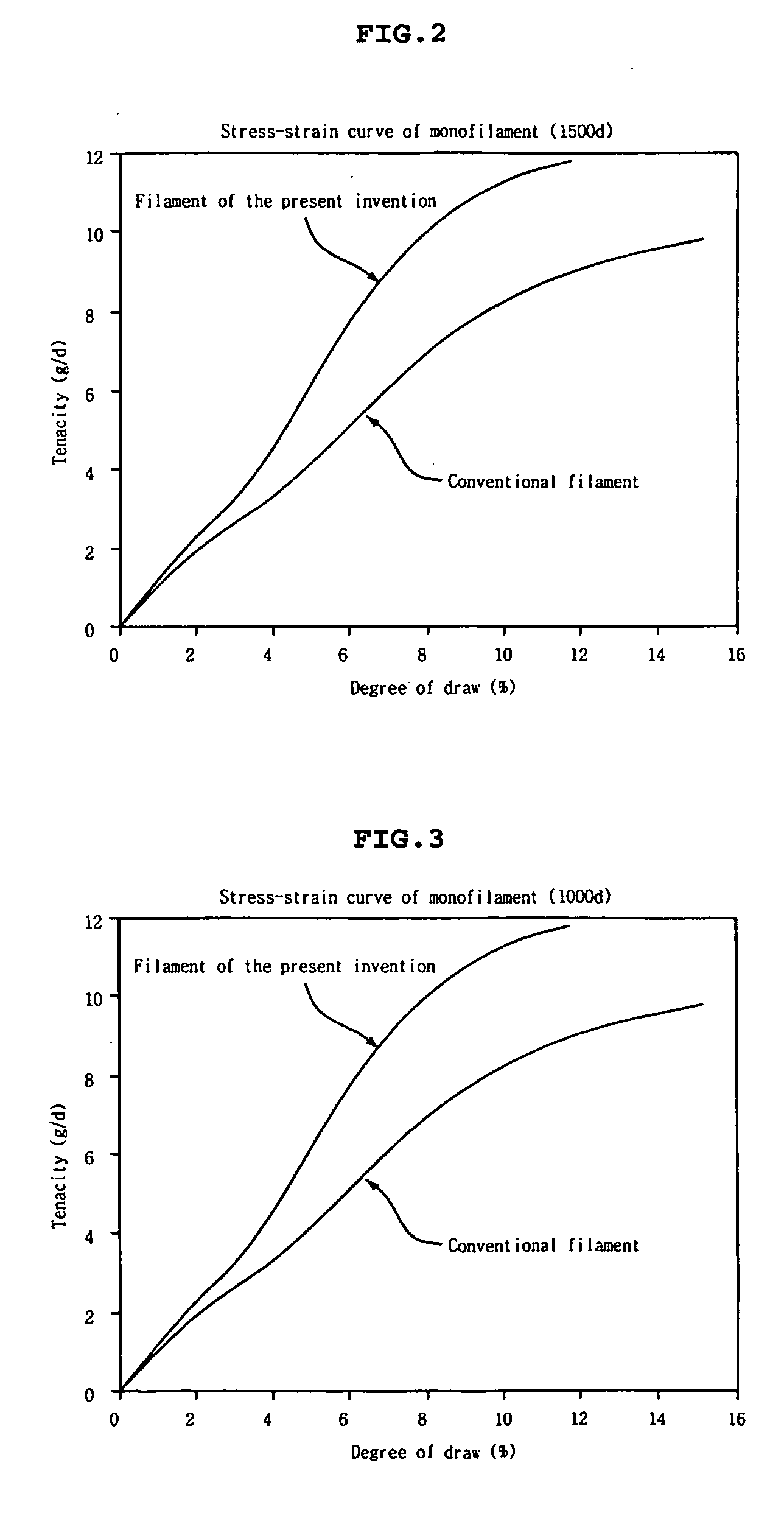
[0048] A polyester chip having an intrinsic viscosity of 1.00 was melted, and the melt polymer was extruded through a nozzle having 192 orifices, each orifice having a diameter of 0.6 mm and a ratio of length and diameter (L / D) of 3. The extruded polymer was quenched with air at 15° C., gathered and oiled. Subsequently, the filament was subjected to winding 5 turns at the second godet rollers (primary drawing point) at 100° C., and 7 turns at the third godet rollers (secondary drawing point) at 125° C., with the ratio of the primary draw at the second godet rollers and the third godet rollers to the secondary draw at the third godet rollers and the fourth godet rollers being 75%:25%. A guide in a flat form having a 4 mm-wide groove was applied before the second godet rollers and the third godet rollers. The speed of the fourth godet rollers was set at 2700 m / min. Thus, filaments of 1500 denier each were spun and drawn under the spinning conditions presented in Table 1. The results a...
examples 4 to 6
[0051] A polyester chip having an intrinsic viscosity of 1.05 was melted, and the melt polymer was extruded through a nozzle having 192 orifices, each orifice having a diameter of 0.6 mm and a ratio of length and diameter (L / D) of 3. The extruded polymer was quenched with air at 15° C., gathered and oiled. Subsequently, the filament was subjected to winding 6 turns at the second godet rollers (primary drawing point) at 100° C., and 7 turns at the third godet rollers (secondary drawing point) at 125° C., with the ratio of the primary draw at the second godet rollers and the third godet rollers to the secondary draw at the third godet rollers and the fourth godet rollers being 73%:27%. A guide in a flat form having a 4 mm-wide groove was applied before the second godet rollers and the third godet rollers. The speed of the fourth godet rollers was set at 2700 m / min. Thus, filaments of 1500 denier each were spun and drawn under the spinning conditions presented in Table 2. The results a...
examples 7 to 9
[0054] A polyester chip having an intrinsic viscosity of 1.00 was melted, and the melt polymer was extruded through a nozzle having 192 orifices, each orifice having a diameter of 0.6 mm and a ratio of length and diameter (L / D) of 3. The extruded polymer was quenched with air at 15° C., gathered and oiled. Subsequently, the filament was subjected to winding 5 turns at the second godet rollers (primary drawing point) at 100° C., and 8 turns at a third godet rollers (secondary drawing point) at 125° C., with the ratio of the primary draw at the second godet rollers and the third godet rollers to the secondary draw at the third godet rollers and the fourth godet rollers being 75%:25%. A guide in a flat form having a 4 mm-wide groove was applied before the second godet rollers and the third godet rollers. The speed of the fourth godet rollers was set at 3000 m / min. Thus, filaments of 1000 denier each were spun and drawn under the spinning conditions presented in Table 3. The results are...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Fraction | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Fraction | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Fraction | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com