Protease susceptibility II
a tropoelastin and susceptibility technology, applied in the field of tropoelastin susceptibility ii, can solve the problems of inadequate or faulty elastin fiber repair at the site of injury, the soluble precursor of elastin is far more susceptible to proteolysis, and the elastin molecule is not shown in the study
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
examples
Materials and Methods
Reagents
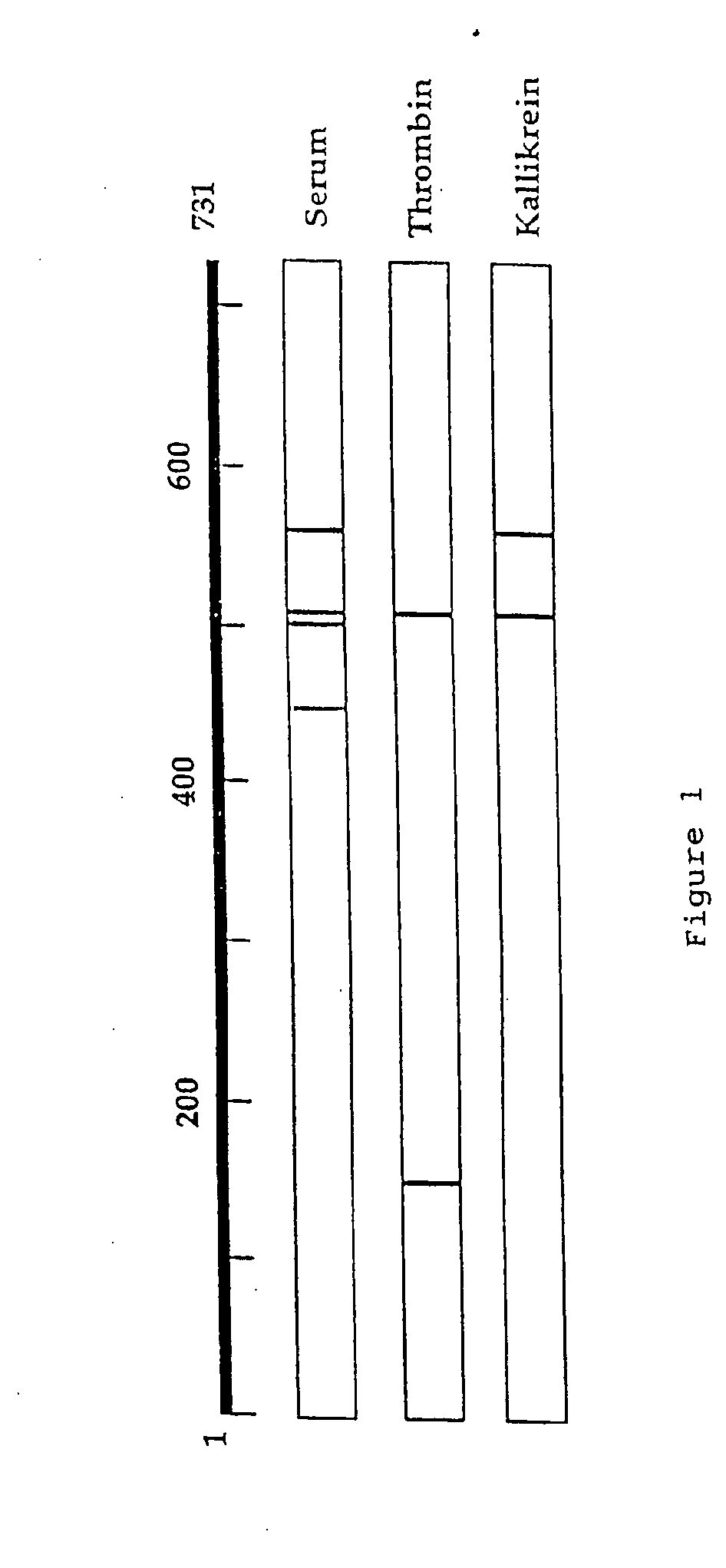
[0140] Hirudin, PMSF, human thrombin, human plasma kallikrein, human plasmin and human leukocyte elastase (HLE) were obtained from Sigma. Bovine trypsin and Pefabloc SC were from Boehringer-Mannheim and Pefabloc PK was from Pentapharm, Switzerland. Gelatinase A (72 kDa gelatinase) and gelatinase B (92 kDa gelatinase) were obtained from Boehringer Mannheim Roche Diagnostics.
[0141] SHEL was obtained by the method described in WO94 / 14958.
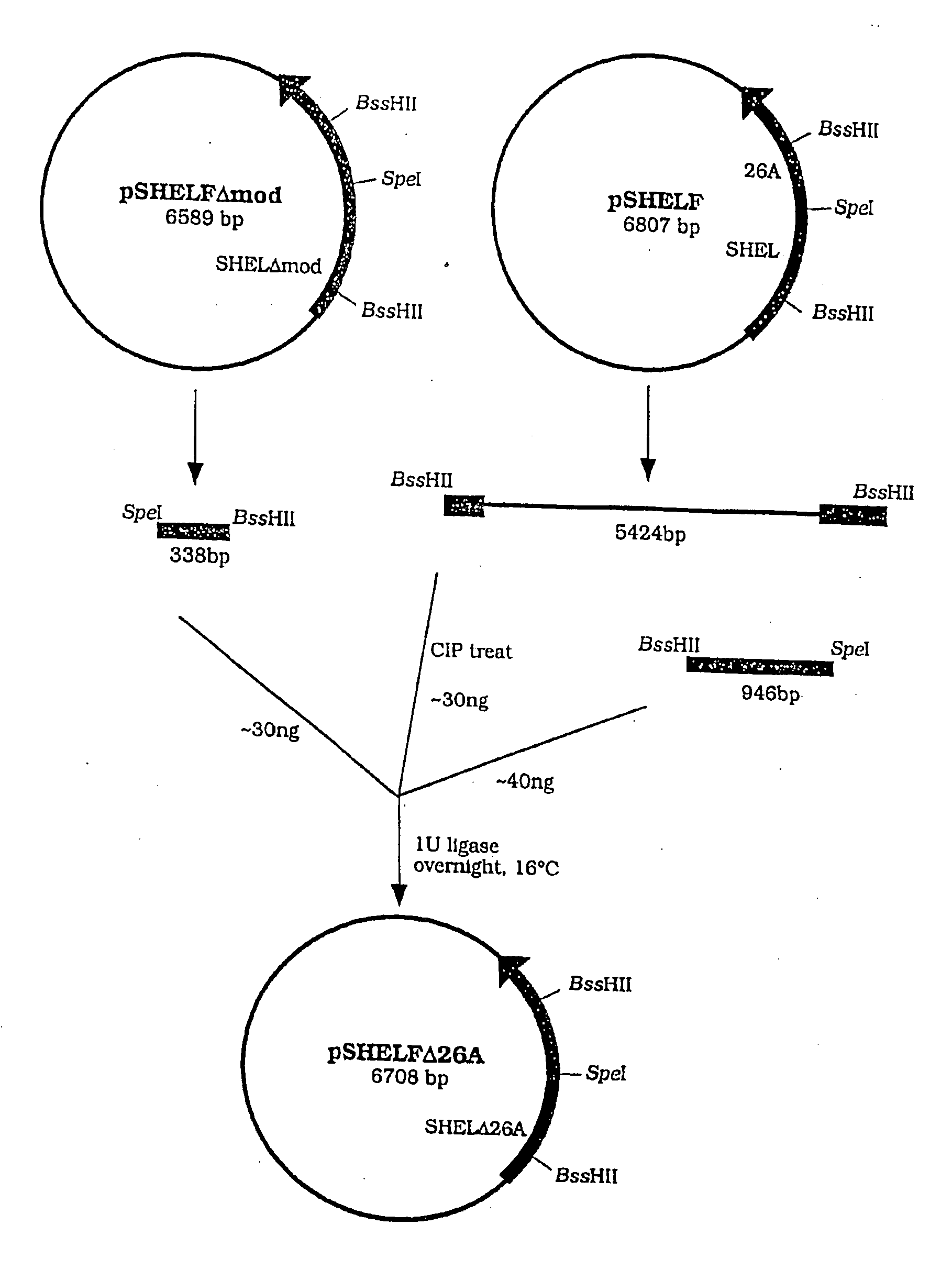
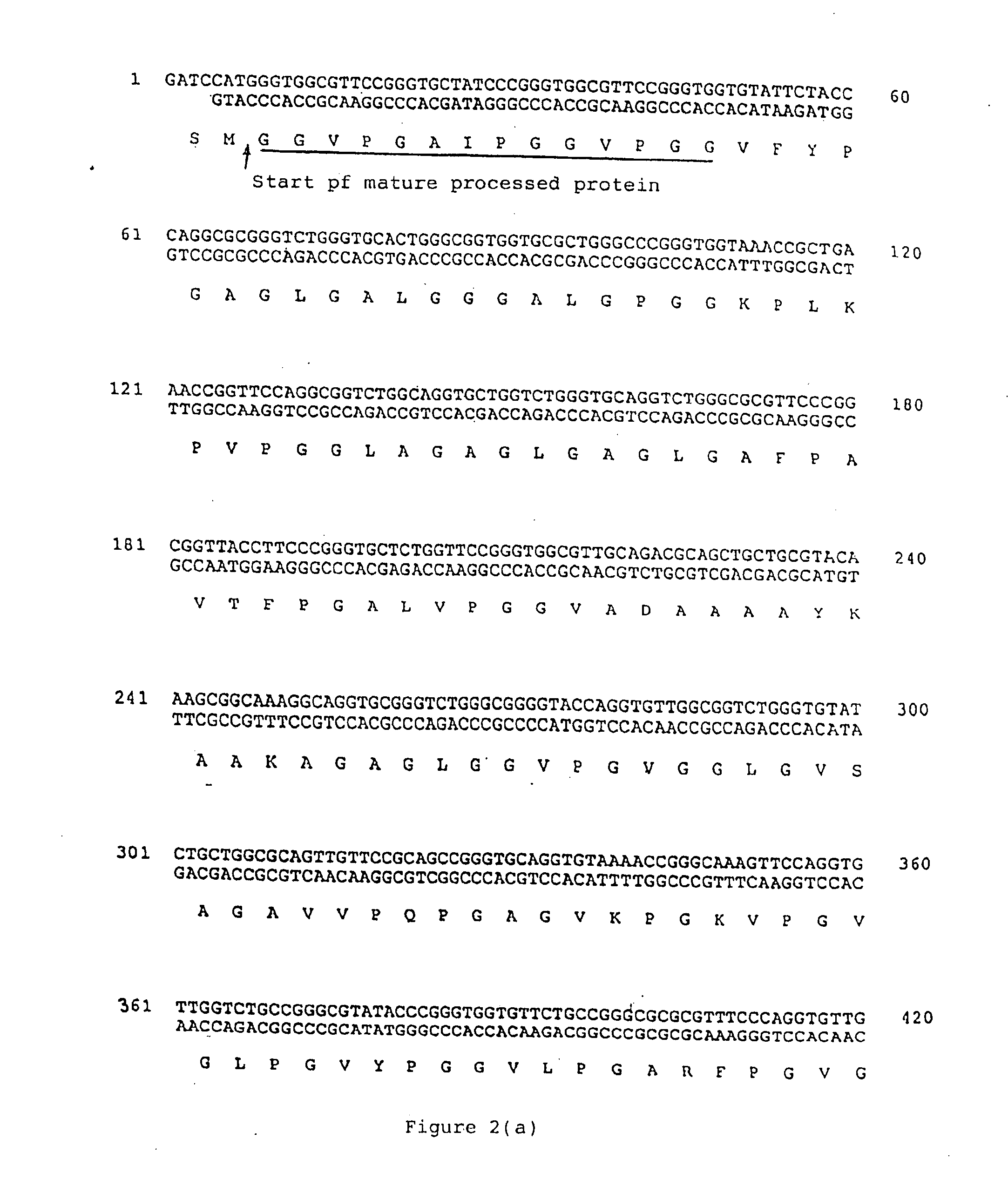
[0142] SHELδ26A can be derived from SHEL by removing the synthetic coding sequence corresponding to exon 26A. A comparison of the sequence of SHEL with that of SHELδ26A is provided at FIG. 3. Its protein product is apparently identical to a naturally made human splice form of tropoelastin.
[0143] The Transformer Mutagenesis Kit (Clontech USA) was used with pSHELF (described in WO94 / 14958) in accordance with the supplied protocol to remove DNA corresponding to exon 26A. The sequence of the mutagenic primer used (manufac...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| pH | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| total volume | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| pH | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com