Method for the Prediction of the Risk Potential for Cancerous Diseases and Inflammatory Intestinal Diseases and Corresponding Tests
a cancerous disease and risk potential technology, applied in the direction of biochemistry apparatus, peptide sources, transferases, etc., can solve the problems of difficult to find statistically confirmed associations, complex human metabolism, and clearly adverse metabolic consequences, so as to improve the early detection
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
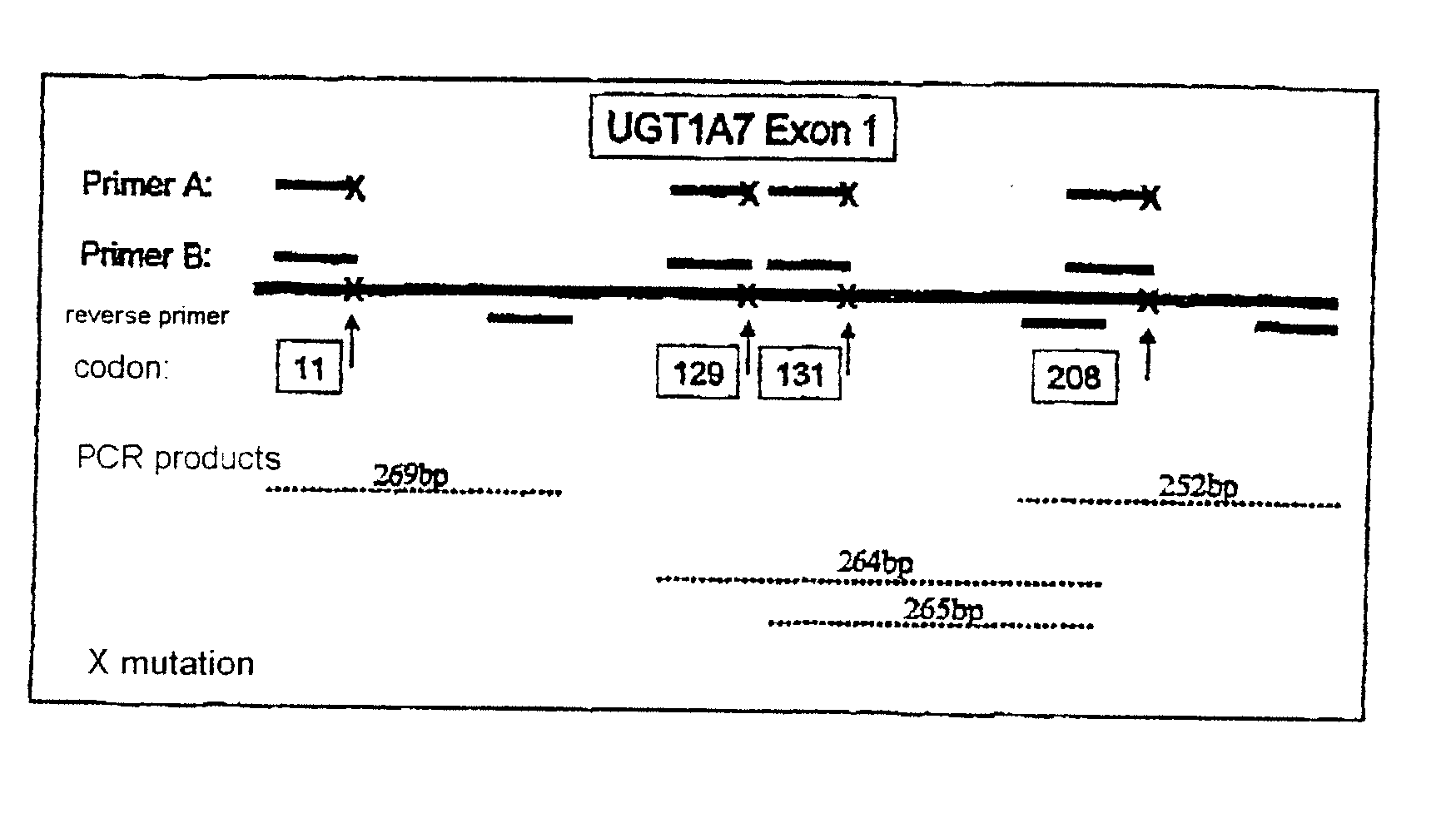
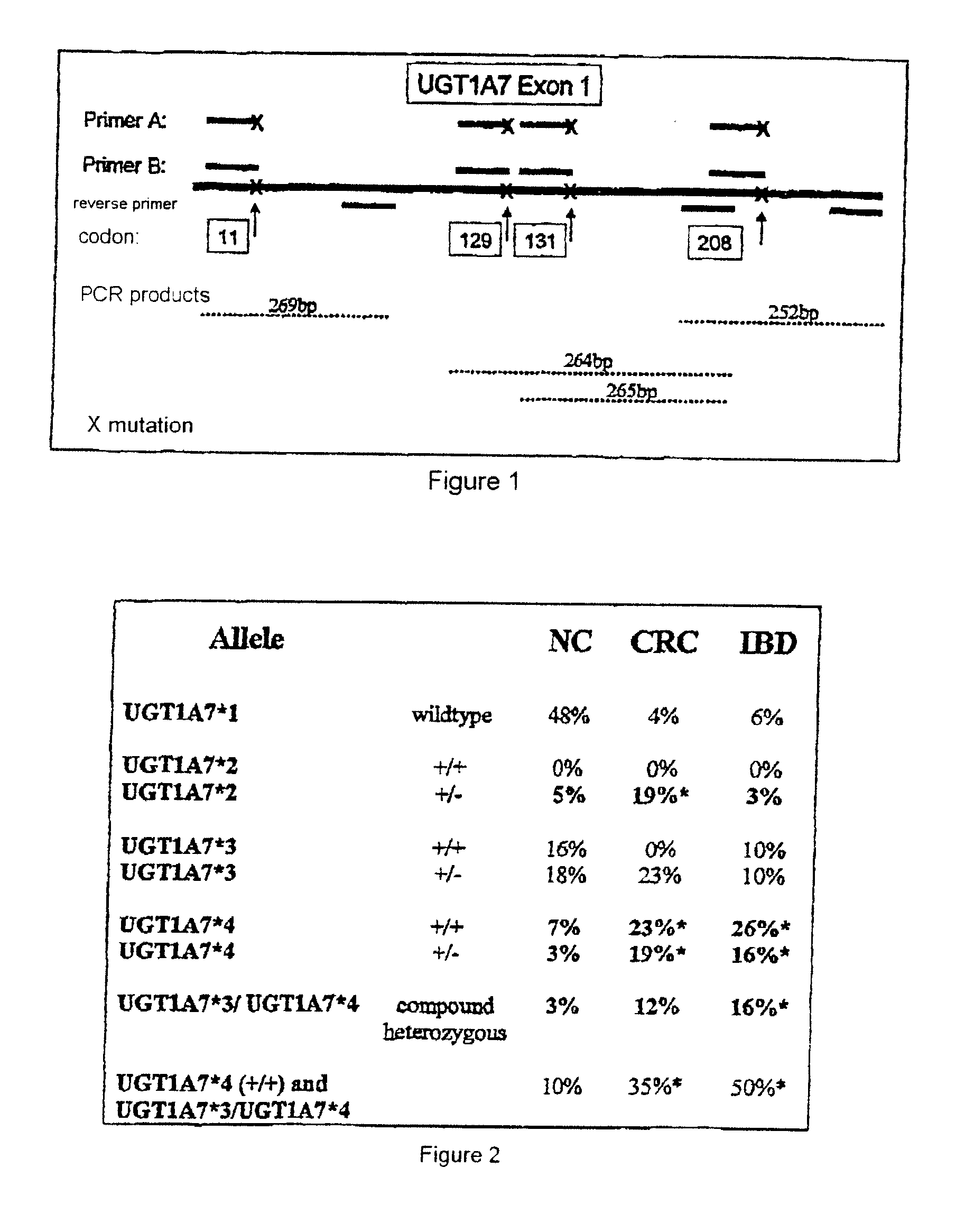
[0060]FIG. 1 shows a UGT1A7 polymorphism diagnostic method in which the region around the identified polymorphisms is amplified by polymerase chain reaction (PCR). Specific primer pairs which bind about 50 base pairs upstream and downstream of codon 11, of codon 129 / 131 and of codon 208 are used for this. This PCR generates complementary deoxyribonucleic acid fragments (cDNAs) which are 100 to 150 bp in size and which correspond to the wild-type allele or carry the identified polymorphisms.
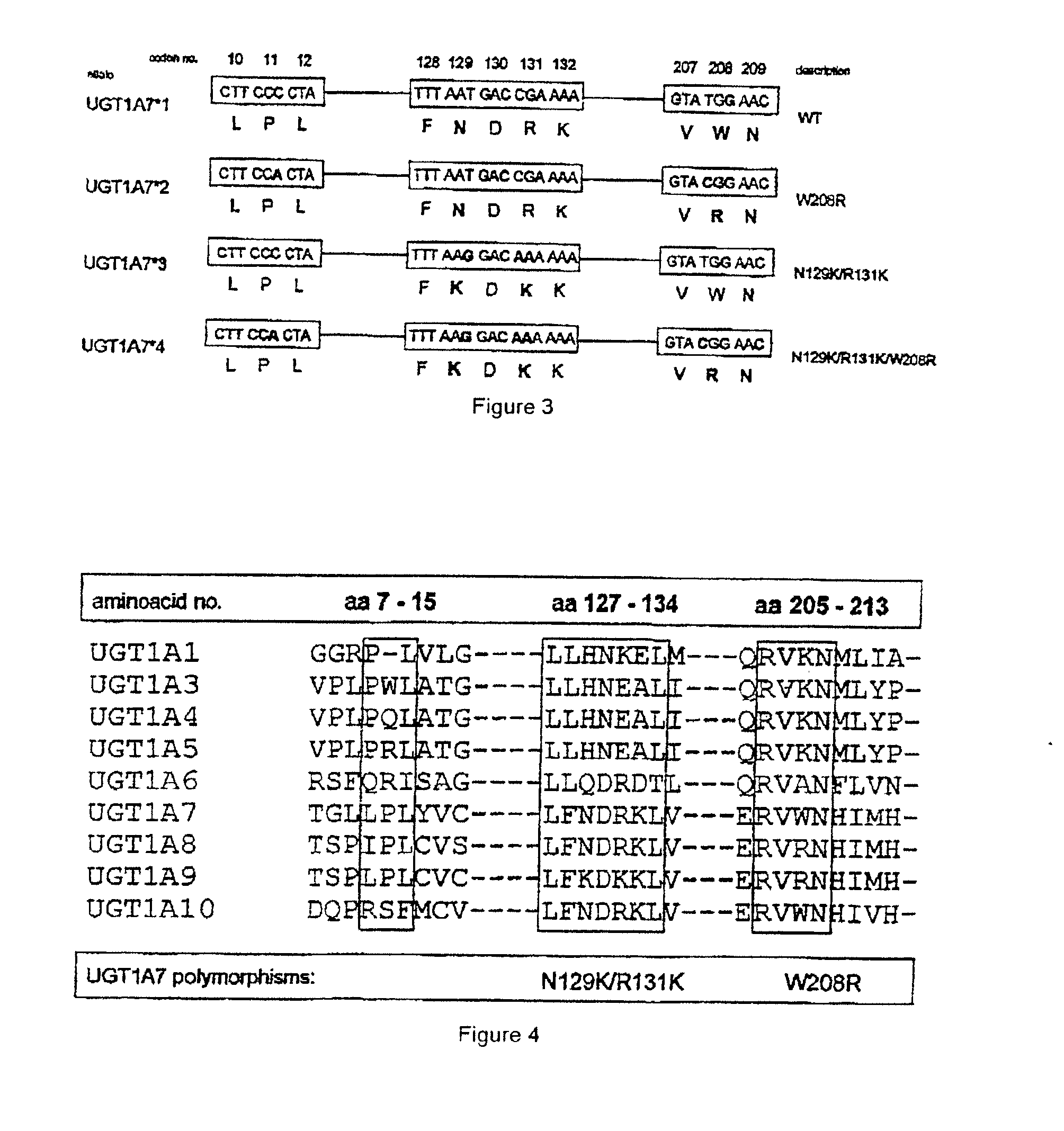
[0061]FIG. 2 shows the analysis of the prevalence of the polymorphic UGT1A7 alleles as defined in FIG. 3. This analysis, which is based on the defined polymorphic UGT1A7 alleles, shows a, significant association of UGT1A7*4 (SEQ ID NO: 21) and UGT1A7*2 (SEQ ID NO: 19) with colorectal cancer (CRC) and the low occurrence of these alleles in the normal control group (NC). In contrast thereto, inflammatory bowel diseases (IBD) are associated only with the presence of UGT1A7*4 (SEQ ID NO: 21). No sign...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| pH | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| volume | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com