Method of manufacturing abrasive cutting string
a manufacturing method and cutting string technology, applied in the field of manufacturing abrasive cutting string, can solve the problems of viscous periphery of the string in which abrasive particles are embedded, and achieve the effects of improving the cutting string, enhancing the cutting efficacy of the cutting string, and simple and inexpensive methods
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
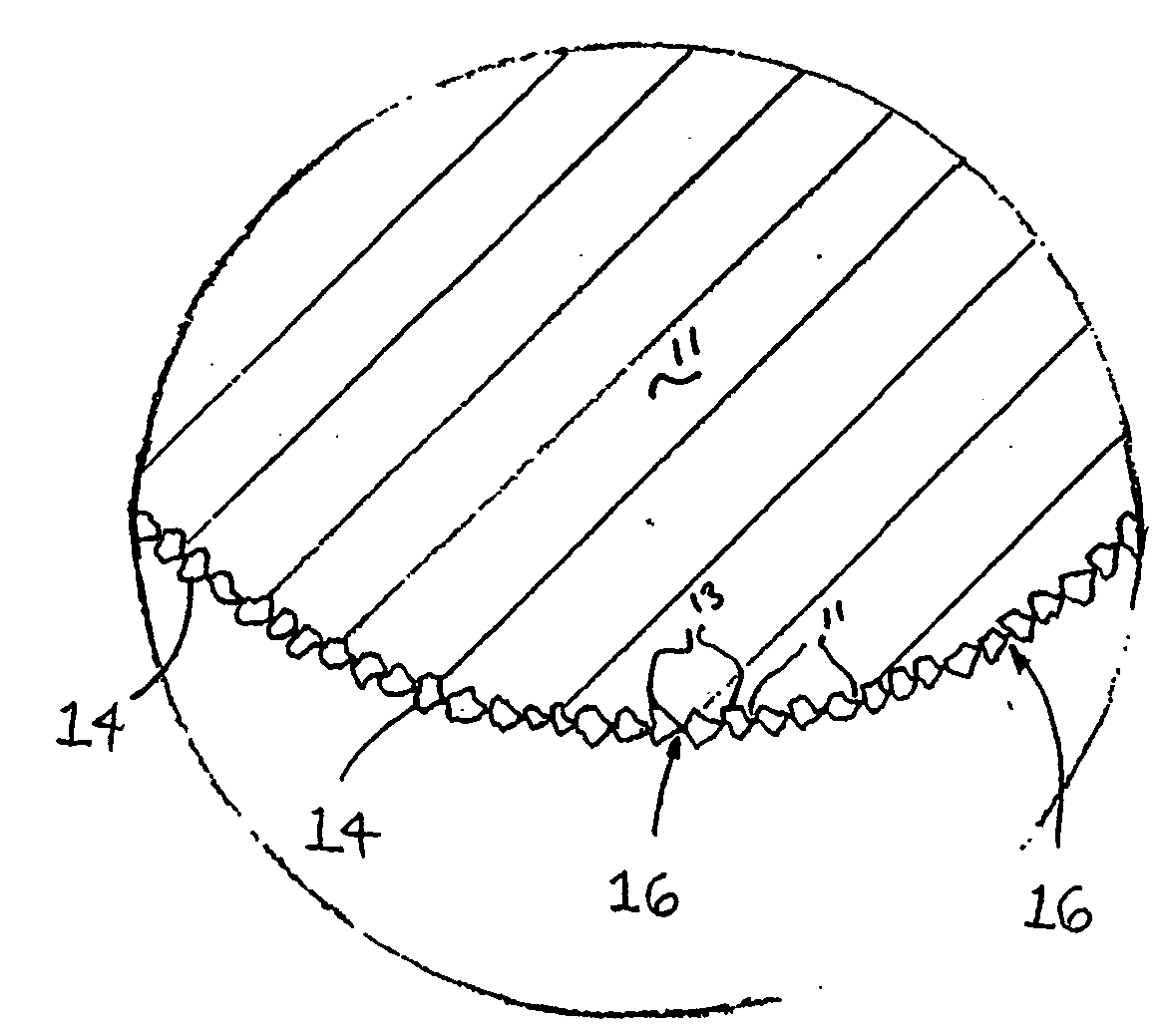
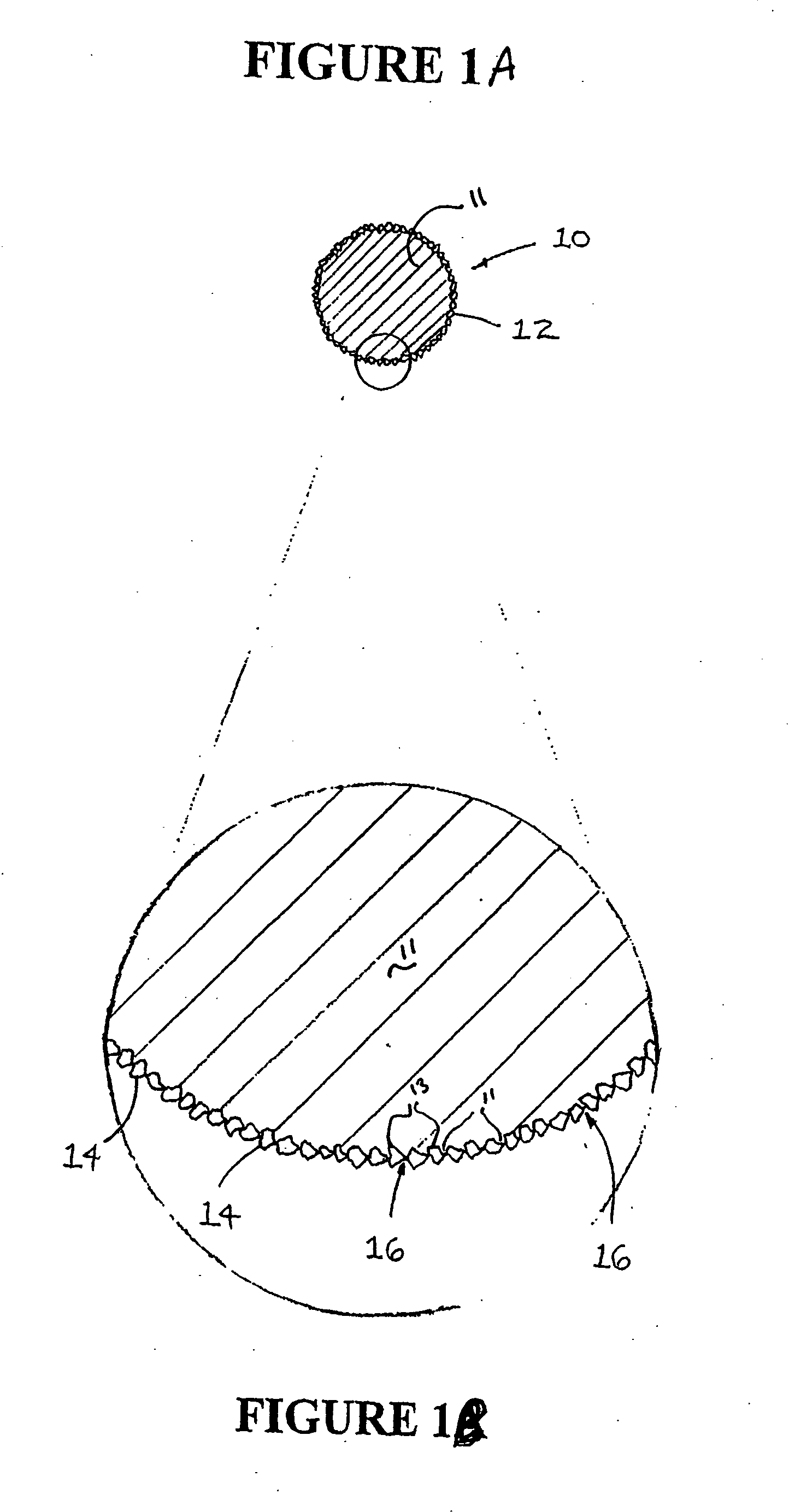
[0018]Referring now to the drawings, a cutting string 10 and a preferred method for making the cutting string of the invention are illustrated by FIGS. 1 through 2. As shown in FIG. 1A, a preferred cutting string is designated generally by reference numeral 10. The cutting string 10 is composed of a plastomeric material 11 such as Nylon 6 or Nylon 66 that is extruded to have a substantially circular cross-sectional shape. It is contemplated within the scope of the invention, however, that cutting string 10 may be composed of any suitable material that may be formed into a string-like configuration. Further, it is contemplated within the scope of the invention that cutting string 10 may be formed to have any suitable cross-sectional shape such as oval, crescent, semi-circular, triangular, square, rectangular, pentagonal, hexagonal, octagonal or any other polygonal shape. It is further contemplated within the scope of the invention that cutting string 10 may be produced by a process o...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com