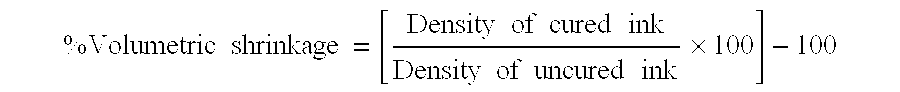Patents
Literature
260results about "Hand composition" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Apparatus For Orienting Magnetic Flakes
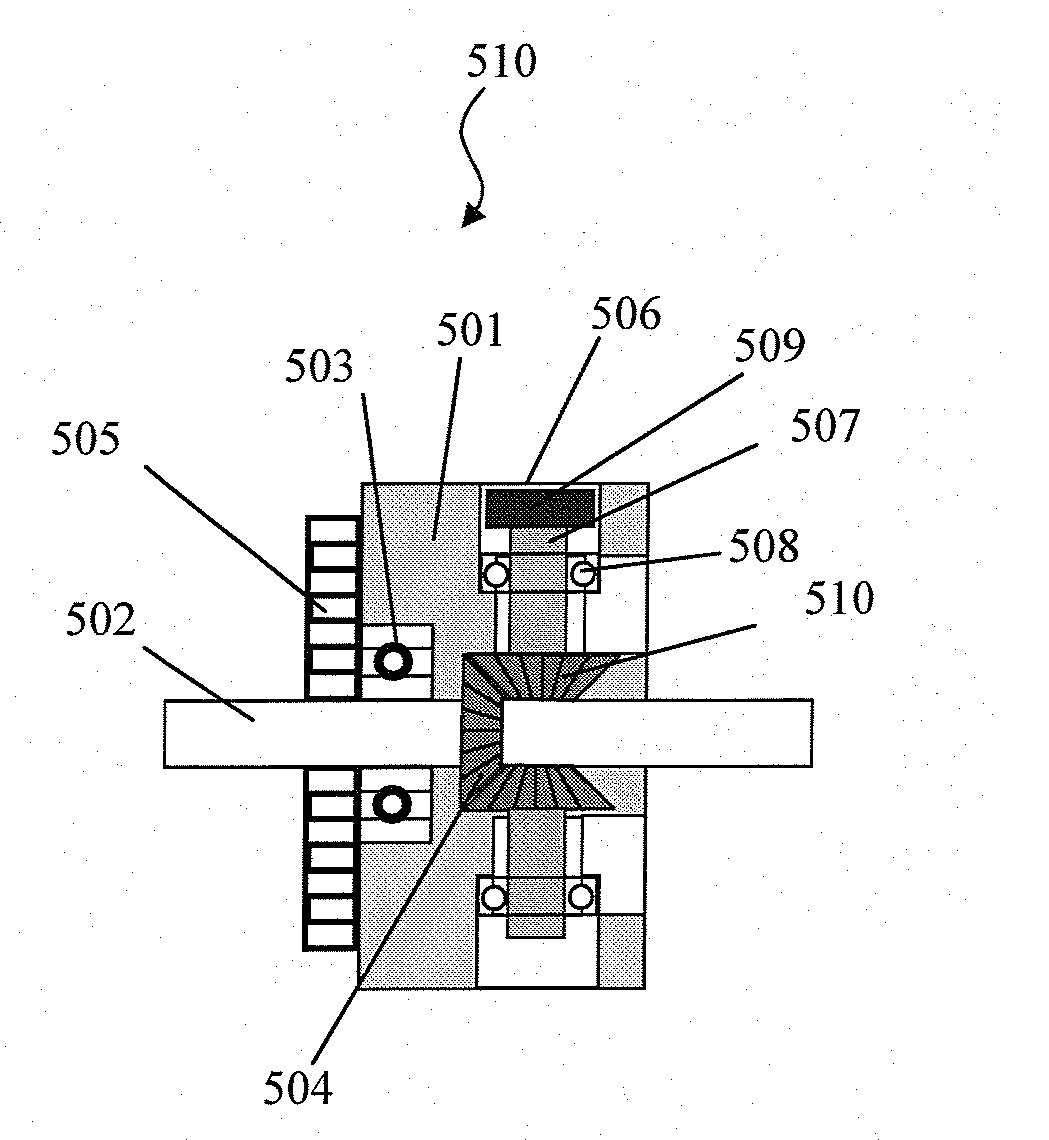
A printing apparatus includes a magnetic rotatable roller with a smooth even outer surface for aligning magnetic flakes in a carrier, such as an ink vehicle or a paint vehicle to create optically variable images in a high-speed, linear printing operation. Images can provide security features on high-value documents, such as bank notes. Magnetic flakes in the ink are aligned using magnetic portions of the roller, that can be formed by permanent magnets embedded in a non-magnetic roller body, or selectively magnetized portions of a flexible magnetic cover of the roller. In some embodiments, the roller is assembled for a plurality of interchangeable sections, which can include spinning magnets. Selected orientation of the magnetic pigment flakes can achieve a variety of illusive optical effects that are useful for decorative or security applications.
Owner:VIAVI SOLUTIONS INC
Imaging system
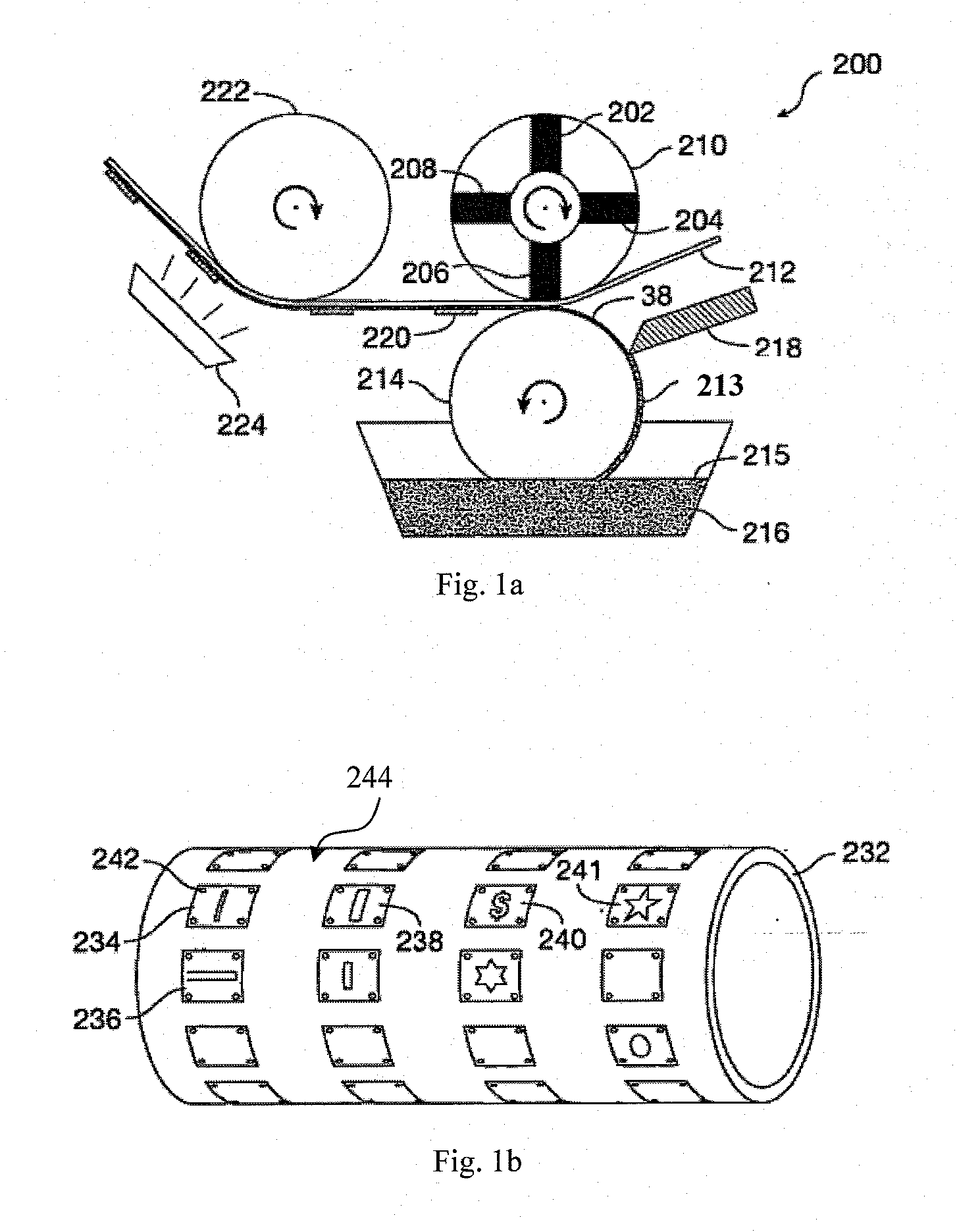
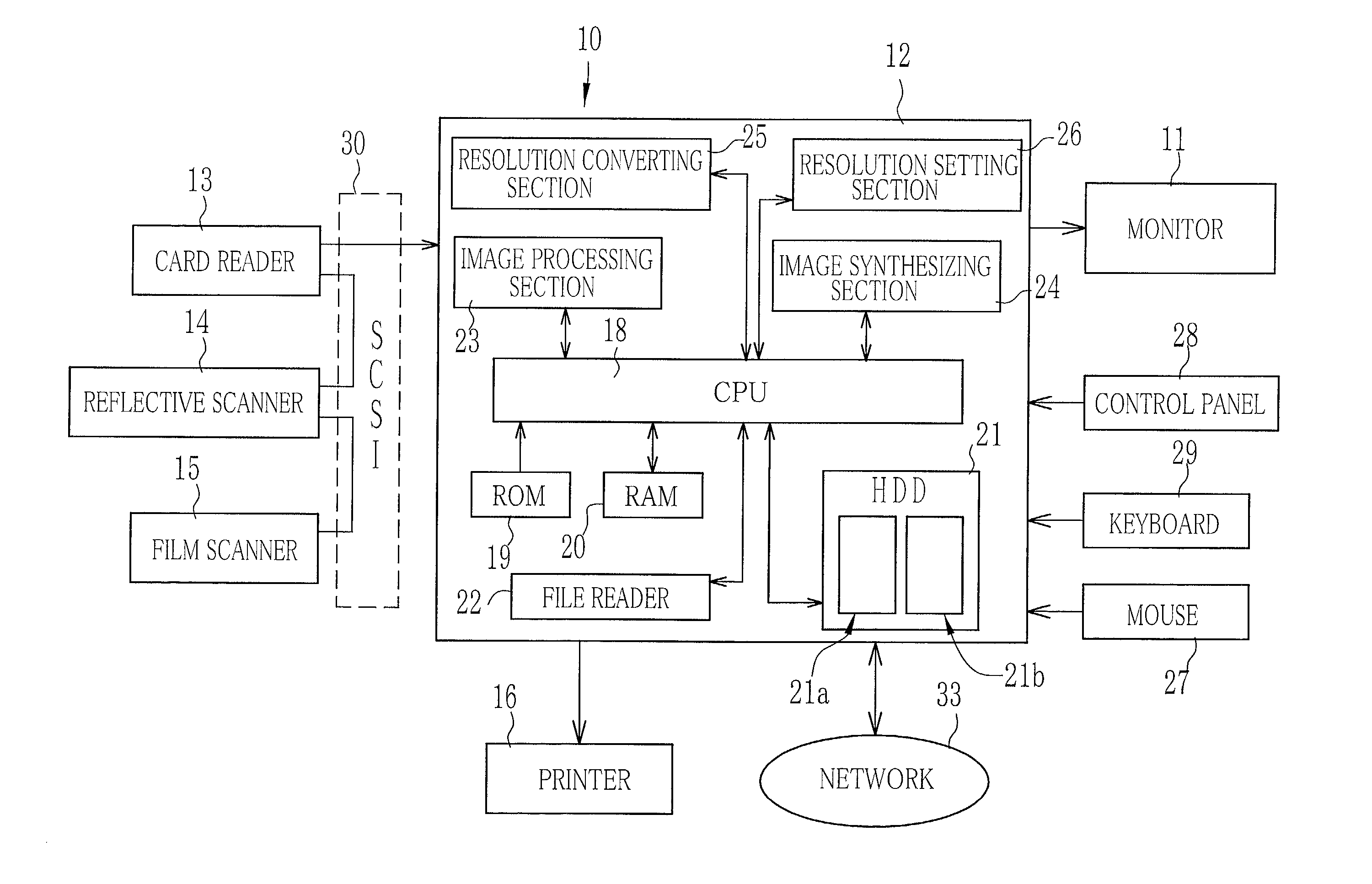
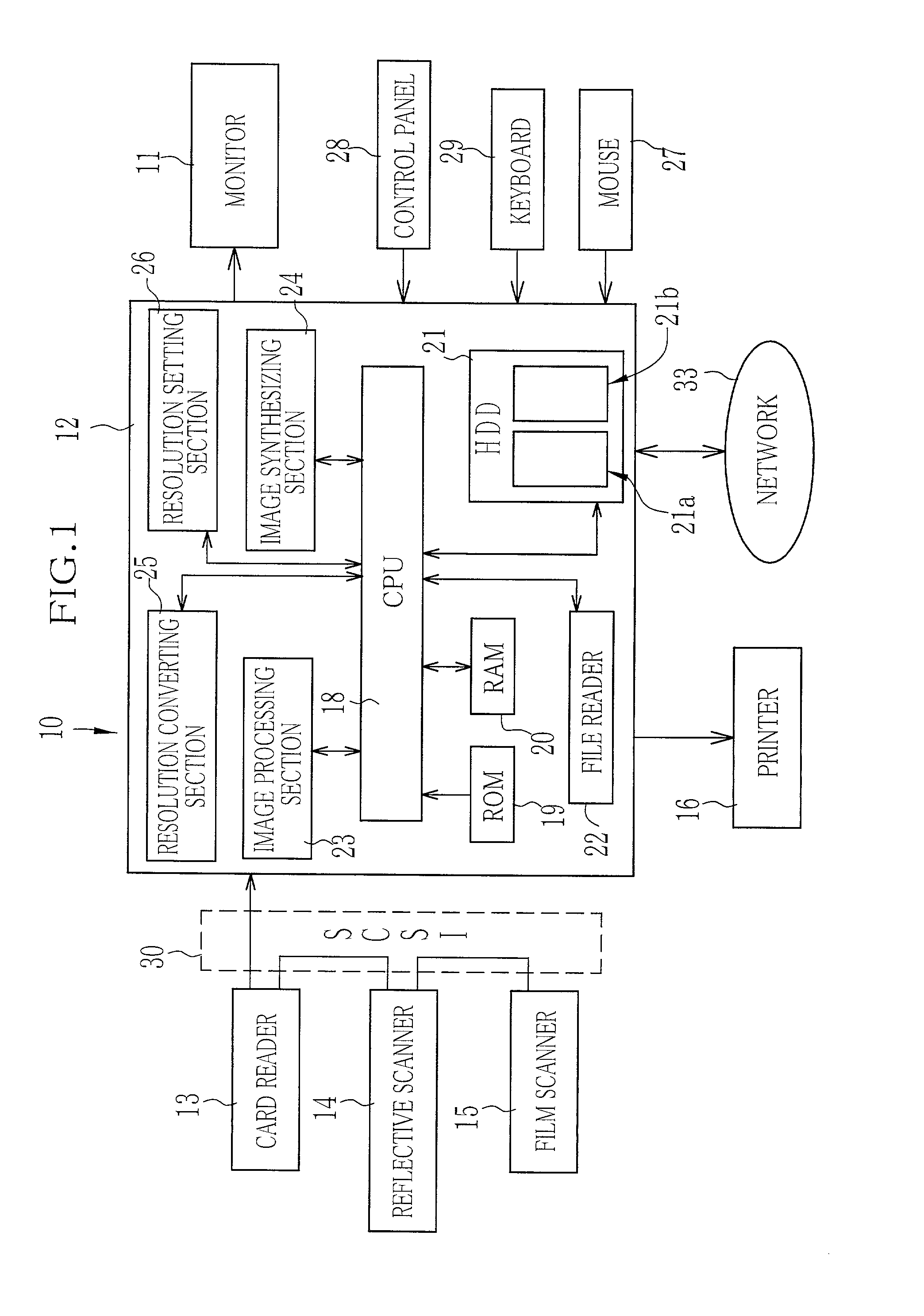
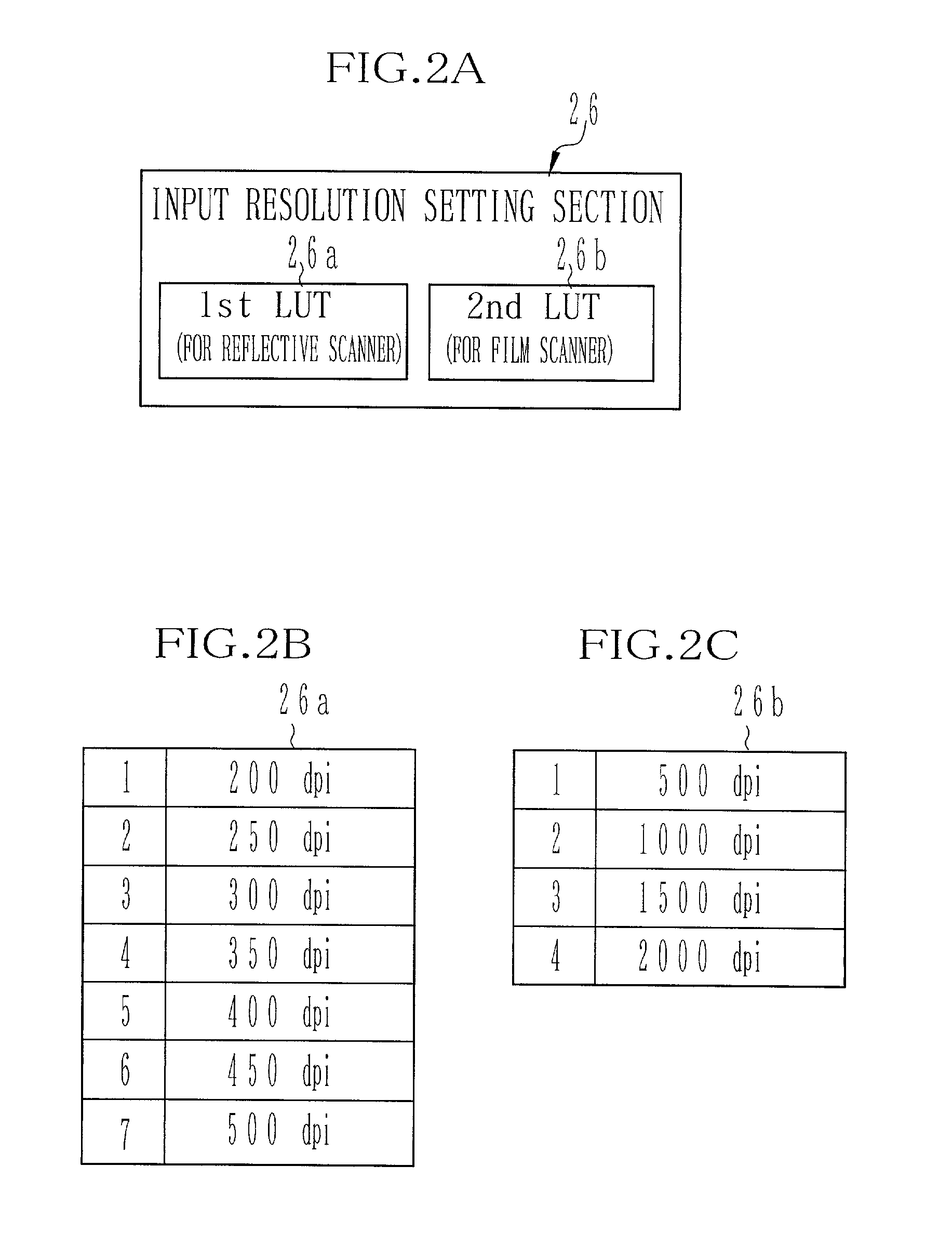
An imaging device (10) has a card reader (13), a reflective scanner (14) and a film scanner (15). The scanners has a pre-scanning mode of a low resolution and a fine scanning mode of a higher resolution. A preview image is displayed on the basis of image data taken from an original image through the scanner in the pre-scanning mode, and a cropping area of the original is designated on the preview image. An input resolution setting section (26) automatically sets the higher resolution for the fine scanning in accordance with the original size of the cropping area, a print size of the cropping area, and an output resolution of a printer (16). Based on image data taken at the higher resolution from the cropping area of the original image, the printer prints out an image.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP +1
Method for manufacturing a flexographic printing master
InactiveUS20060055761A1Fast and simple and environmentalImprove image qualityPlate printingHand compositionOligomerPolymer science
A method for manufacturing a flexographic printing master comprising the steps of: (a) providing an ink-receiver surface; (b) jetting a curable jettable fluid on the ink-receiver surface characterized in that the curable jettable fluid comprises at least one photo-initiator, at least one monofunctional monomer, at least 5 wt % of a polyfunctional monomer or oligomer and at least 5 wt % of a plasticizer both based on the total weight of the curable jettable liquid capable of realizing a layer after curing having an elongation at break of at least 5%, a storage modulus E′ smaller than 200 MPa at 30 Hz and a volumetric shrinkage smaller than 10%.
Owner:AGFA NV
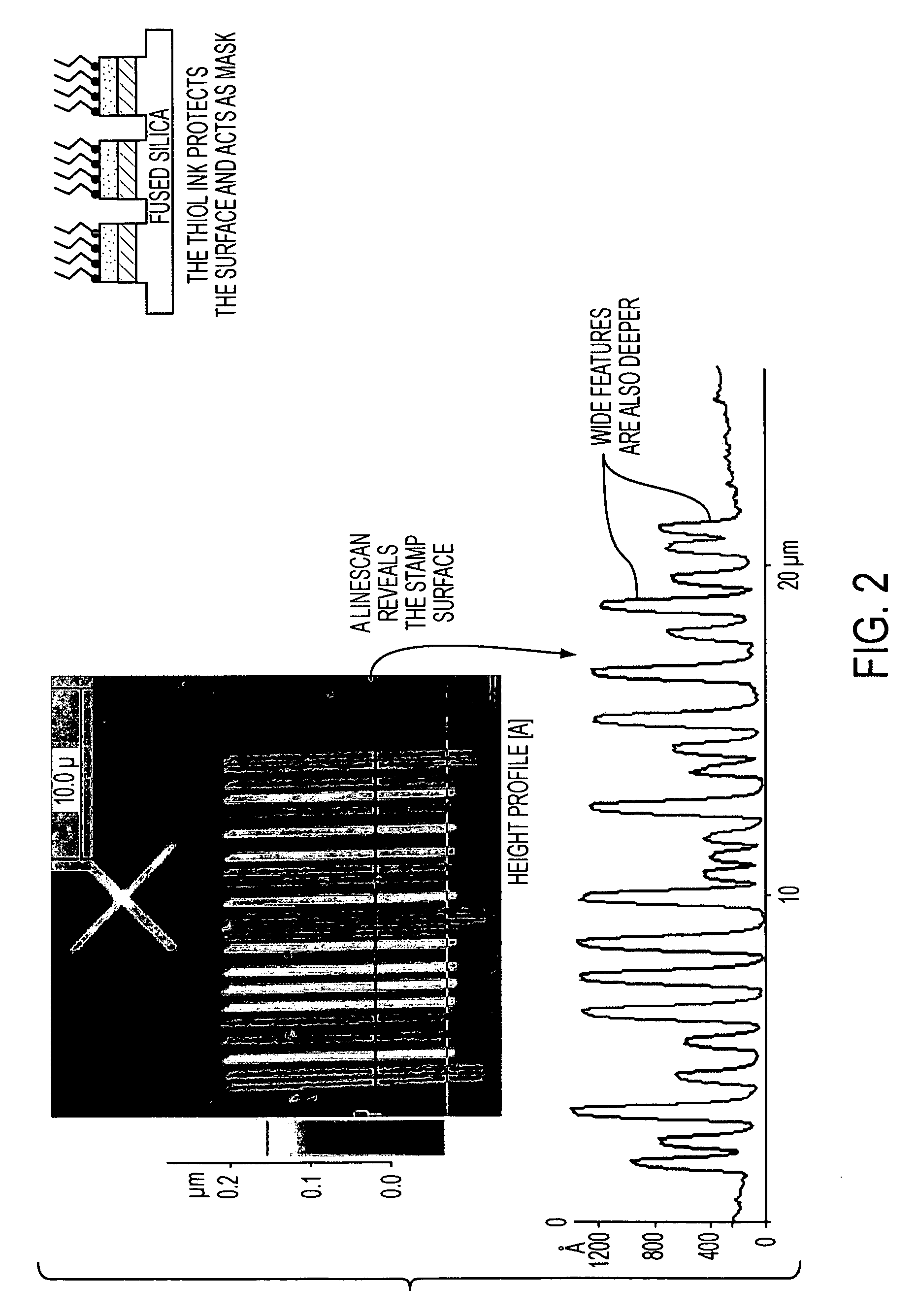
Stamp having an antisticking layer and a method of forming of repairing such a stamp
InactiveUS20050039618A1Good effectStable antisticking layerNanoinformaticsPhotomechanical apparatusCouplingNanoscopic scale
A stamp for use in transferring a pattern in nano-scale has a monomolecular antisticking layer. The anti-sticking layer comprises molecular chains, which are covalently bound to the surface of the stamp and which each comprise at least one fluorine-containing group. Each molecular chain contains a group Q, which comprises a bond which is weaker than the other bonds in the molecular chain as well as the covalent bond that binds the molecular chain to the surface of the stamp. Splitting of said bond in the group Q creates a group Q1, which is attached to the part of the molecular chain being left on the surface of the stamp and which is capable of reacting with a fluorine-containing compound to restore the antisticking layer. In a method of manufacturing a stamp for use in transferring a pattern in nanoscale, the stamp is provided with the above-mentioned molecular chain. In a method of repairing a damaged antisticking layer of the above-mentioned stamp, the stamp is treated with a repairing reagent, which has a coupling end, which is capable of reacting with the group Q1, and a fluorine-containing group located at the other end of the repairing reagent.
Owner:OBDUCAT AB SE
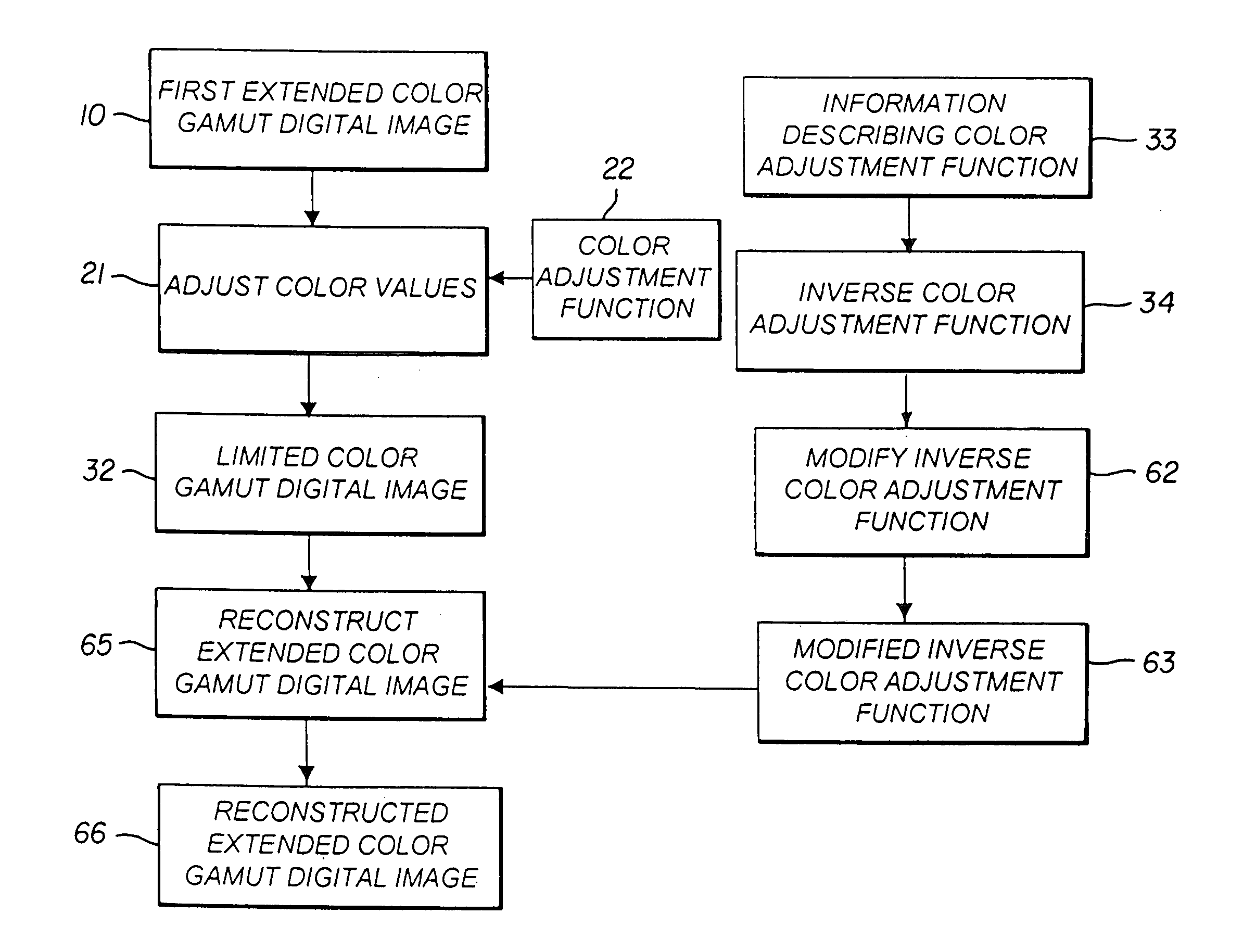
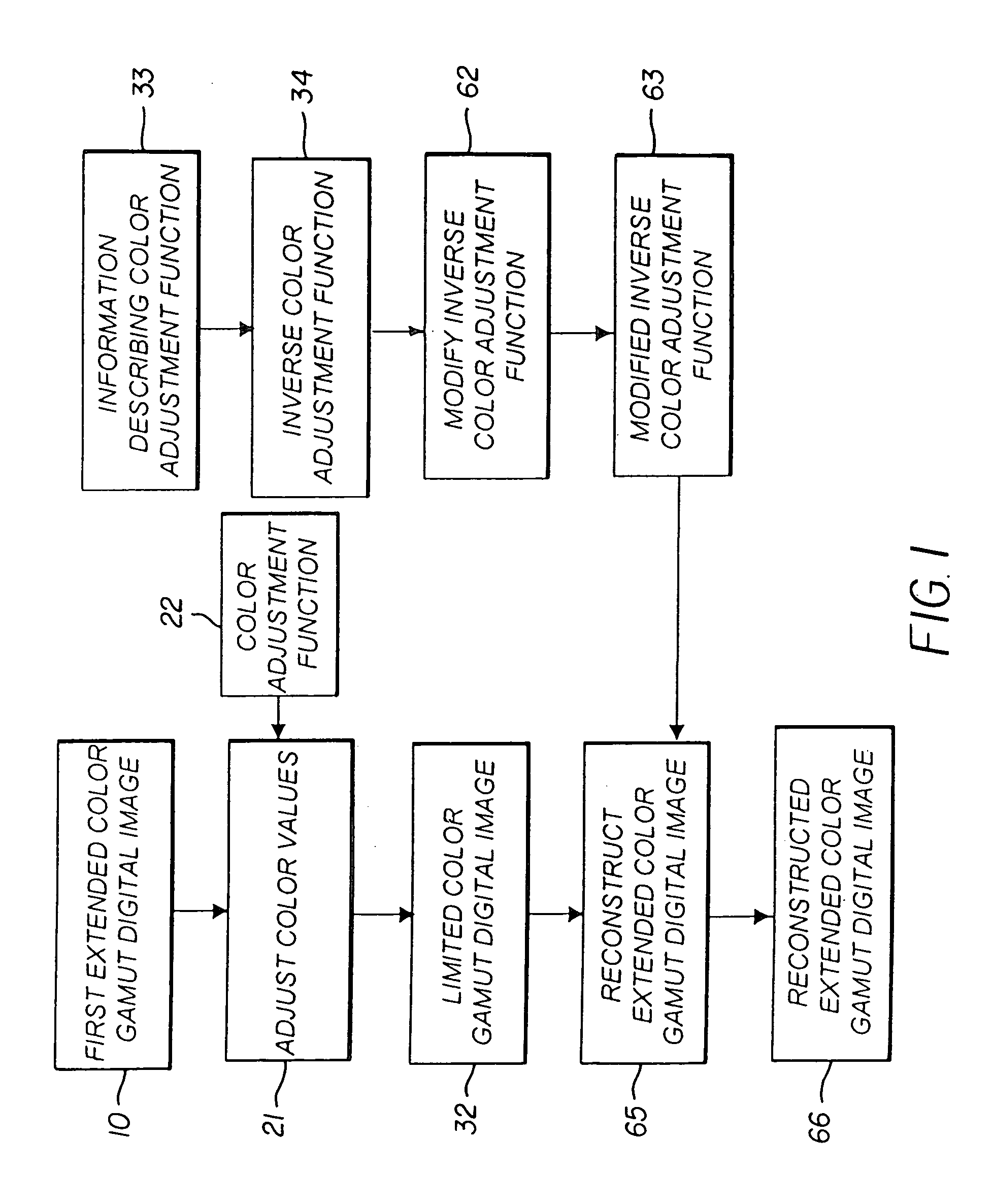
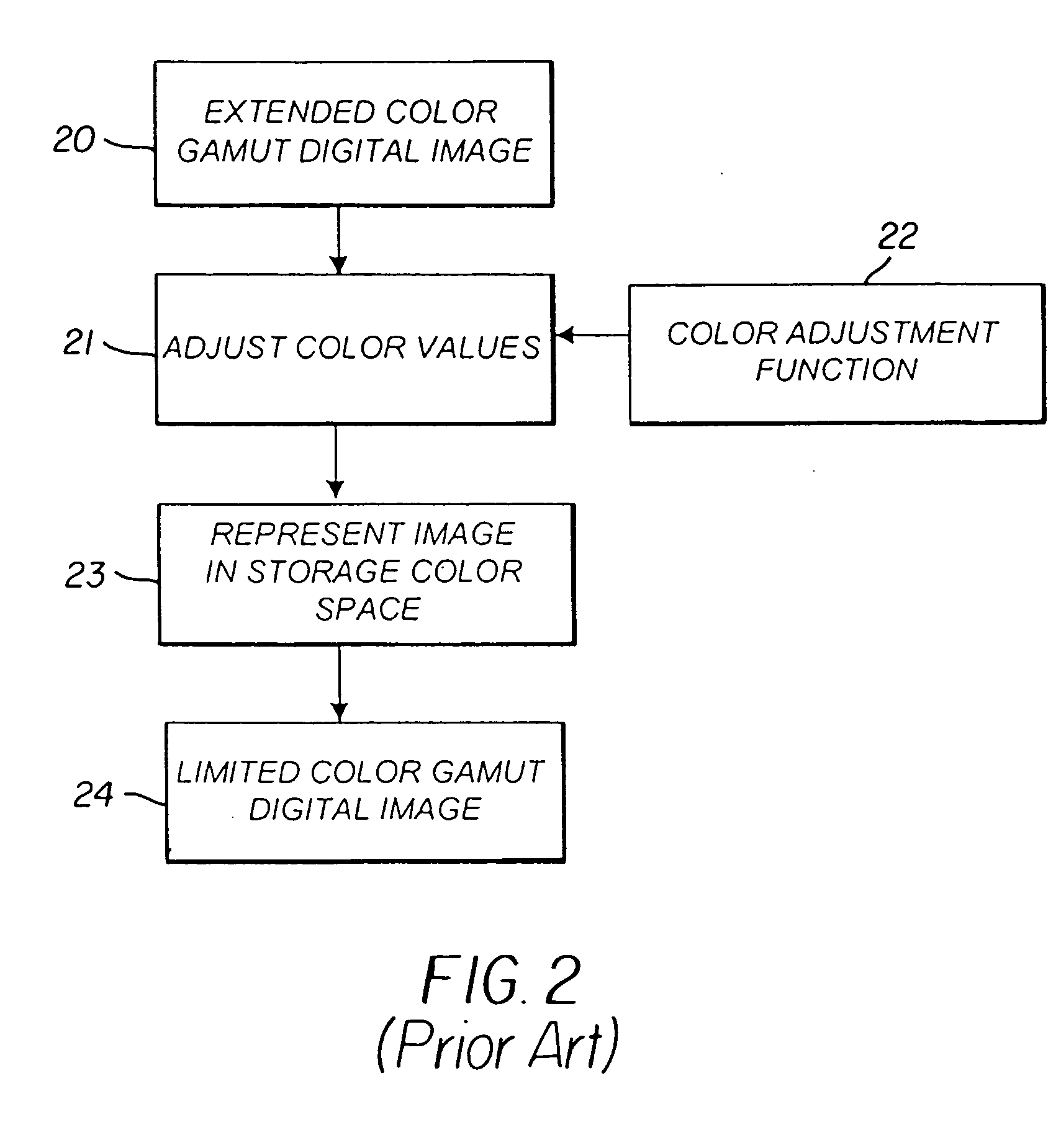
Constructing extended color gamut digital images from limited color gamut digital images
InactiveUS20050152597A1Reduced color saturationPromote lowerDigitally marking record carriersDigital computer detailsGamutColor saturation
A method for reconstructing an extended color gamut digital image from a limited color gamut digital image includes transforming the limited color gamut digital image in the particular limited color gamut color space to a reference color space forming a limited color gamut digital image in a reference color space; providing a modified inverse color adjustment function which, when such function operates on the limited color gamut digital image in the reference color space, produces the reconstructed extended color gamut digital image having reduced highlight color saturation for highlight color values when compared with corresponding color values of the initial extended color gamut image; and operating on the limited color gamut digital image in the reference color space with the modified inverse color adjustment function to form the reconstructed extended color gamut digital image having reduced levels of color contouring and quantization artifacts.
Owner:MONUMENT PEAK VENTURES LLC
Simple mechanism for profile selection
In a system where the color space conversion process uses color profile look-up tables to select a profile for each of the possible attribute value combinations, assigning a value of wildcard to one or more attributes. In this case, if all of the values of one of the attributes can not be exactly matched, and that attribute has a wildcard value, the wildcard value is selected. The profile associated with the wildcard is designed to enable a reasonable color conversion in any case where an attribute calls for a particular value and the printer does not have a corresponding profile. The result is that the printer will most likely still print a reasonable image in the case where there is no matching profile.
Owner:XEROX CORP
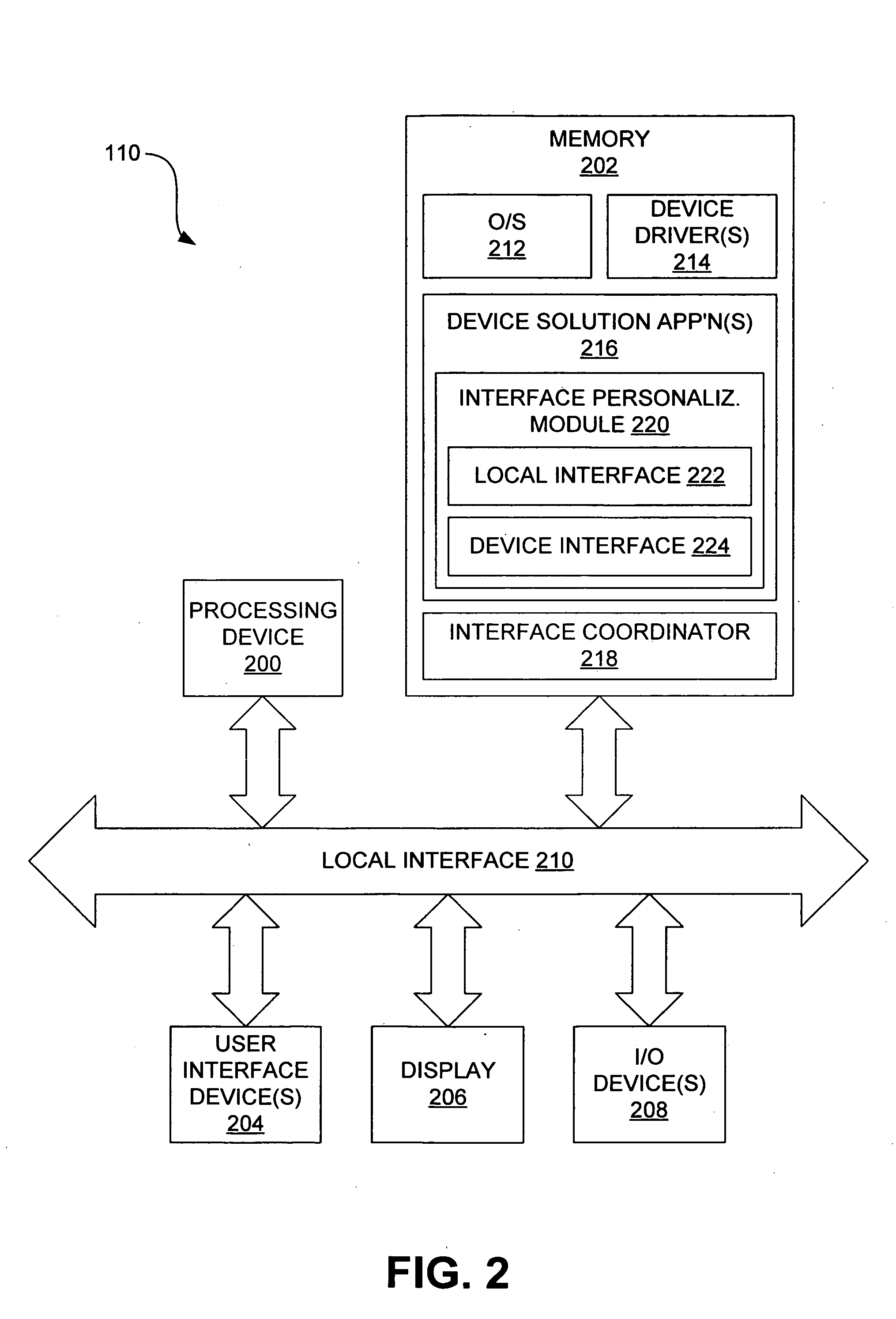
System and method for personalizing an electrical device interface
InactiveUS20050120313A1Hand compositionExecution for user interfacesPersonalizationElectrical devices
The present disclosure relates to such systems and methods for personalizing an electrical device interface. In one arrangement, personalization involves presenting a variety of different default interface options to the user, the interfaces being configured to control operation of an electrical device, receiving selection of a default interface made by a user, and presenting the selected interface to the user. Several other examples of interface personalization are described in detail in this disclosure.
Owner:HEWLETT PACKARD DEV CO LP
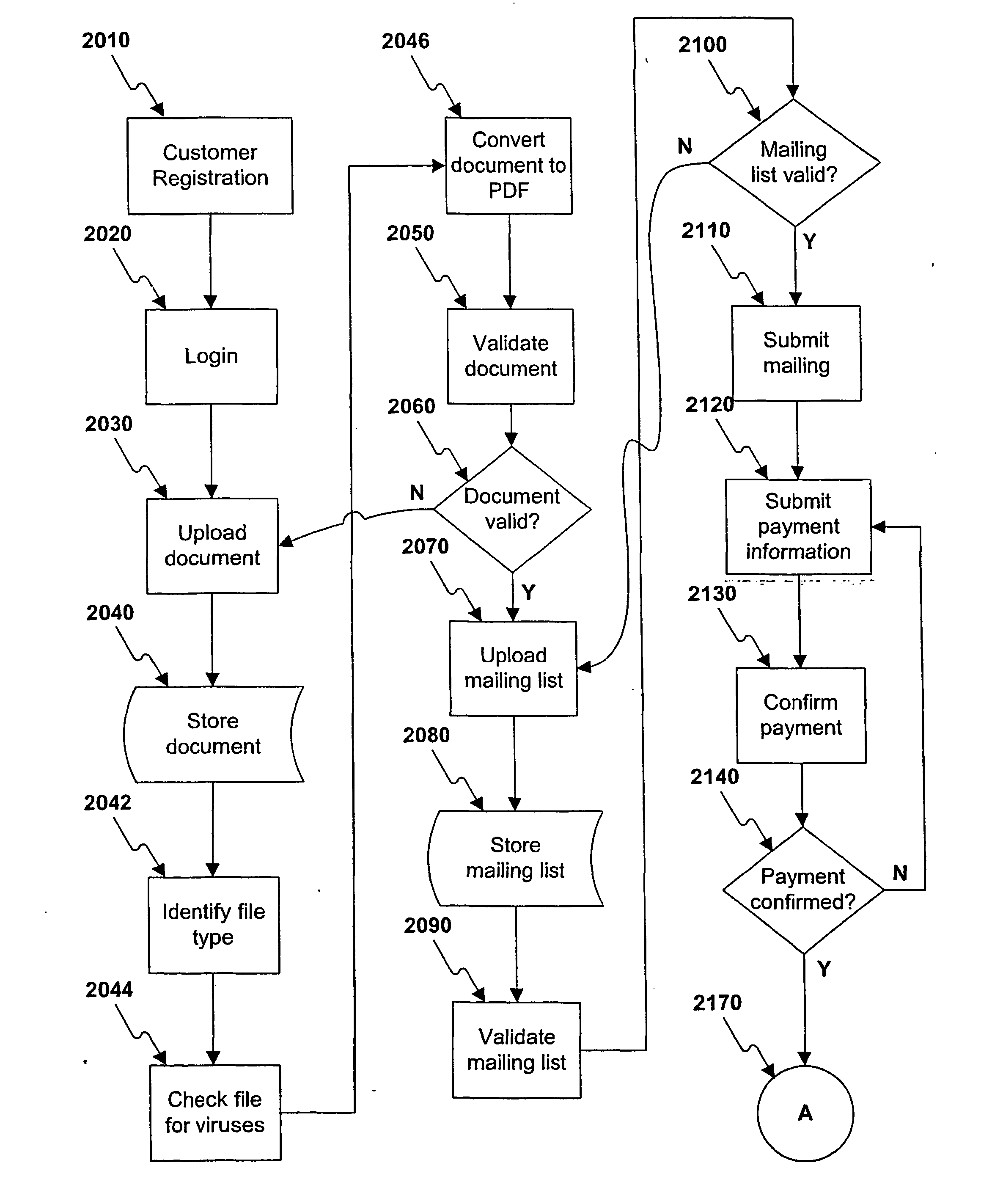
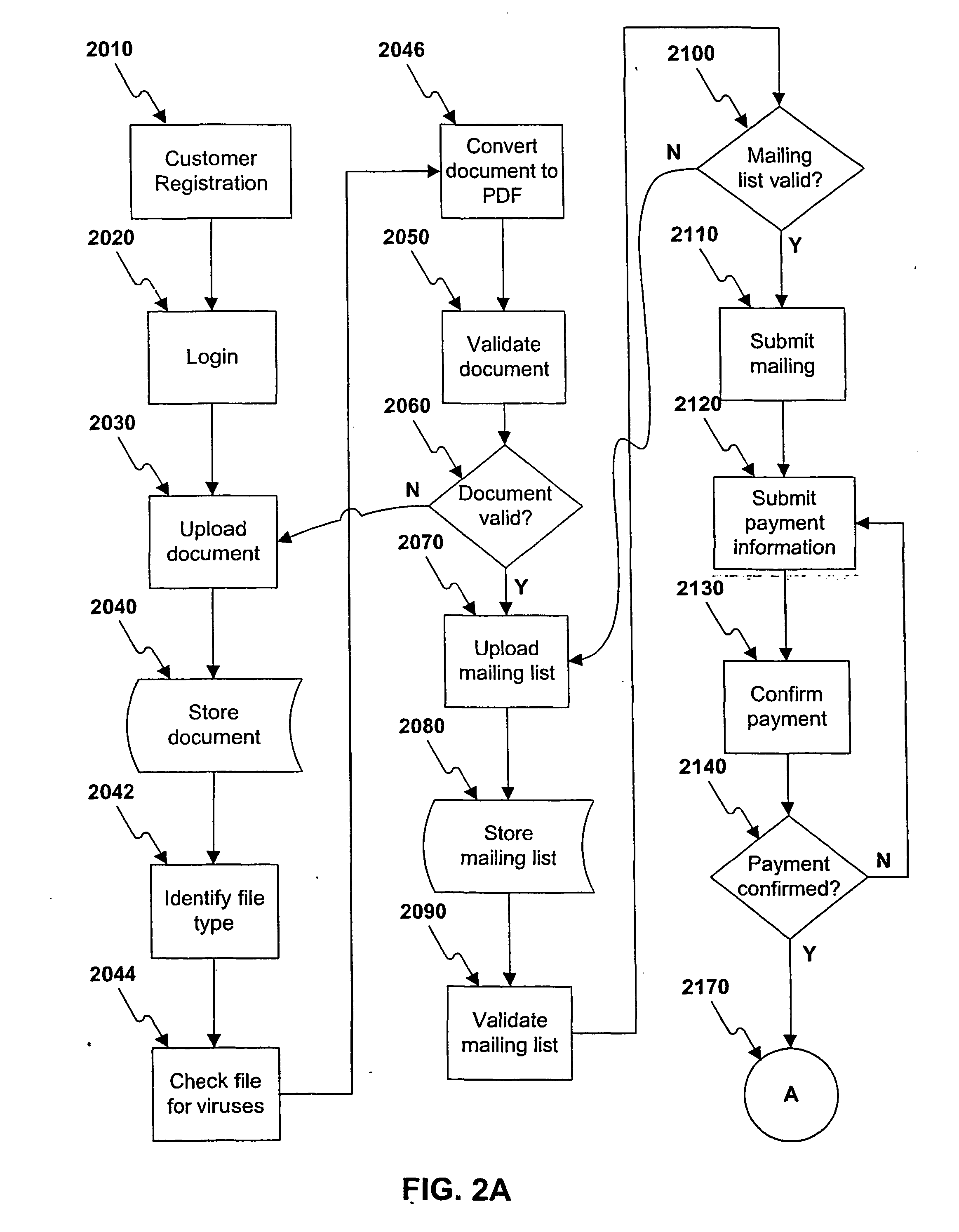
Mailing online operation flow
A method and system are provided for delivery of a printed document using at least one processor (1030) interfacing a network (1020). The processor (1030) may receive first information, through the network 81020) specifying an electronic version of a document. Then the processor (1030) may provide second information indicating one or more options for printing the document, and a customer may select a printing option. The processor (1030) may receive third information indicating at least one physical delivery address for sending the document, process the document accordint to the selected printing option to create a print file, select a printing site (1040). The print file may be printed at the selected printing site (1040) and provided to a service provider (1050) for transport to a delivery address.
Owner:US POSTAL SERVICE
Image layout device
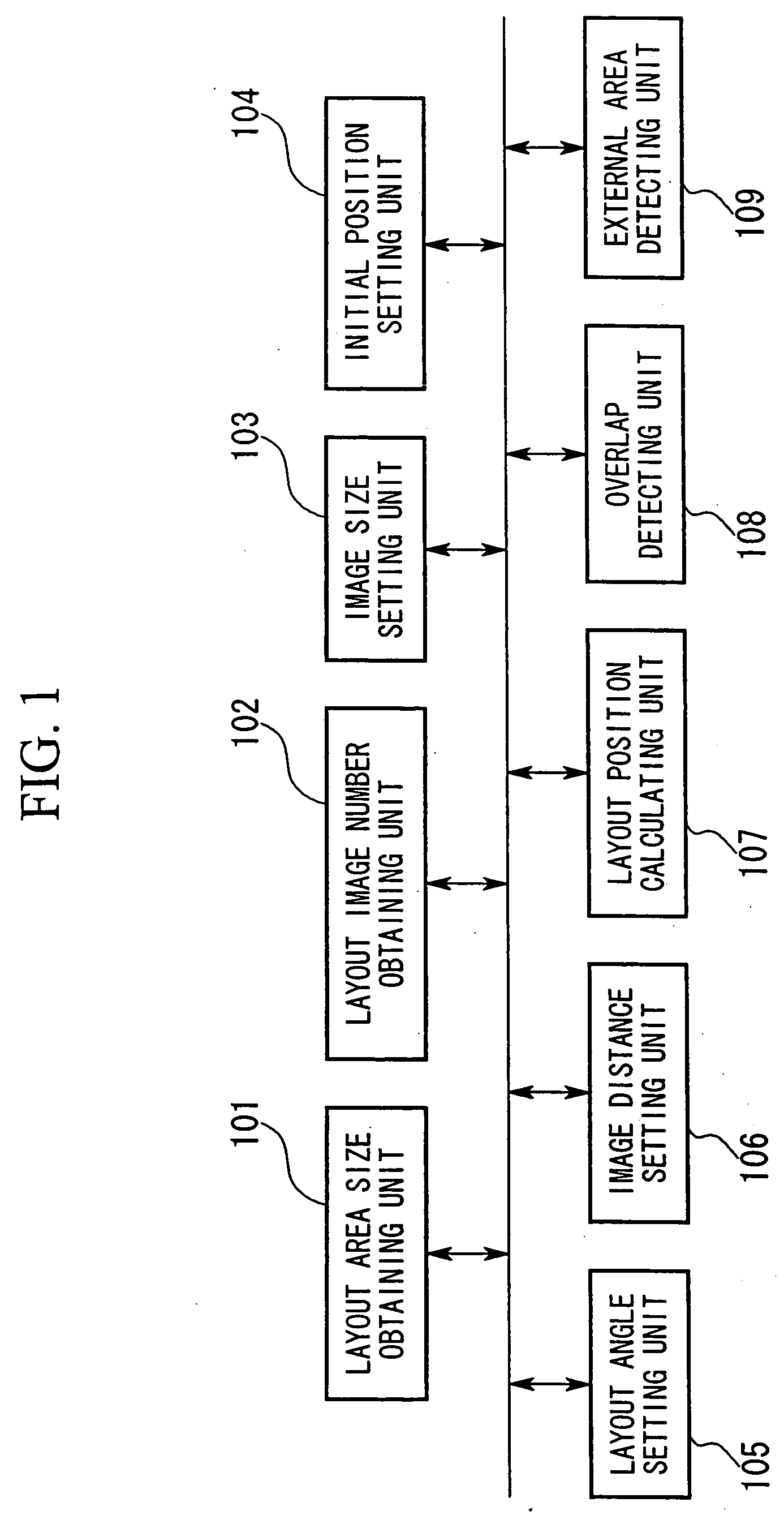
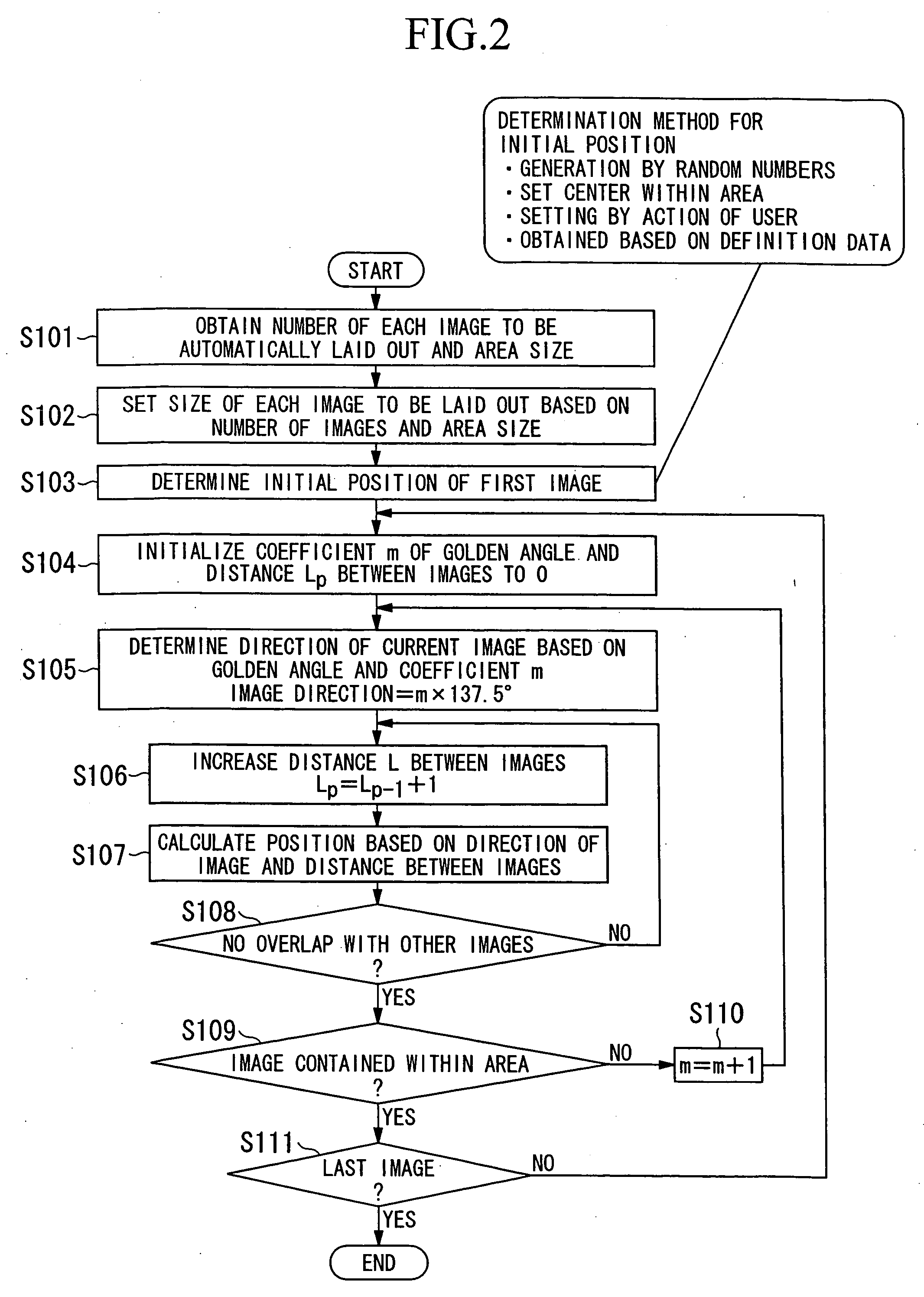
InactiveUS20050091599A1Simple calculationImprove efficiencyCharacter and pattern recognitionCathode-ray tube indicatorsComputer graphics (images)Golden angle
Aspects of the invention can relate to an image layout device and an image layout method. The image layout device of the invention can be a device that automatically arranges a plurality of images within a particular area, and can include a layout angle determining device that determines the layout angle for each of the images based on an angle that is an integer multiple of a golden angle, and a layout position determining device that determines the layout position for each of the images depending on the overlap between each of the images due to the angle determined by the layout angle determining device.
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
Internet delivery of digitized photographs
InactiveUS20020135794A1Digitally marking record carriersDigital data information retrievalFailoverInternet delivered
An improved Internet delivery system for digitized photographs is described. The system embodies methodologies that speed the delivery of digitized images from photographic film scan centers to consumers across the Internet with high reliability. By delivering all the digital images to a more powerful centralized server infrastructure prior to the consumer's earliest opportunity to view them on-line, these images or pictures can be downloaded to a viewer of interest (e.g., user or family member) quickly enough to provide an appropriate Web response. Optimizations are also described that streamline the throughput with load balancing and provide virtually guaranteed uniform service with fail-over. In this manner, the system provides improved access, storage, and on-line availability of digital images.
Owner:RPX CORP
Printing method and apparatus having multiple raster image processors
InactiveUS20020060801A1Reduction in concurrent bus contentionReduce overheadDigitally marking record carriersDigital computer detailsGraphicsImage resolution
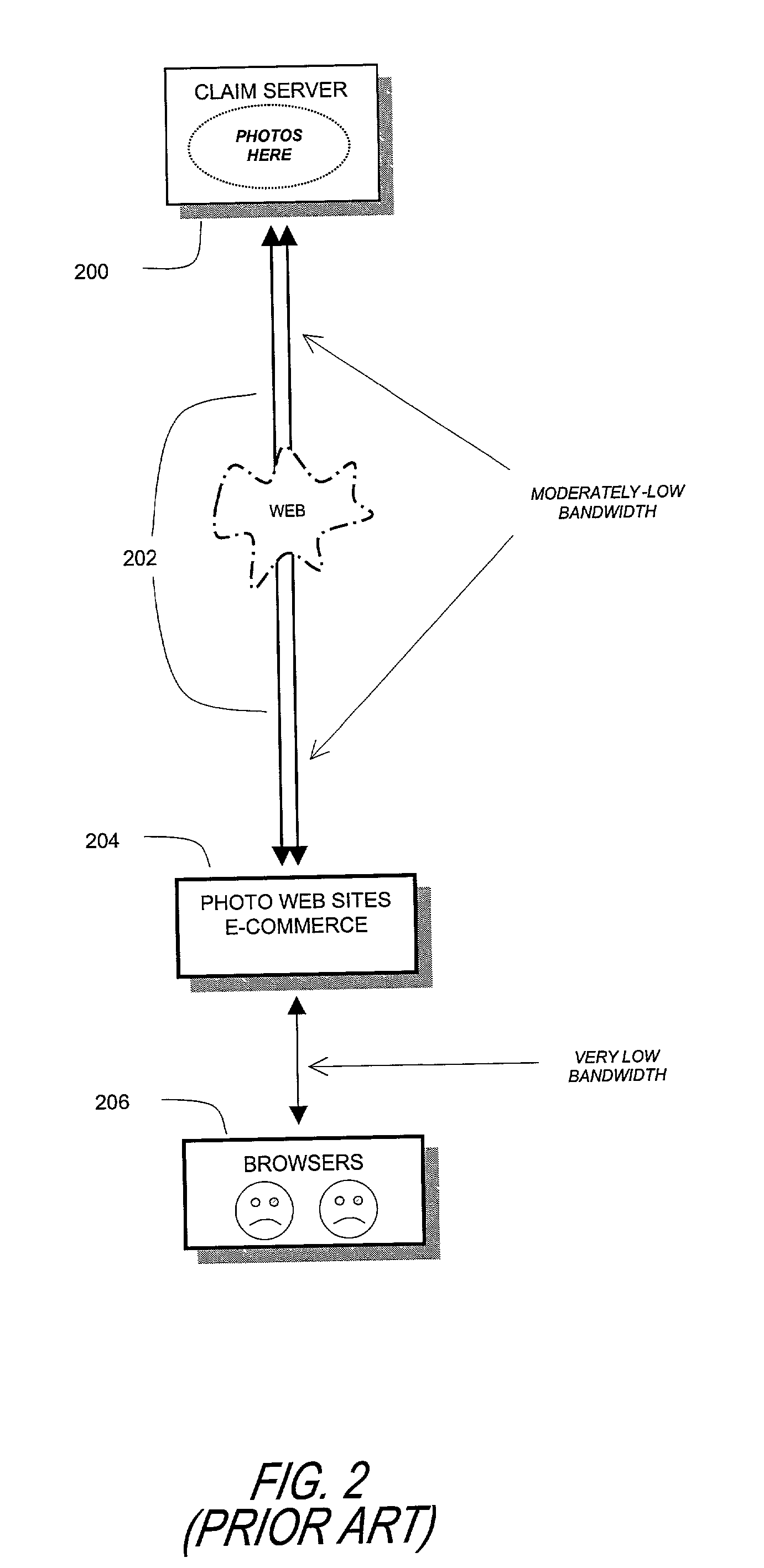
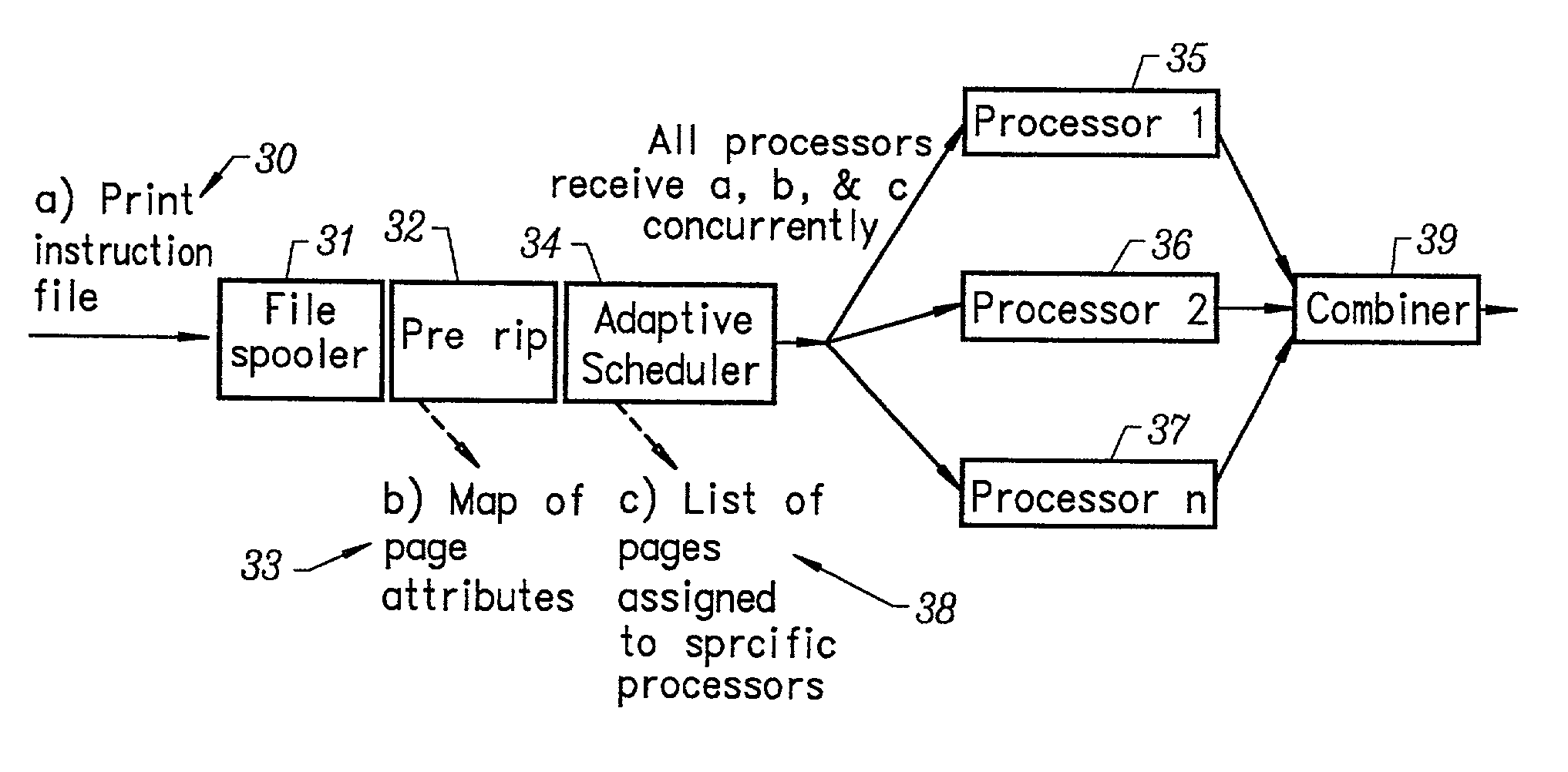
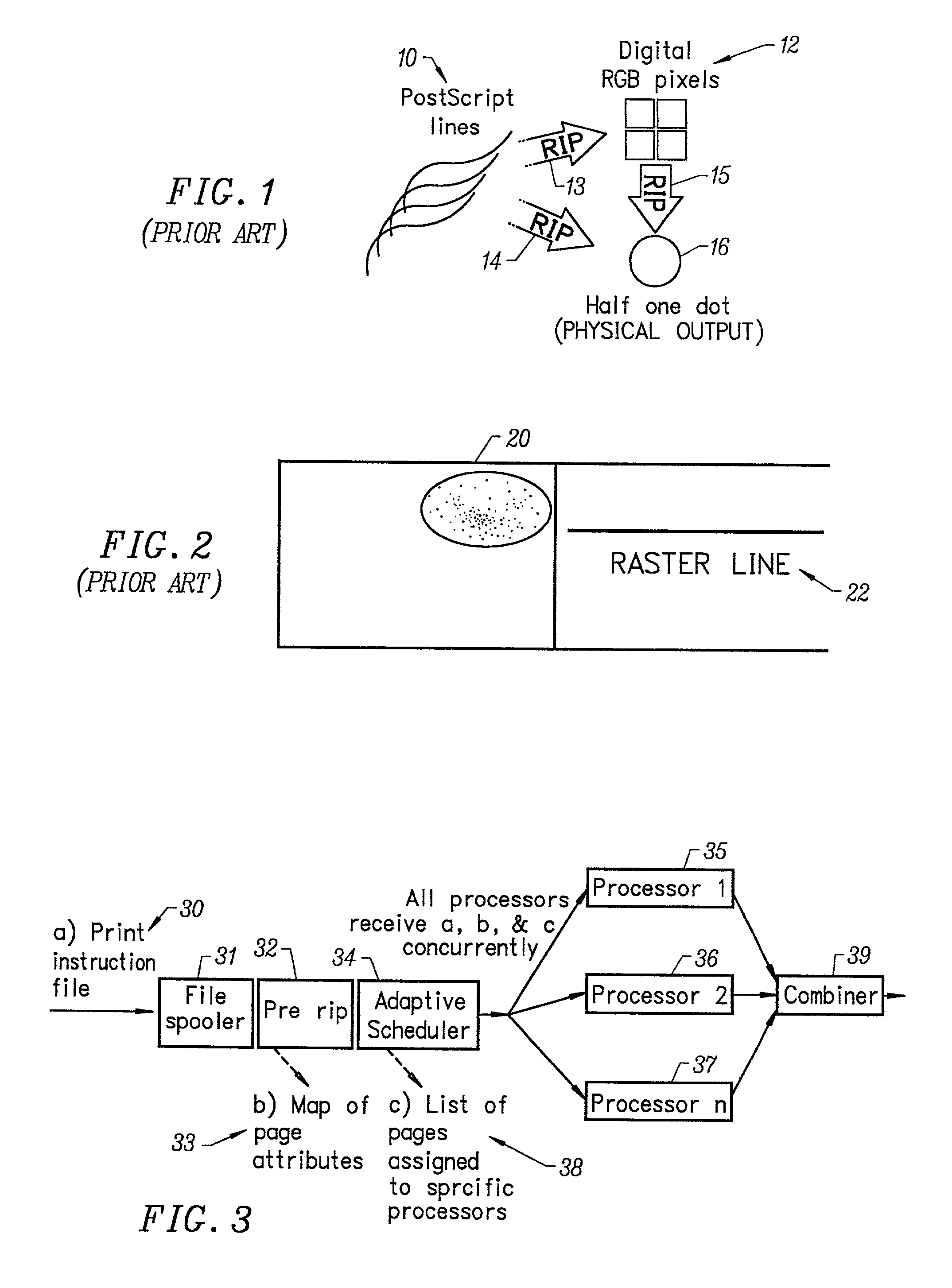
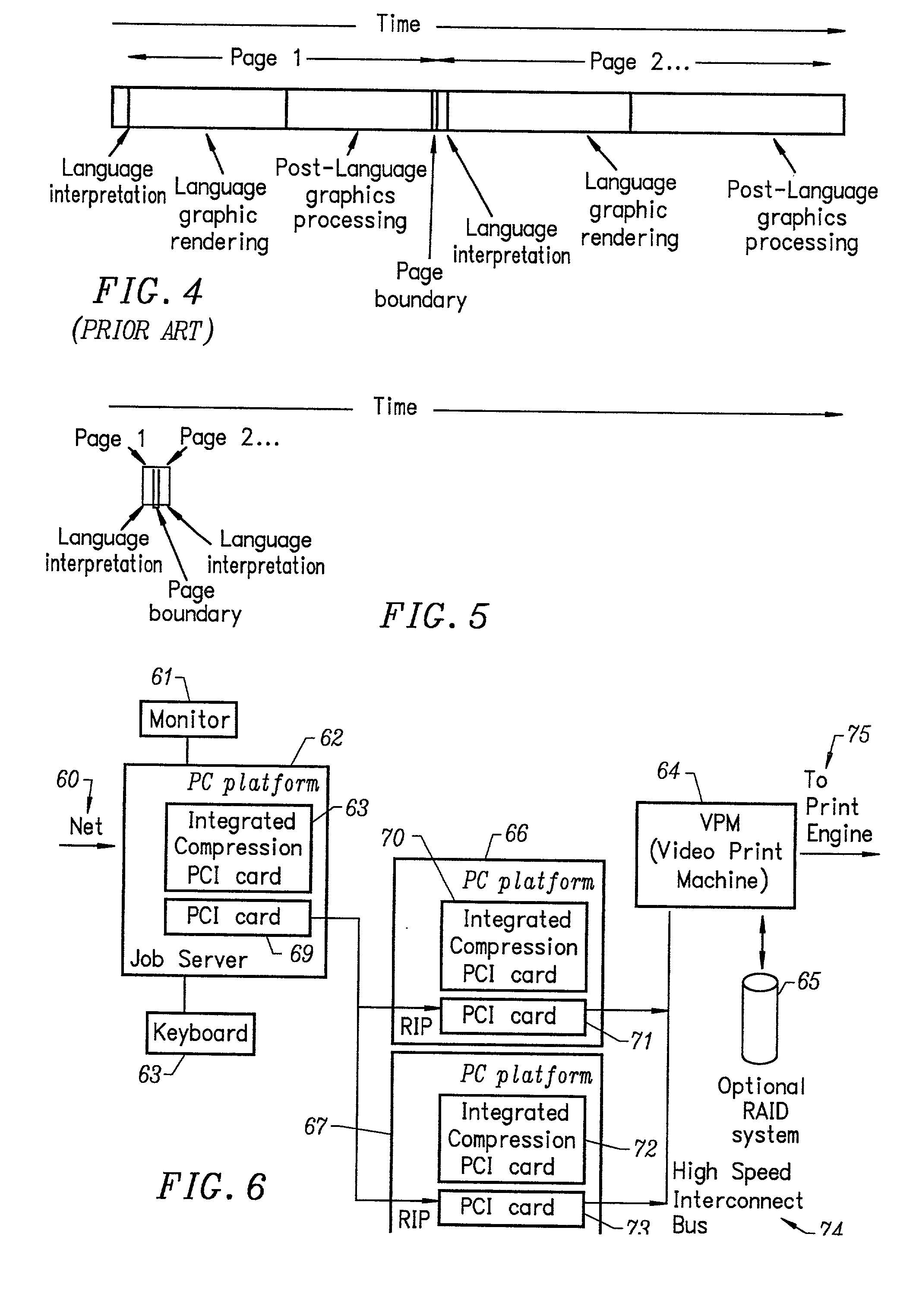
A multiple raster image processor (RIP) system which enables faster system performance over multiple processors includes a zero RIP feature consisting of a language interpreter sub-RIP that interprets a print instruction file but does not process the graphics rendering steps or the post-language processing operators. The zero RIP discovers page related attributes for individual pages within a multipage job and reports any potential errors or warnings with the file. A thumb RIP consists of a very low resolution RIP that is used specifically for the creation of thumbnail images. A skip RIP interprets selected pages in a way that skips all or most of the processing for that page. Pages to be skipped are scheduled for a different processor, thereby saving processing time and enabling the provision of a multiple processor RIP. A rules based scheduler on an page / face or machine characteristic basis supports a dynamic assignment and assessment algorithm. Scheduling results in optimum use of available resources and requested print constraints (e.g. constrained time window) and optimum use of system bandwidth (e.g. bandwidth control). Archiving and editing capability enables tagged archiving of jobs or parts of jobs in a post RIPed (i.e. raster) format in a special cache located with in the multiRIP system.
Owner:ELECTRONICS FOR IMAGING
Screened film intermediate for use with flexographic printing plate having improved solids rendition
InactiveUS6492095B2Digitally marking record carriersInking apparatusColor saturationMechanical engineering
flexographic printing plate having solid image areas which are covered by a plurality of very small and shallow cells similar to the ink carrying cells found in anilox ink metering rolls. These cells fill with ink during the plate inking step and reproduce solid image areas with better color saturation while at the same time reducing the halo typical of flexographic printing of solids. Associated with this plate is a method for producing the cells, including the use of an intermediate screened film and of a computer program for generating the film intermediate.
Owner:ESKO SOFTWARE
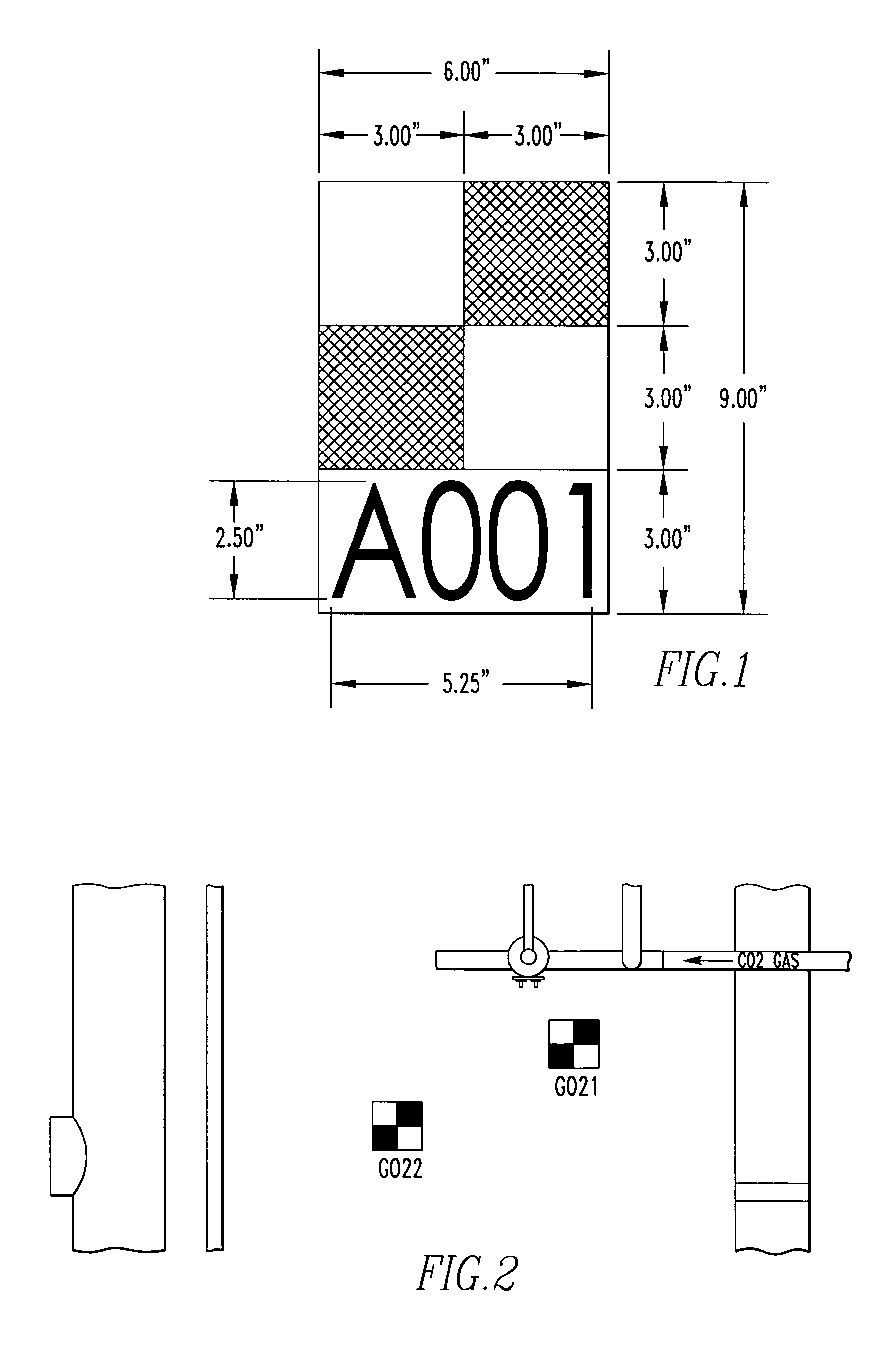
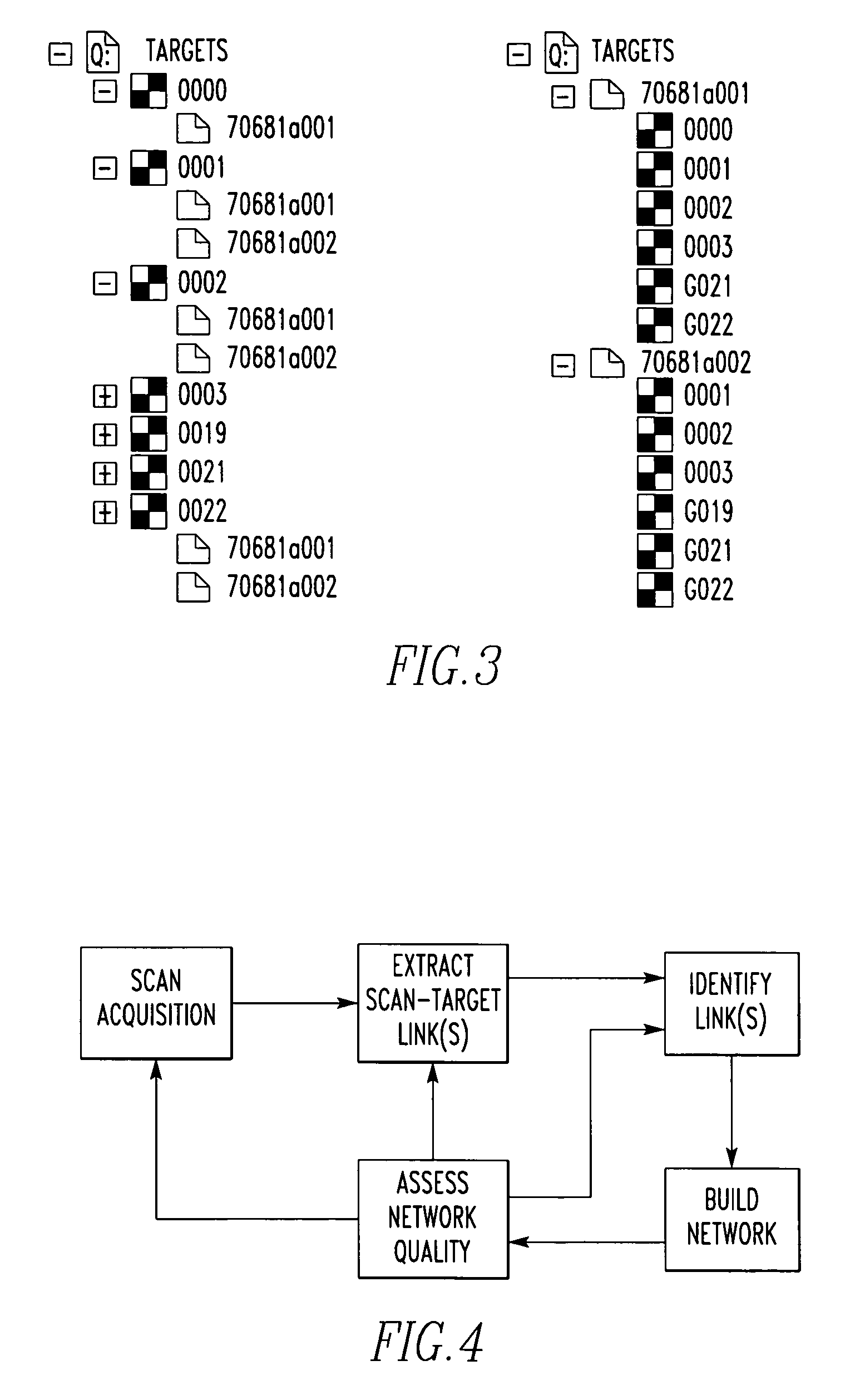
Method and apparatus for creating a registration network of a scene
InactiveUS20050190384A1Simple processImprove throughputDigitally marking record carriersRadiation pyrometryLaser scanningArtificial intelligence
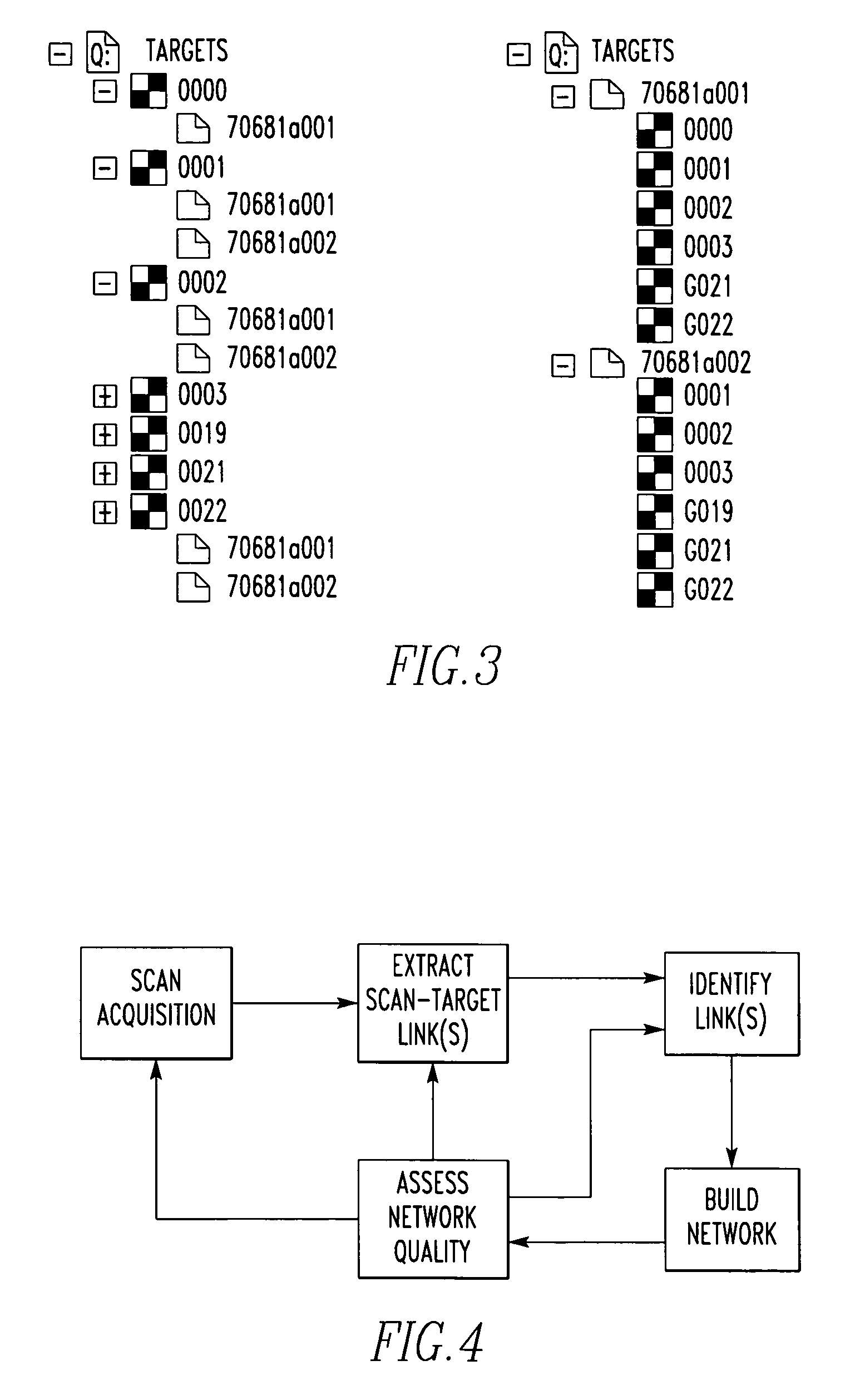
An apparatus for creating a registration network of a scene includes a laser scanner for scanning the scene and obtaining data of the scene. The apparatus includes a plurality of targets placed in the scene. The apparatus includes a mechanism for forming a registration network using only the laser scanner data. A method for creating a registration network of the scene.
Owner:QUANTAPOINT
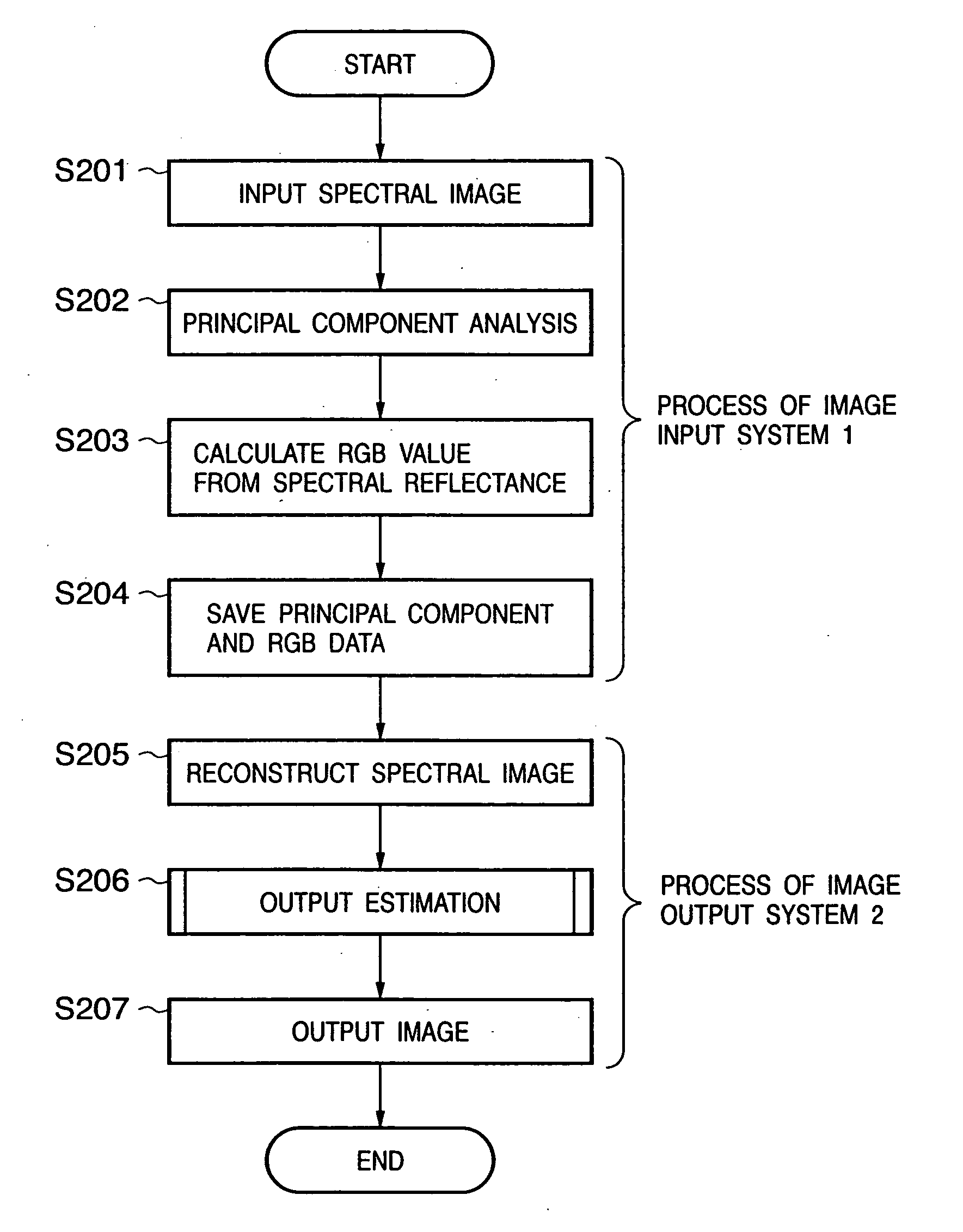
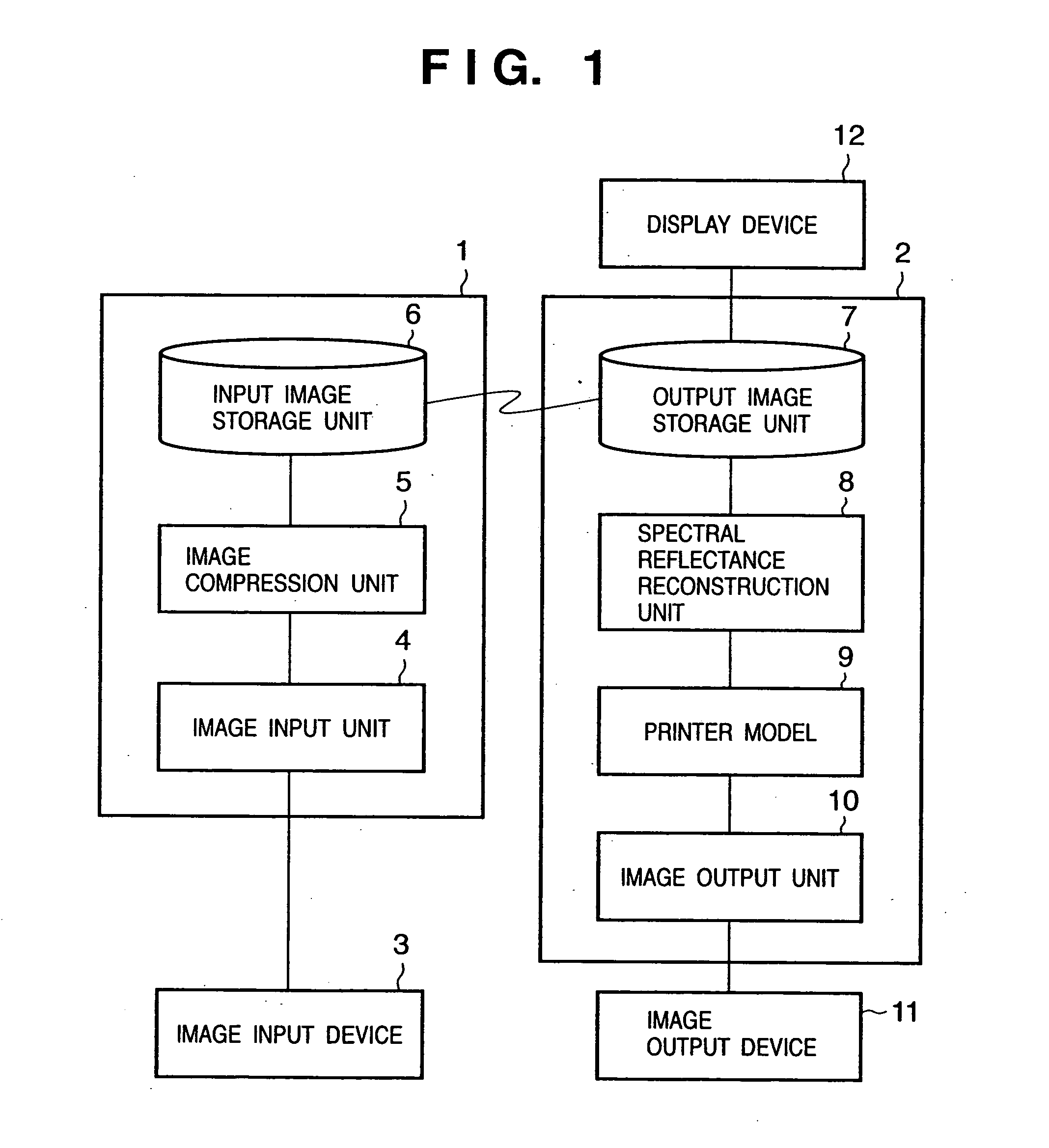
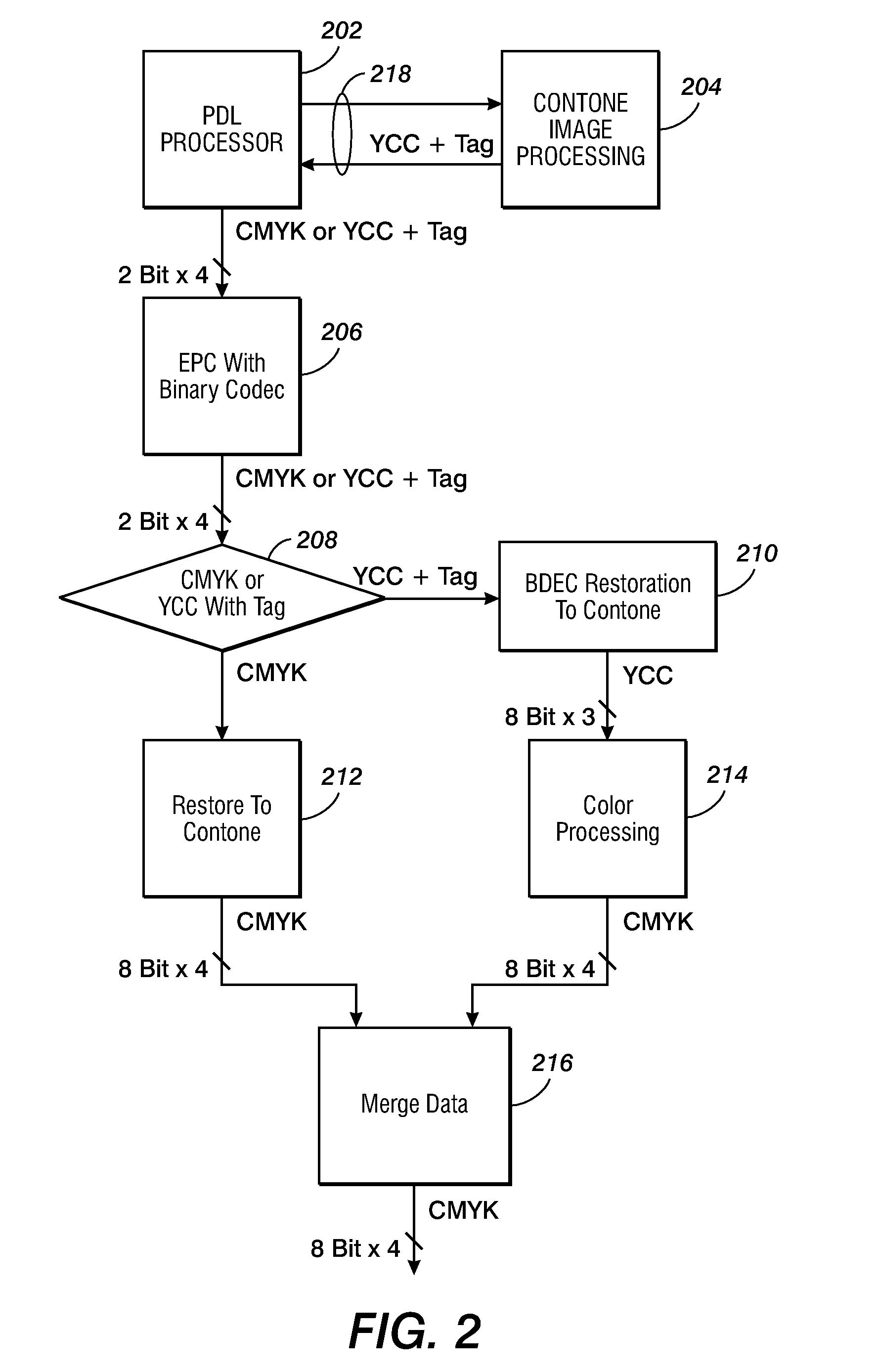
Image processing system, apparatus, and method, and color reproduction method
InactiveUS20050111017A1Accurate color reproductionFaithfully reproducedDigitally marking record carriersColor signal processing circuitsPrincipal component analysisOutput device
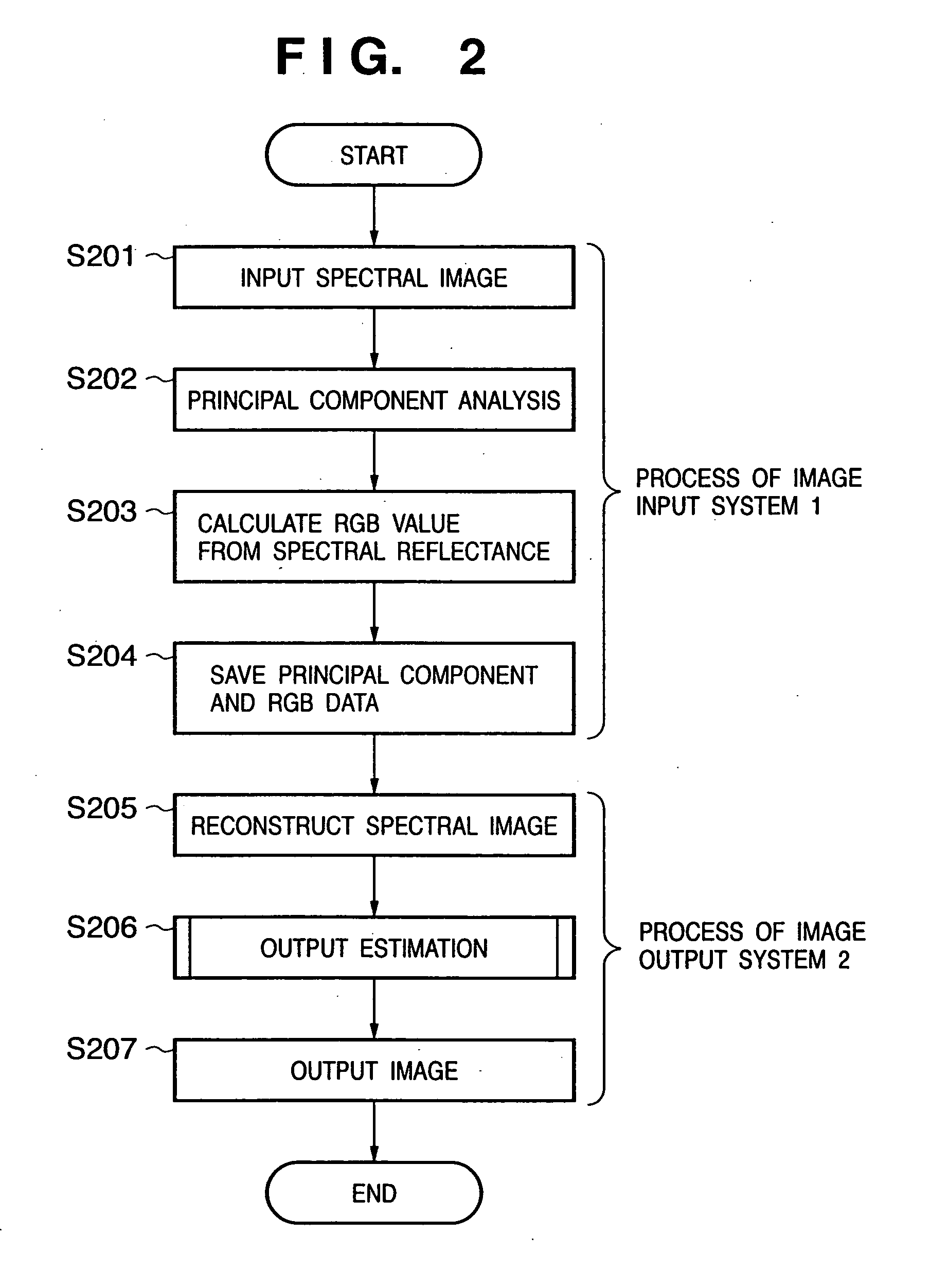
In a system for converting an input image signal input from an image input device into an output image signal to be output by an image output device, an image compression unit converts a spectral image input via an image input unit into R, G, and B data, obtains principal component data by making principal component analysis of the spectral image, and stores these data in an input image storage unit. When the principal component data and R, G, and B data are loaded and stored in an output image storage unit, a spectral reflectance reconstruction unit reconstructs the spectral reflectance of each pixel using these data. A printer model determines the dot quantities of inks used to record each pixel in an image output device on the basis of the calculated spectral reflectance, and generates an output image signal for the image output device. In this way, image data which allows to estimate the spectral reflectance characteristics of an input image is provided, and faithful color reproduction can be realized.
Owner:CANON KK
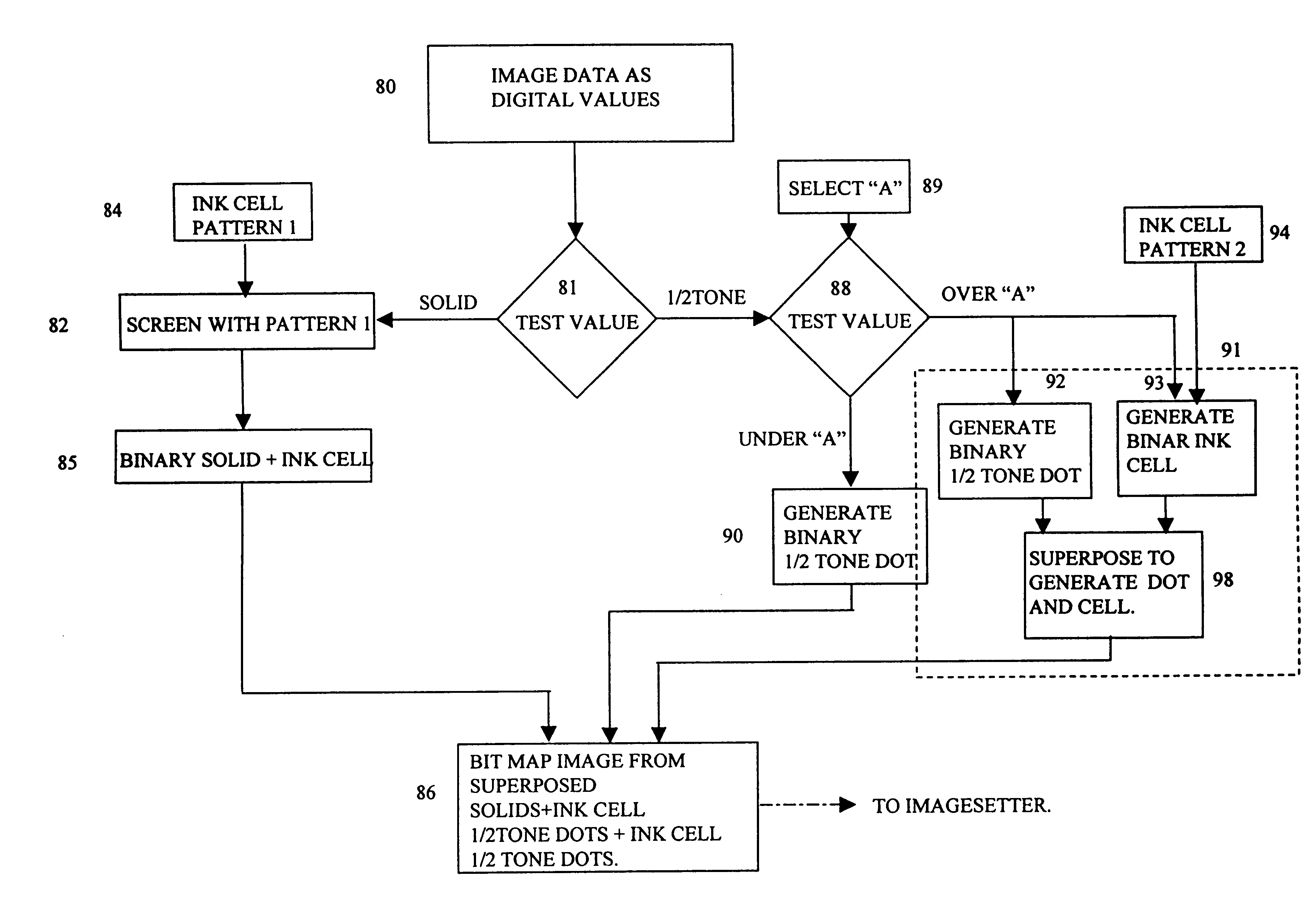
Printing plates containing ink cells in both solid and halftone areas
InactiveUS20020083855A1Photosensitive materialsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingVolumetric Mass DensityComputer science
A method, associated software and resulting printing plate having both solid and halftone areas comprising ink cells. Ink cells may be provided in the solid areas according to a first pattern with a first density and size of cells per unit area, and in the halftone areas superposed on selected numbers of halftone dots. The selection of halftone dots with superposed ink cells may be according to a second pattern with a second density and size of cells in the halftone area that is a function of halftone dot size and that may or may not be related to the first pattern.
Owner:ESKO SOFTWARE
Anamorphic object optimized function application for printer defect pre-compensation
InactiveUS6341020B1Better addressImage enhancementDigitally marking record carriersDigital dataHead movements
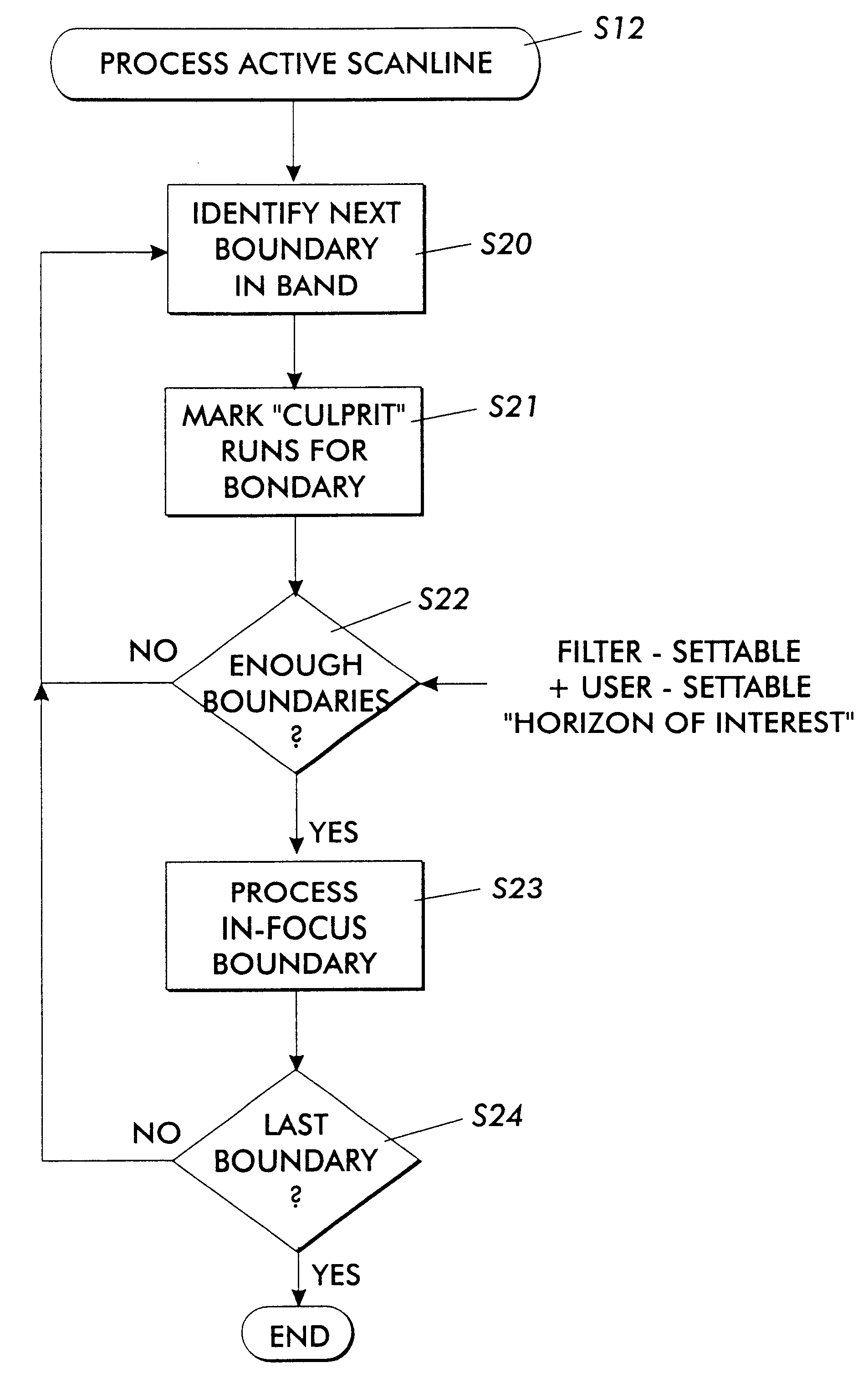
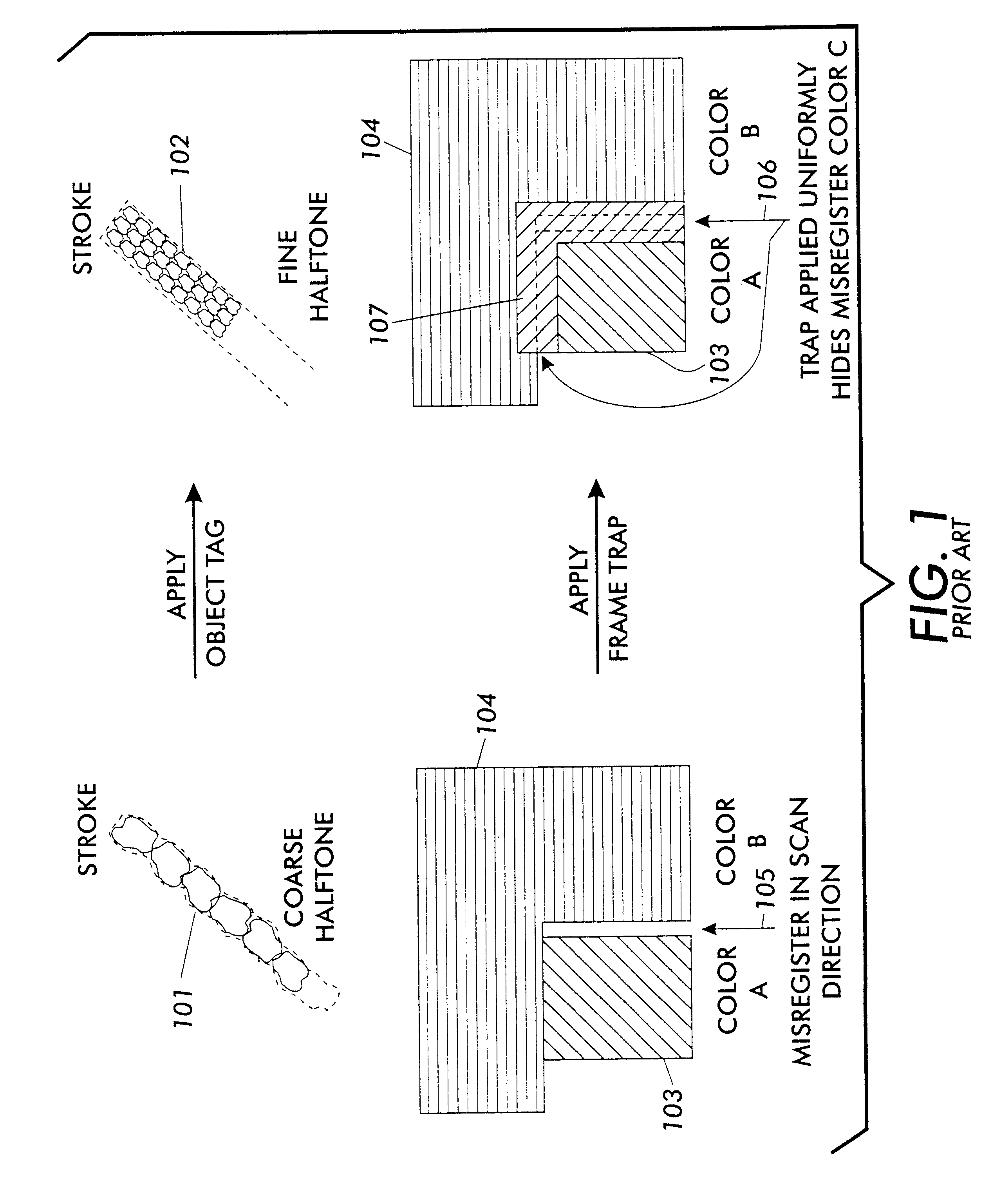
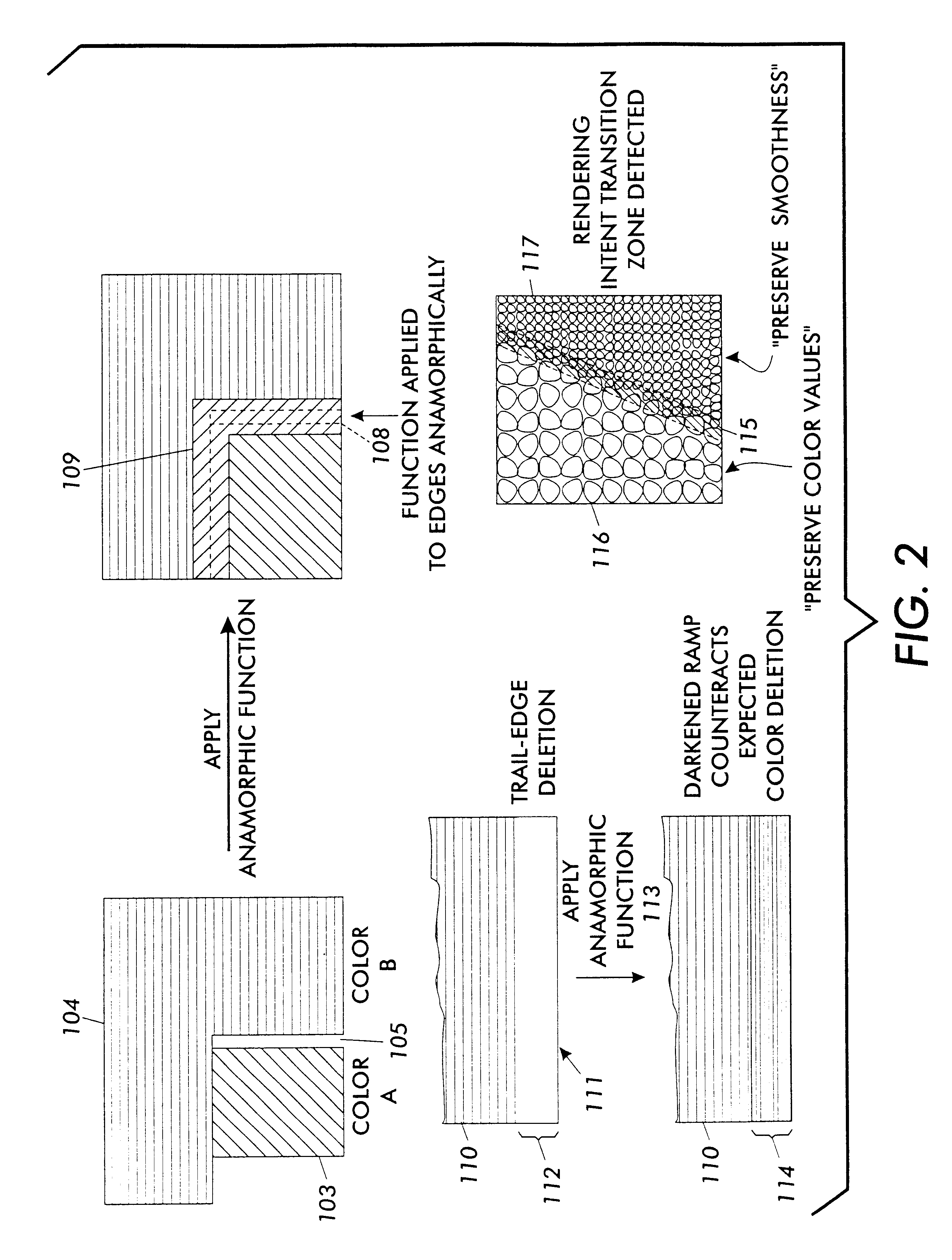
Every printing system has characteristic defects which detract from high quality printing. Xerographic printing systems show defects such as banding, mottled colors in large fill areas, trail-edge deletion and starvation where toner concentrations drop at certain color edges, misregistration, and so on. Ink jet printing systems can show ink bleeding, streaking in the direction of head movement, and so on. One approach to reducing printer defects is to refine the electro-mechanics for more precise printing. Another approach which works for predictable defects is to modify the digital data being sent to the printer to pre-compensate for the defect. The prior art does this to a limited extent for individual object types (strokes, fills, images, text, etc.) and for misregistered color edges (trapping). This invention extends the range of edge-related defects that can be both predicted and pre-compensated for. An embodiment of the invention is described which pre-compensates for defects such as trail-edge deletion, starvation, misregistration, halo, etc. by identifying runs of color which meet the criteria likely to cause the effect and applying a function f(edge-distance, object-type) to such runs to modify them appropriately. Both the prediction criteria and the functions applied are anamorphic (the scan direction and process direction are treated differently) and object-optimized (object attributes are taken into account). Further, both prediction criteria and applied correction functions allow user-settable input.
Owner:XEROX CORP
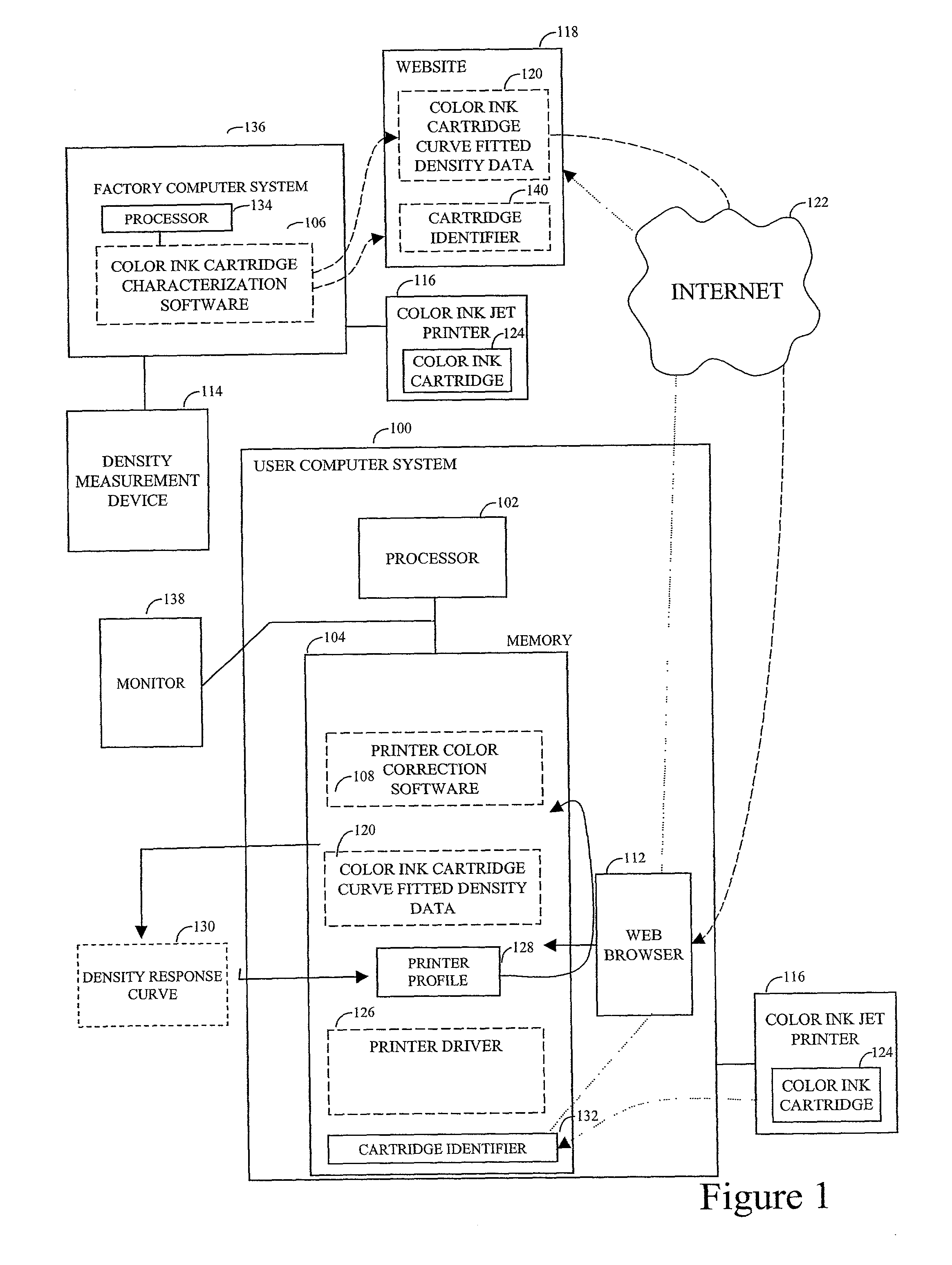
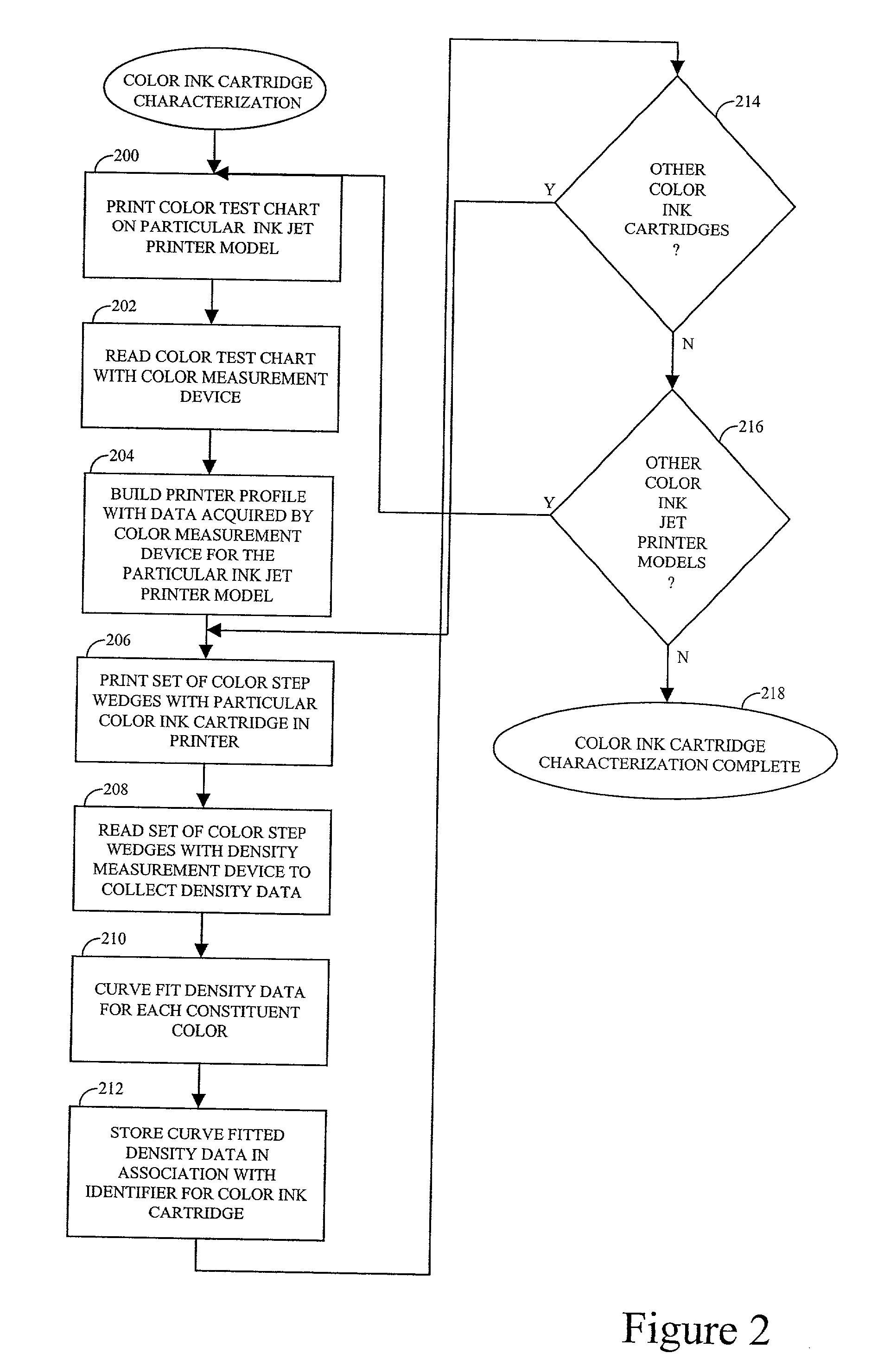
Automatic printer color correction based on characterization data of a color ink cartridge
InactiveUS20020149785A1Digitally marking record carriersDigital computer detailsColor correctionThe Internet
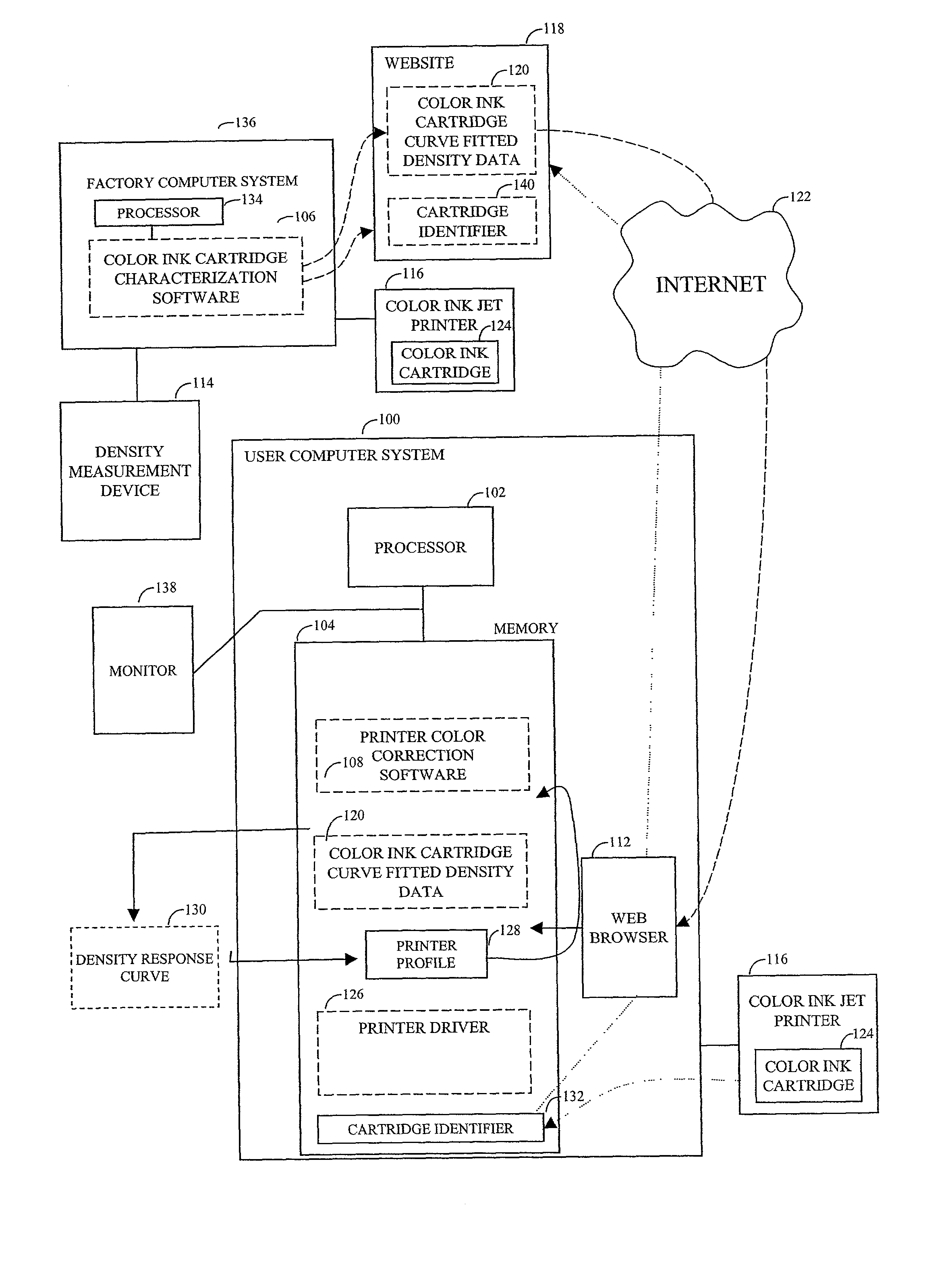
A technique of automatic printer color correction includes accessing characterization data of the color ink cartridge and rendering consistent color for the color ink jet printer based on the characterization data. The characterization data can be stored on a website and accessed over the Internet by providing an identifier of the color ink cartridge. The identifier can, for example, be the serial number of the color ink cartridge. The characterization data-density data, for example-can be added to a printer profile for the color ink jet printer.
Owner:HEWLETT PACKARD DEV CO LP
Cruable U-NII wireless radio with secure, integral antenna connection via SM BIOS in U-NII wireless ready device
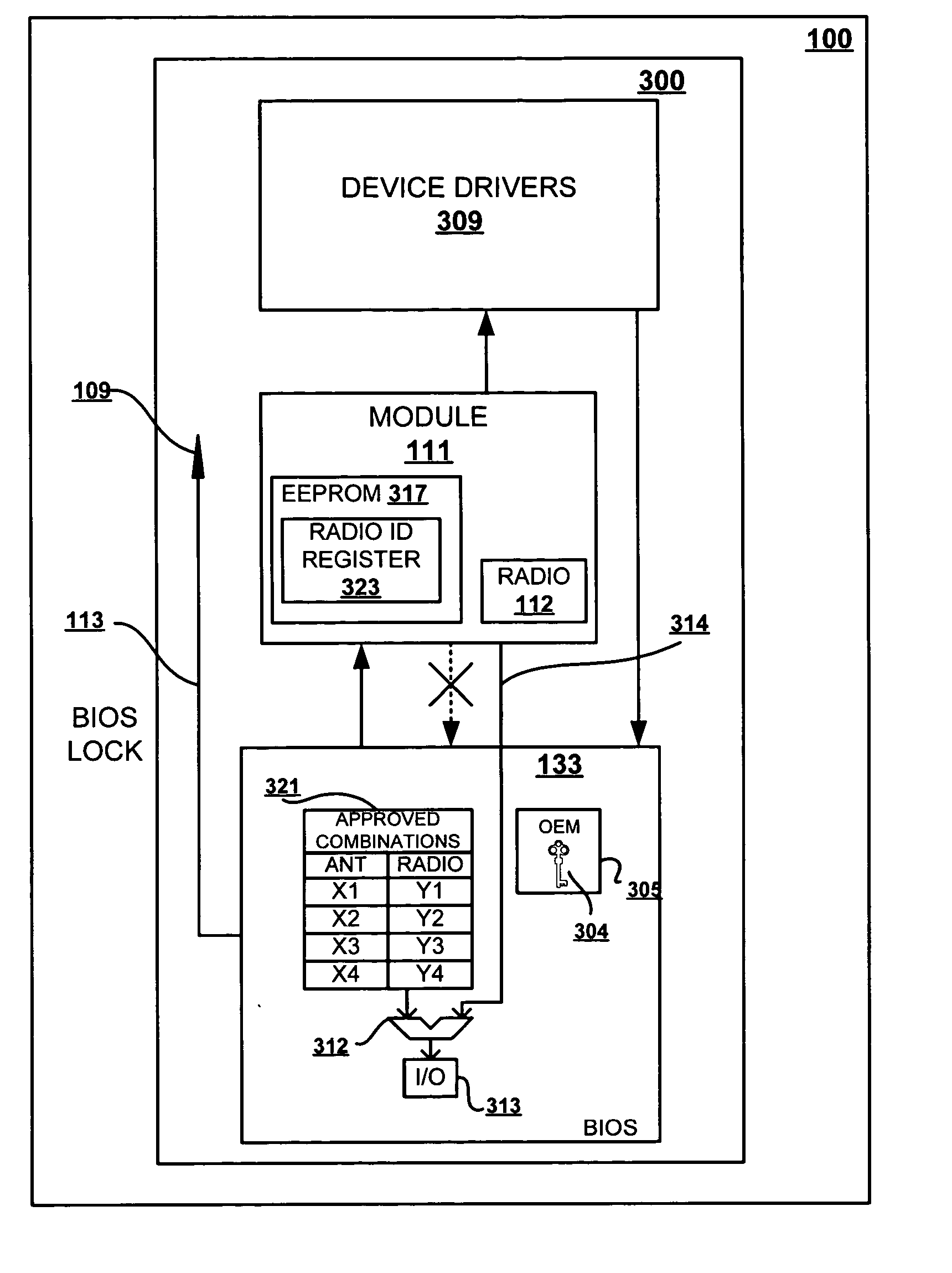
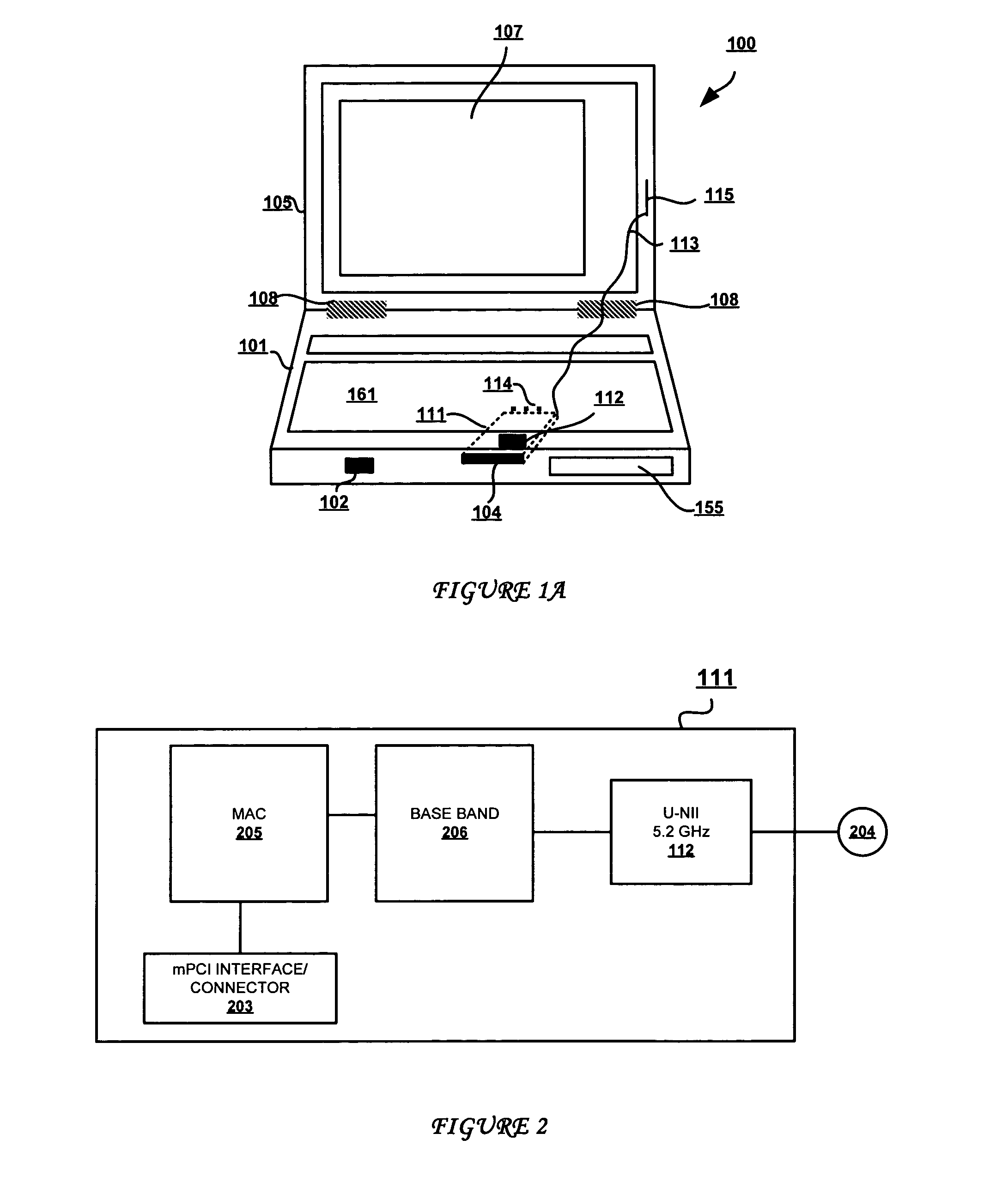
ActiveUS20050074123A1Avoid modificationAntenna supports/mountingsUser identity/authority verificationBIOSEmbedded system
A method that utilizes software and hardware mechanisms to meet the FCC requirement for a U-NII antenna to be an integral part of the device in which it operates, while providing wireless ready U-NII devices and CRUable U-NII radios. Enhancements are made to the software BIOS, including the inclusion of a table of approved radio-antenna PCI ID pairs to create an authentication scheme that verifies and authenticates the radio and antenna combination as being an FCC-approved unique coupling during boot-up of the system. The BIOS also comprises an OEM field that stores an encrypted secret key utilized to complete a second check of the radio model placed in the device. During boot up of the device, the PCI ID pairs from the BIOS are compared against the PCI ID of the radio and the secret key is checked against the radio model. Only a system with an approved combination of radio and antenna is allowed to complete the boot process, indicating an FCC approved device-antenna-radio combination under the “integral” requirement.
Owner:LENOVO PC INT
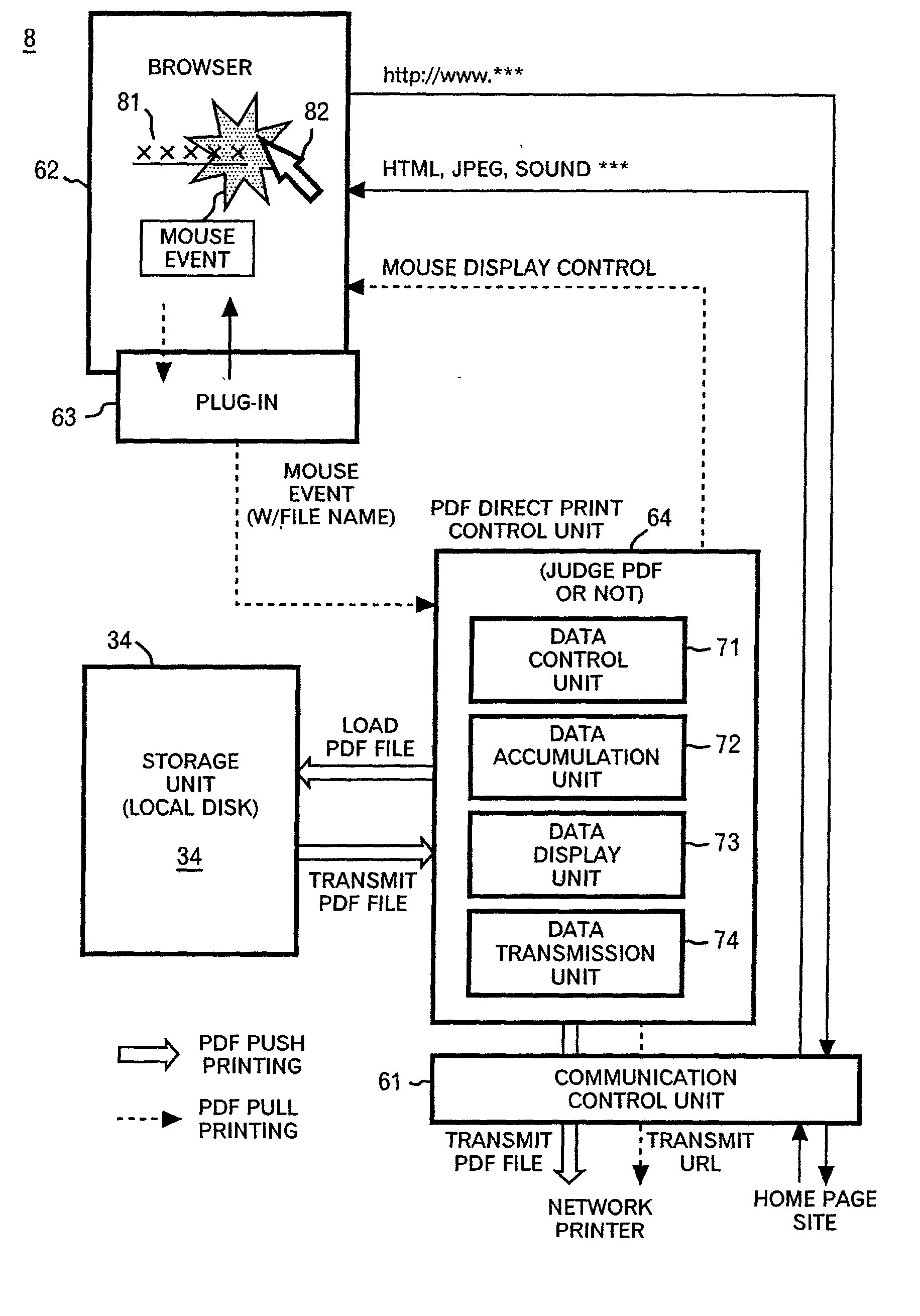
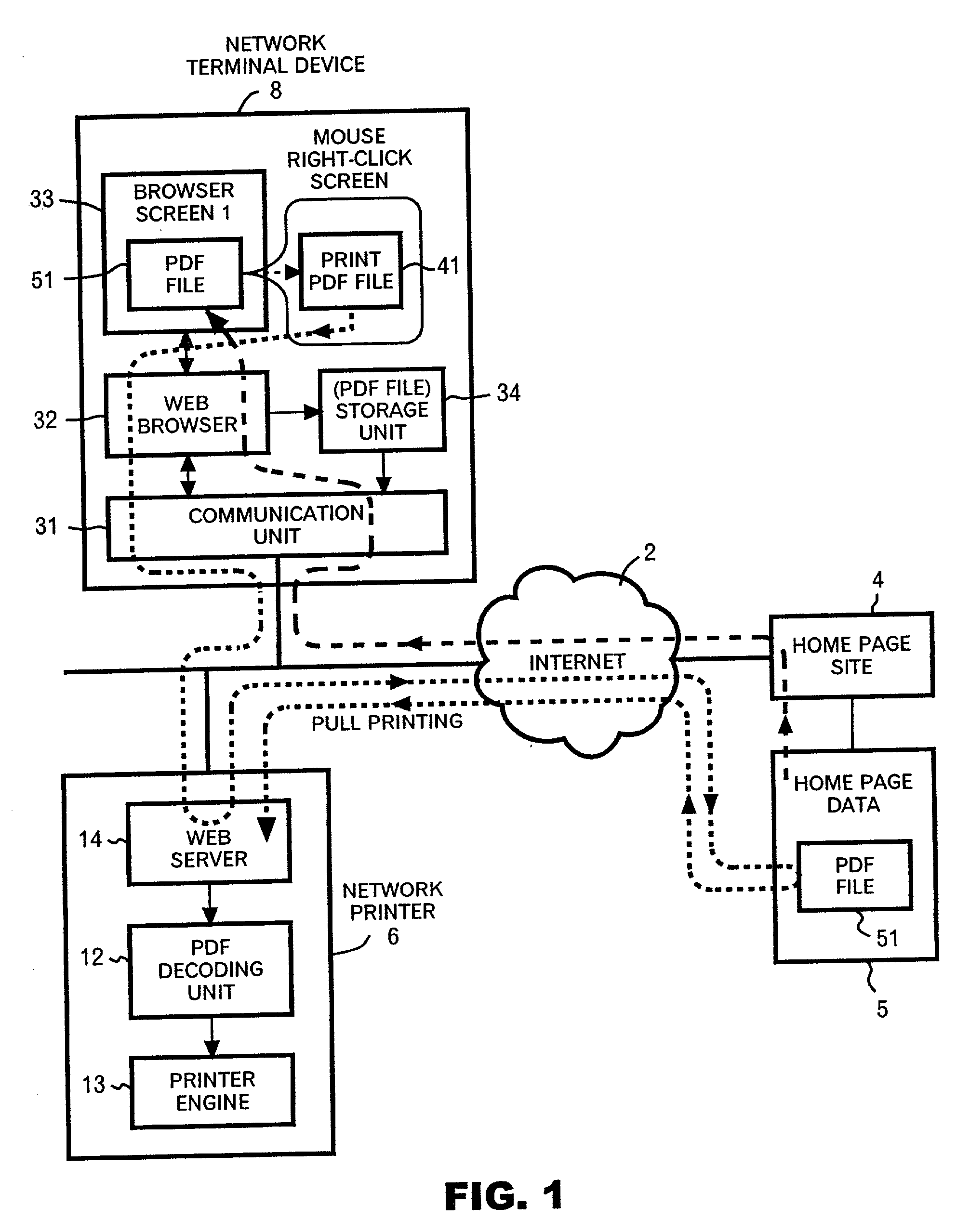
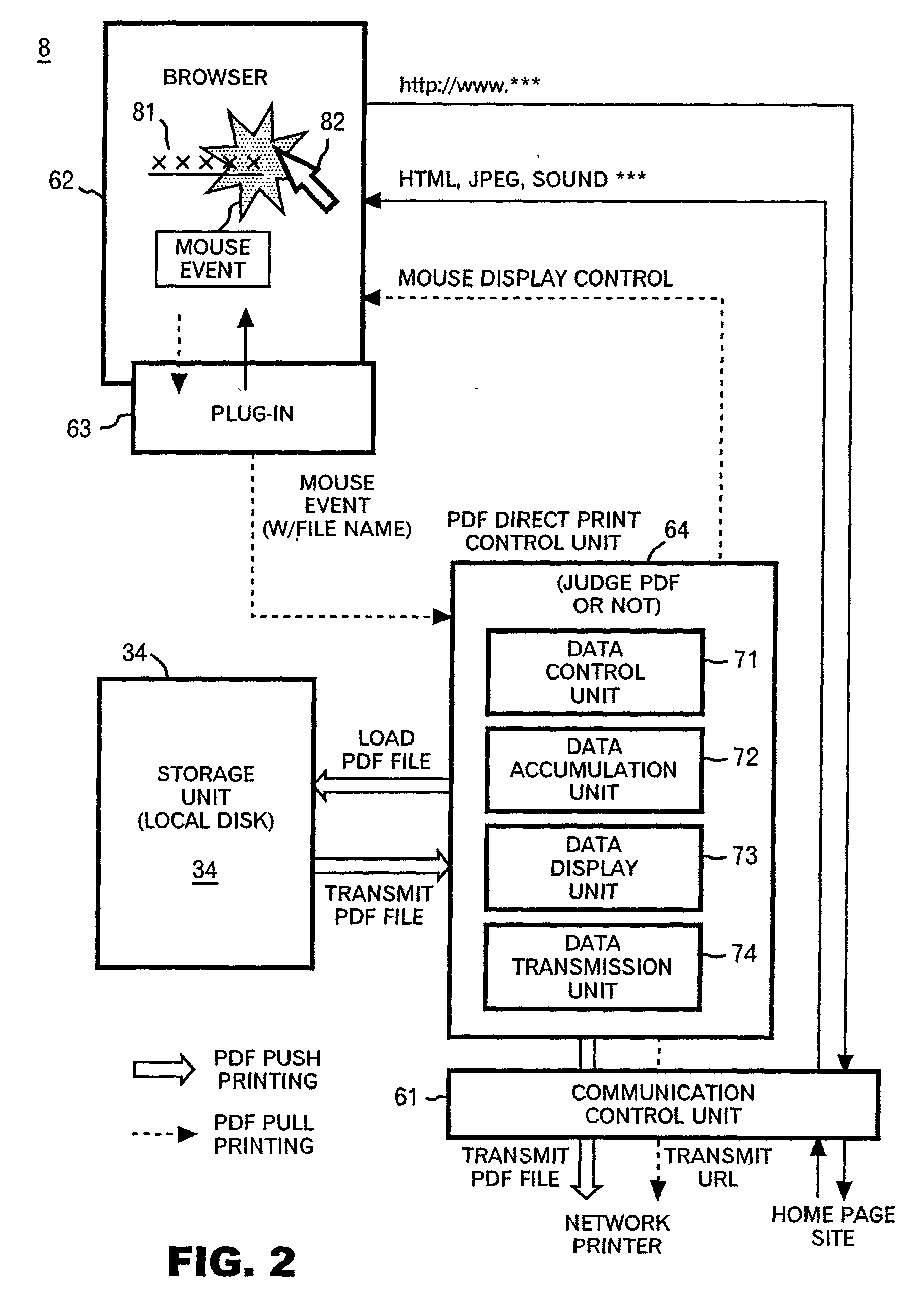
Program and method of print instruction for printer with PDF direct printing function
InactiveUS20020126306A1Easy for to instruct print operationEasy to operateData processing applicationsDigital computer detailsNetwork terminationWeb browser
A print instruction program and method for allowing a network terminal device to send print instructions to a PDF direct-printing printer in a communications network in an efficient and advantageous manner. The program and method includes the capability to obtain PDF file name and network address data from the location of a mouse pointer in a web browser screen. The file name and address data can be stored locally on the network terminal device, preferably in a list format. The program and method also provides for the display and operation of a direct print menu in association with a click on a control button of the mouse. The program and method allows the PDF file name and address data to be sent to the network-attached printer, either singly or as part of a list and either as a network address or as an actual file.
Owner:RICOH KK
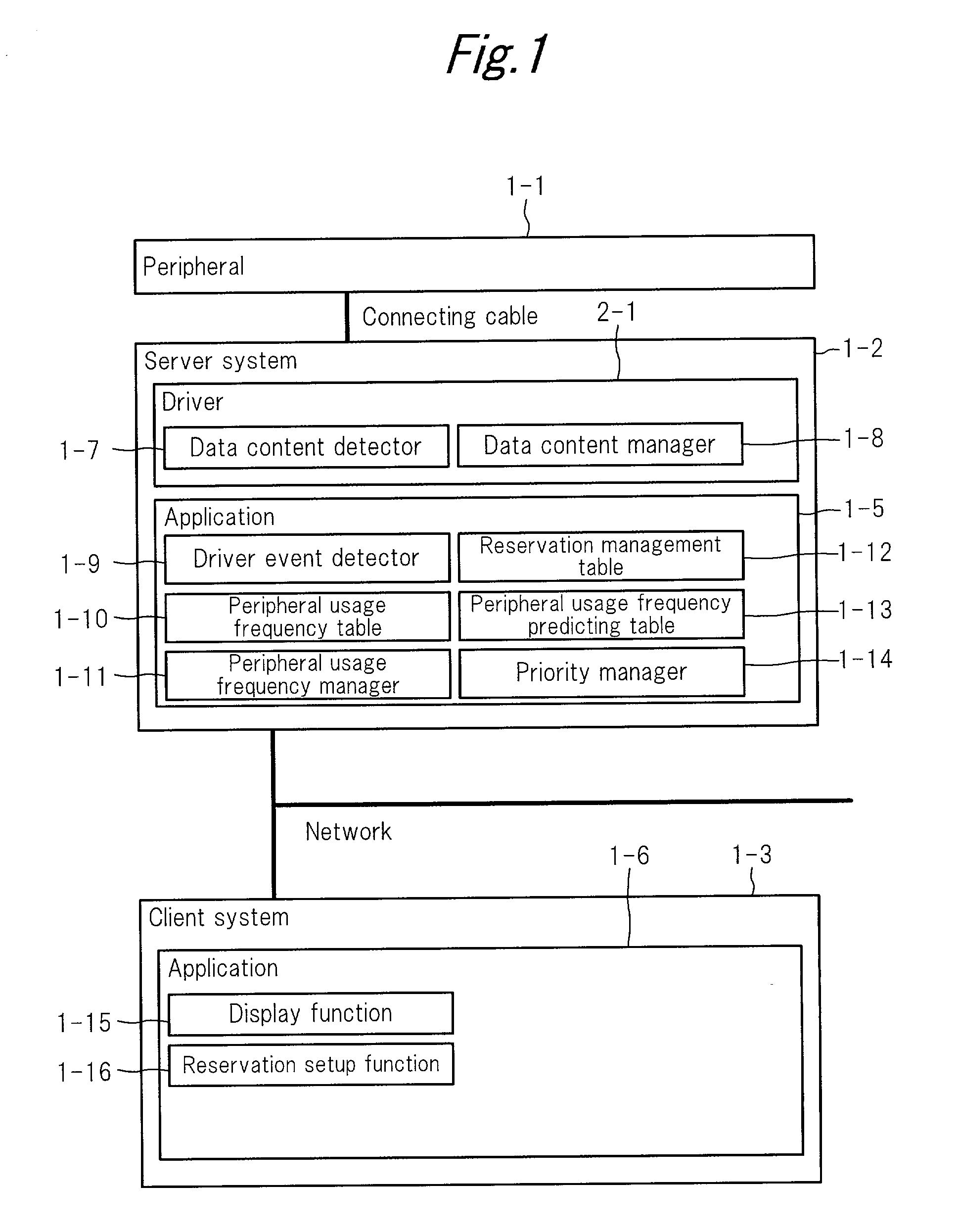
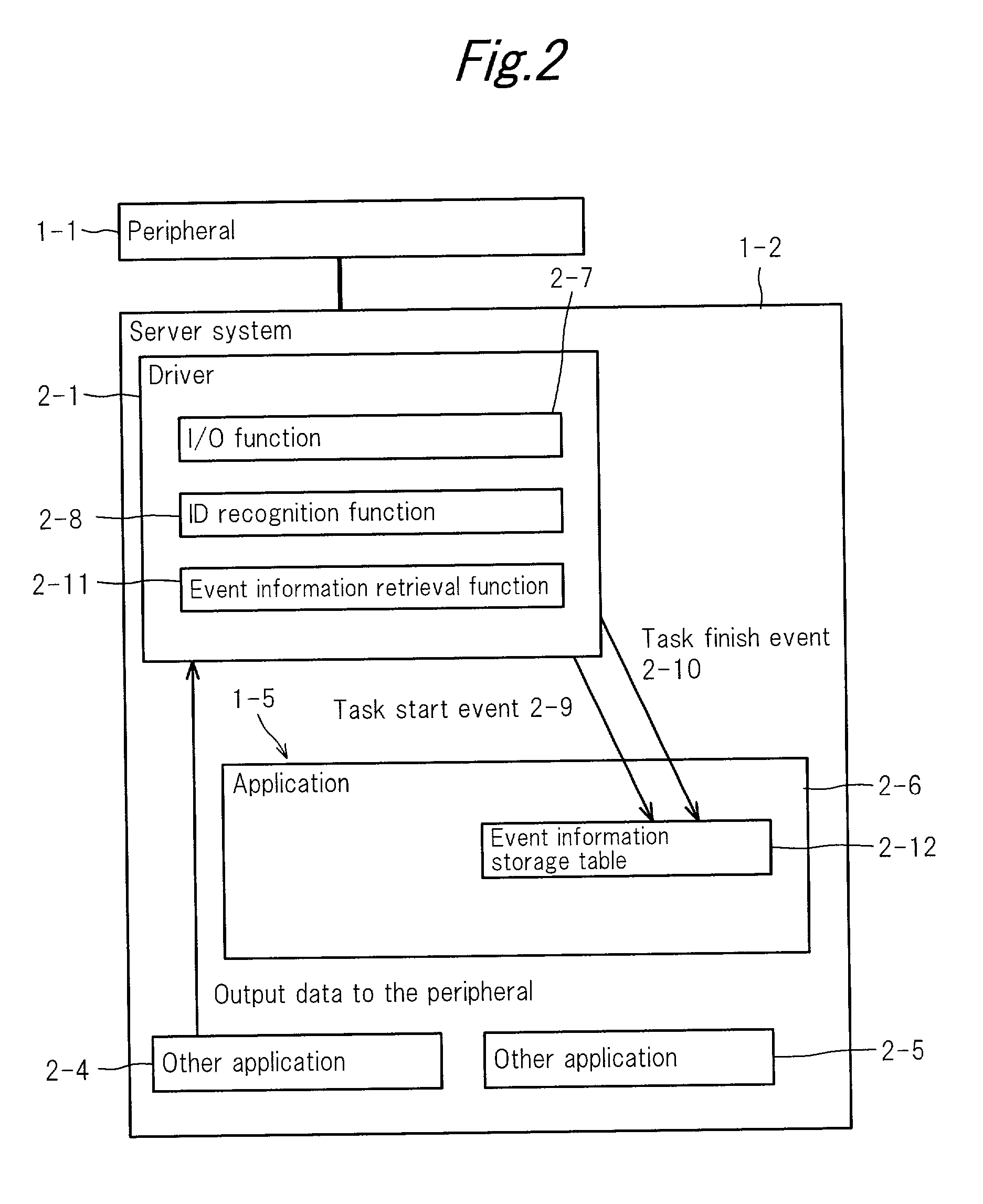
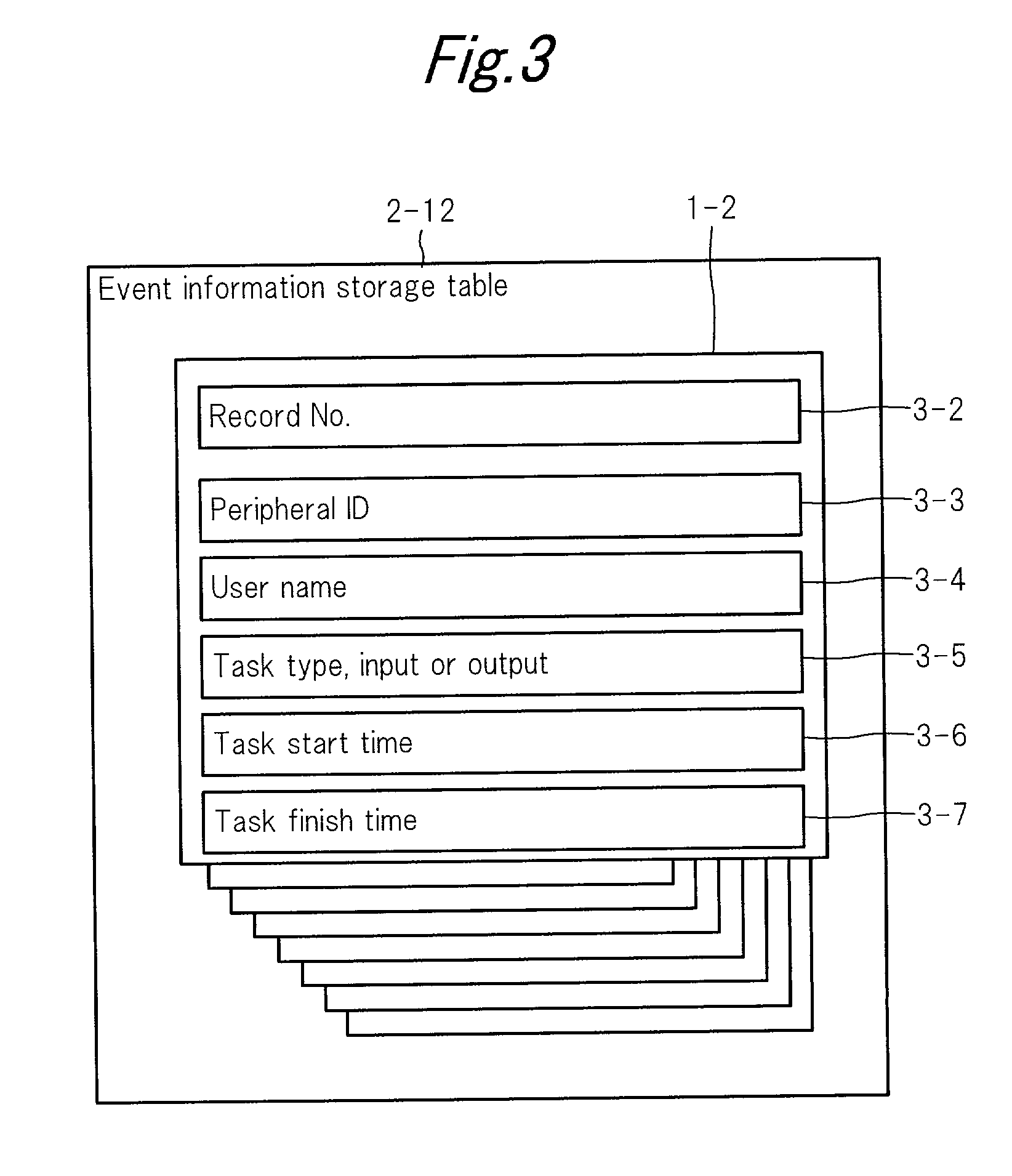
Usage reservation system for networked peripherals
InactiveUS20010015817A1Smoothly doneEasy to masterHand compositionDigital output to print unitsDriver/operatorClient system
A server system includes: a driver for allowing client systems to use peripherals; a driver event detecting portion; a usage frequency management table for recording the usage history and a usage history frequency management portion; a reservation management table for registering reservations by operating the usage frequencies and predicting the usage time periods of a peripheral; a data content detecting portion for detecting the content processed through the driver; and a data content management portion for recording the content. The system is configured so that management of setup usage reservations of the peripheral and changing reservations in response to a user request from a client system can be performed.
Owner:SHARP KK
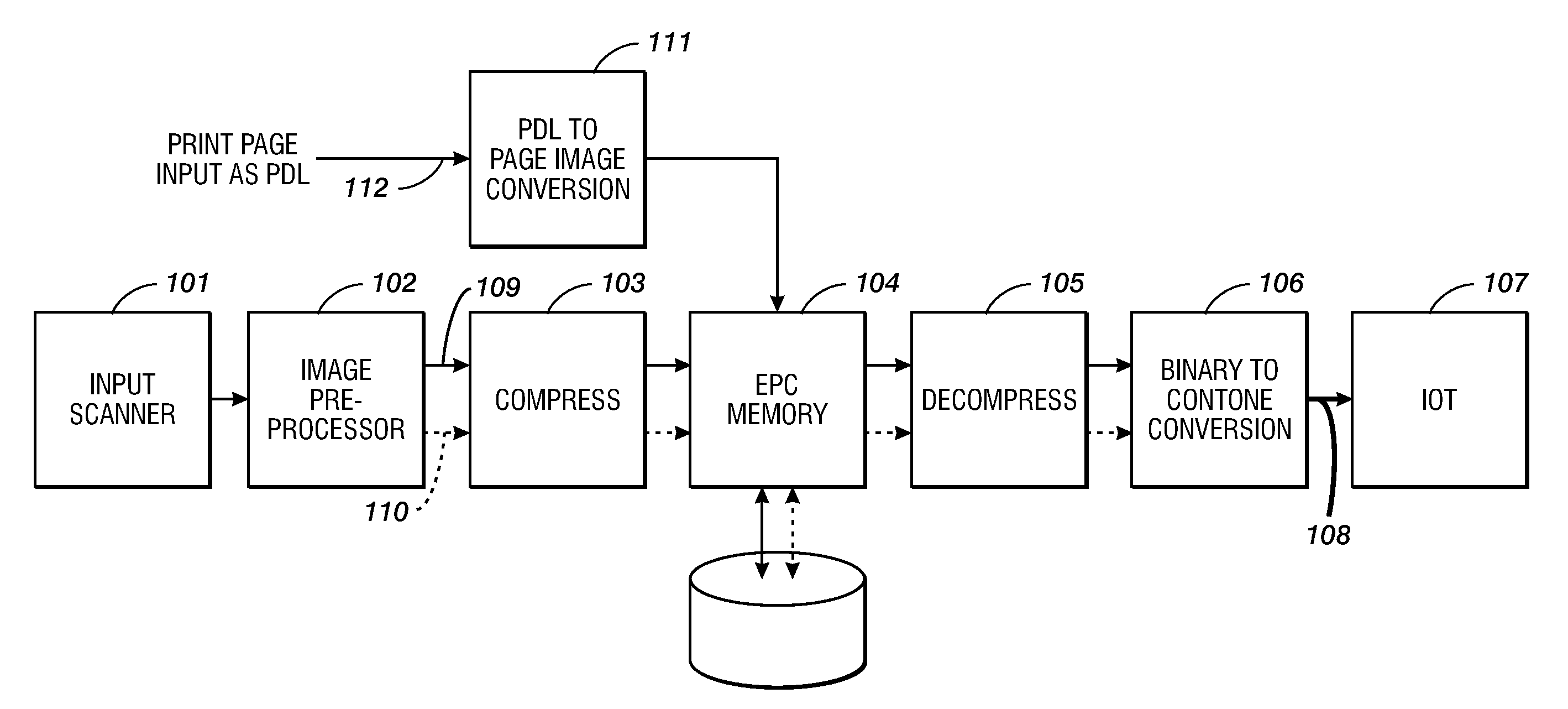
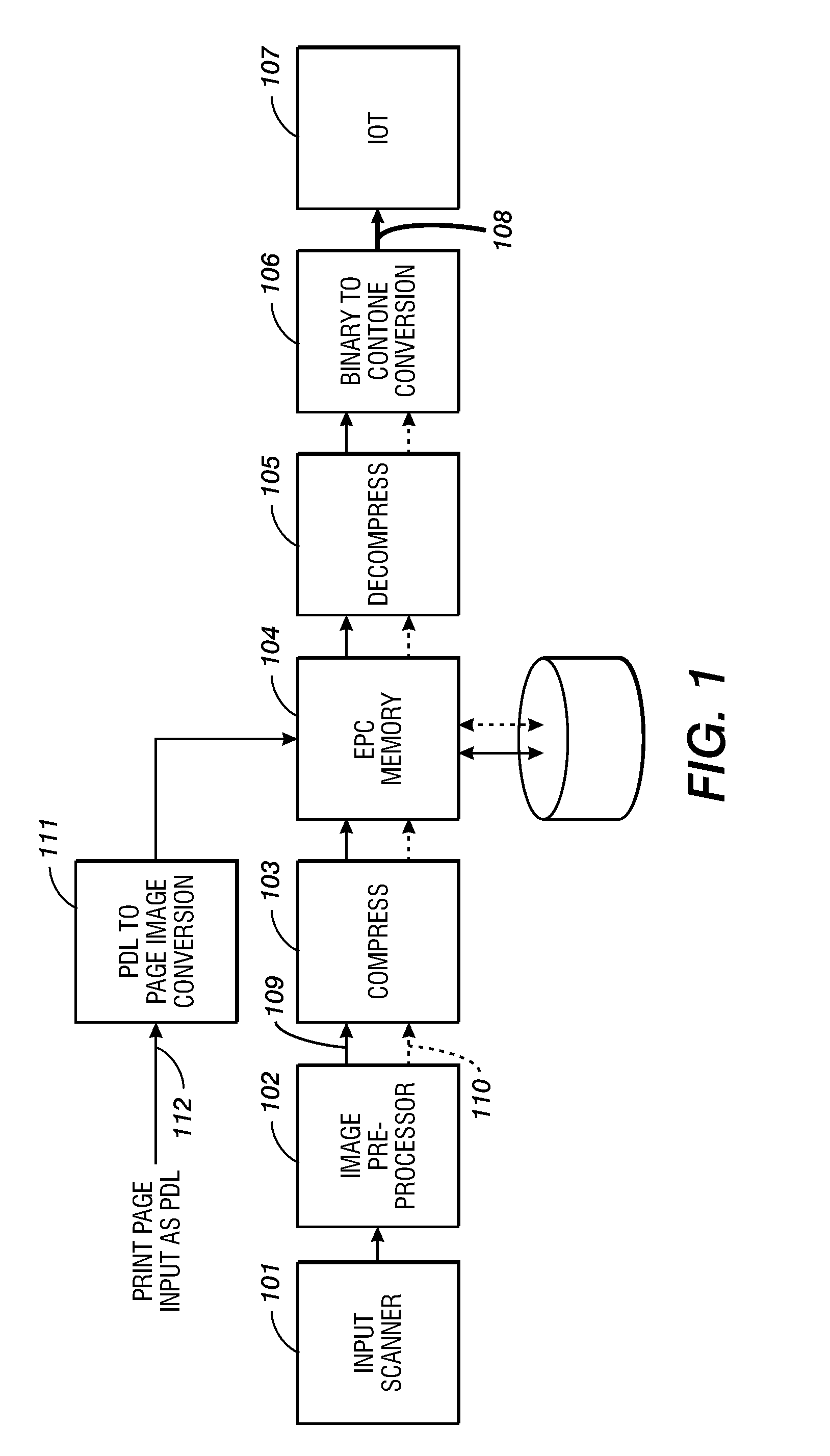
Method and system for generating contone encoded binary print data streams
ActiveUS7352490B1Maximum image qualityMinimum lossImage enhancementDigitally marking record carriersData streamPattern matching
A method and system to convert an electronic image file described in a page description language containing both contone and non-contone image objects to an intermediate binary format image. The intermediate format image separately encodes the contone and non-contone image objects. The contone image objects are edge-tagged. Prior to printing, the intermediate binary format page image is separated into the contone and non-contone image objects. The contone image objects are converted back to a contone form using the edge tagging to modify the filter weights of a digital filter. The non-contone image objects are converted to contone form by means of a pattern matching scheme.
Owner:XEROX CORP
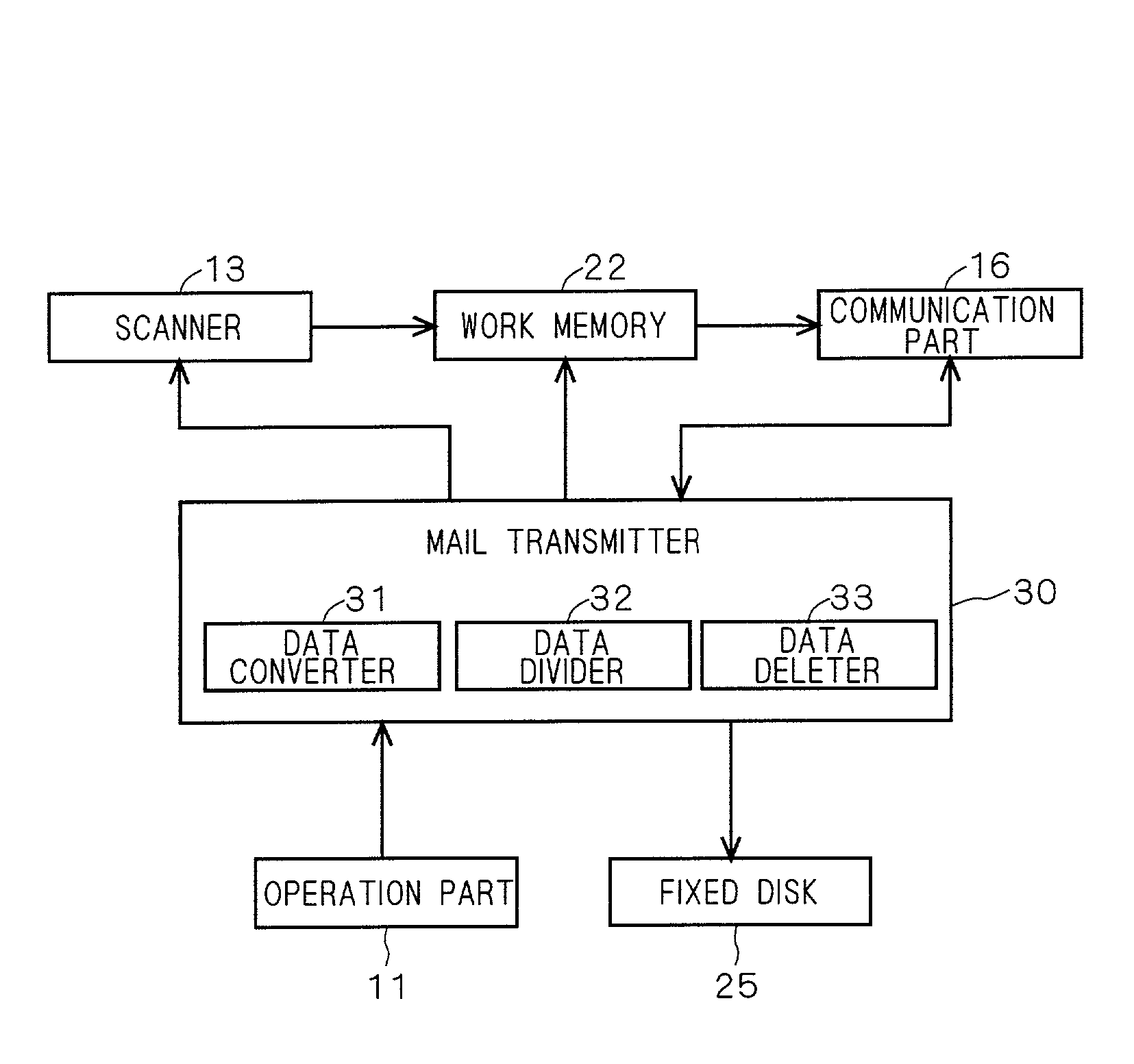
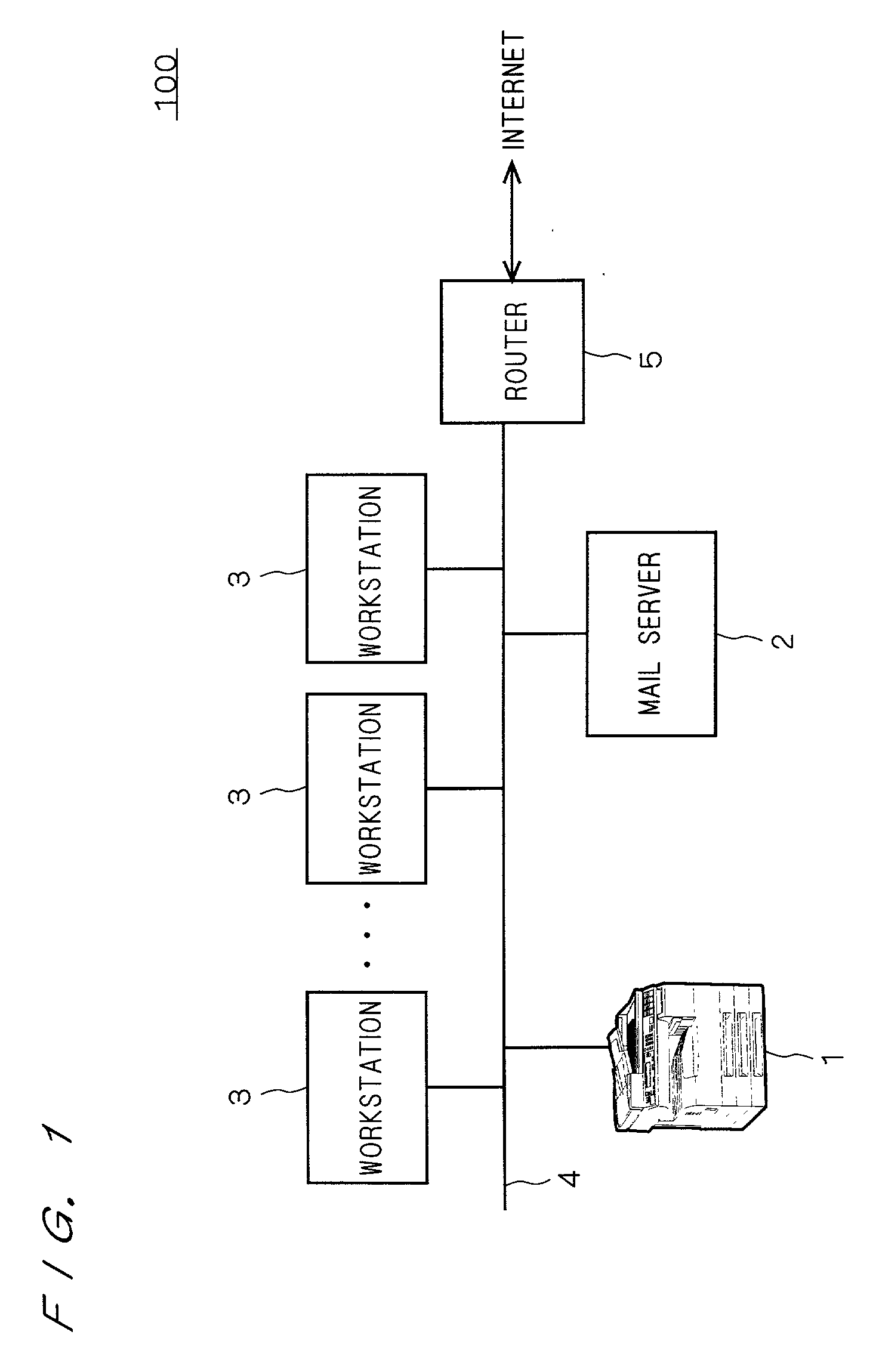
Image processing apparatus
InactiveUS20020140960A1Easy to useEfficiently re-transmittedDigitally marking record carriersHand compositionImaging processingComputer graphics (images)
An MFP can transmit image data read by a scanner by attaching it to E-mail. At the time of transmission, the image data input by the scanner and stored in a work memory is converted into mail data so as to be transmitted by E-mail, and the mail data is stored again into the work memory. The mail data is divided every predetermined reference data size into divided files which are sequentially transmitted as divided mails. When completion of transmission of divided mails corresponding to a unit image is confirmed, the image data and mail data of the unit image are eliminated from the work memory. By sequentially performing such a process, the memory use efficiency can be improved while holding image data of a unit image which has not been transmitted yet.
Owner:MINOLTA CO LTD
System and method for generating color digital watermarks using conjugate halftone screens
InactiveUS20020102007A1Digitally marking record carriersDigital computer detailsPattern recognitionImproved method
The present invention is directed to an improved method for producing color watermarks in digitally reproducible color documents. The color watermarks are generated by producing a halftone pattern, which appears as stochastically distributed dots, in at least one or more color separations of the color document. A second halftone pattern, which also appears as stochastically distributed dots and is spatially displaced from the first halftone pattern, is generated in at least one or more different color separations. Portions of the first and second halftone patterns are auto-correlated or conjugally correlated, therefore, when the two halftone patterns are laid over each other, watermark patterns of highly contrasting colors become markedly visible.
Owner:XEROX CORP
Distribution system for digital image content and reproducing method and medium recording its reproduction program
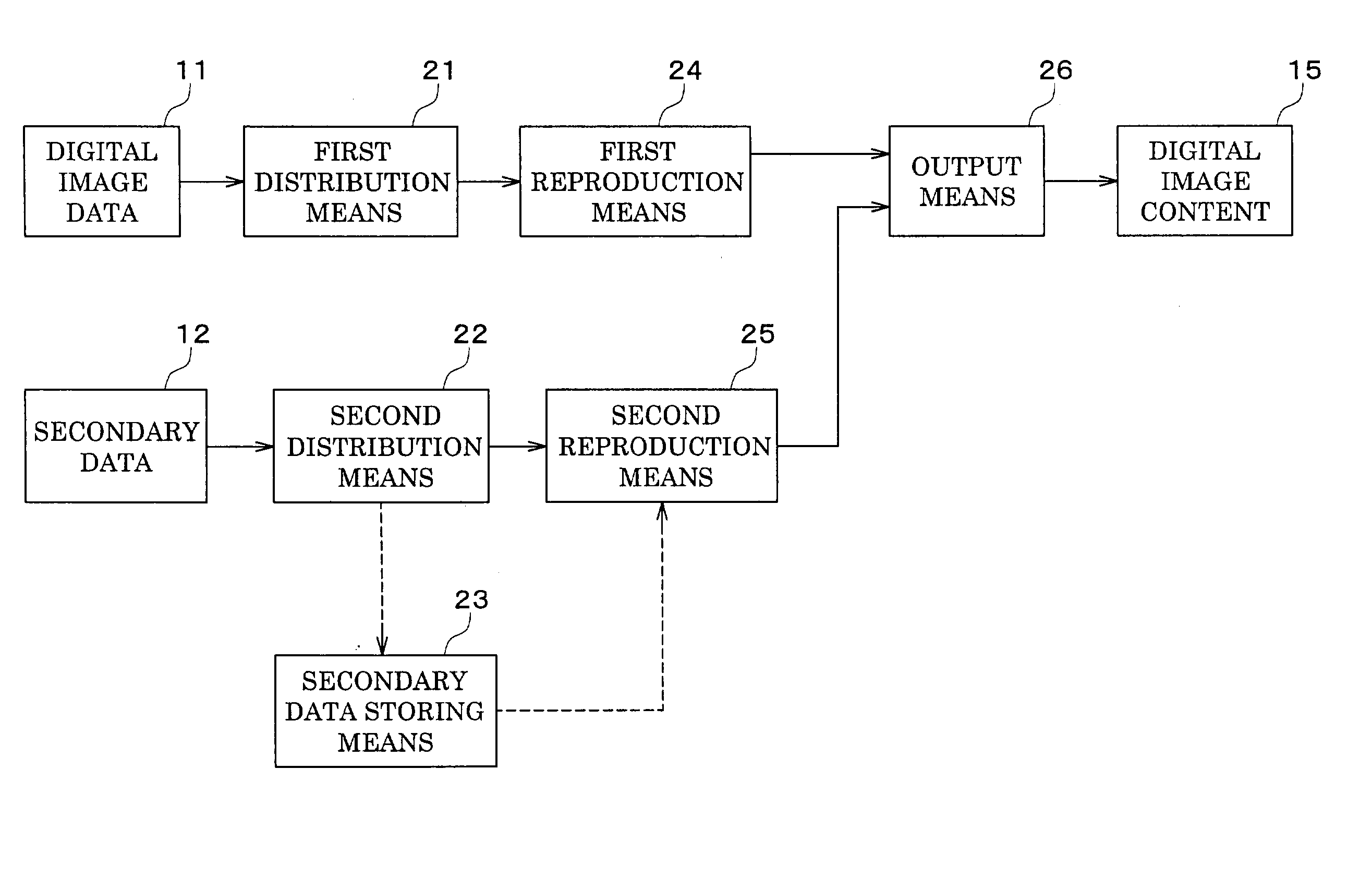
InactiveUS20030090711A1Efficient executionEasy to correctTelevision system detailsDigitally marking record carriersDigital contentIp address
A distribution system for digital image content, a method of reproducing digital image content, and a medium recording a program for reproducing digital image content are disclosed. The system comprise: a first distribution means (21) for distributing digital image data (11); a second distribution means (22) for distributing secondary data (12); a first reproduction means (24) for reproducing the digital image data (11); a second reproduction means (25) for reproducing the secondary data (12); and an output means (26) for superimposing the two reproduced data. The secondary data (12) is prepared using a markup language such that a reproduction start point and a reproduction endpoint correspond to an image frame-specific code for specifying an image of the digital image data (11) and that the secondary data (12) distributable from a different server having a different IP address is reproduced synchronously with the reproduction of the digital image data (11).
Owner:FUJIYAMA CO LTD
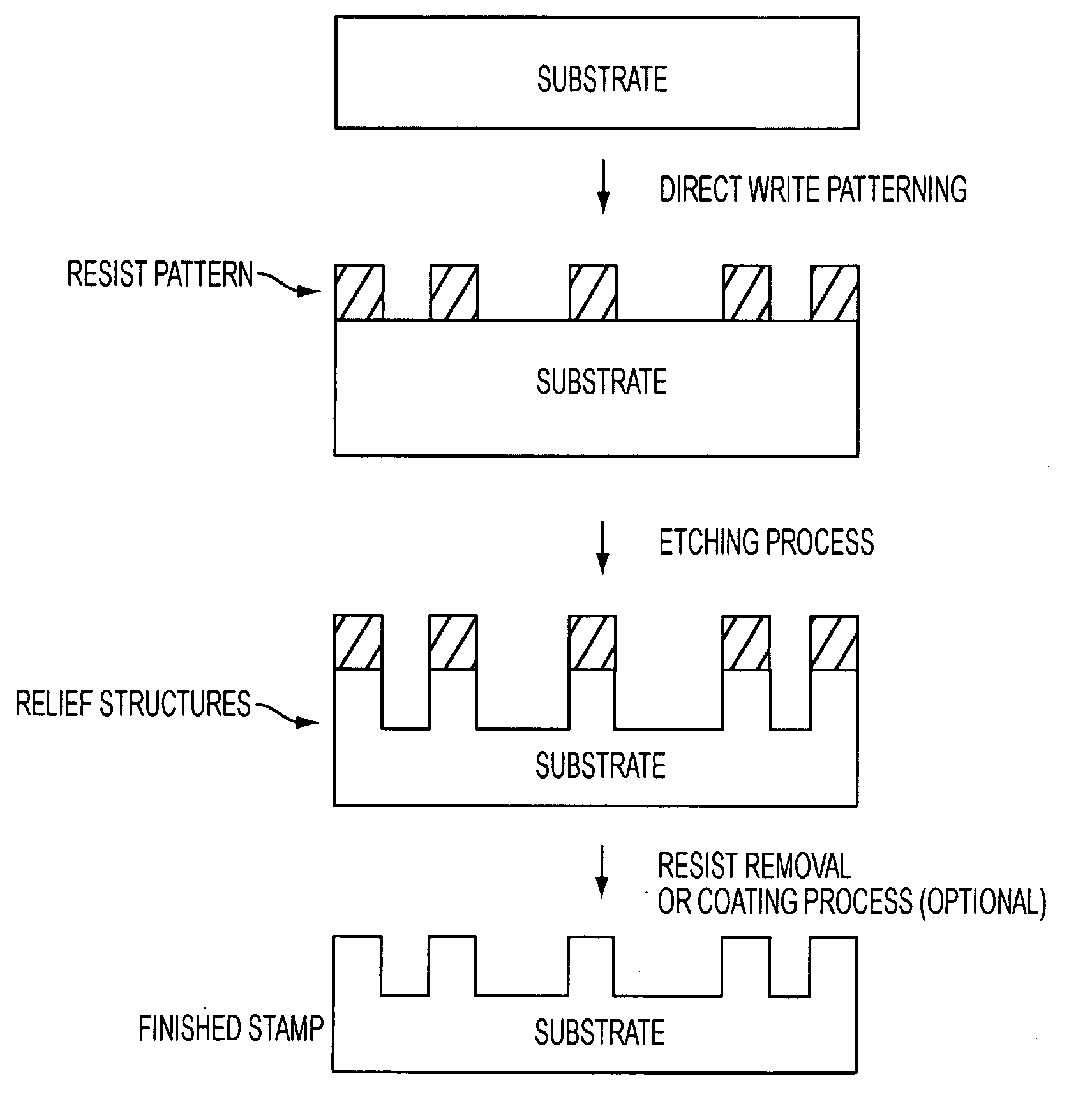
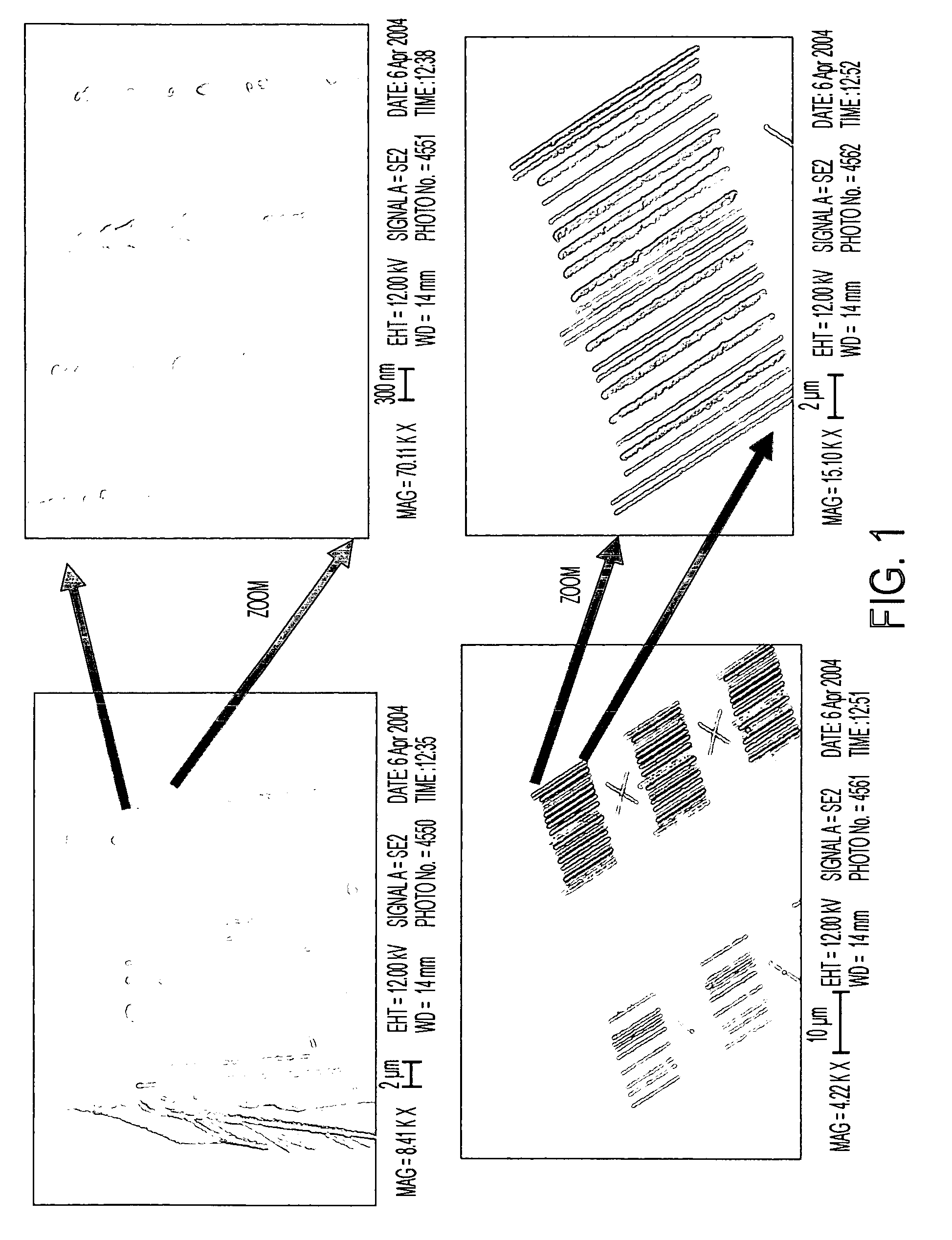
Stamps with micrometer-and nanometer-scale features and methods of fabrication thereof
InactiveUS20100294146A1Digitally marking record carriersMechanical working/deformationMicrometerElectron-beam lithography
Stamps and methods of making stamps for applications in anti-counterfeiting and authentication. The stamps are relatively small in size and feature nanoscale and microscale identification regions and features. High throughput manufacturing and high resolution methods are used to make the stamps including electron beam lithography and optical lithography. Anti-fouling coatings can be applied.
Owner:NANOINK INC +1
Method and apparatus for creating a registration network of a scene
InactiveUS7180072B2Simple processImprove throughputDigitally marking record carriersImage analysisPattern recognitionComputer graphics (images)
Owner:QUANTAPOINT
Printer, method for controlling the printer and computer readable medium
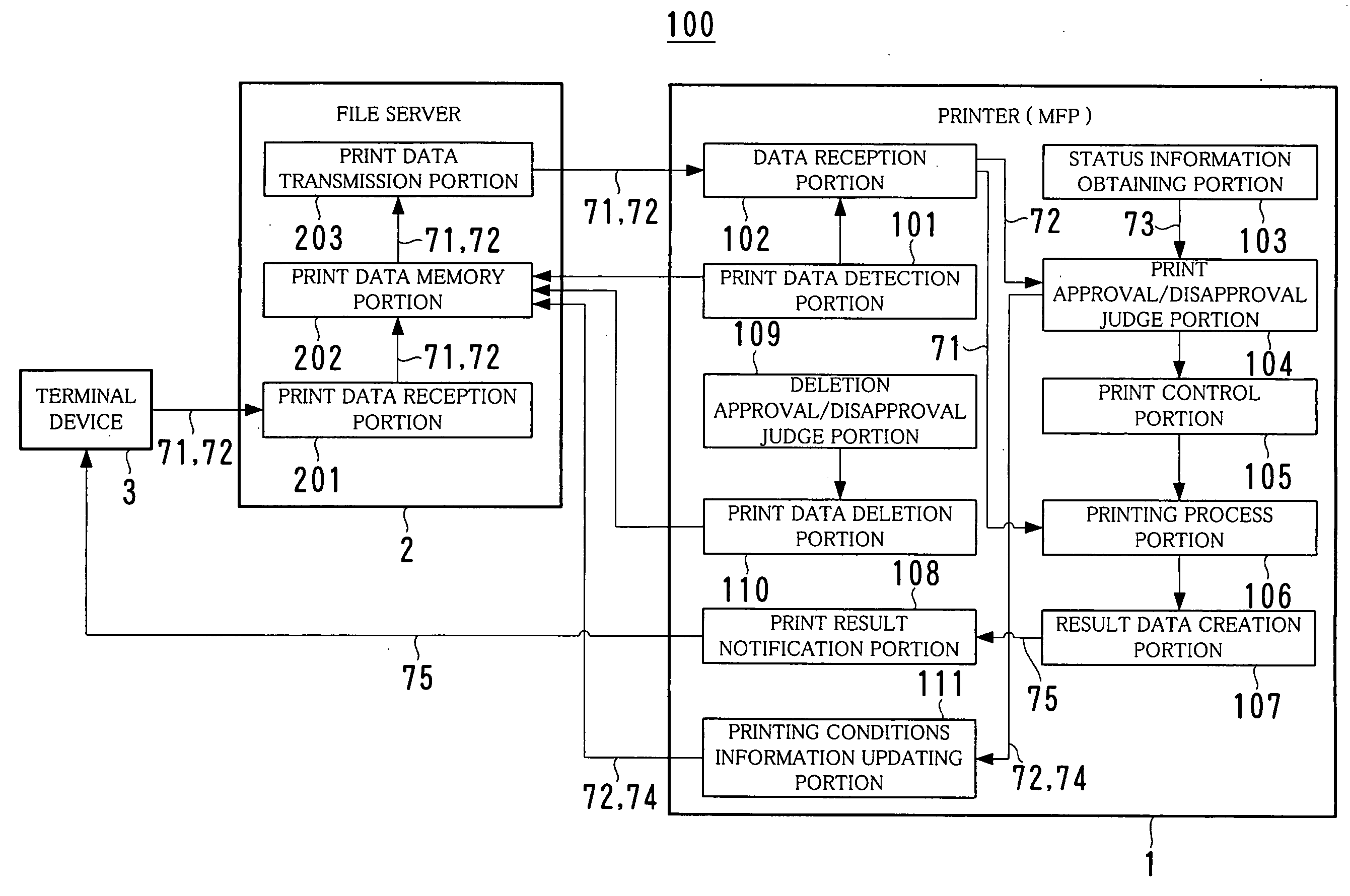
InactiveUS20050068566A1Easy to useEasy to addDigitally marking record carriersDigital computer detailsComputer printingTerminal equipment
A printer is provided that can be used easily and preferably without introducing an additional structure into a terminal device and a server. The printer includes a printing process portion for printing based on print data, a print data detection portion for detecting print data stored in a file server, a data reception portion for obtaining print data and the corresponding printing conditions information from the file server when the print data are detected, a print approval / disapproval judge portion for judging approval / disapproval of printing based on the obtained printing conditions information and a print control portion for controlling the printing process portion so that printing is performed based on print data corresponding to the printing conditions information when it is determined to be printable, and for controlling the same so that printing is not performed when it is determined to be unprintable.
Owner:KONICA MINOLTA BUSINESS TECH INC
Printing plates containing ink cells in both solid and halftone areas
InactiveUS6731405B2Photosensitive materialsDuplicating/marking methodsVolumetric Mass DensityComputer science
Owner:ESKO SOFTWARE
System and method for print system monitoring
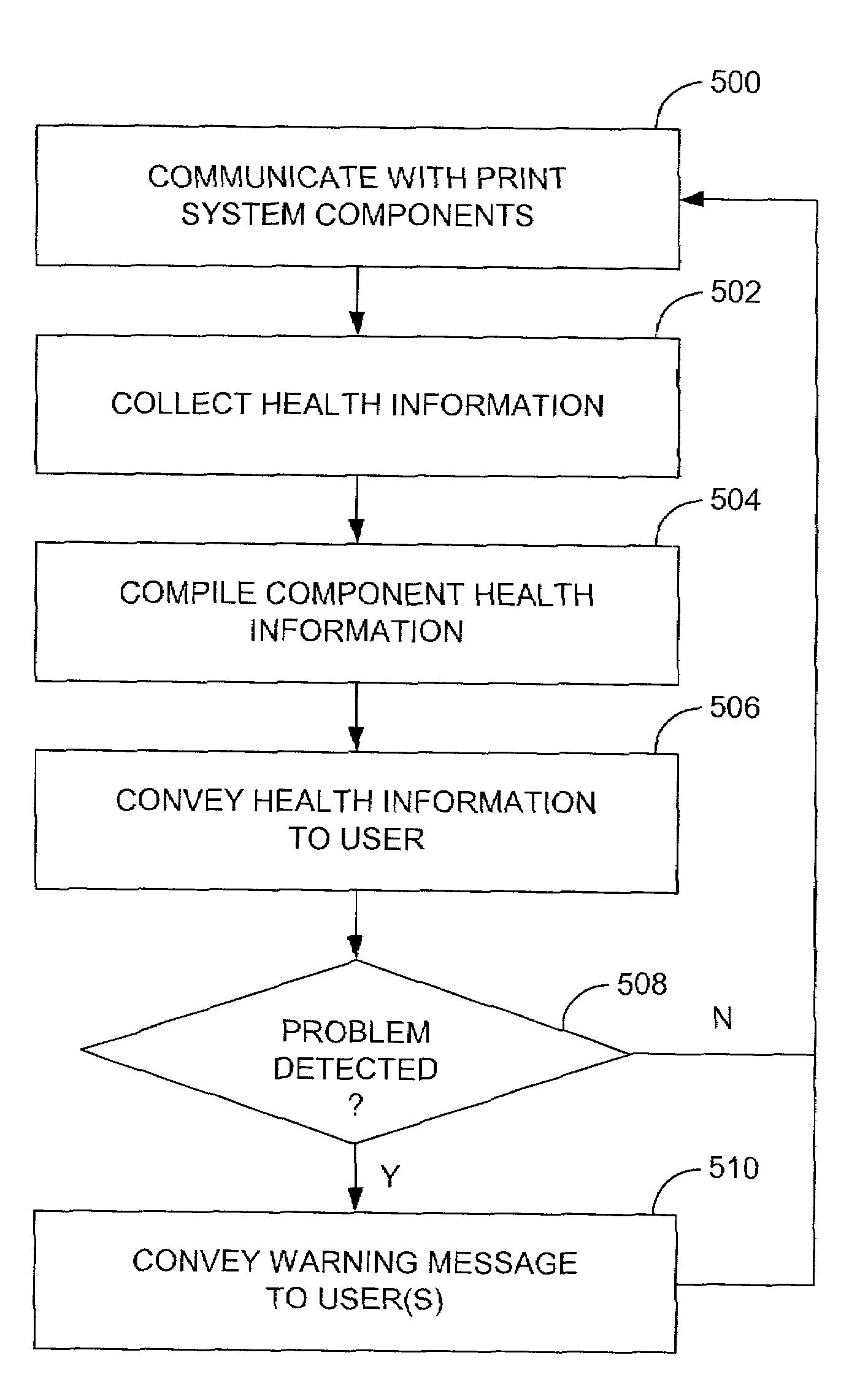
ActiveUS7265819B2Digitally marking record carriersError detection/correctionSystem monitorSystem monitoring
The present disclosure relates to a system and method for monitoring a print system. The system includes a print system monitor that is adapted for communicating with components of the print system, collecting health information regarding the operation of the print system components, compiling the health information regarding the operation of the print system components, and conveying the health information regarding the operation of the print system components and print system as a whole together to a user. Normally, the print system monitor is in communication with each component of the print system such that information as to operation of each component of the print system can be conveyed together to the user. Operating in this manner, the print system monitor automatically provides important information as to each component of the print system and the system as a whole for purposes of rectifying and avoiding printing problems.
Owner:HEWLETT PACKARD DEV CO LP
Color matching in lighting reproduction systems
ActiveUS20050018223A1Digitally marking record carriersDigital computer detailsSpectral responseEffect light
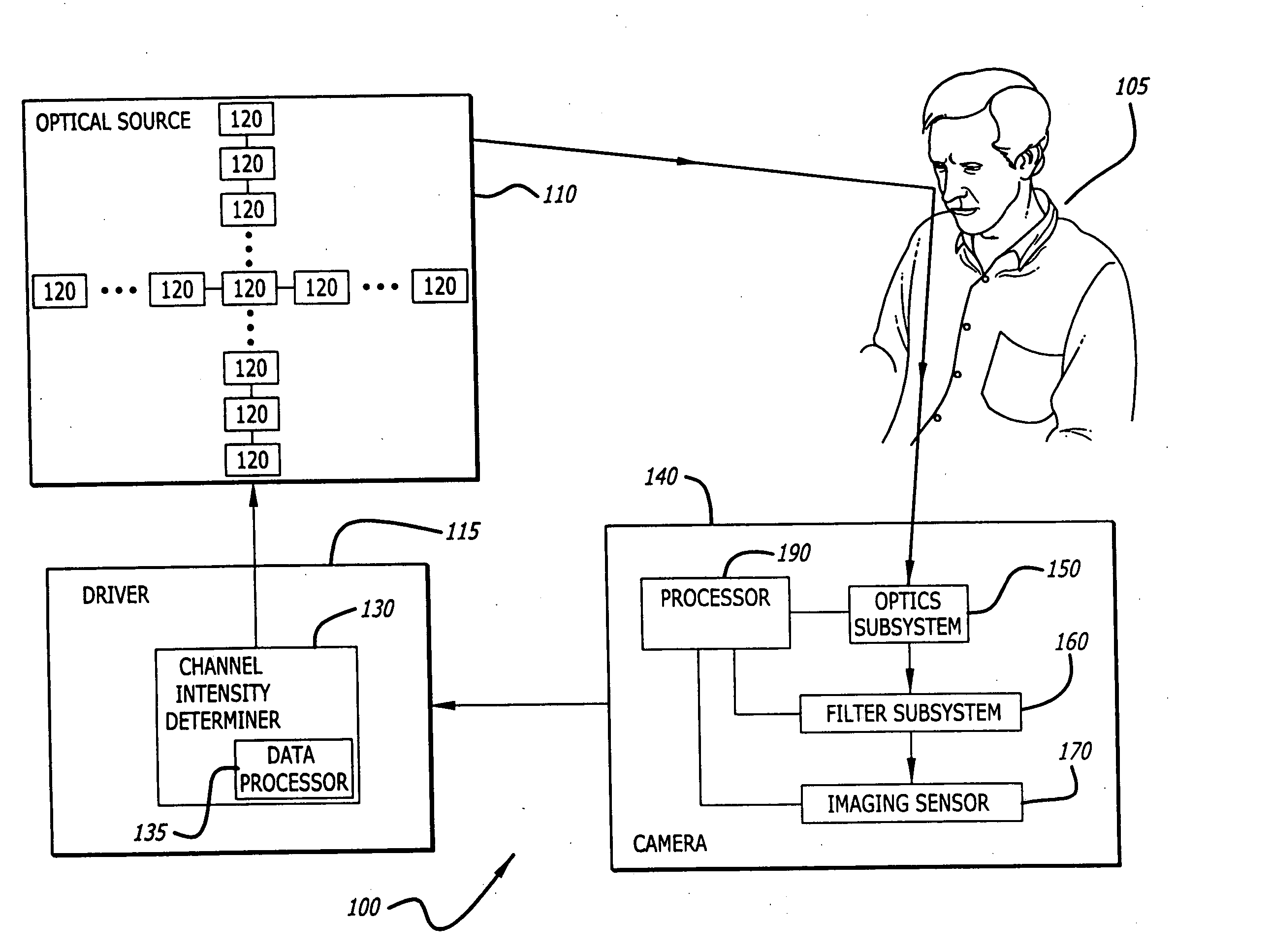
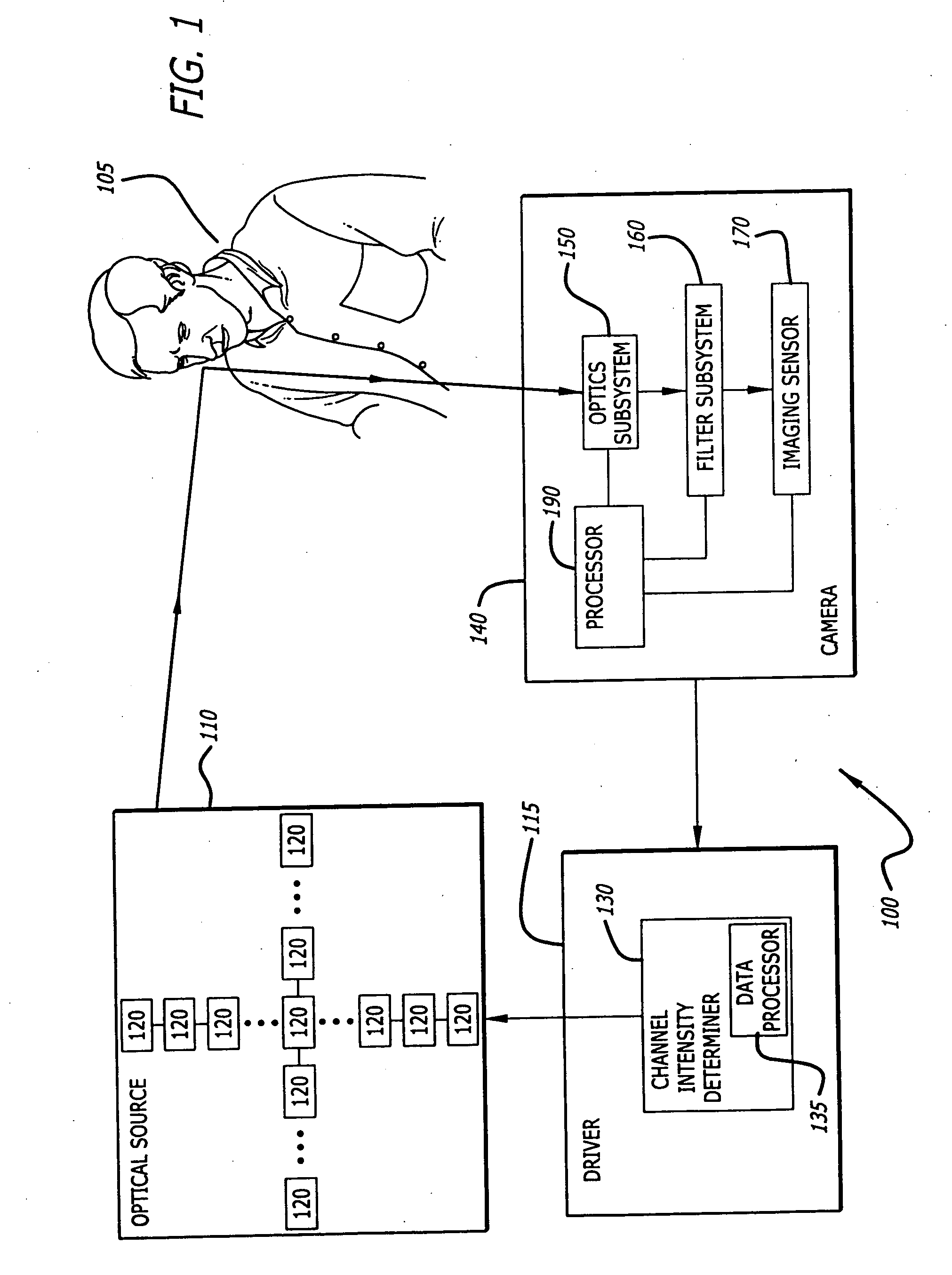
A lighting reproduction apparatus for illuminating a subject includes a reproduction light optical source that generates reproduction light. The optical source includes a plurality of light emitters, each characterized by an individual color channel. There may be nine different color channels. A driver drives the light emitter color channels with intensity values at which a substantial spectral match is achieved between the reproduction light and the desired illuminant, so that the subject appears to be illuminated by the desired illuminant. These channel intensity values may be determined by solving a minimization equation that minimizes a sum of square residuals of the reproduction light spectra to the desired illuminant spectra. The output reproduction light may be metamerically, matched with the desired illuminant, with respect to a particular camera's spectral response. One or more spectral reflectances of the subject may be measured and incorporated into the optimization process.
Owner:UNIV OF SOUTHERN CALIFORNIA
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com