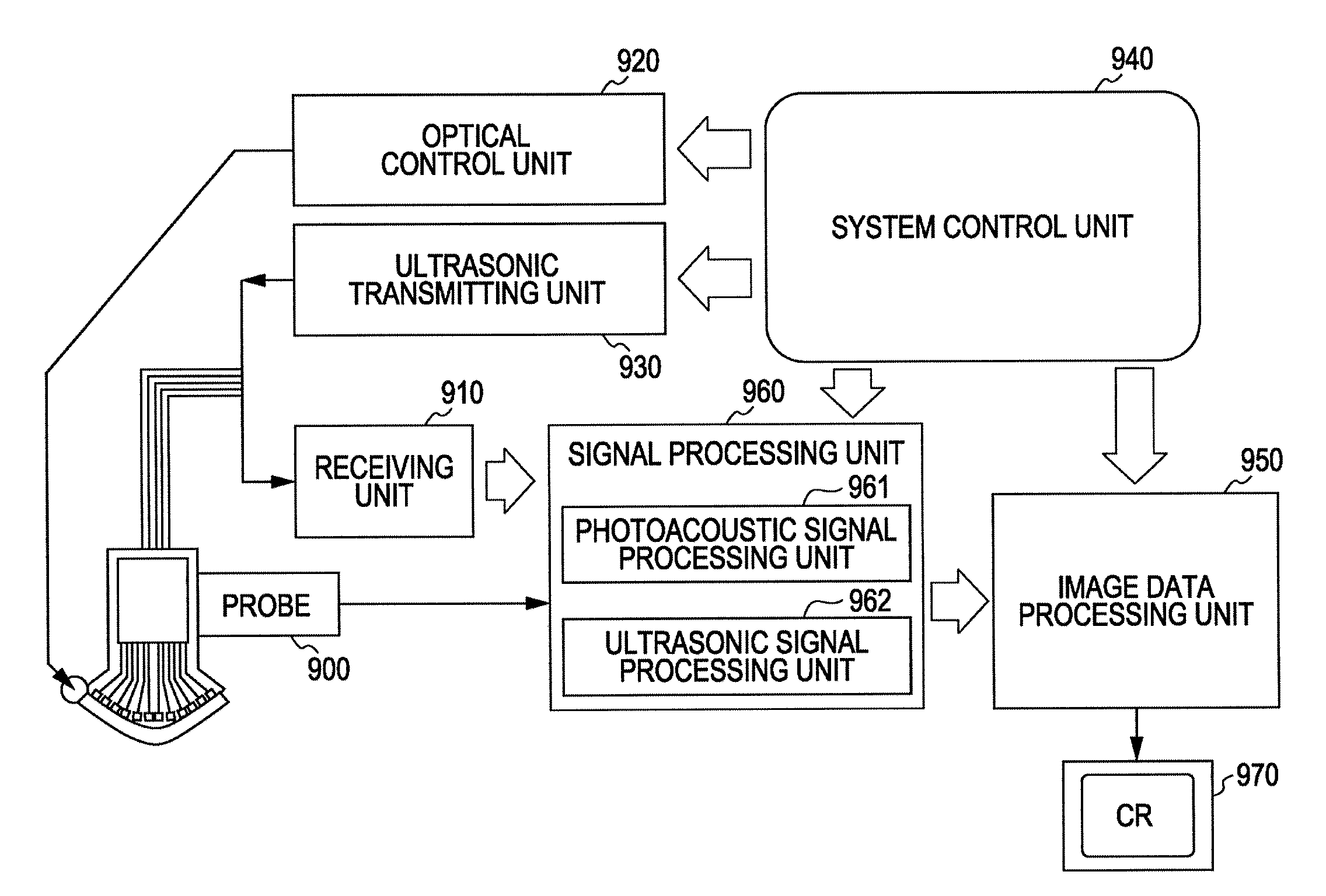
Ultrasonic probe and inspection apparatus equipped with the ultrasonic probe
a technology of ultrasonic probe and inspection apparatus, which is applied in the direction of tomography, applications, instruments, etc., can solve the problems of affecting the satisfaction of the demand by itself, and the difficulty of fabricating the ultrasonic prob
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
first exemplary embodiment
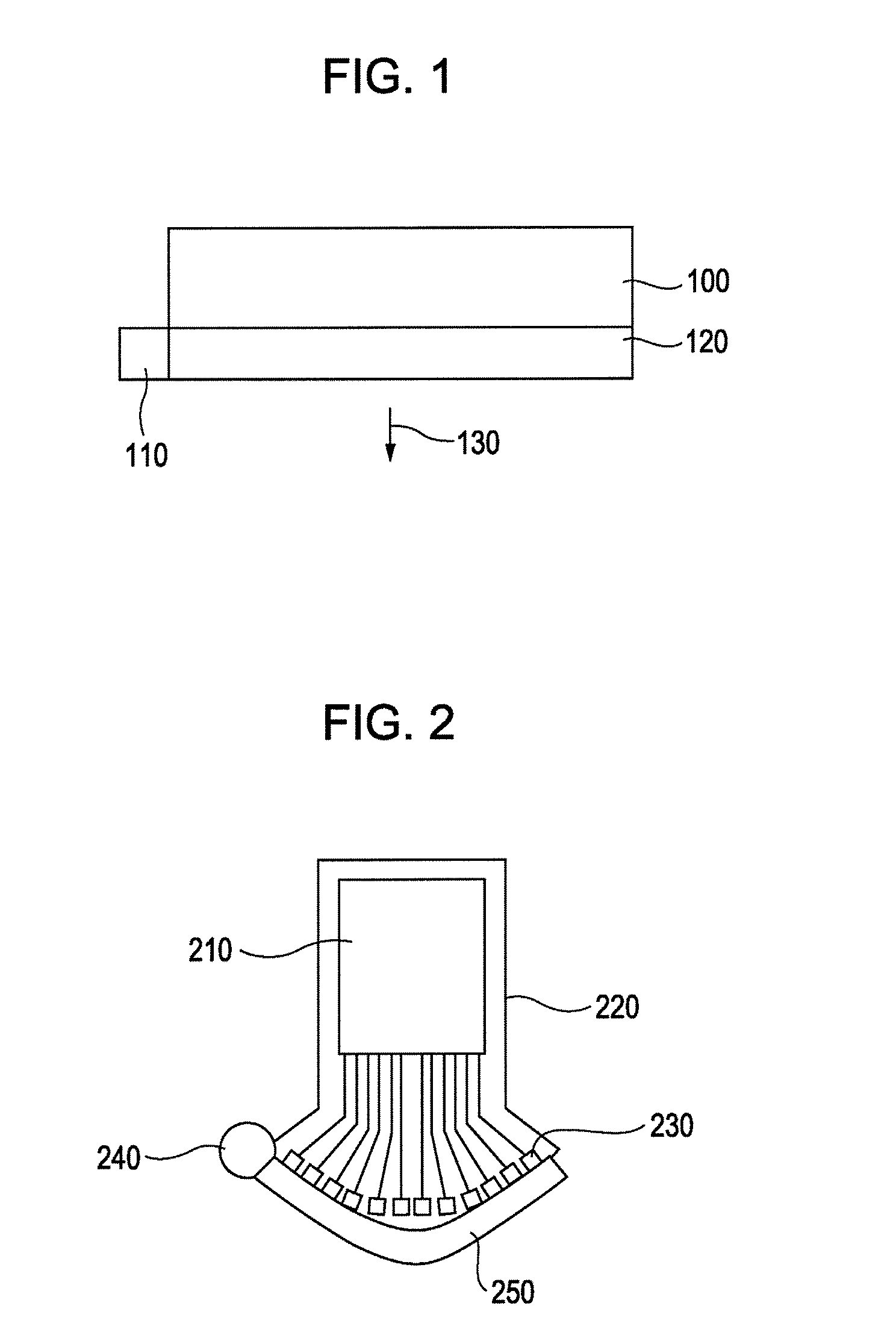
[0041]An ultrasonic probe according to a first exemplary embodiment of the present invention will be described with reference to FIG. 1.
[0042]In FIG. 1, numeral 100 denotes an ultrasonic probe, 110 denotes a light source, 120 denotes a diffusion plate for diffusing light, and 130 denotes an irradiated light.
[0043]More specifically, as shown in FIG. 1, the diffusion plate 120 for diffusing light is disposed on the ultrasonic receiving surface side, and the light is radiated through the diffusion plate 120 in a direction opposed to the direction in which ultrasonic transducing portions receive ultrasonic waves.
[0044]The present invention is intended to minimize a physical distance between an inspection target, e.g., a living body, and a light source and a physical distance between the inspection target and the ultrasonic probe, thus reducing attenuations of both the light radiated from the light source and the ultrasonic waves generated from the inside of the living body, which are ca...
second exemplary embodiment
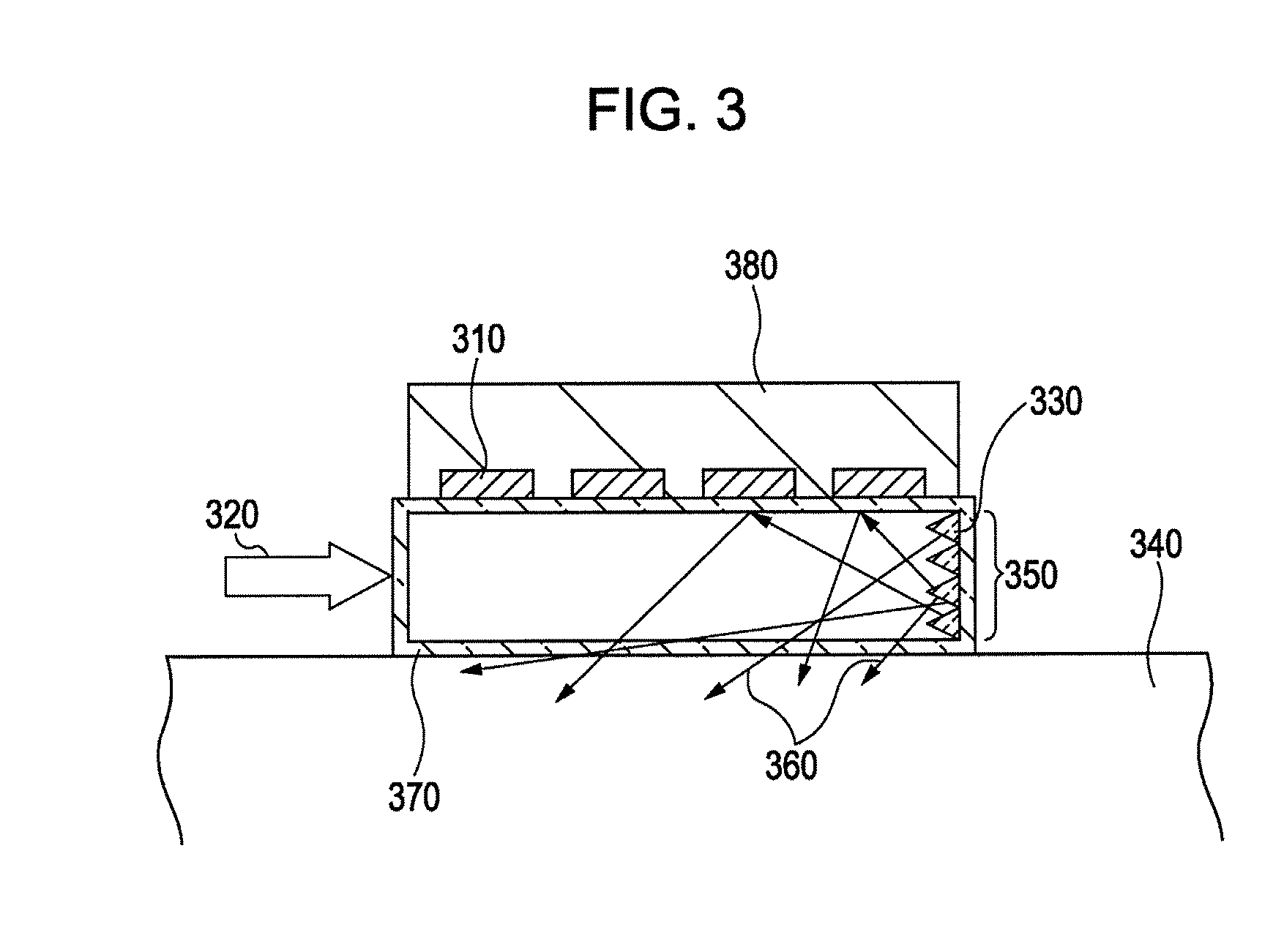
[0066]An ultrasonic probe according to a second exemplary embodiment of the present invention will be described with reference to FIG. 3. FIG. 3 is a schematic sectional view illustrating the ultrasonic probe according to the second exemplary embodiment.
[0067]In FIG. 3, the ultrasonic probe comprises an ultrasonic transducing portion 310, such as a piezoelectric transducer or a CMUT, an input light (laser) 320 introduced from a light source, a scatterer 330, an inspection target 340, an end surface 350 of a light guide member 370, a laser beam 360, the light guide member 370, and a substrate 380 of the ultrasonic probe.
[0068]On one side of the substrate 380 of the ultrasonic probe, the ultrasonic transducing portions 310 are arranged in a two-dimensional array. For example, the substrate 380 has a 3-cm square shape, and each of the ultrasonic transducing portions 310 has a 0.5-mm square shape. Those ultrasonic transducing portions 310 are arranged at a pitch of 2 mm in each of the l...
third exemplary embodiment
[0072]An ultrasonic probe according to a third exemplary embodiment of the present invention will be described below with reference to FIGS. 4A and 4B. FIG. 4A is a sectional view of the ultrasonic probe according to the third exemplary embodiment, and FIG. 4B is a plan view.
[0073]On one side of a substrate 400 of the ultrasonic probe, ultrasonic transducing portions 401, such as piezoelectric transducers or CMUTs, are arranged in a two-dimensional array.
[0074]A light guide member 402 is disposed on a surface of the substrate 400 on the side including the ultrasonic transducing portions 401. Terminal ends 403 of optical fibers are fixed to opposite ends of the light guide member 402. The light guide member 402 contacts the inspection target 404 with an acoustic coupling member 405 interposed between them.
[0075]A light 406 having propagated through the optical fibers 403 is introduced into the light guide member 402 from the opposite ends thereof. The light 406 introduced into the li...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| reflectivity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| velocity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com