Method and system for a modular building structure
a modular building and building structure technology, applied in the field of building structures, can solve the problems of increasing the total installed cost of the shed, and the general load capacity of installed shelves is generally limited, and achieves the effects of low factory cost, minimal on-site labor, and rapid and efficient manner
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
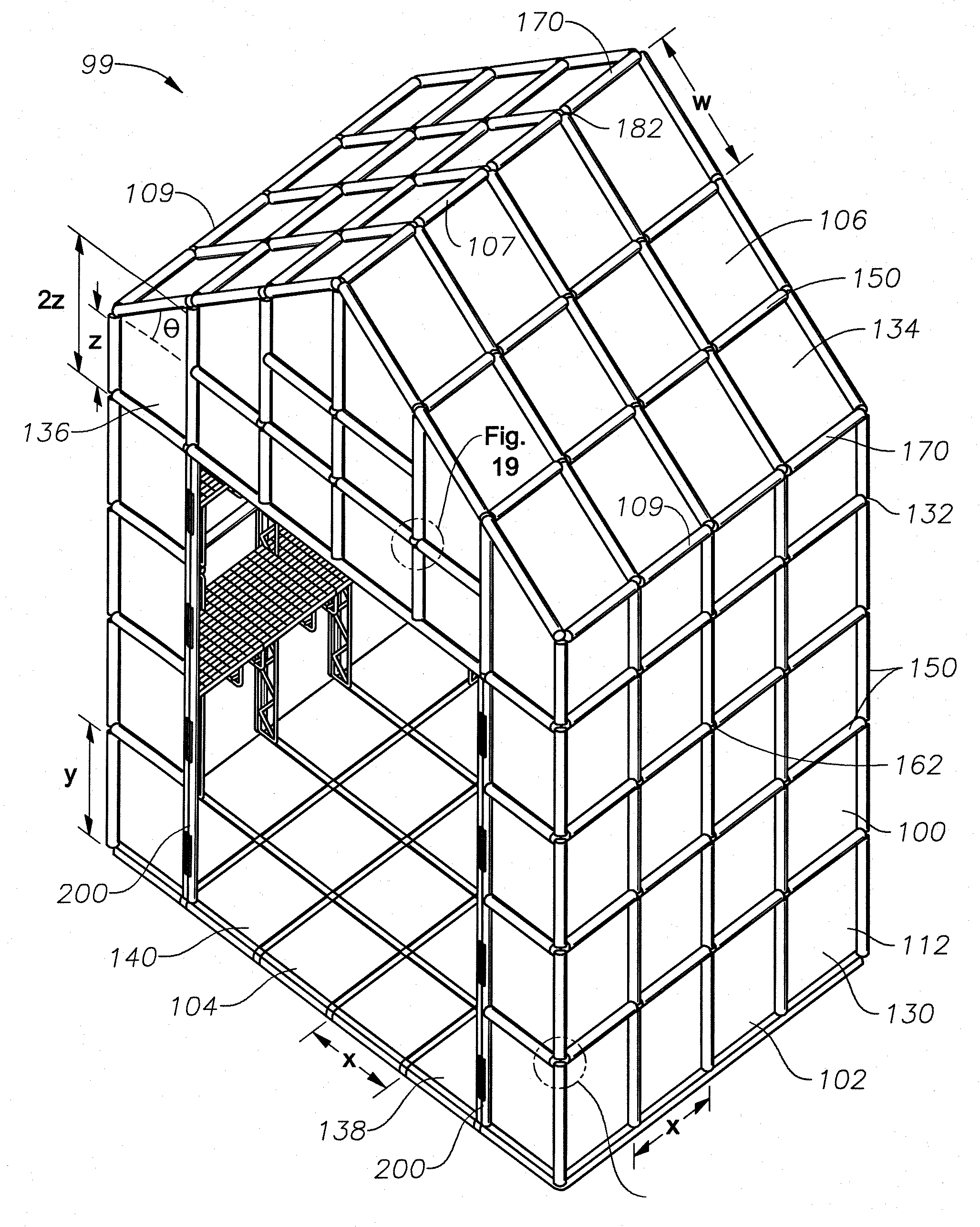
[0053]A preferred embodiment of the invention includes a system of interlocking building components to form a shed 99 as shown in the perspective view of FIG. 14. The building system includes a number of interlocking panels 100, each of which may be used to interchangeably form a portion of a wall surface 102, floor surface 104, ceiling surface (not illustrated), or roof surface 106 of shed 99. Although shed 99 is shown and described herein as having a floor surface 104 formed by interlocking panels, alternative materials, such as a concrete slab, for example, may be used to create the floor surface 104 if desired.
[0054]Referring to FIG. 14, each panel 100 is ideally manufactured in one of five standard sizes to allow buildings of various dimensions and complexities to be built entirely from a limited number of panel sizes. This reduces production and inventory costs. Standard panel types include standard panel 130, short panel 132, elongated roof panel 134, trapezoidal panel 136, a...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com