Manufacturing method and manufacturing apparatus of semiconductor substrate
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
embodiment mode 1
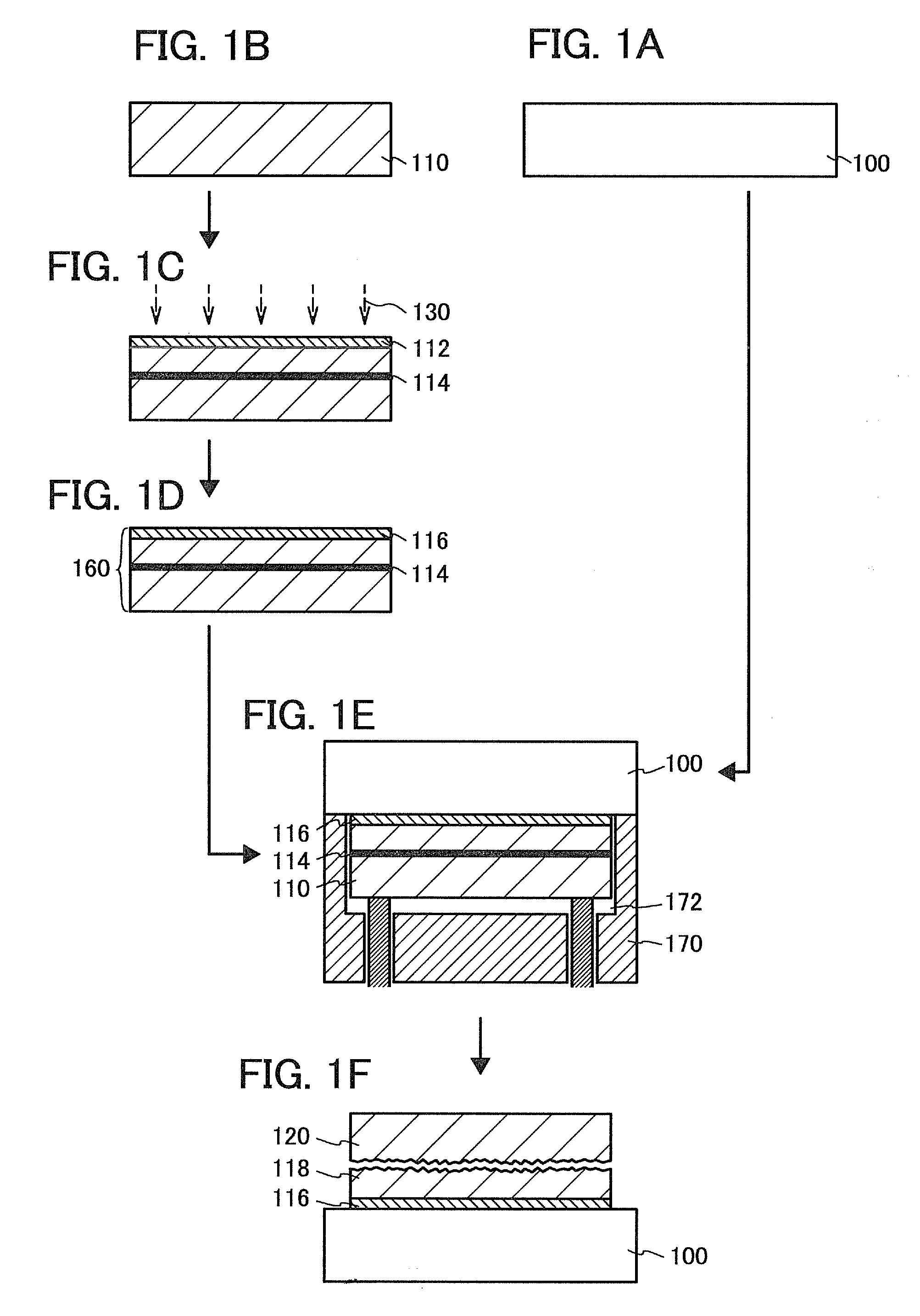
[0048]In this embodiment mode, an example of a manufacturing method of a semiconductor substrate of the present invention will be described with reference to FIGS. 1A to 1F, FIGS. 2A and 2B, FIGS. 3A to 3D, and FIGS. 4A to 4C.
[0049]First, a base substrate 100 is prepared (see FIG. 1A). As the base substrate 100, a light-transmitting glass substrate used for a liquid crystal display device or the like can be used. A substrate having a strain point of greater than or equal to 580° C. (preferably greater than or equal to 600° C.) may be preferably used as a glass substrate. Further, it is preferable that the glass substrate be a non-alkali glass substrate. As a material for the non-alkali glass substrate, a glass material such as aluminosilicate glass, aluminoborosilicate glass, or barium borosilicate glass is used, for example.
[0050]Note that, as the base substrate 100, in addition to the glass substrate, an insulating substrate which is formed of an insulating material, such as a cer...
embodiment mode 2
[0102]In this embodiment mode, a manufacturing method of a semiconductor substrate having a plurality of single crystal semiconductor layers will be described with reference to FIGS. 5A and 5B and FIGS. 6A to 6D. Note that there are many common points between the manufacturing method of a semiconductor substrate of this embodiment mode and the manufacturing method of a semiconductor substrate of Embodiment Mode 1. Therefore, in this embodiment mode, different points will be mainly described and the descriptions of the common points are partially omitted.
[0103]First, by the method described in Embodiment Mode 1, the base substrate 100 and the single crystal semiconductor substrate 110 are processed (see FIGS. 1A to 1D). Note that in this embodiment mode, a case will be described in which a plurality of single crystal semiconductor layers is provided over the base substrate 100. That is, it needs to be noted that since a plurality of single crystal semiconductor substrates 110 is used...
embodiment mode 3
[0124]In this embodiment mode, another example of a manufacturing method of a semiconductor substrate having a single crystal semiconductor layer will be described with reference to FIGS. 7A to 7C. Note that in this embodiment mode, a state of bonding and an apparatus for bonding will be briefly described.
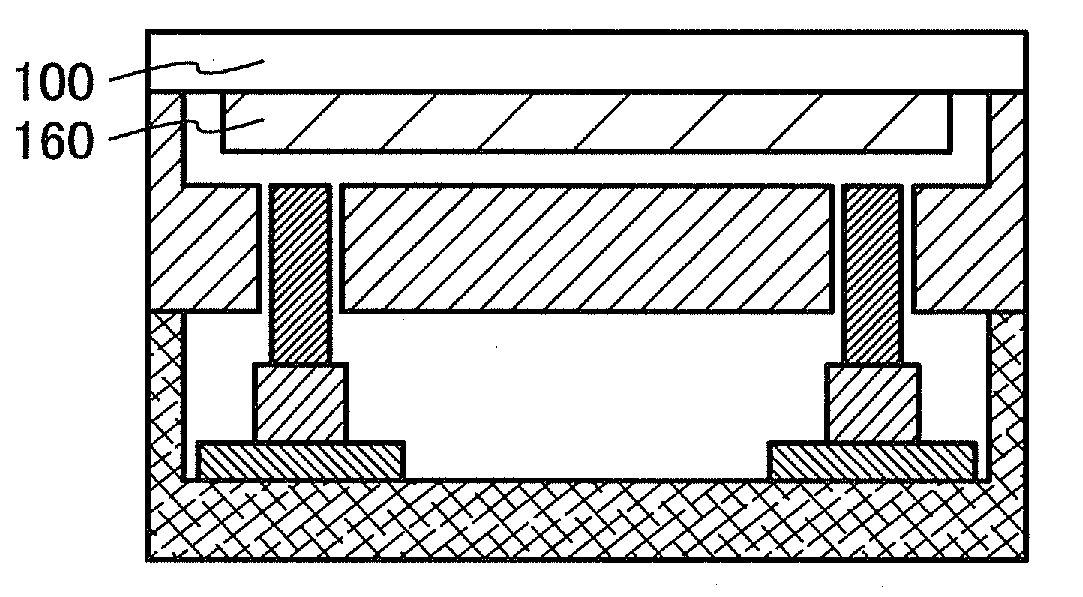
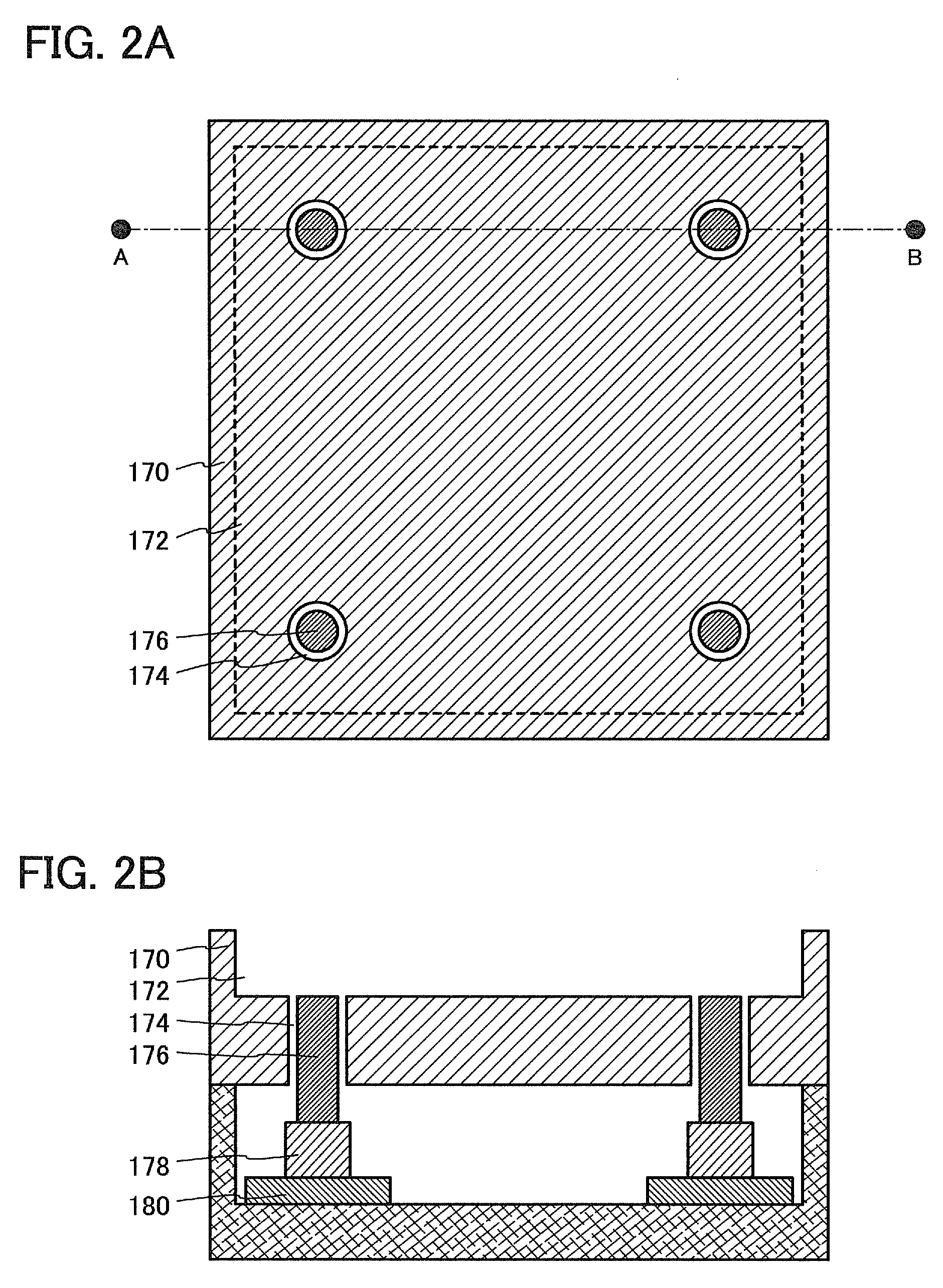
[0125]FIG. 7A illustrates an example of a state of bonding and an apparatus for bonding in this embodiment mode. Here, the substrate 160 is disposed in a substrate arrangement region 772 of a substrate supporting base 770 and the base substrate 100 is fixed with the use of a mechanism 700 having substrate supporting mechanisms 776 and raising and lowering mechanisms 778. Here, the substrate supporting mechanism 776 includes a mechanism which adsorbs the base substrate 100. That is, in FIG. 7A, the base substrate 100 is not in contact with the substrate supporting base 770. In bonding, the base substrate 100 is lowered by the substrate supporting mechanisms 776 and the raising and l...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Pressure | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com