Structural element and methods of use thereof
a structural element and structural technology, applied in the field of structural elements and structural components, can solve the problems of poor underside surface finish, large cost of existing construction systems using pre-cast elements, and large cost of pre-cast elements
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
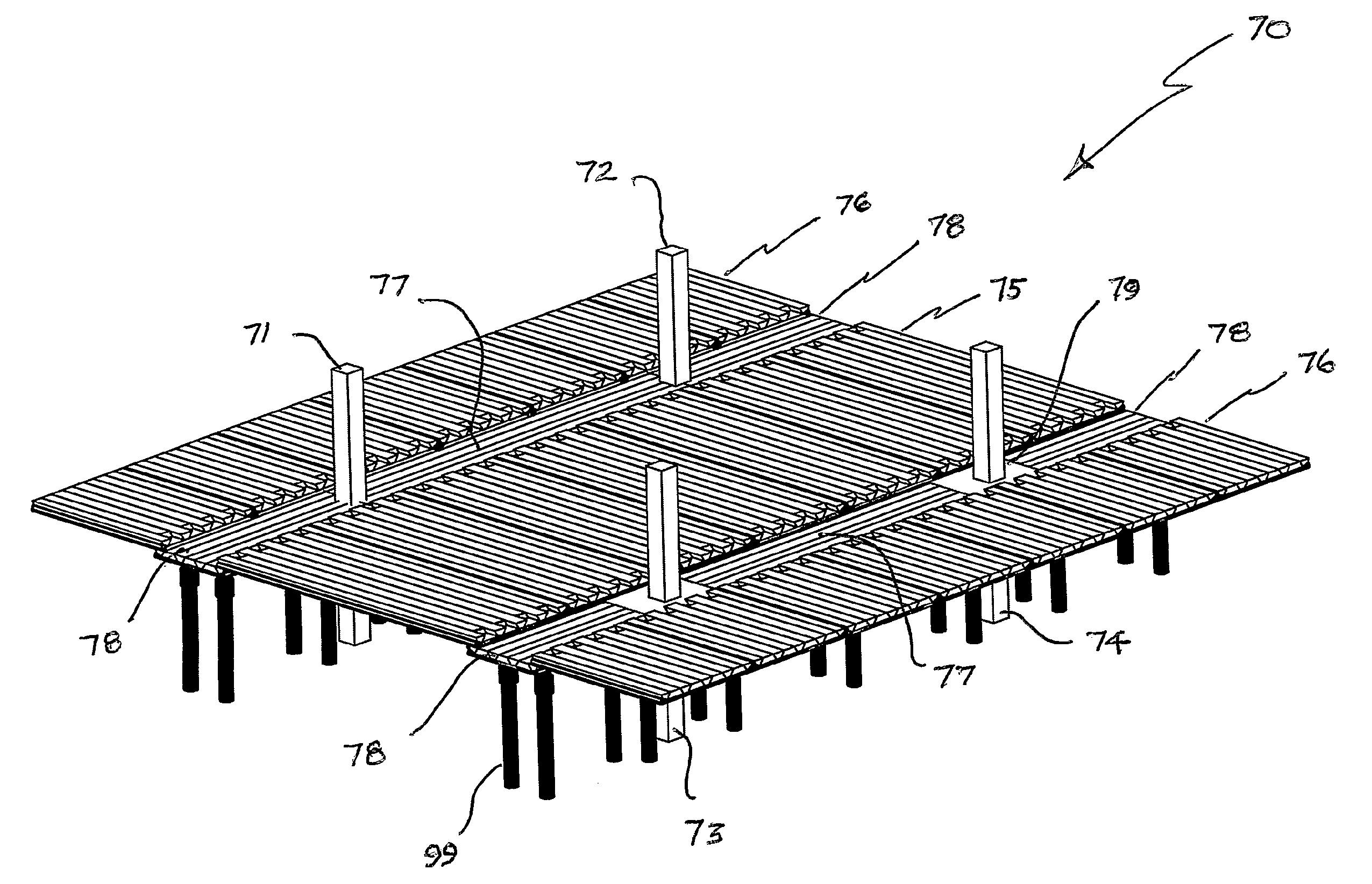
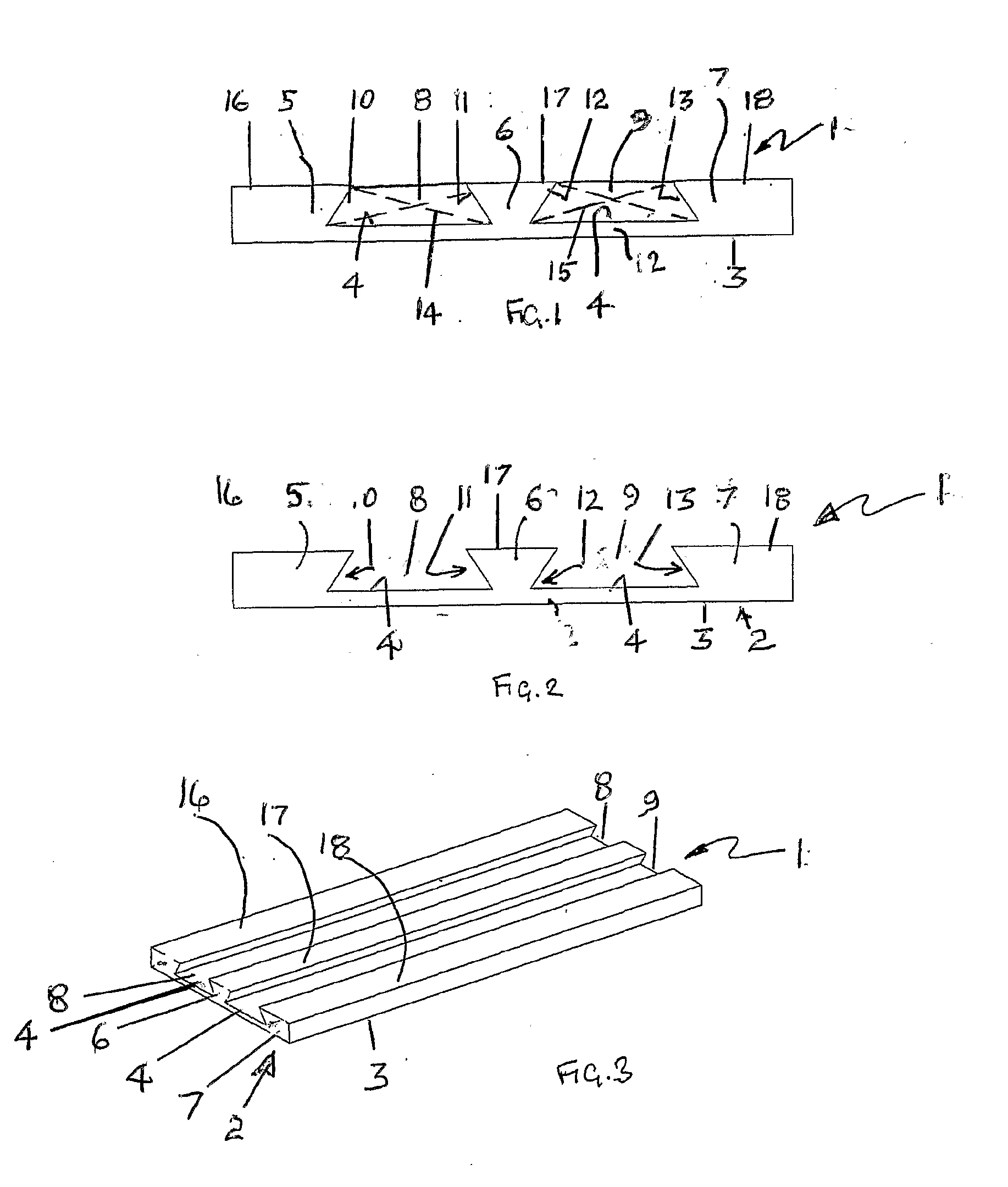
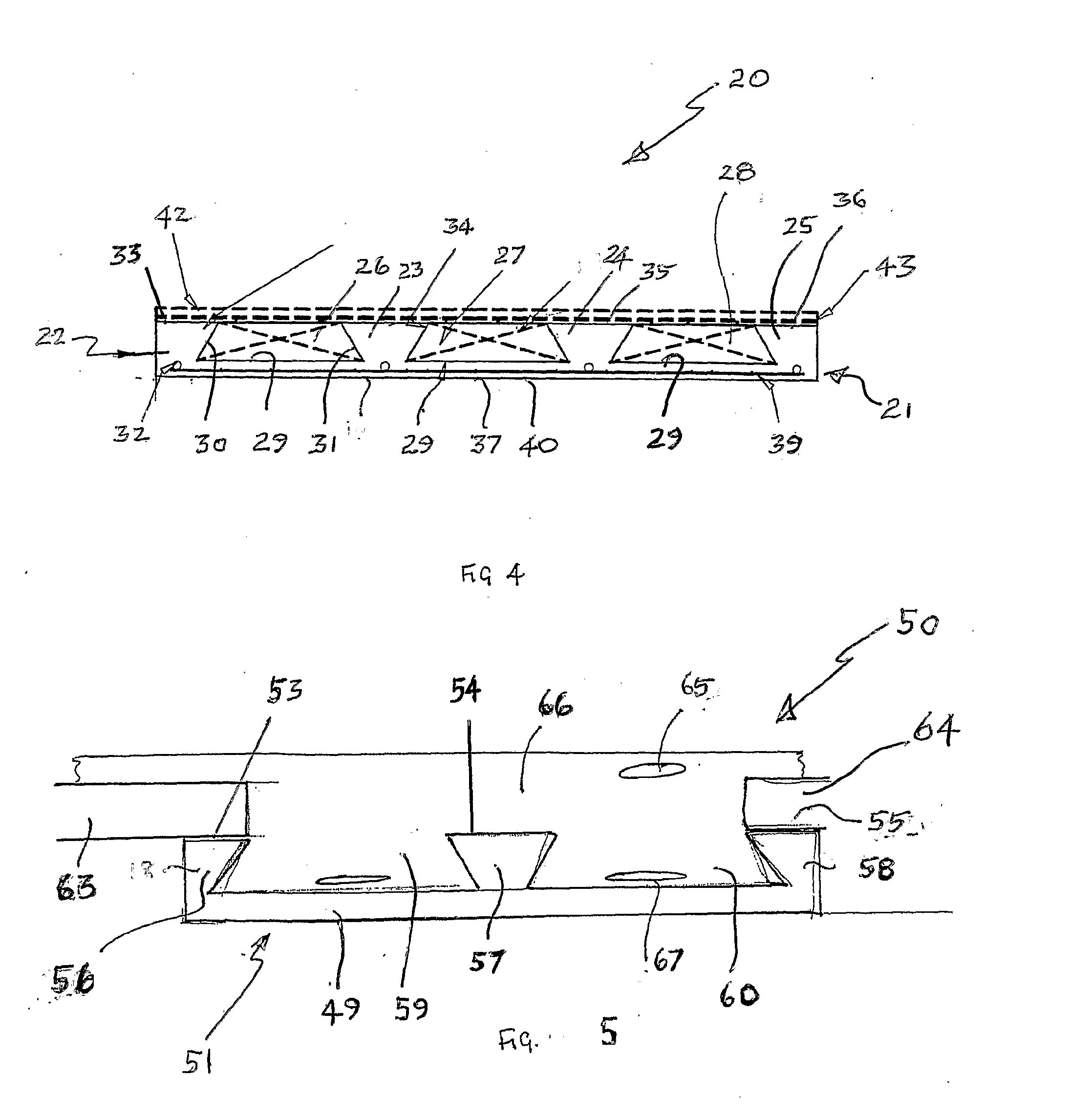
[0068]FIG. 1 shows an end view of a pre-cast concrete element 1 comprising a base 2 having an underside surface 3 and upper surface 4. Element 1 further comprises formations 5, 6 and 7 which define void spaces 8 and 9. Void 8 is defined by upper surface 4 and side walls 10 and 11. Void 9 is defined by upper surface 4 and side walls 12 and 13. In the embodiment of FIG. 1 voids 8 and 9 are filled with polystyrene or similar lightweight material which maintains a lighter weight than an equivalent element with voids filled with concrete or cement. Element 1 typically includes reinforcing (not shown) in base 2, typically reinforced with steel bars or prestressed reinforcement above which two or more polystyrene void formers 14 and 15 preferably in the shape of an isosceles trapezium are located.
[0069]Formations 5, 6 and 7 comprise ribs with longitudinal extent and whose width increases as the distance from surface 4 increases so that there is more material at the top of the formations 5,...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com