Martensitic Creep Resistant Steel Strengthened by Z-Phase
a martensitic or martensiticferritic steel alloy technology, applied in the field of martensitic or martensiticferritic steel alloys, can solve the problems of unexpected breakdown of creep strength to strength levels below those of the currently available steels, high temperature properties of materials used in boilers, steam lines and turbines, etc., to achieve the effect of improving long-term creep properties
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
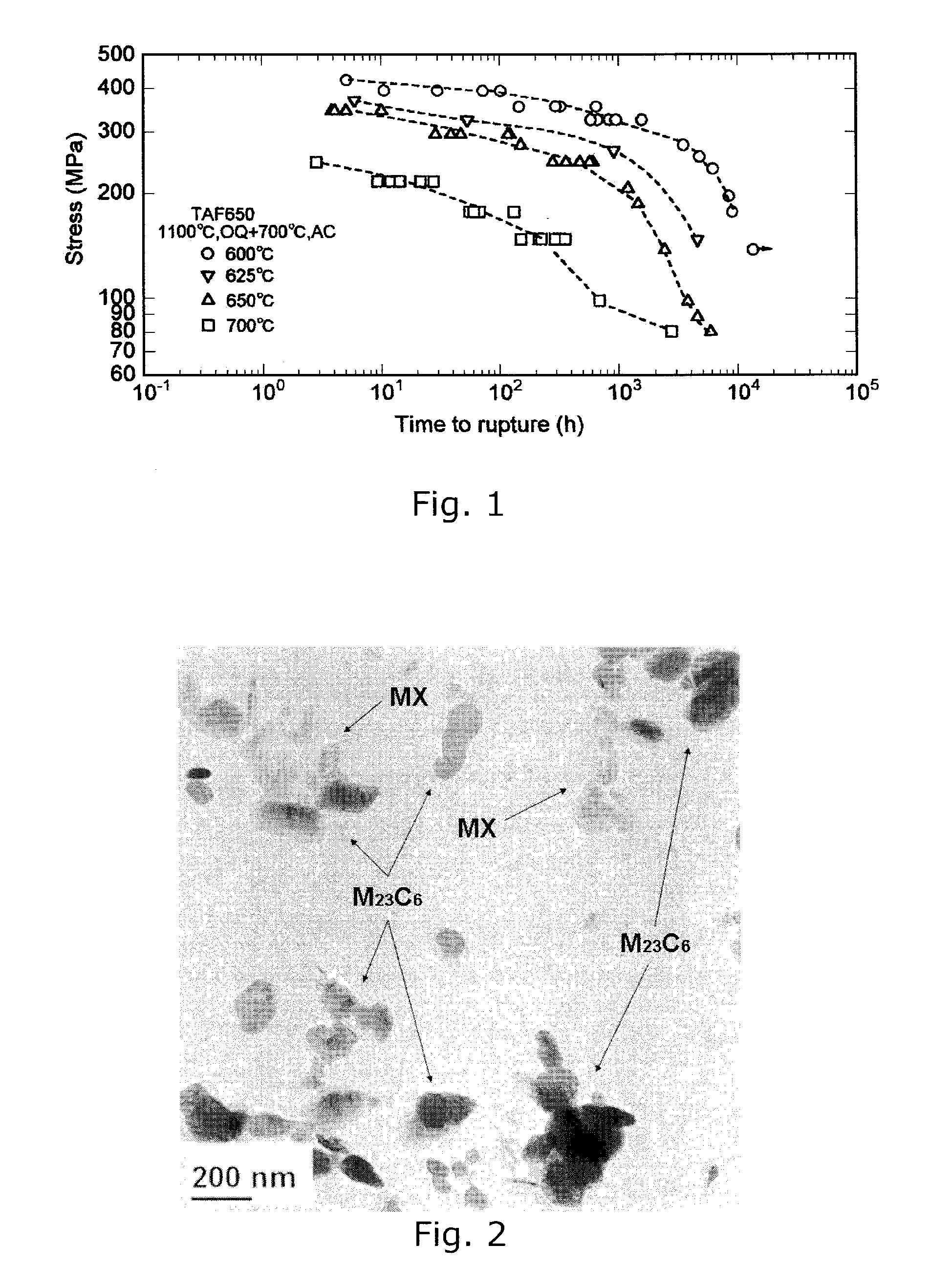
[0026]Components for use in power plants should be designed to operate at high temperatures and stresses for very long times, preferably more than 30 years. It is not practical to test new materials for so long, and therefore long-term properties are estimated by extrapolating results from shorter-term tests. Double logarithmic plots of test stress vs. rupture time normally show smooth curves, but many 11-12% Cr steels suffer a breakdown in long-term strength and the curves bend after several thousand hours of testing. An example of such bent curves is given in FIG. 1, showing creep test results for a steel with 0.1% C, 11% Cr, 3% Co, 3% W, and minor contents of V, Nb and N.
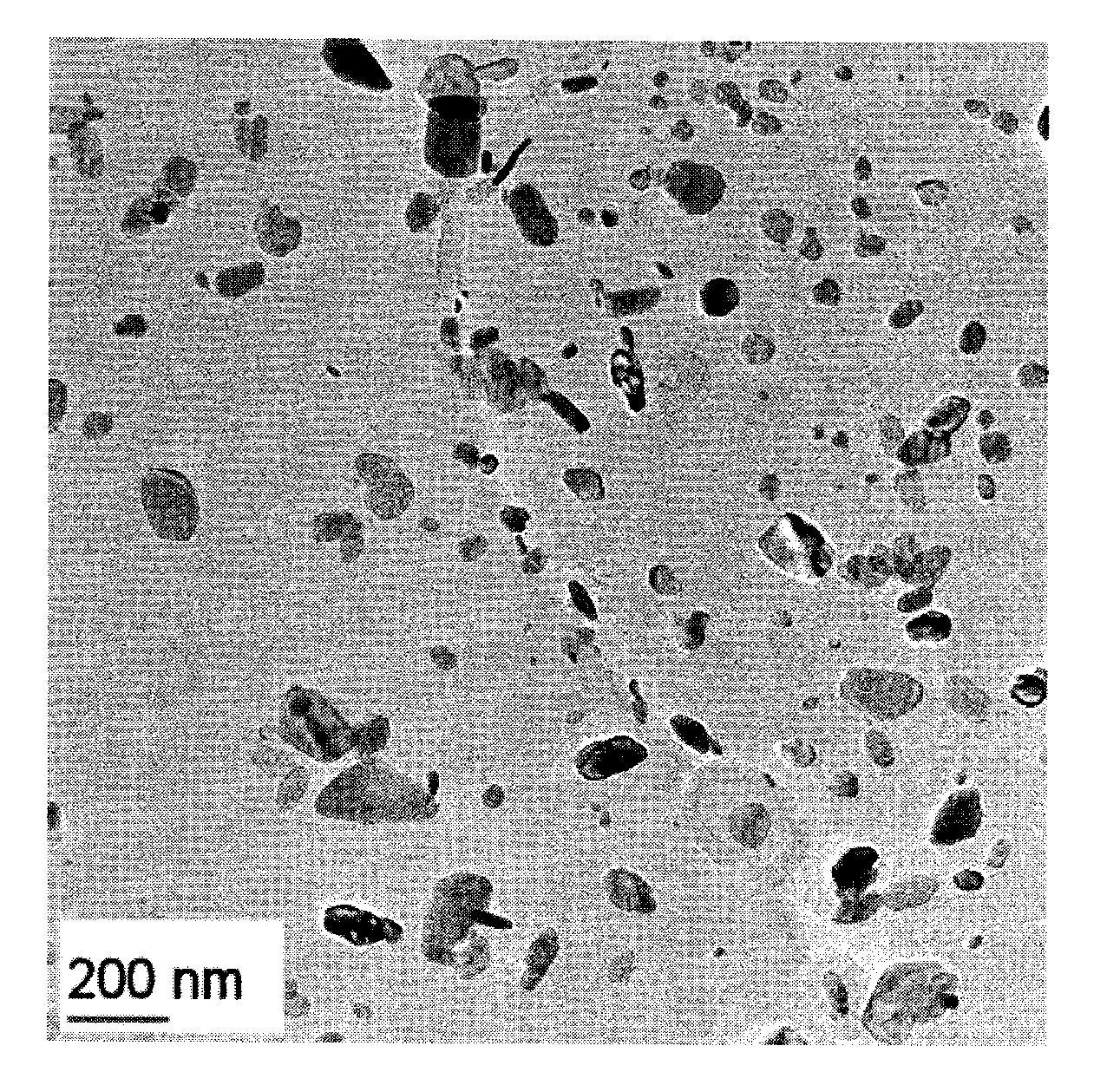
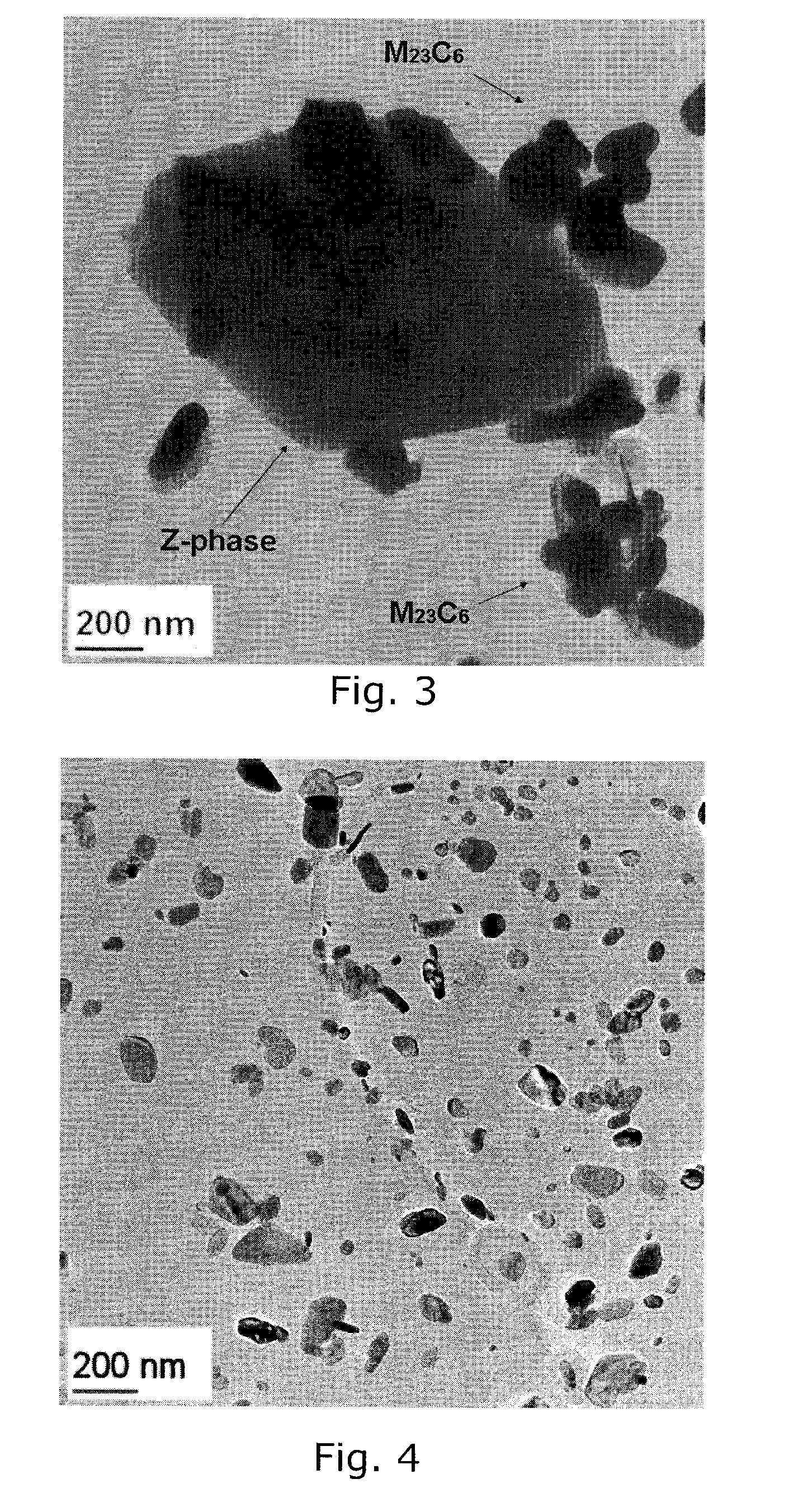
[0027]High long-term creep strength of steel alloys has recently been obtained by compositions resulting in precipitation of fine MX nitride particles in the form (V,Nb)N in addition to coarser M23C6 carbide particles. An example of such an alloy is given in FIG. 2, which shows particles in a steel with 0.1% C, 9...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com