Systems and Techniques for Suppressing Backward Lasing in High-Power Cascaded Raman Fiber Lasers
a cascaded raman fiber laser, high-power technology, applied in the direction of laser details, active medium shape and construction, basic electric elements, etc., can solve problems such as component failure, and achieve the effects of preventing light power buildup, low loss, and high loss
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
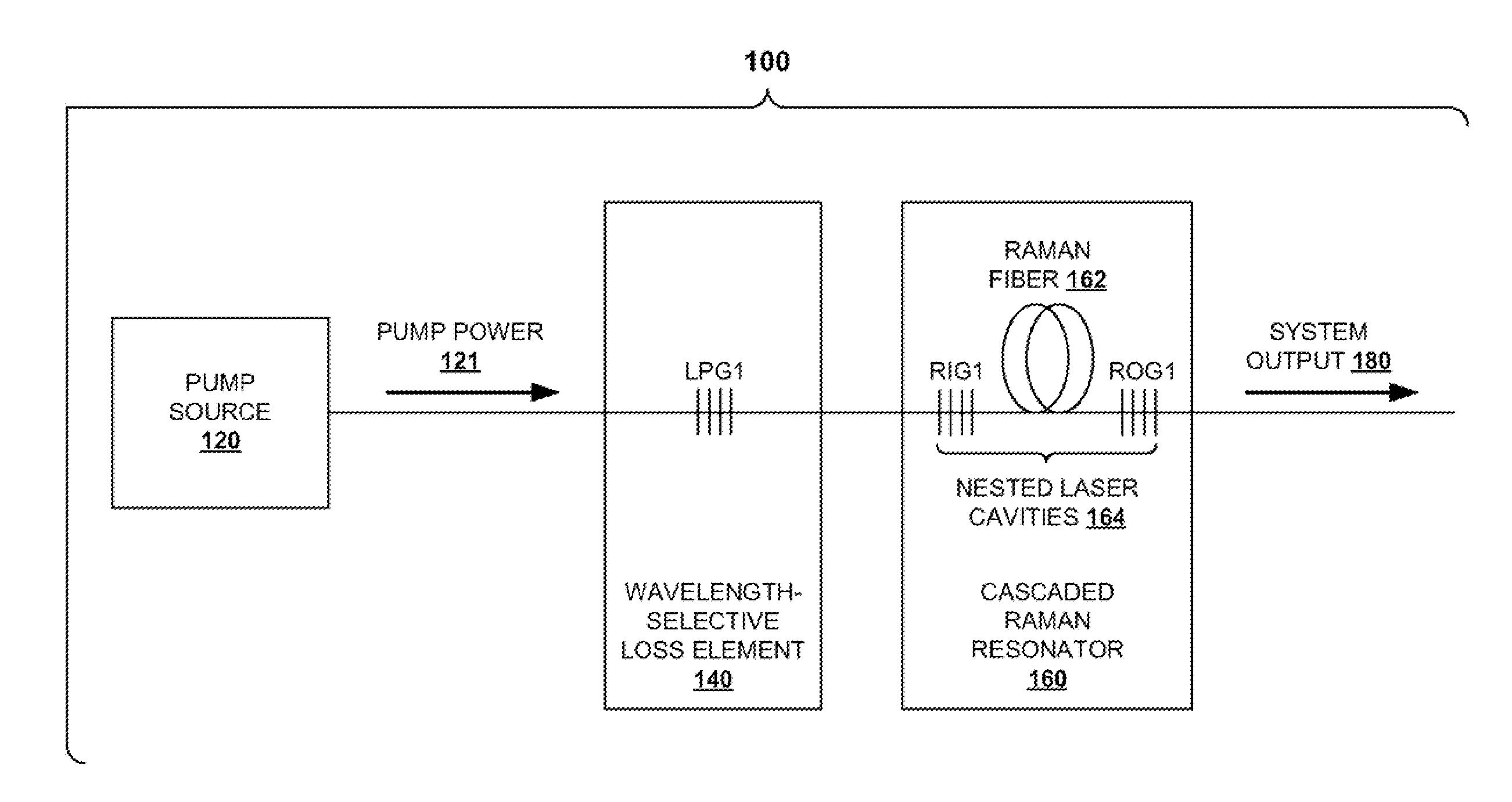
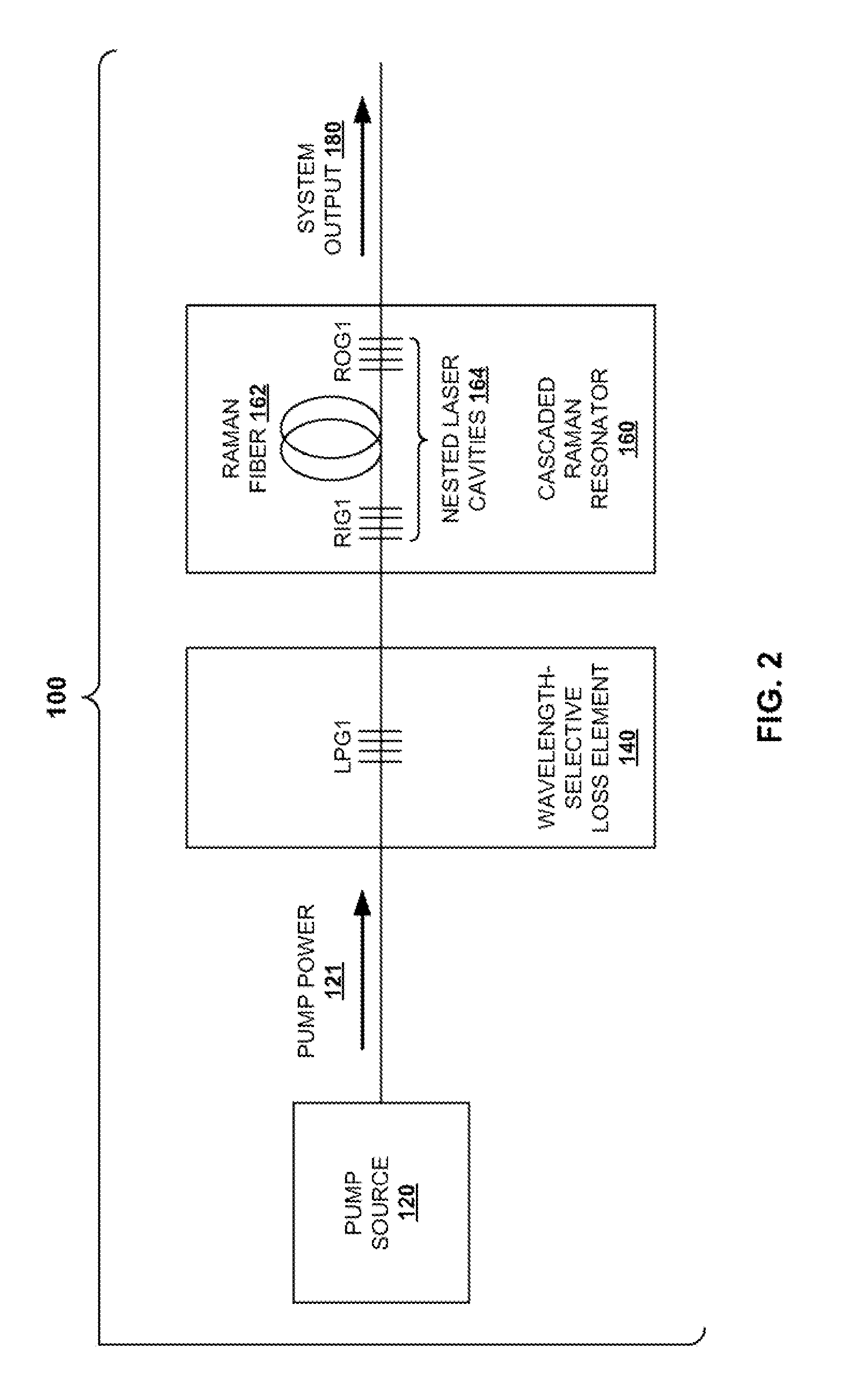
[0024]An aspect of the invention provides systems and techniques for suppressing backward lasing in high-power cascaded Raman fiber lasers. As described herein, suppression of backward lasing is accomplished by identifying signatures that point to the onset of backward lasing. The identification of these signatures is a very powerful technique. The temporal disturbances caused by backward lasing can lead to pulsing, which can destroy components at higher powers.
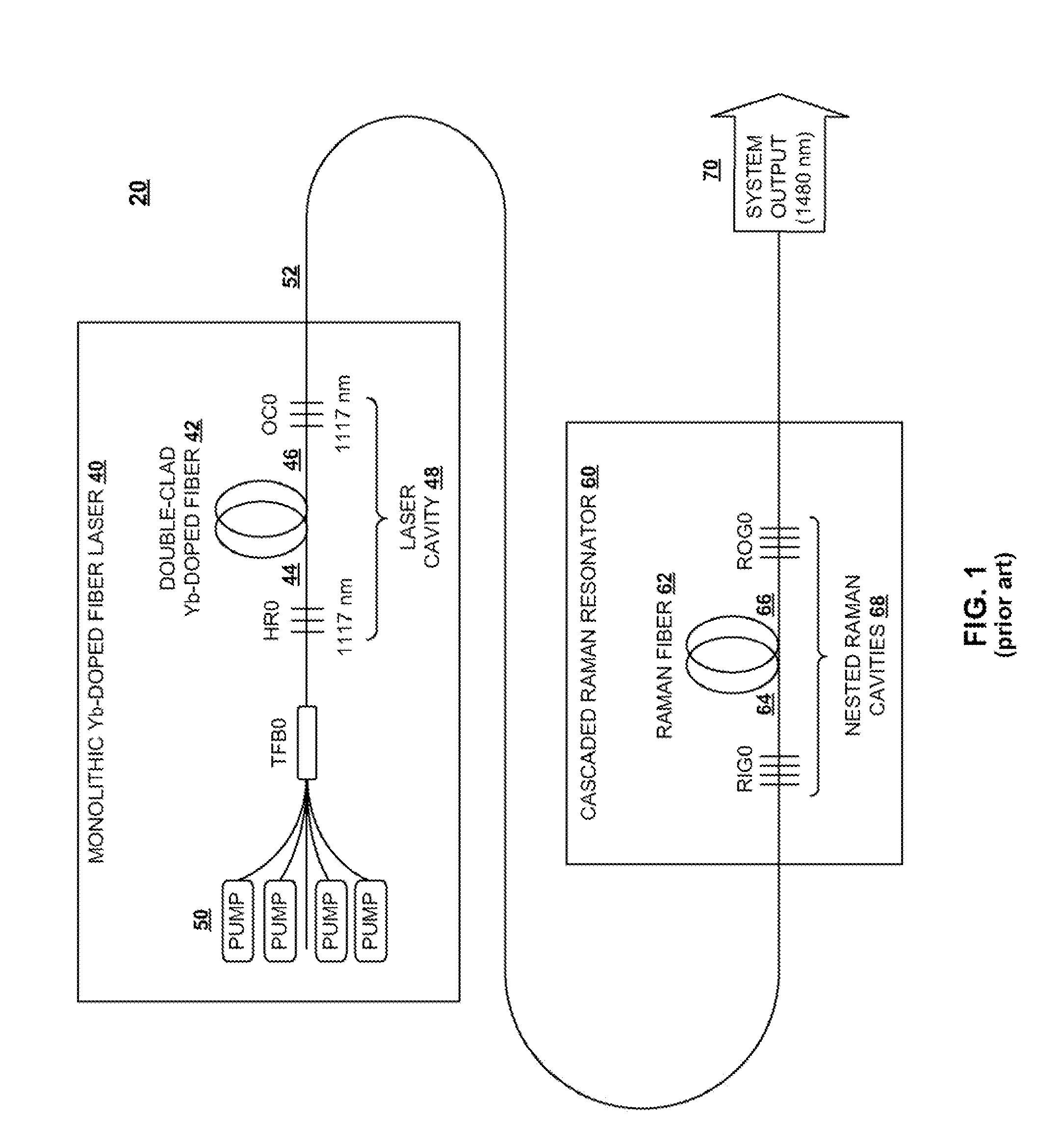
[0025]A further aspect of the invention provides a Raman lasing system in which a wavelength-dependent loss element is used to eliminate backward lasing from a cascaded Raman resonator by frustrating the buildup of radiation at the first Stokes shift. When a system according to the prior art, such as the FIG. 1 system discussed above, is operated at higher powers, this radiation building and backward lasing may result in failure, for example, of the pump laser high reflector (HR) when external devices are connected. According...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com