Continuous fiber nonwoven fabric
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
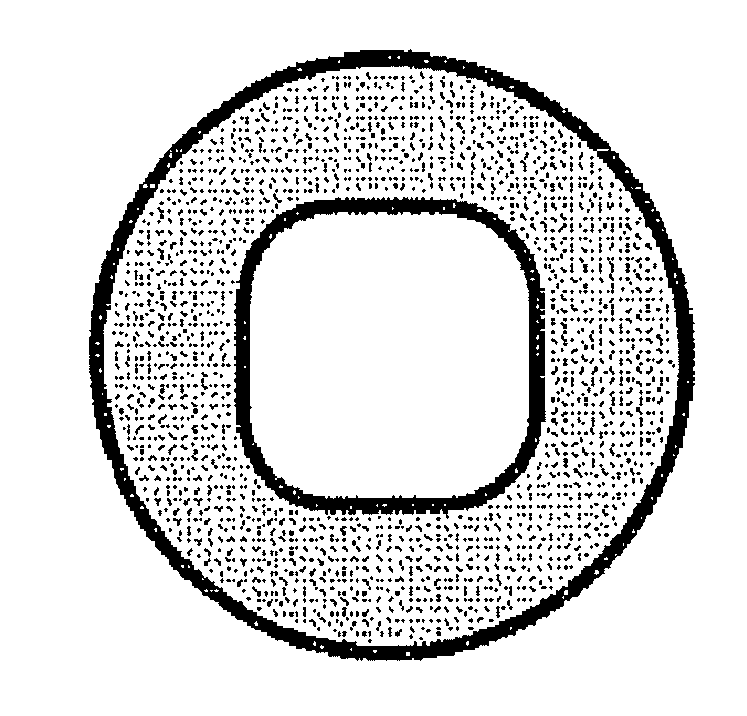
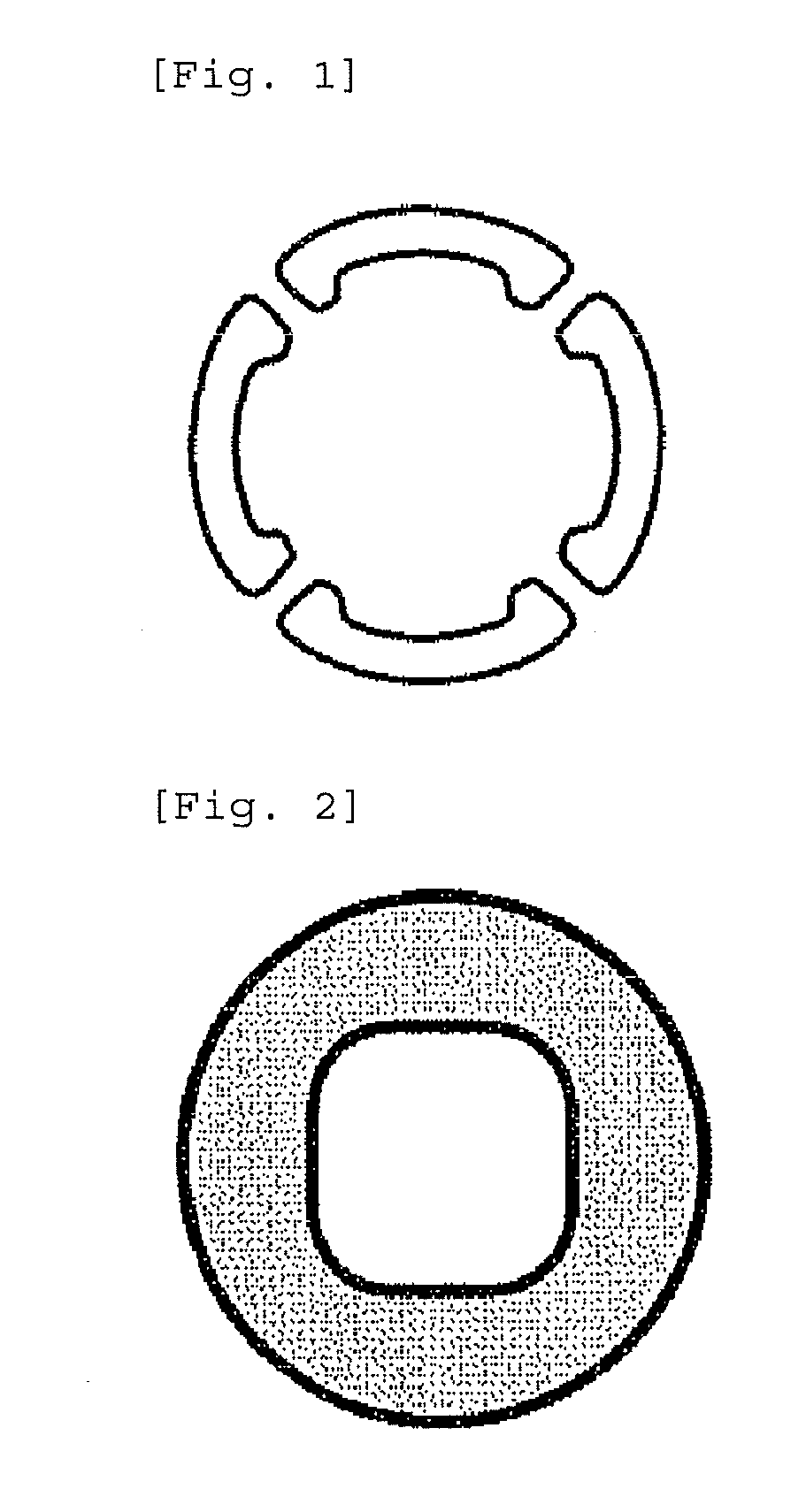
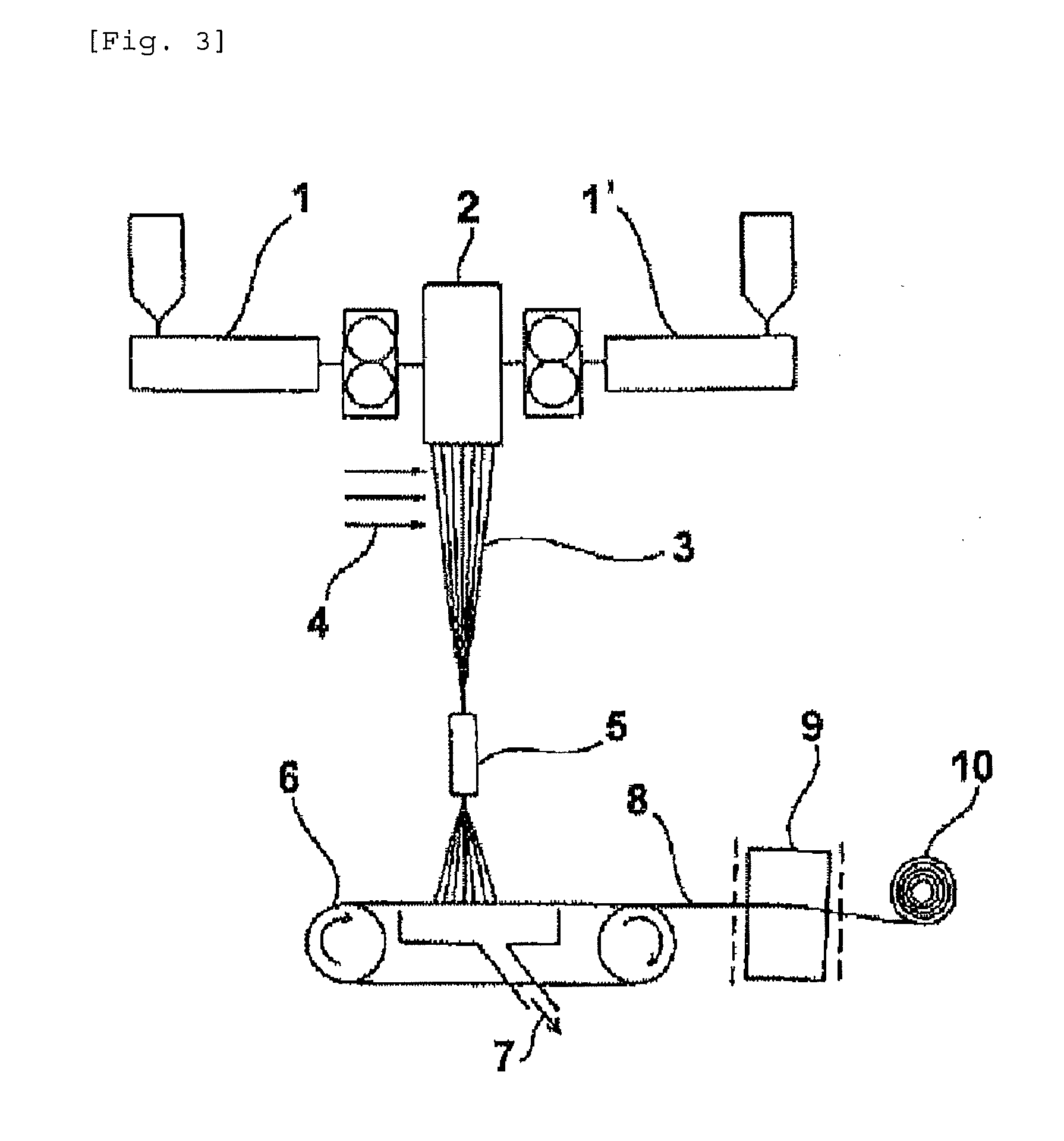
[0053]A propylene polymer used was a propylene homopolymer (PP-1) having a MFR at 230° C. under 2160 g load of 24 g / 10 min [Achieve 3854 manufactured by Exxon Mobil Chemical, Mw / Mn: 2.3, Mz / Mw: 1.8, melting point (Tm): 148° C., produced with metallocene catalyst]. The propylene homopolymer was molten in an extruder (screw diameter: 75 mm) at a shaping temperature of 210° C. The molten polymer was spun with use of a nonwoven fabric manufacturing apparatus (a spunbonding apparatus, 320 mm in length perpendicular to the machine direction on a collecting surface) as illustrated in FIG. 3 which had a spinneret having nozzle pitches 4.5 mm in vertical direction and 4.0 mm in horizontal direction and orifices as illustrated in FIG. 1 capable of giving a fiber cross section as shown in FIG. 2, at a throughput of 0.6 g / min per orifice and a spinning rate of 2550 m / min. The fibers were cooled with 25° C. cooling air and deposited on a collecting belt. The web was thermally pressure treated wi...
example 2
[0056]A propylene polymer used was a propylene homopolymer (PP-2) having a MFR at 230° C. under 2160 g load of 65 g / 10 min [Mw / Mn: 2.6, Mz / Mw: 1.7, melting point (Tm): 155° C., produced with metallocene catalyst]. The propylene homopolymer was molten in an extruder (screw diameter: 75 mm) at a shaping temperature of 190° C.
[0057]The molten polymer was spun with use of a nonwoven fabric manufacturing apparatus (a spunbonding apparatus, 320 mm in length perpendicular to the machine direction on a collecting surface) as illustrated in FIG. 3 which had a spinneret having nozzle pitches 4.5 mm in vertical direction and 4.0 mm in horizontal direction and orifices as illustrated in FIG. 1 capable of giving a fiber cross section as shown in FIG. 2, at a throughput of 0.6 g / min per orifice and a filament velocity of 3158 m / min. The fibers were cooled with 25° C. cooling air and deposited on a collecting belt. The web was thermally pressure treated with an embossing roll (emboss area percenta...
example 3
[0059]A propylene polymer used was a propylene homopolymer (PP-3) having a MFR at 230° C. under 2160 g load of 65 g / 10 min [Mw / Mn: 2.8, Mz / Mw: 1.8, melting point (Tm): 155° C., produced with metallocene catalyst]. The propylene homopolymer was molten in an extruder (screw diameter: 75 mm) at a shaping temperature of 190° C. The molten polymer was spun with use of a nonwoven fabric manufacturing apparatus (a spunbonding apparatus, 320 mm in length perpendicular to the machine direction on a collecting surface) as illustrated in FIG. 3 which had a spinneret having nozzle pitches 4.5 mm in vertical direction and 4.0 mm in horizontal direction and orifices as illustrated in FIG. 1 capable of giving a fiber cross section as shown in FIG. 2, at a throughput of 0.6 g / min per orifice and a filament velocity of 2769 m / min. The fibers were cooled with 25° C. cooling air and deposited on a collecting belt. The web was thermally pressure treated with an embossing roll (emboss area percentage: 2...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Fraction | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Fraction | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com