Method and system for regenerating particulate filter
a technology of particulate filter and regenerative system, which is applied in the direction of machine/engine, separation process, electric control of exhaust gas treatment, etc., can solve the problem of difficult expansion of heat contained in exhaust gas at optional times, achieve effective burning of matter trapped, increase the amount of oxygen, and increase the flow rate of compressed air
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
first embodiment
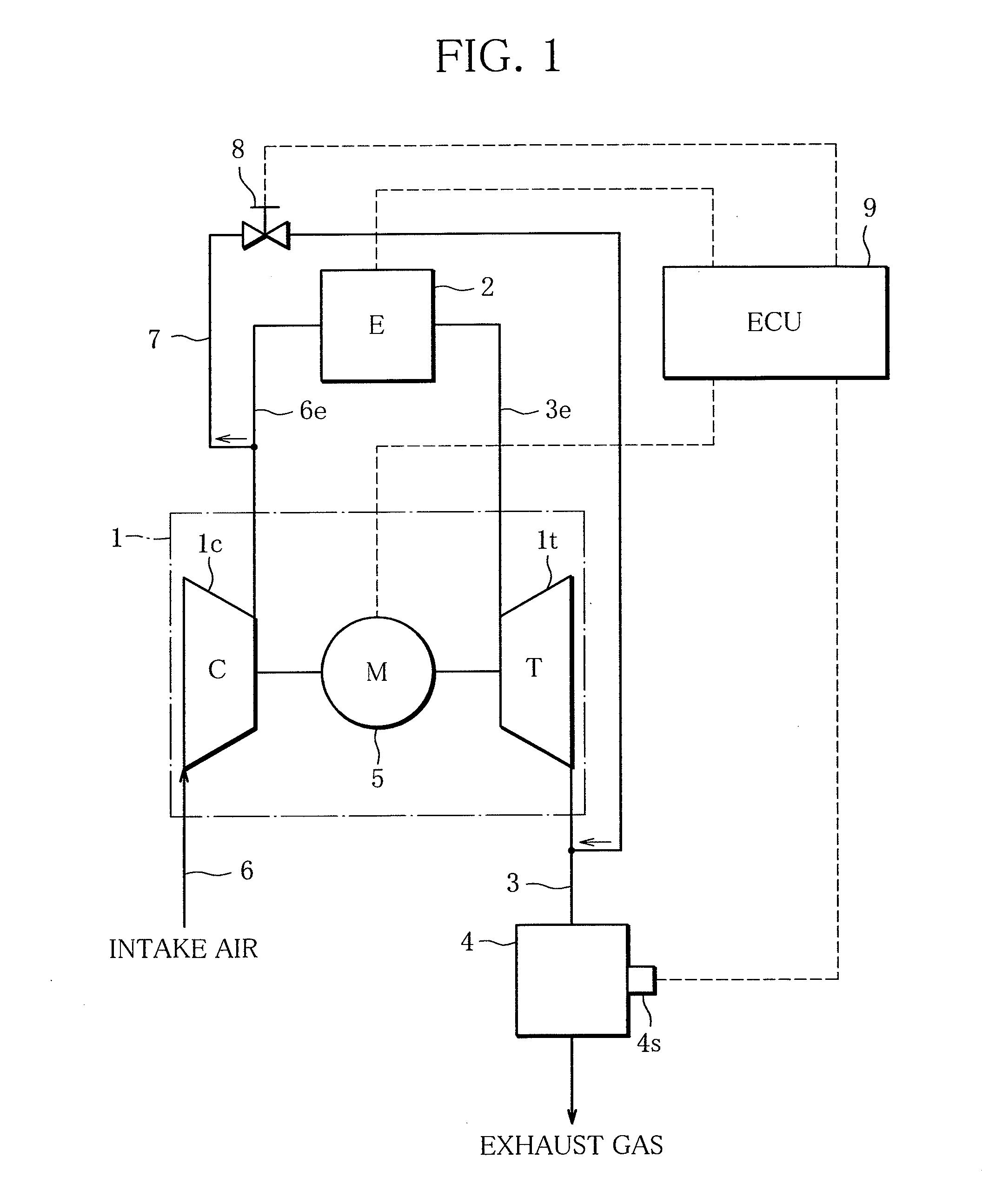
[0022]Referring to FIGS. 1 to 8, embodiments of the present invention will be described. FIG. 1 is a diagram schematically showing a configuration of particulate filter regeneration system according to the present invention.
[0023]The particulate filter regeneration system according to the present invention shown in FIG. 1 is designed to regenerate a particulate filter 4 arranged in an exhaust line 3 of an engine (internal combustion engine) 2 equipped with a turbocharger 1 by raising the temperature of exhaust gas, thereby burning matter trapped on the particulate filter 4 at times that the particulate filter 4 requires regeneration, and comprises an electric motor 5 functioning as an intake quantity regulation means capable of increasing the flow rate of compressed air without depending on the flow rate of exhaust gas flowing across a turbine 1t of the turbocharger 1, a bypass line 7 connecting a section of an intake line upstream of the engine 2 (an engine intake line 6e) to a sec...
second embodiment
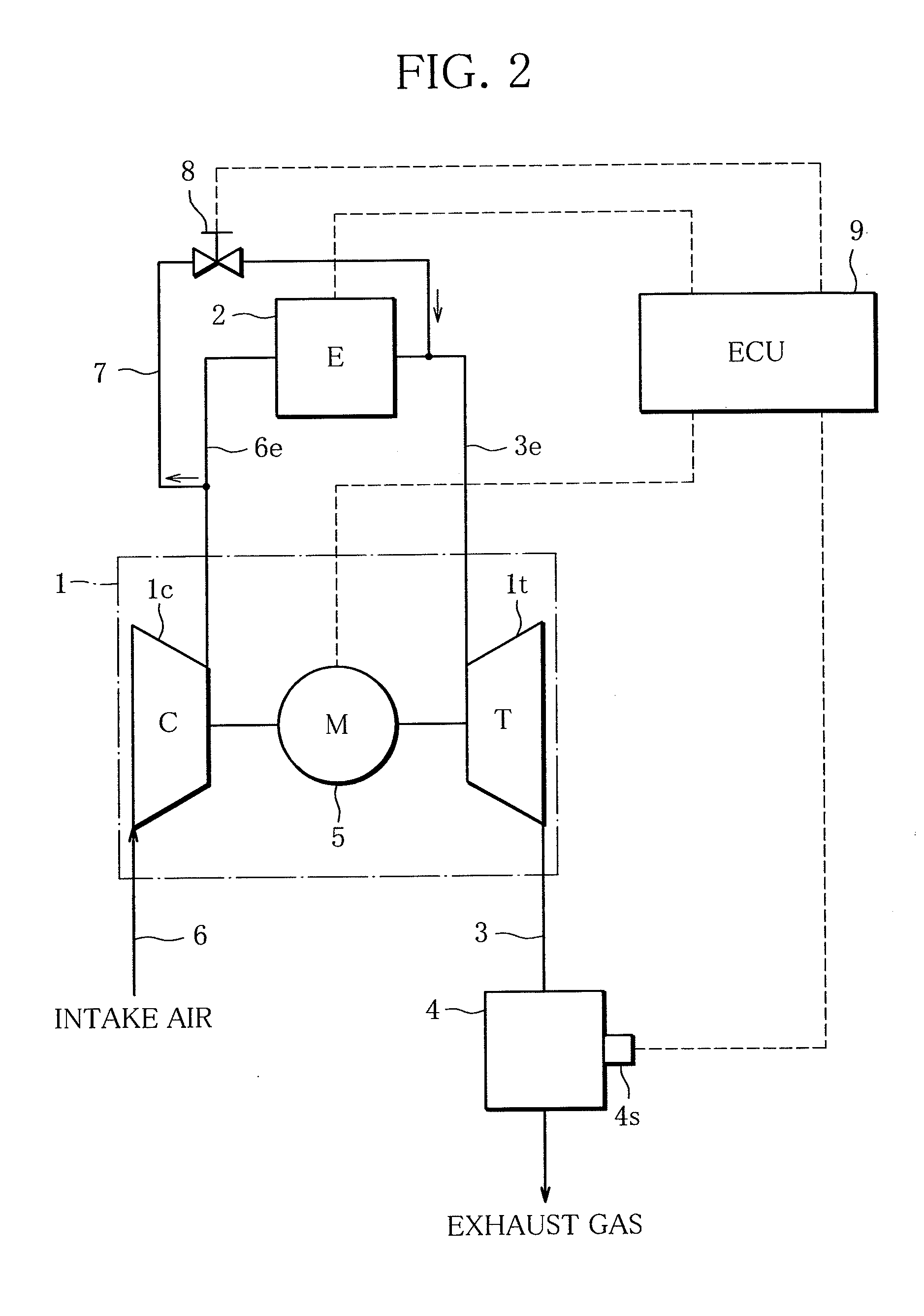
[0037]In the present invention shown in FIG. 2, the outlet of the bypass line 7 is connected to the engine exhaust line 3e. It is desirable that the outlet of the bypass line 7 be connected to the engine exhaust line 3e, immediately after the engine 2. Connecting the bypass line 7 at this position enables burning of unburned fuel in the engine exhaust line 3e, resulting in an increase in heat contained in exhaust gas (exhaust gas energy). In this case, part of the compressed air bypassing the engine is consumed to burn unburned fuel. Thus, the degree to which the flow rate regulation valve 8 is opened is controlled taking account of such consumption.
third embodiment
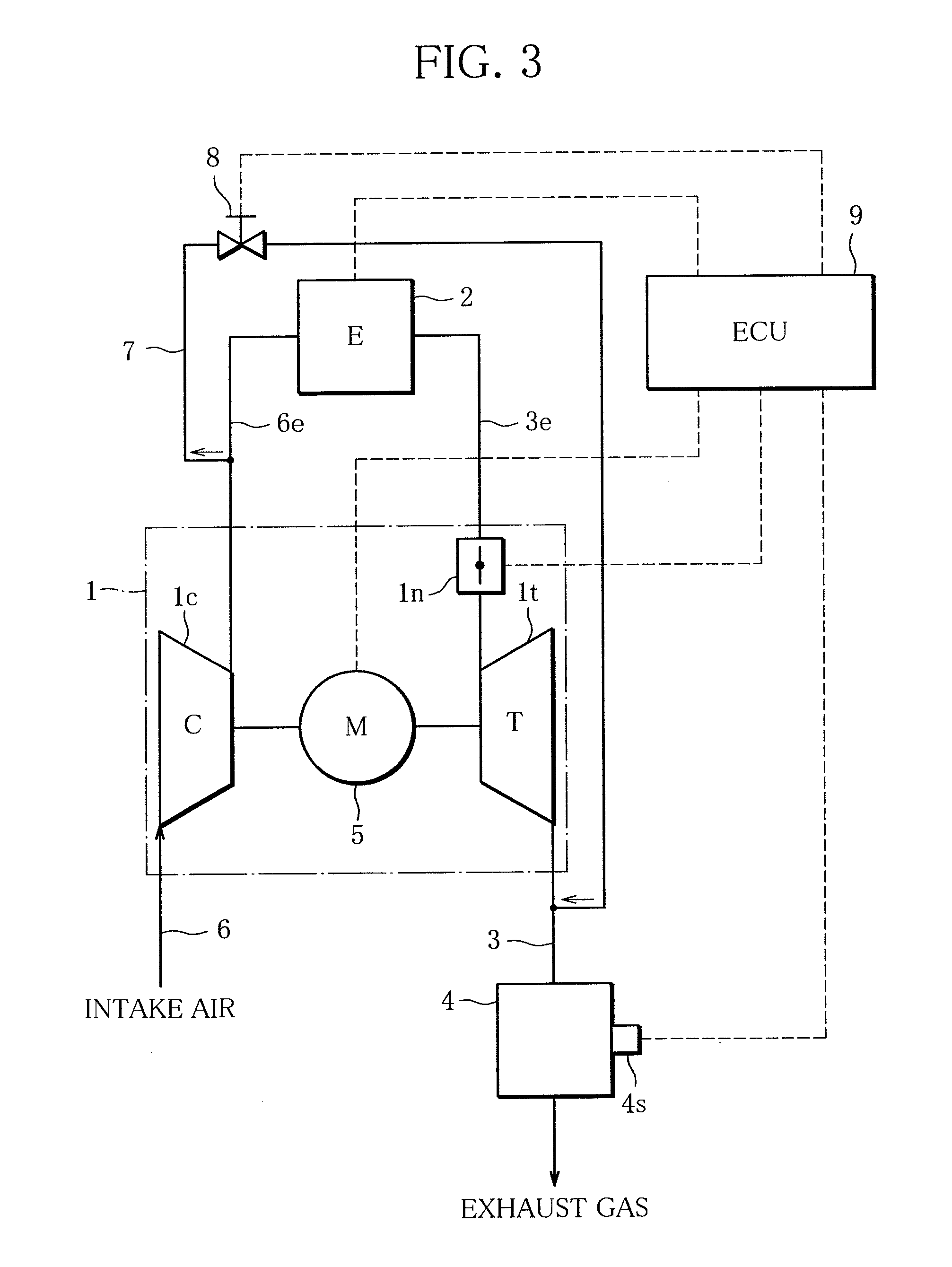
[0038]In the present invention shown in FIG. 3, the turbocharger 1 has a turbine flow regulation means regulating the flow rate of exhaust gas entering the turbine 1t, and the control means 9 regulates the turbine flow regulation means to reduce the energy loss that the exhaust gas suffers in the turbine 1t. In the illustrated example, the turbine flow regulation means consists of a variable nozzle 1n which makes the turbocharger 1a so-called variable displacement turbocharger. The variable displacement turbocharger can control the flow velocity or flow rate of exhaust gas entering the turbine 1t by opening and closing the variable nozzle 1n, thereby controlling the flow rate of compressed air delivered to the engine 2.
[0039]Such variable displacement supercharge 1 can, by itself, cover a wide range of engine 2 operation and provide high supercharging efficiency. The term “variable nozzle 1” is used to encompass all the variable mechanisms which can make the turbocharger 1a variable...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| mass ratio | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| flow rate | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com