Blade deflection measurement with magnetostrictive sensor
a magnetostrictive sensor and blade deflection technology, applied in the direction of instruments, marine propulsion, vessel construction, etc., can solve the problems of large dynamic mechanical load on the rotor blade of the wind turbine, large fatigue load in the root, and damage to the rotor blade, so as to achieve accurate determination
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0056]The illustration in the drawing is schematically. It is noted that in different figures, similar or identical elements are provided with the same reference signs or with reference signs, which are different from the corresponding reference signs only within the first digit.
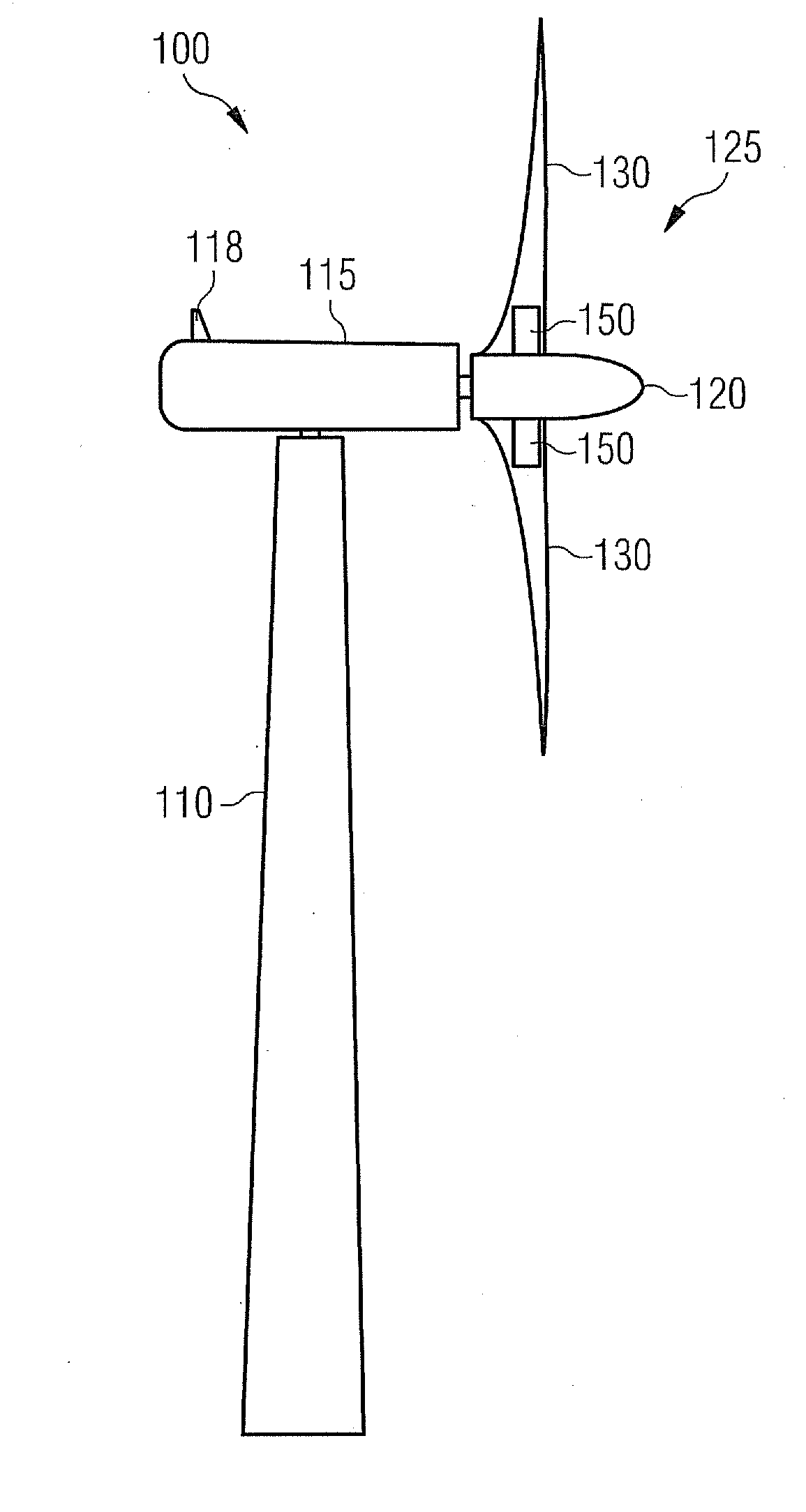
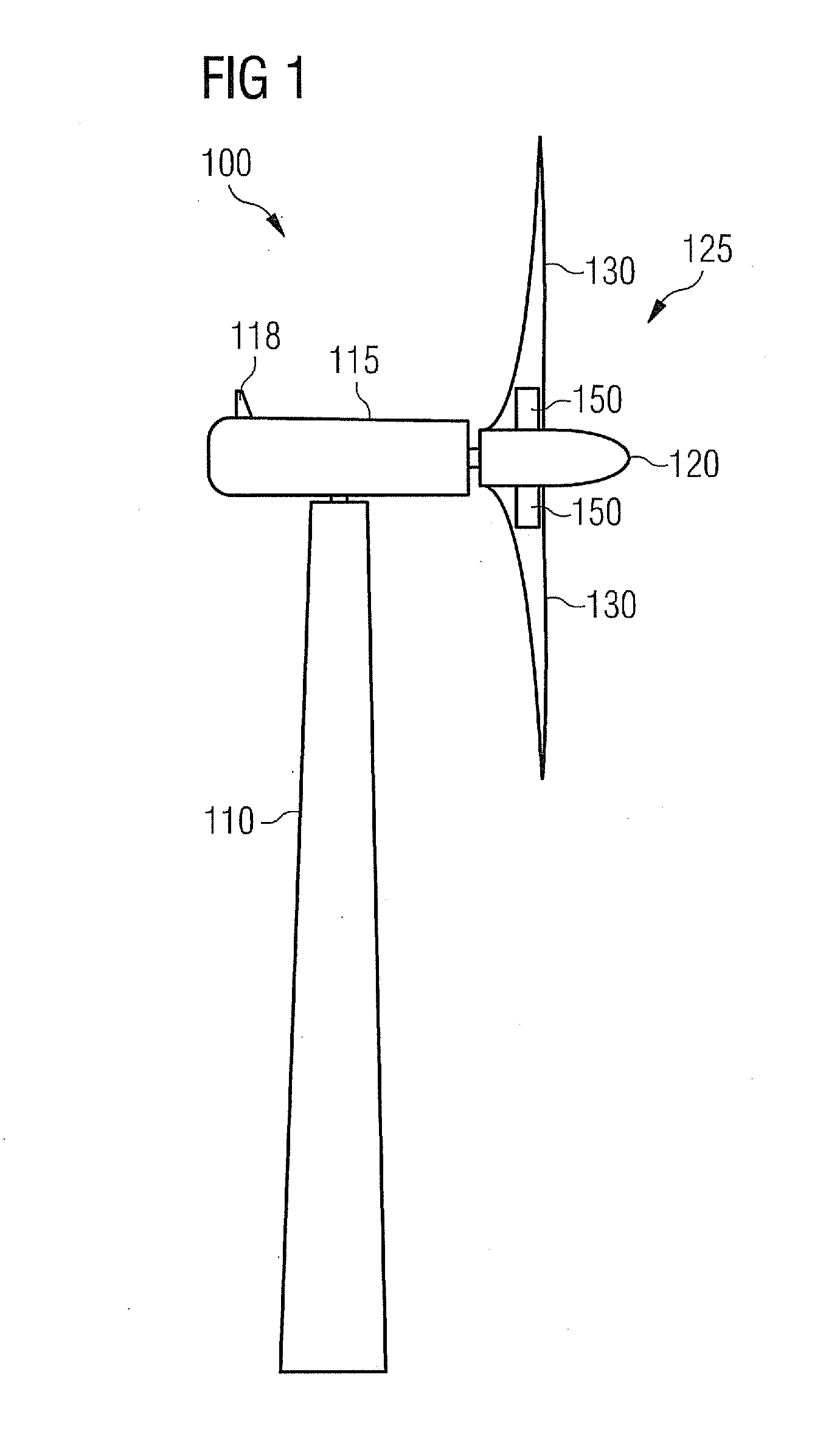
[0057]FIG. 1 shows a wind turbine 100 comprising a tower 110 and a nacelle 115, which is mounted pivotally at a top portion of the tower 110. The nacelle is equipped with a weather station 118, which may comprise for instance a wind measurement sensor (not depicted) for determining the wind speed and the wind direction. A precise knowledge of the wind speed and / or of the wind direction may be useful for operating the wind turbine in an appropriate manner.
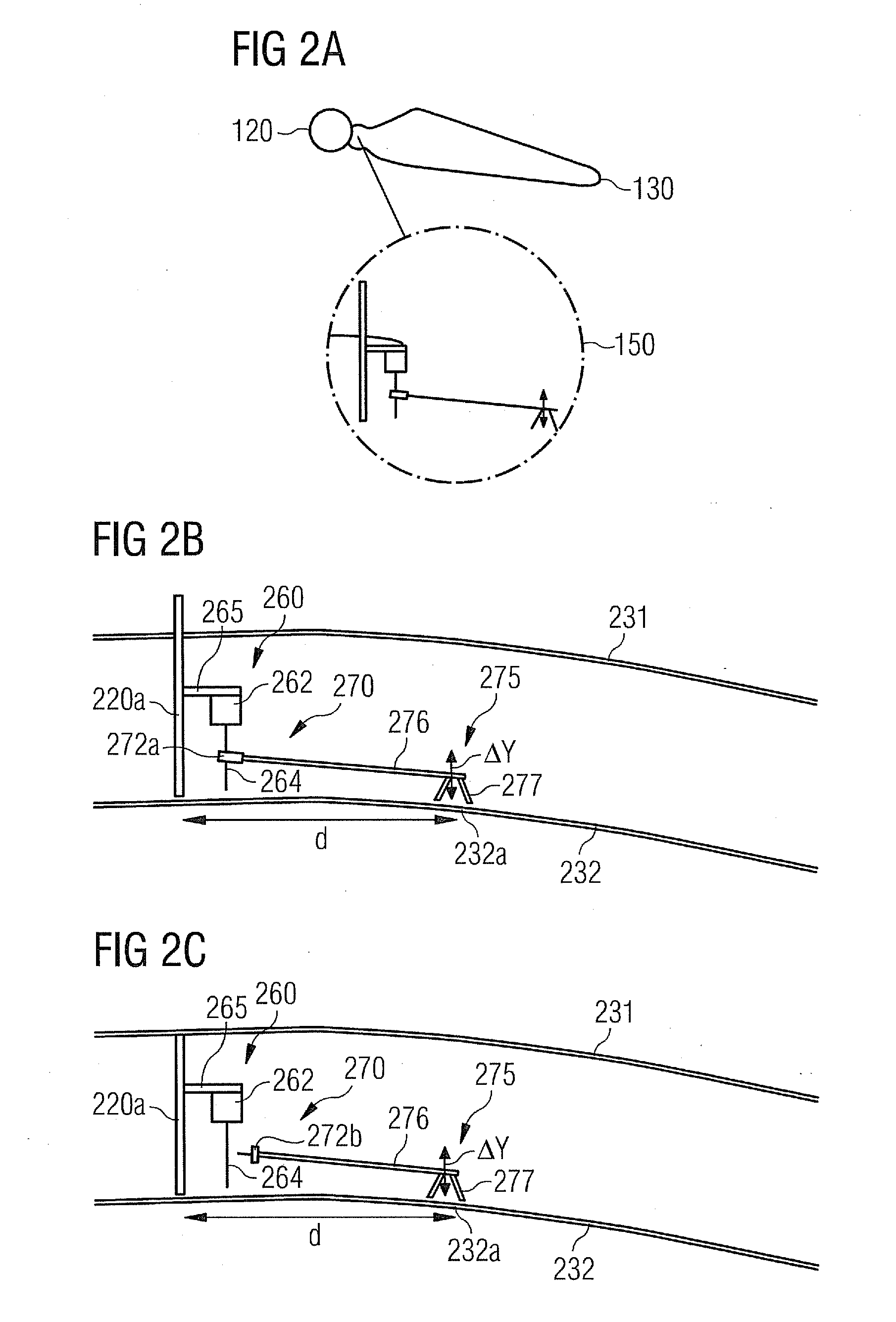
[0058]The wind turbine further comprises a rotor 125. According to the embodiment described here the rotor 125 comprises two blades 130, which are mounted to a hub 120 of the rotor 125. Each blade 130 is provided with a magnetostrictive measurement arrangeme...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com