Reduction of unpolymerized monomers in high internal phase emulsion foam
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example
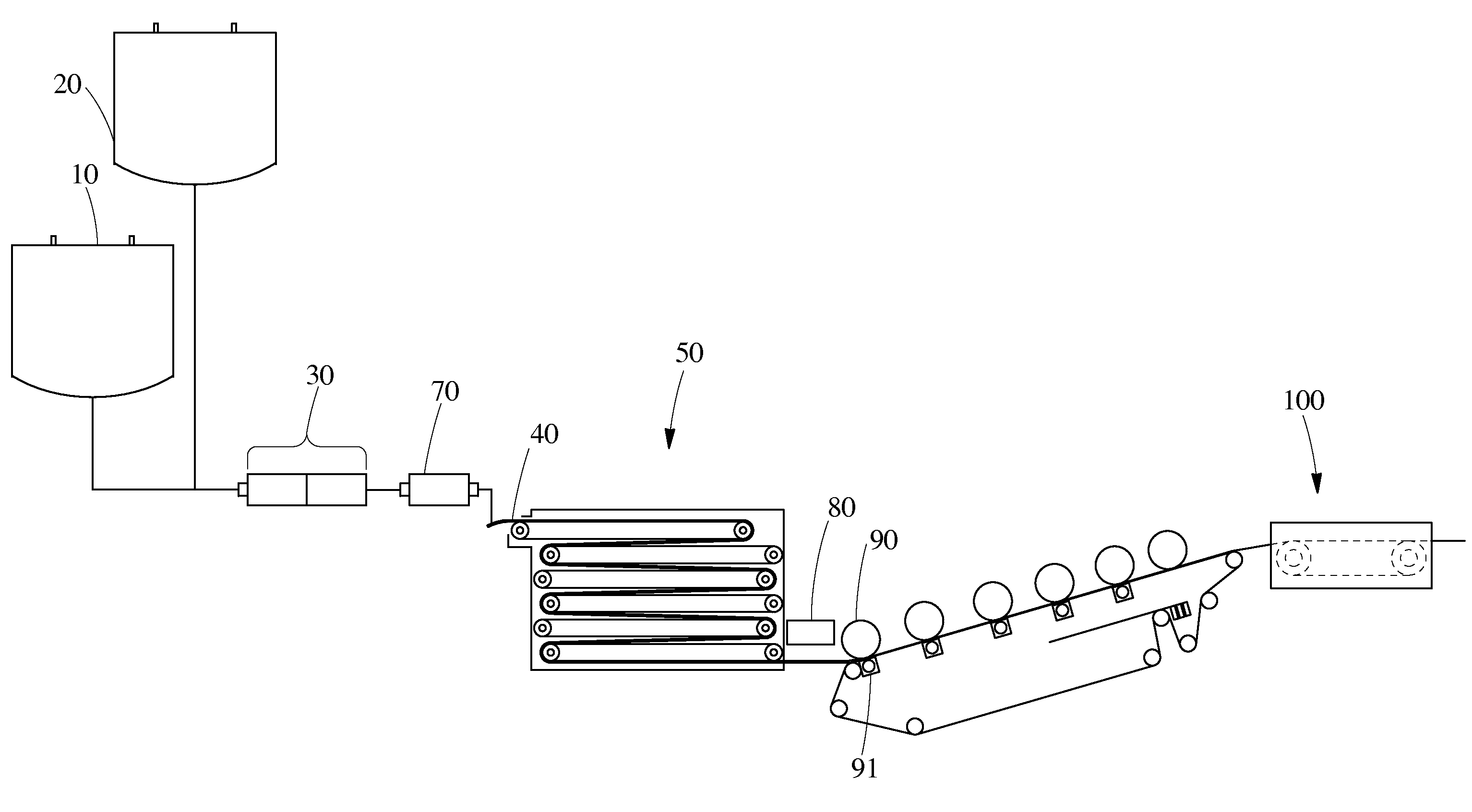
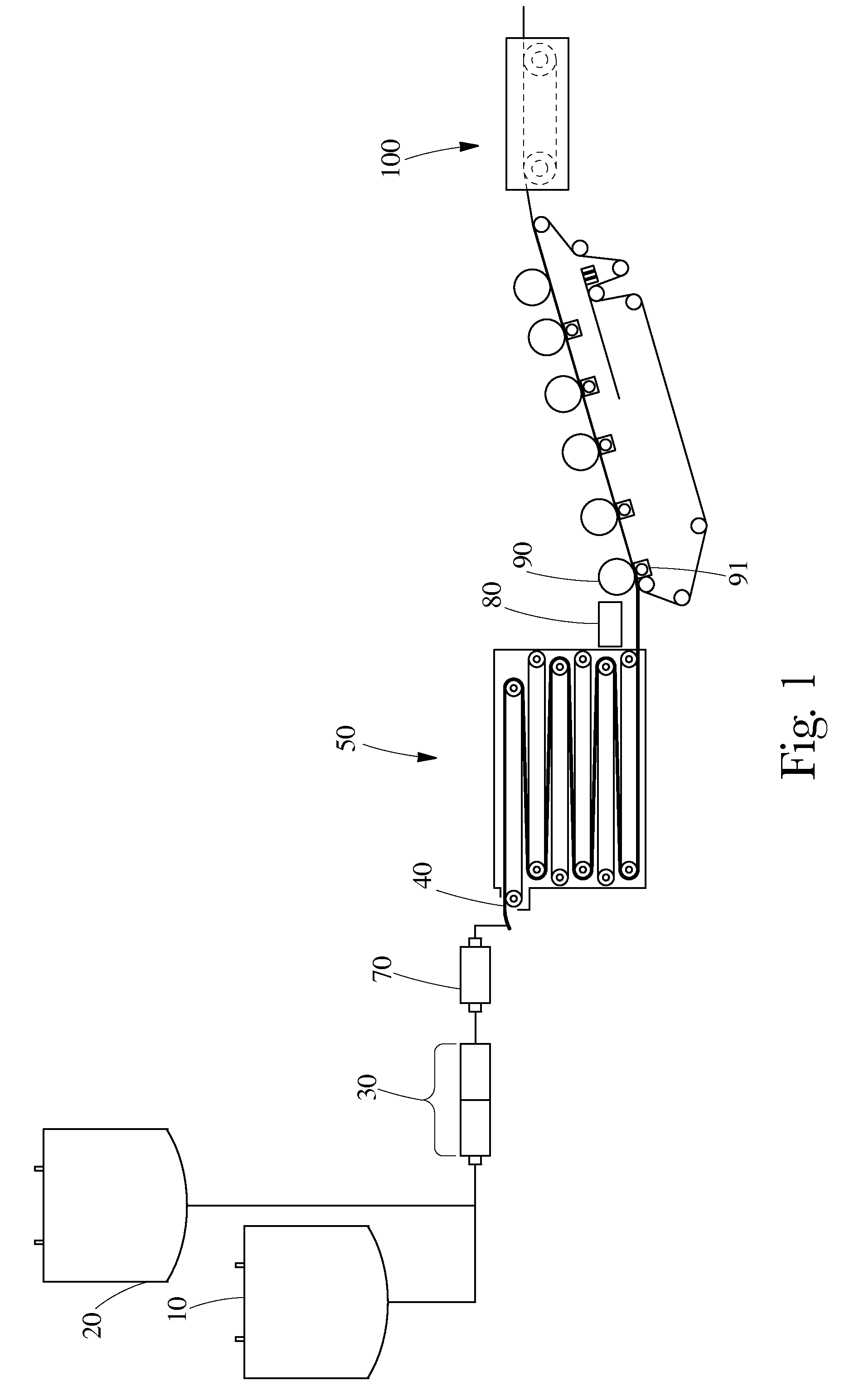
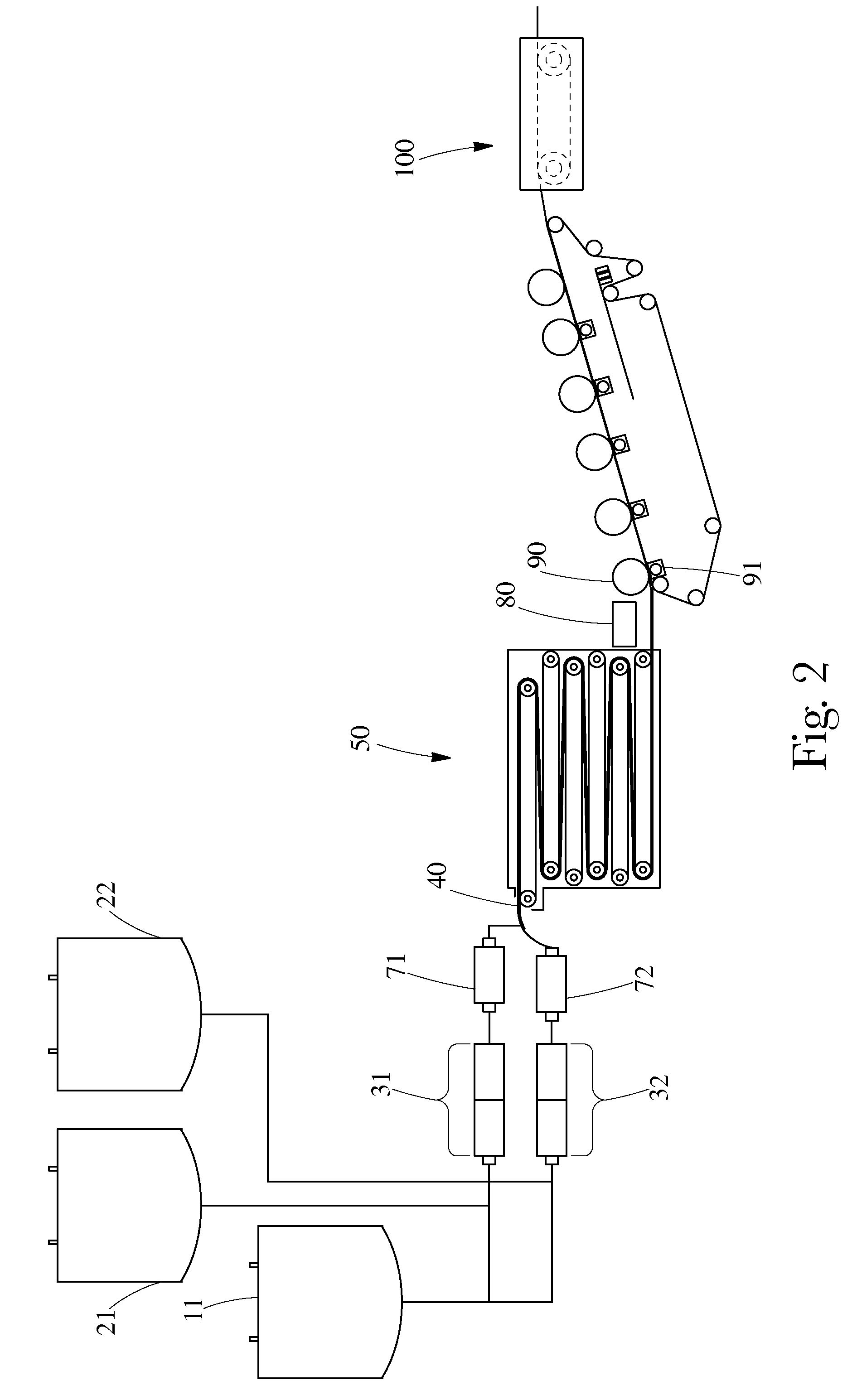
[0042]Preparation of High Internal Phase Emulsions (HIPE) and their subsequent polymerization into absorbent foams are illustrated in the following example. The HIPE samples comprised two layers—a bottom layer and a top layer, wherein the bottom layer had a smaller average pore size of 30 microns and the top layer had a larger average pore size of about 80 microns.
[0043]A. Small Cell Layer HIPE Formation
[0044]Small Cell Layer Components:
[0045]To prepare the bottom small cell layer of the HIPE the aqueous phase, oil phase, and initiator contained the following components as shown below in Table 1.
TABLE 1% Amount Based onOil PhaseTotal Weight of Oil Phase2-ethylhexyl acrylate (EHA)36.7%2-ethylhexyl methacrylate (EHMA)37.61%ethyleneglycol dimethacrylate (EGDMA)17.43%dimethyl ammonium methyl sulfate0.93%(DTDMAMS)Polyglycerol succinate (PGS)6.48%Photoinitiator - Darocur 1173*0.99%Aqueous Phase% Amount Based on Total Weight of Aqueous PhaseCaCl23.85%Water:oil ratio26:1% Amount Based on To...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com