Material for treatment of cerebral infarction and brain tissue regeneration method
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
[0110]This Example shows nerve regeneration by porcine dental pulp tissue-derived CD31− / CD146− SP transplantation into rats after cerebral infarction.
[0111]Middle cerebral artery occlusion was performed using SD (Sprague-Dawley) rats to prepare rat models of cerebral infarction.
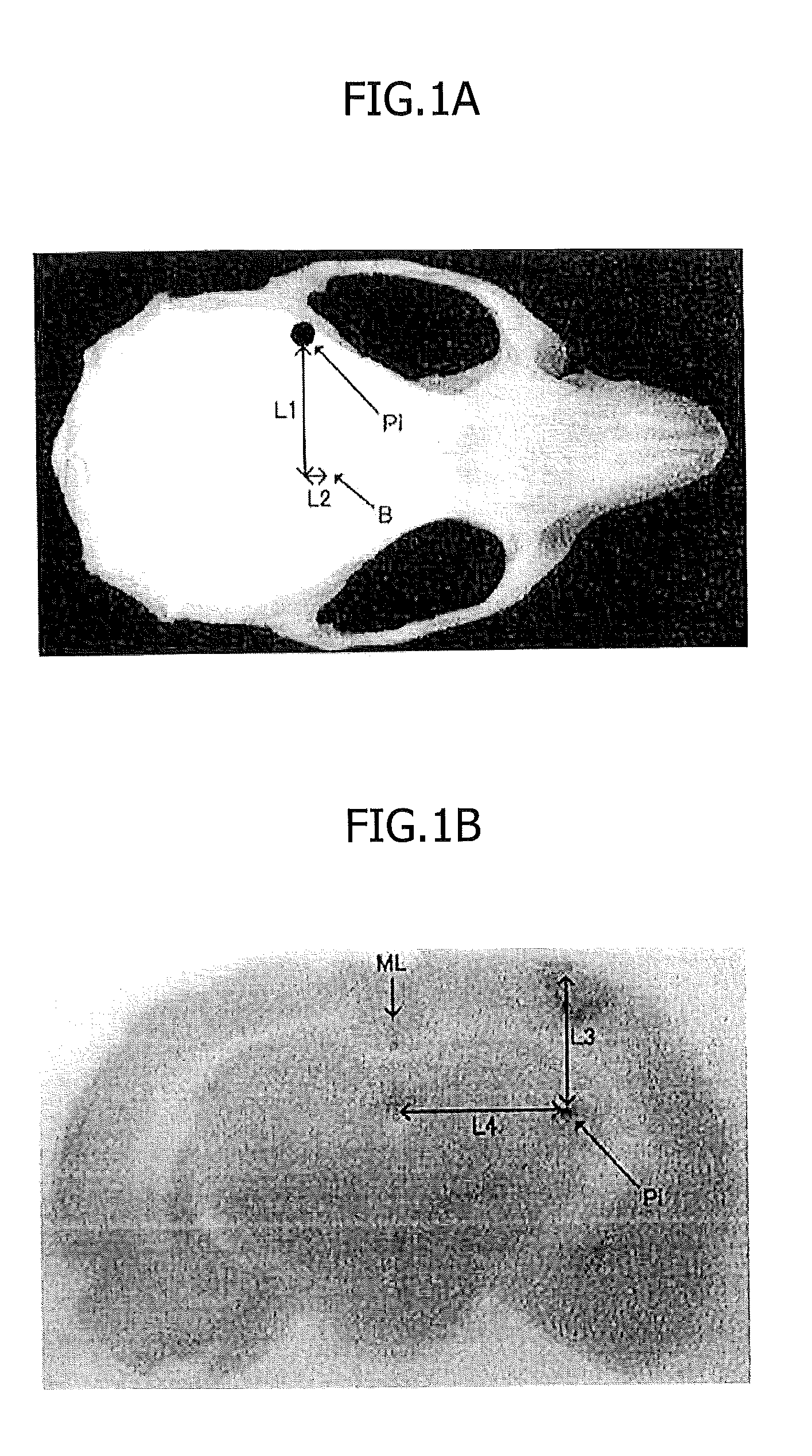
[0112]CD31-negative SP cells were fluorescently labeled with DiI and then transplanted 24 hours after cerebral infarction into an injection site Pi of the brain striatum in the brain tissues, as shown in FIGS. 1A and 1B, A PBS-injected control was used.
[0113]In FIG. 1A, B represents bregma, which is a point of intersection of the sagittal suture with the coronal suture of the cranium. L1 represents 6.0 mm, and L2 represents 1.0 mm.
[0114]FIG. 1B is a macro image of a coronal section. L3 represents 5.0 mm, and L4 represents 6.0 mm. ML represents a midline.
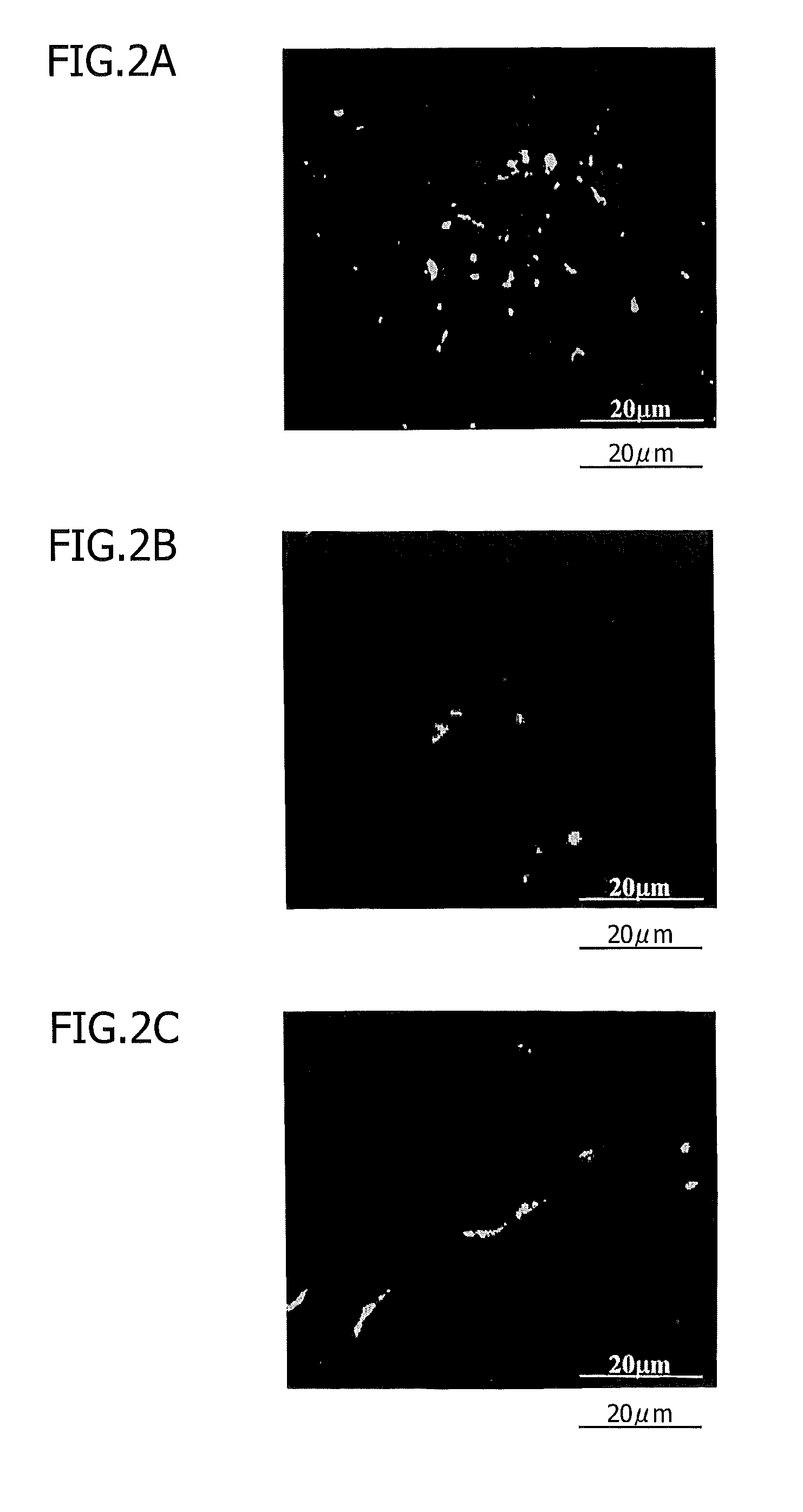
[0115]On day 21 after cell transplantation, perfusion fixation was performed, and frozen sections were prepared according to a routine method and immunostaine...
example 2
[0144]Unlike Example 1, human dental pulp tissue-derived dental pulp cells are used in this Example. Table 1 shows the properties of human dental pulp tissue-derived CD31− SP cells and porcine dental pulp tissue-derived CD31− SP cells.
TABLE 1HumanHuman totalPorcineCD31−dental pulpCD31−SP cellcellSP cell(%)(%)(%)CD310.000.060.00CD1460.0040.580.00CD240.1023.87—CD340.010.0169.00 CD4492.5091.60—CD9098.6772.690.20CD10521.234.35—CD1170.020.060.00CD1330.010.470.00CD1500.210.100.00CD2710.030.0194.00 SSEA10.290.06—
[0145]As shown in Table 1, the human dental pulp tissue-derived CD31−SP cells highly expressed CD90 and CD150 compared with porcine dental pulp tissue-derived CD3 V SP cells, in flow cytometry. Moreover, the human dental pulp tissue-derived CD31−SP cells highly expressed CD105 compared with human total dental pulp cells.
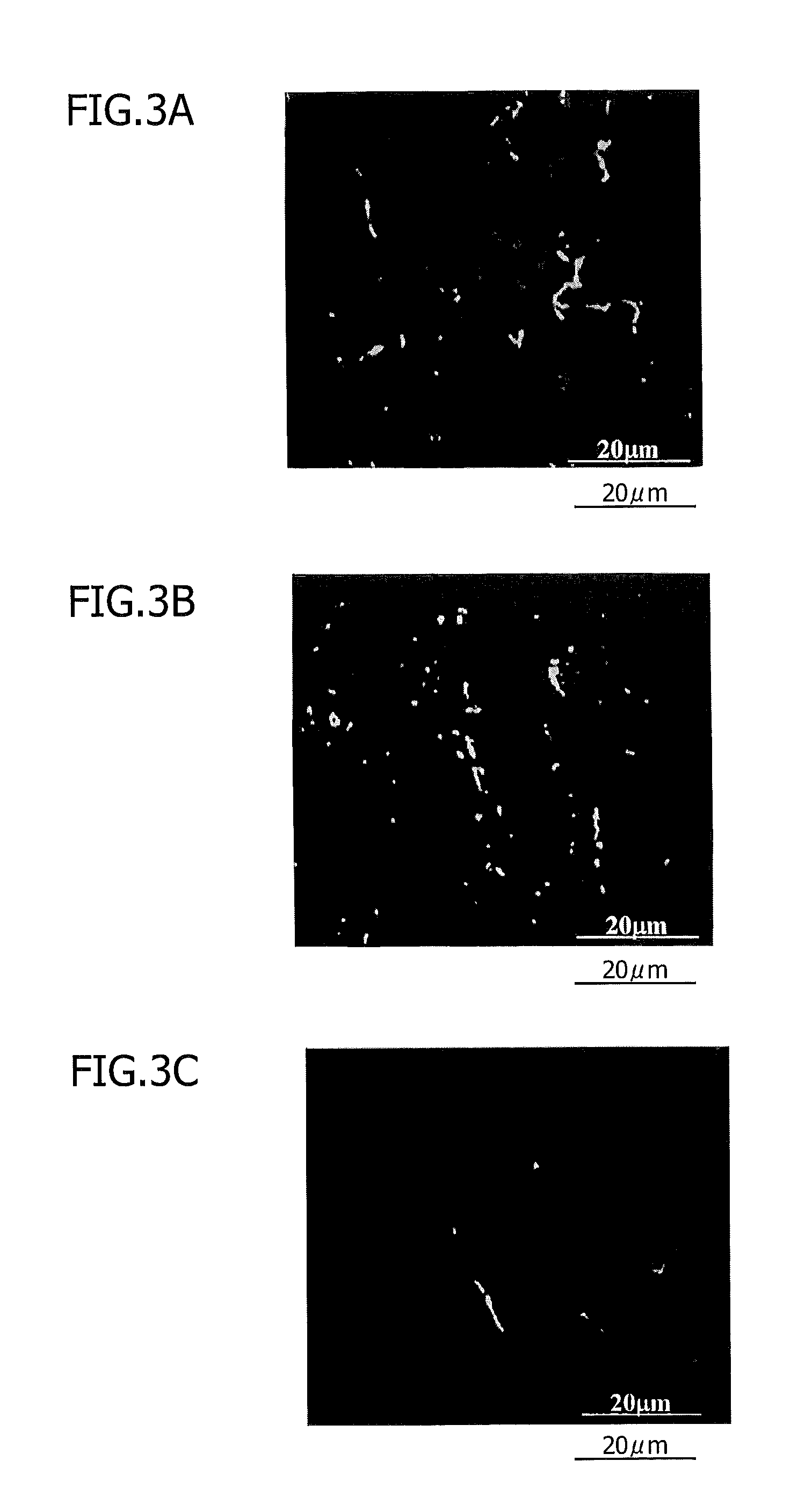
[0146]This Example shows nerve regeneration by the cell transplantation of human dental pulp tissue-derived CD31− / CD146− SP cells and human dental pulp tissue-deriv...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com