Method of Recovering Aqueous N-methylmorpholine-N-Oxide Solution Used in Production of Lyocell Fiber
a technology of lyocell fiber and n-methylmorpholinenoxide, which is applied in the field of recovering an aqueous n-methylmorpholinenoxide solution used in the production of lyocell fiber, can solve the problem of high cost of nmmo solvent and achieve the effect of facilitating nmmo recovery and enhancing nmmo recovery efficiency
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
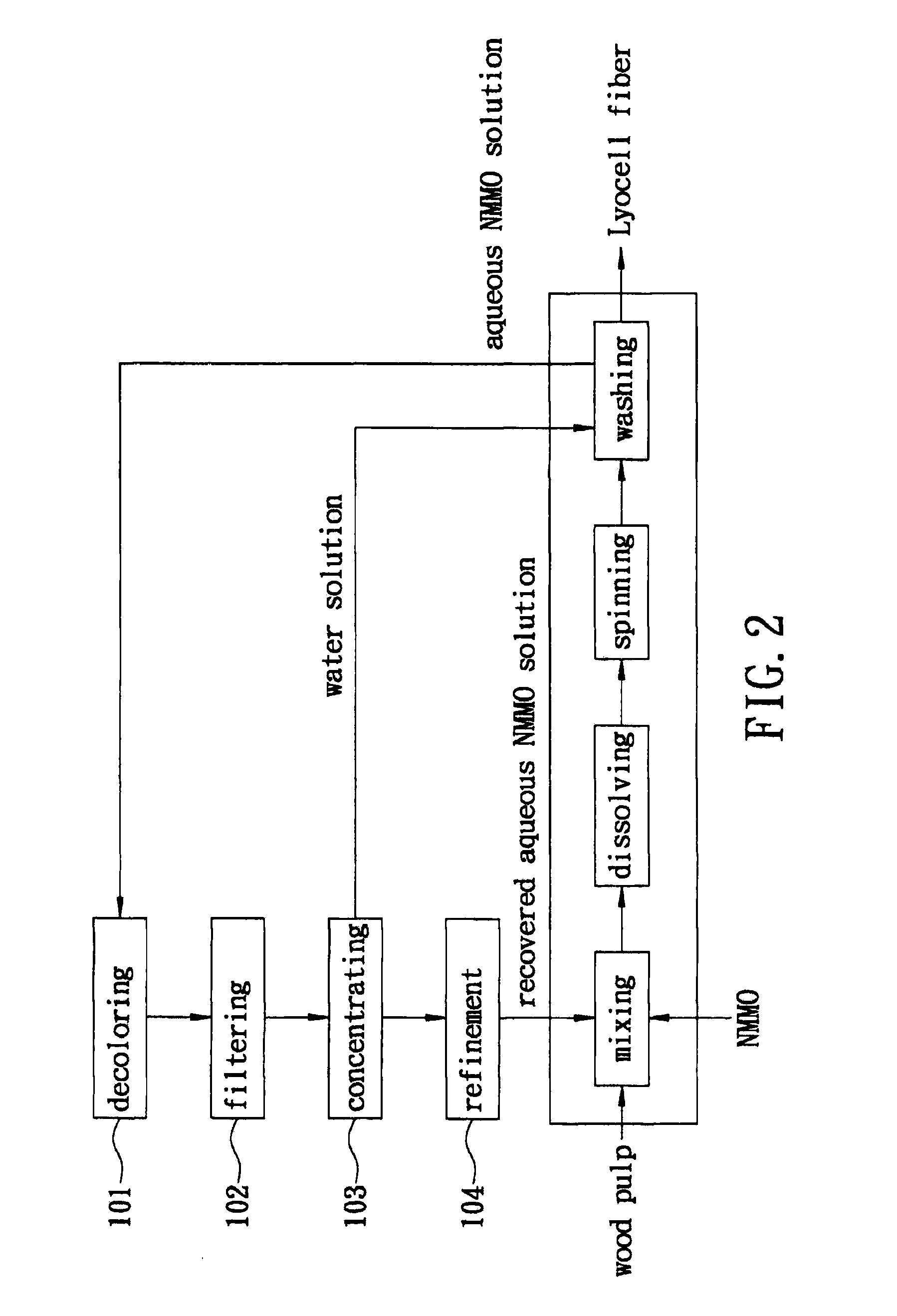
Referring to FIG. 2, according to the present invention, the preferred embodiment of a method of recovering an aqueous N-methylmorpholine-N-oxide (NMMO) solution used in production of Lyocell fiber includes steps 101-104. The conventional method of producing Lyocell fiber shown in FIG. 1 is also illustrated in FIG. 2. After the washing step for production of Lyocell fiber, an aqueous NMMO solution having a low concentration of NMMO is formed. In addition to NMMO, the aqueous NMMO solution also contains a trace of N-methylmorpholine (NMM) that arises from cleavage of NMMO, which is caused by heating during the dissolving step.
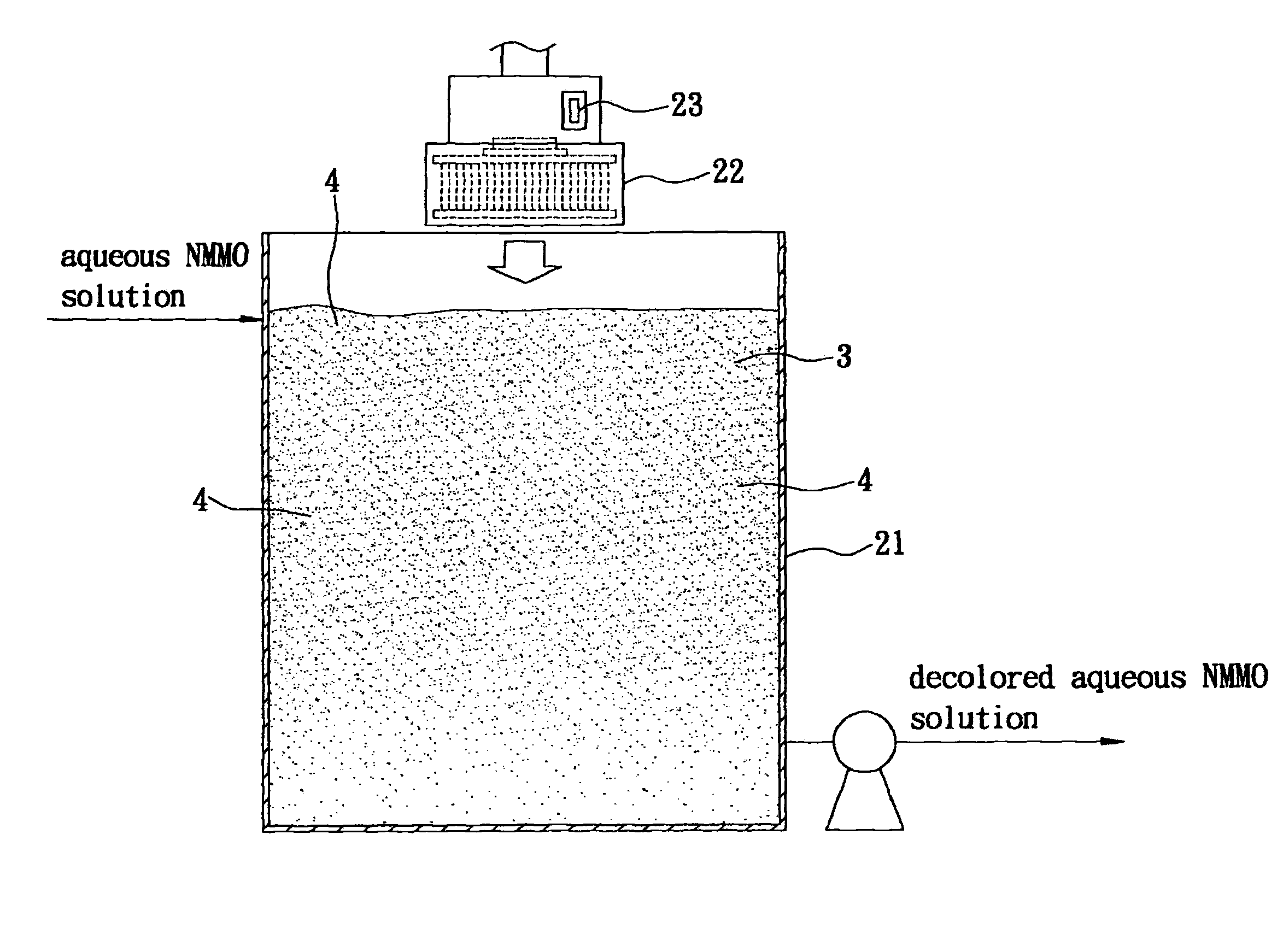
Step 101 is decoloring of the aqueous NMMO solution. Even though heat energy provided during the dissolving step of the conventional method of producing Lyocell fiber is able to increase dissolving efficiency, the heat energy gives rise to coloration. Therefore, the aqueous NMMO solution contains pigments and is required to be decolored. Referring to FIG. 3, the...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| time | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| pore size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| pore size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com