Patents
Literature
157 results about "N-Methylmorpholine N-oxide" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
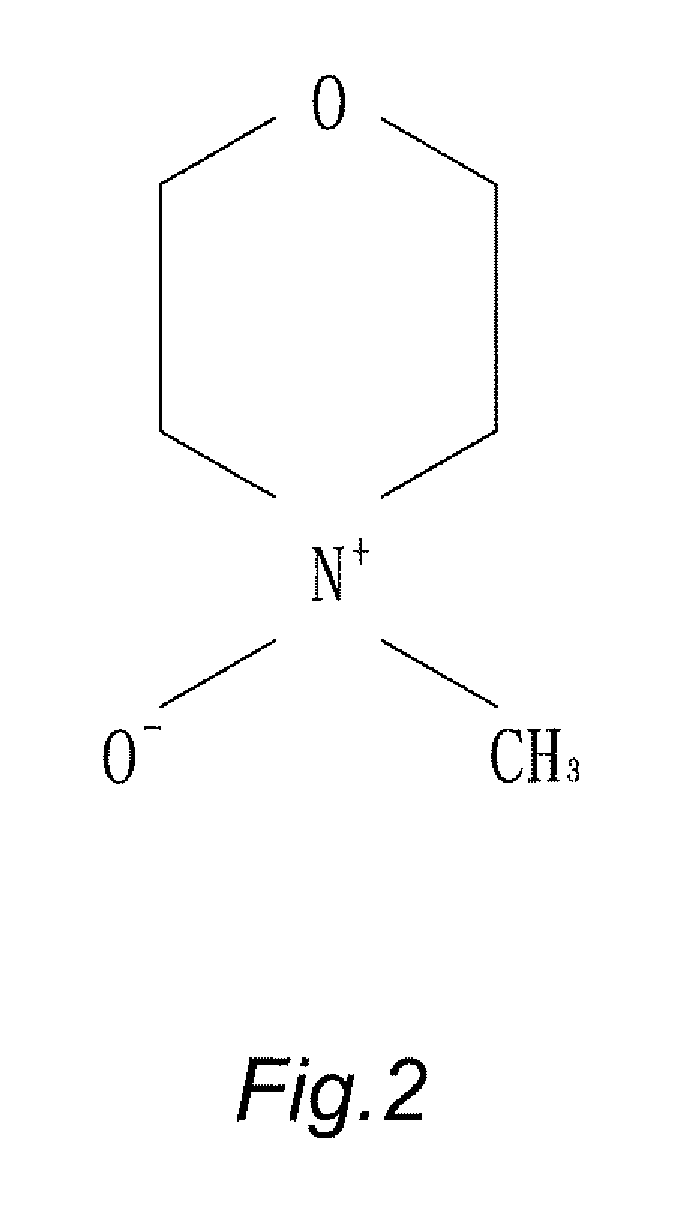
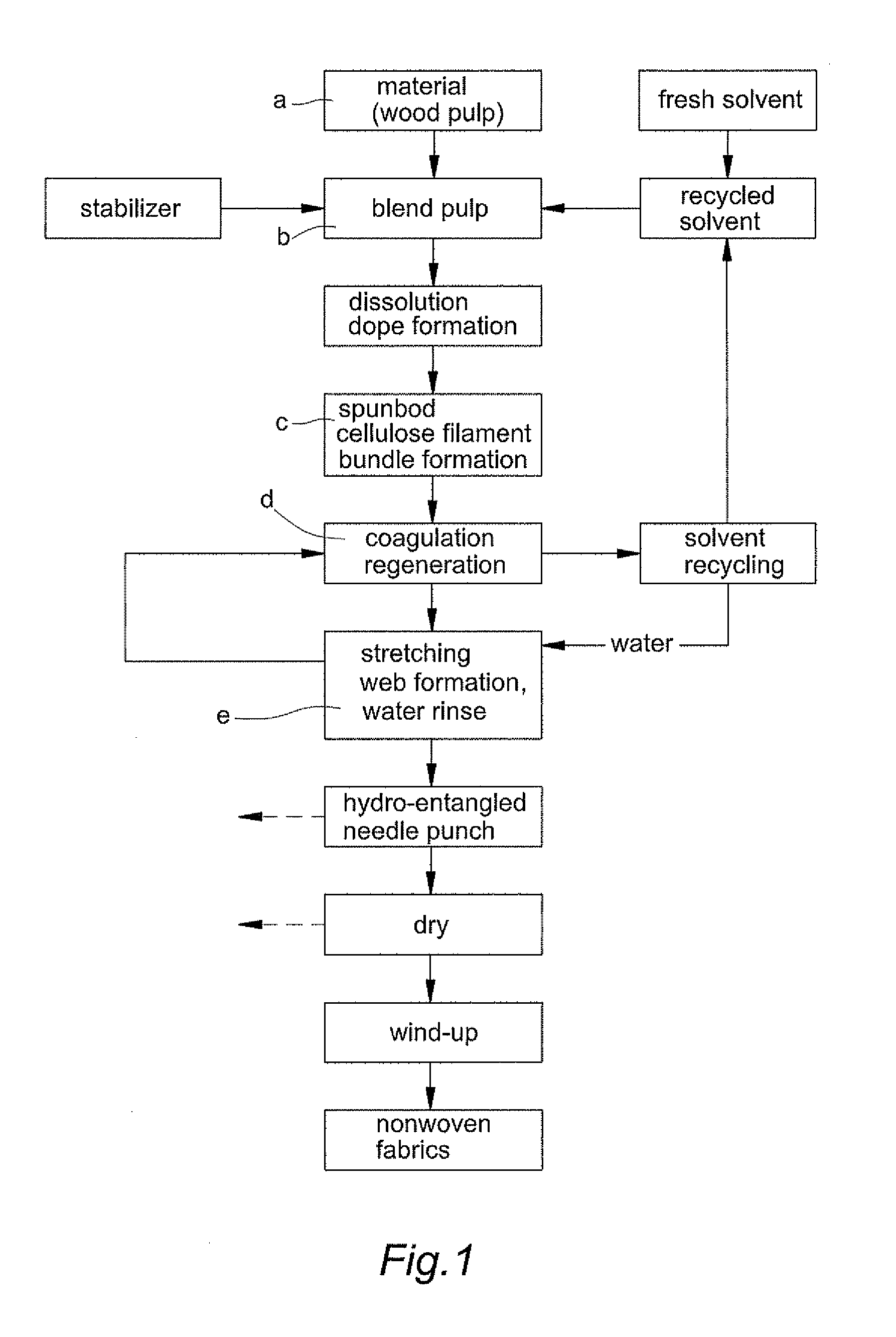
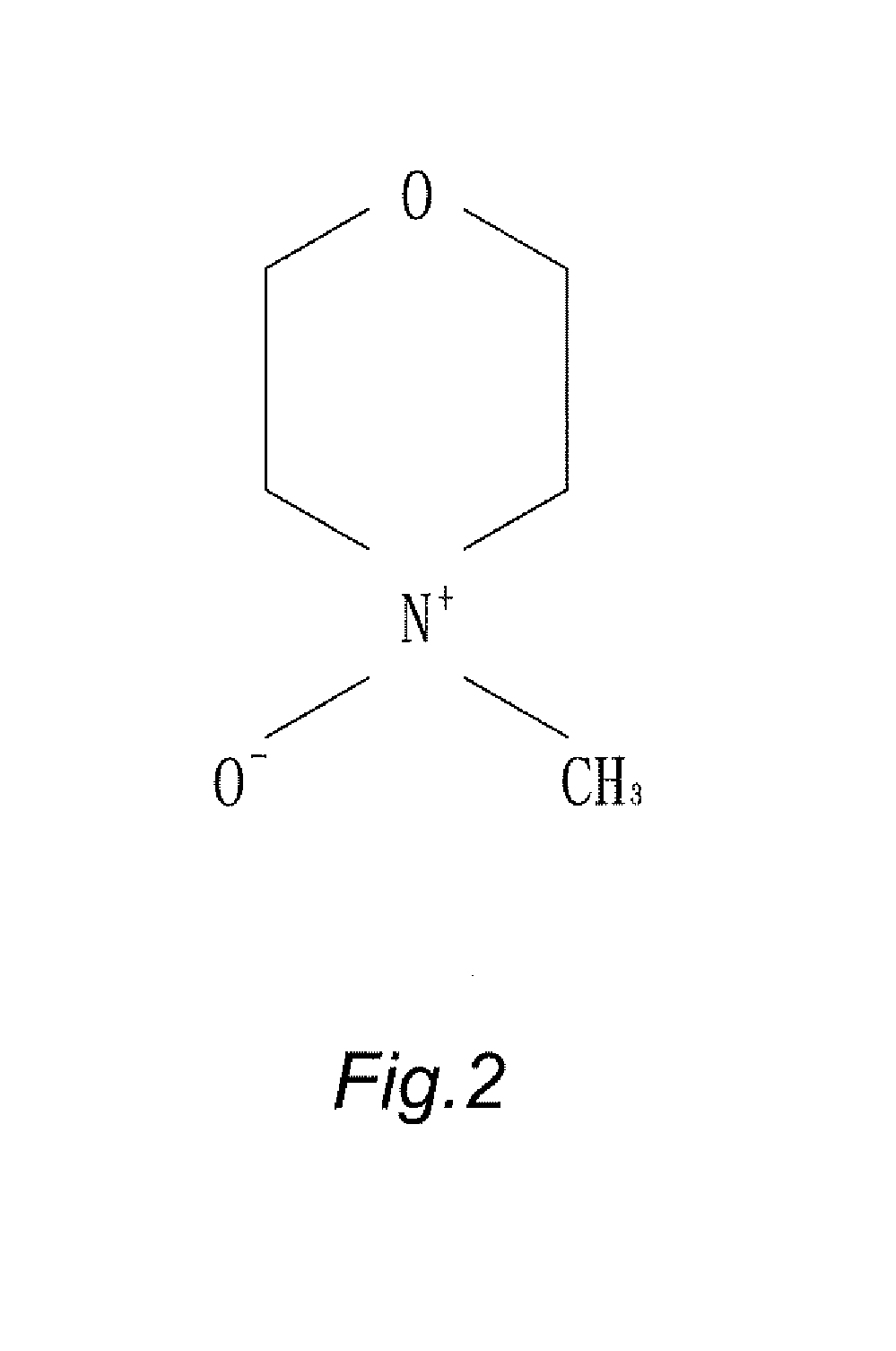
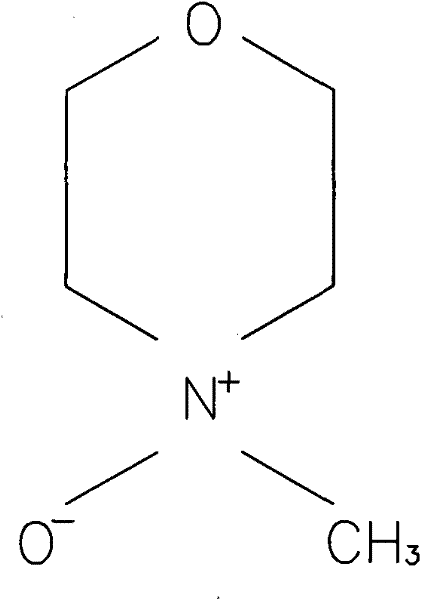
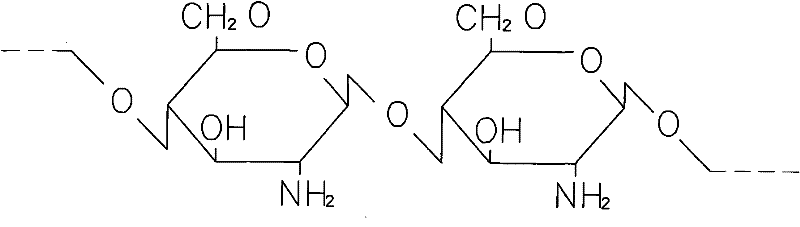
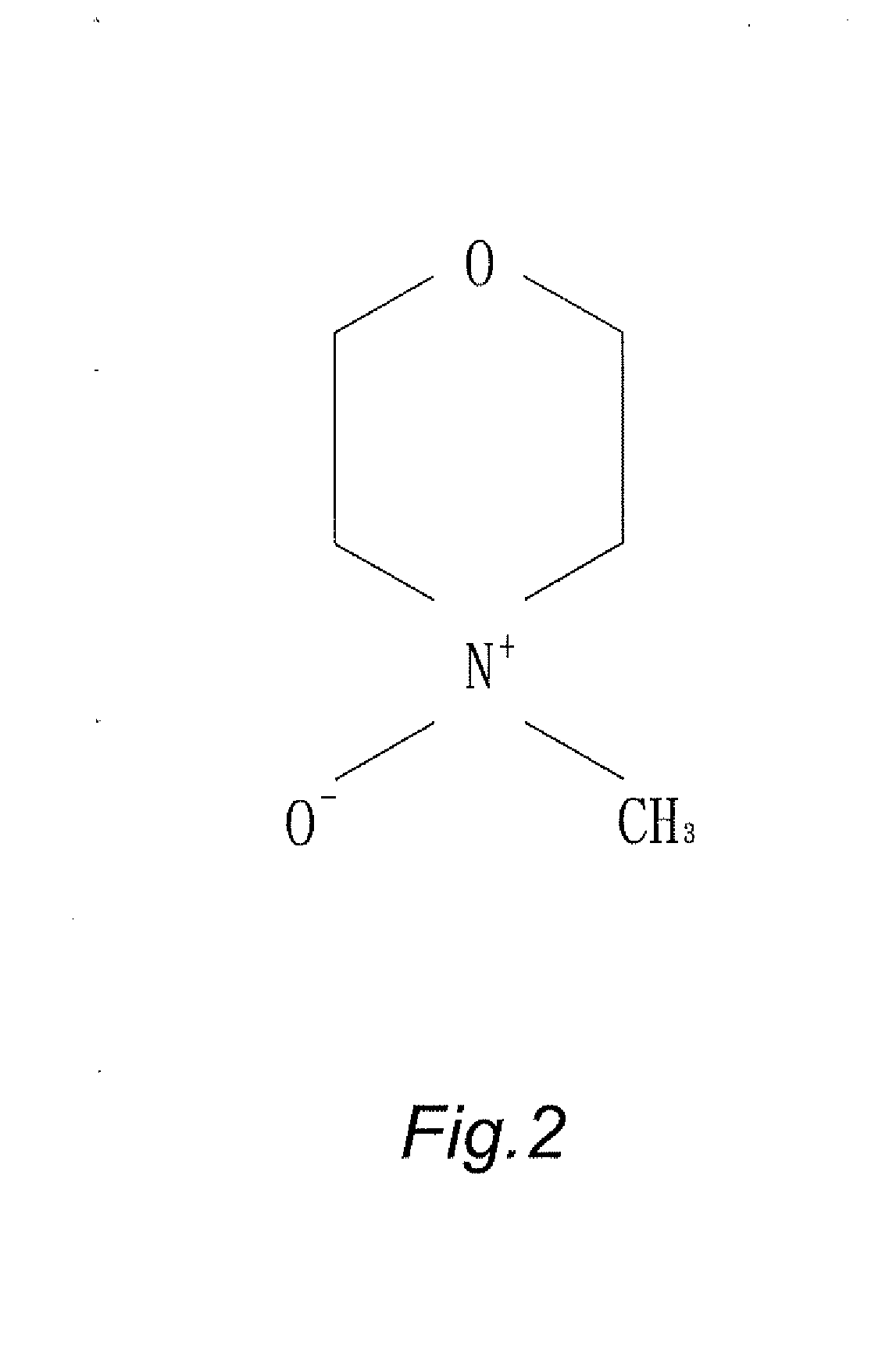
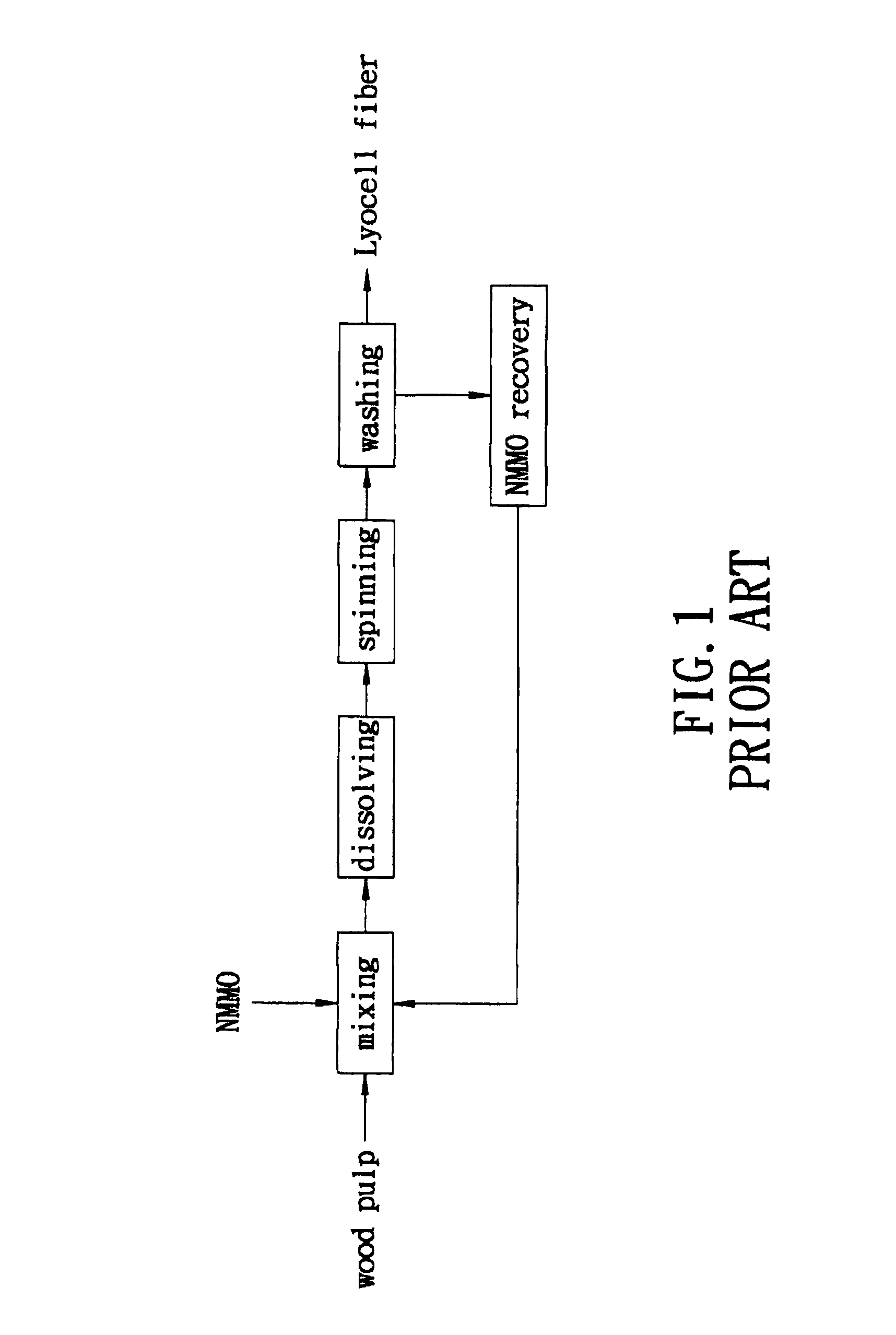
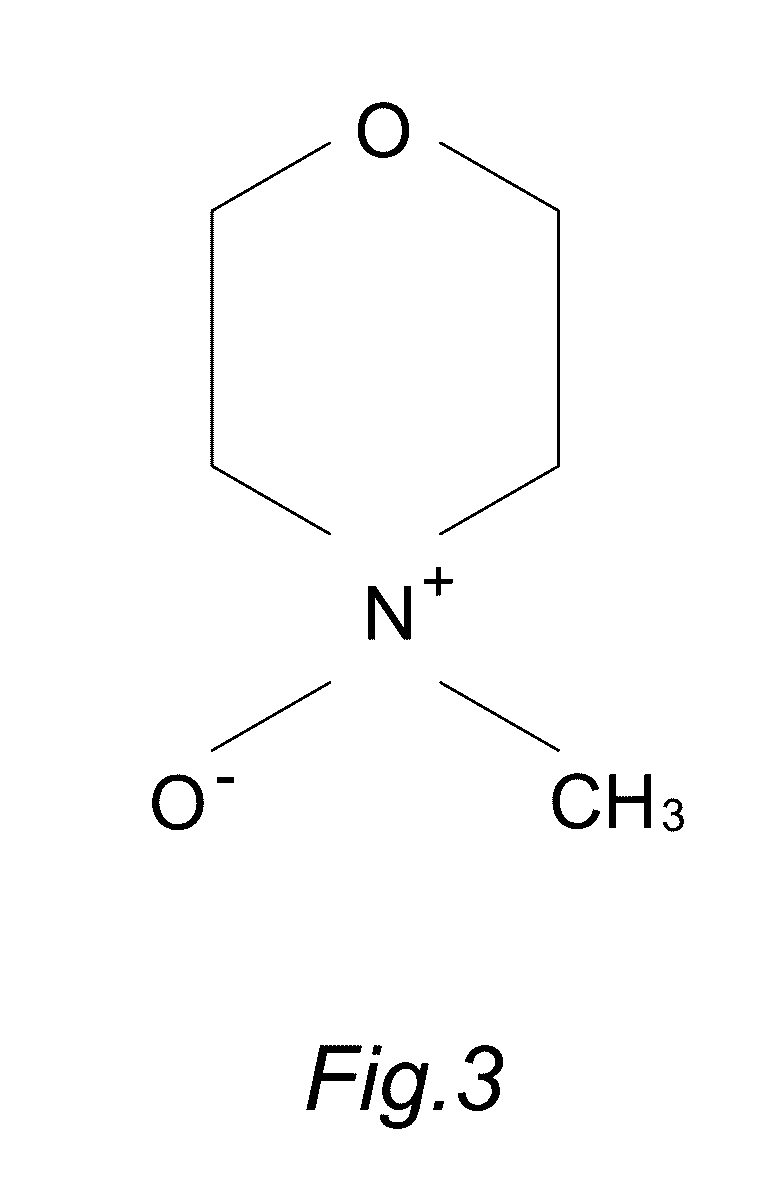
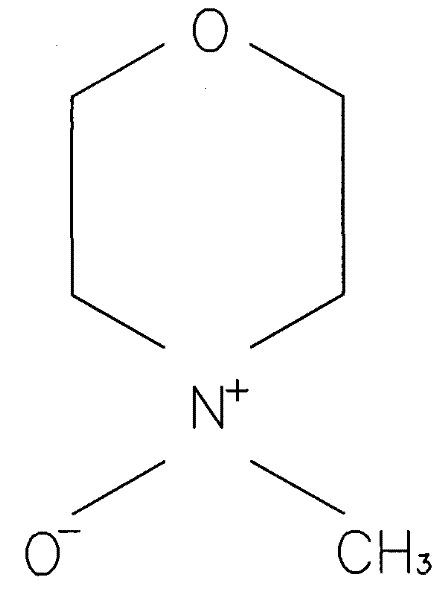
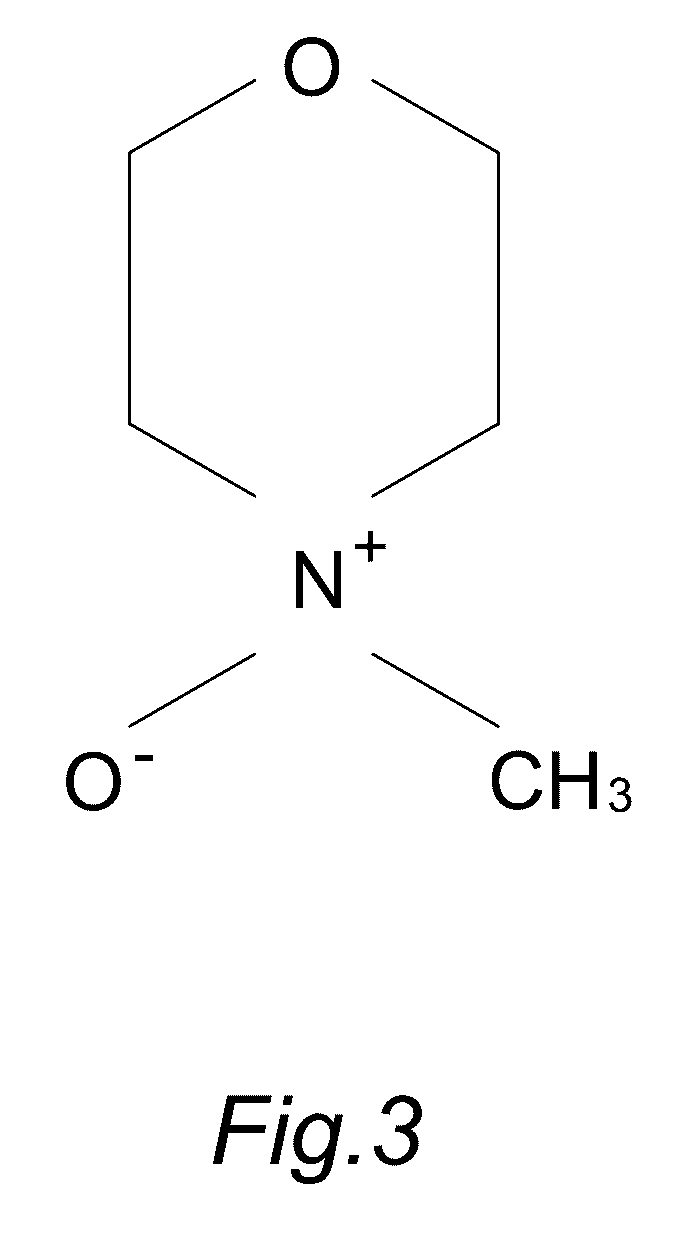
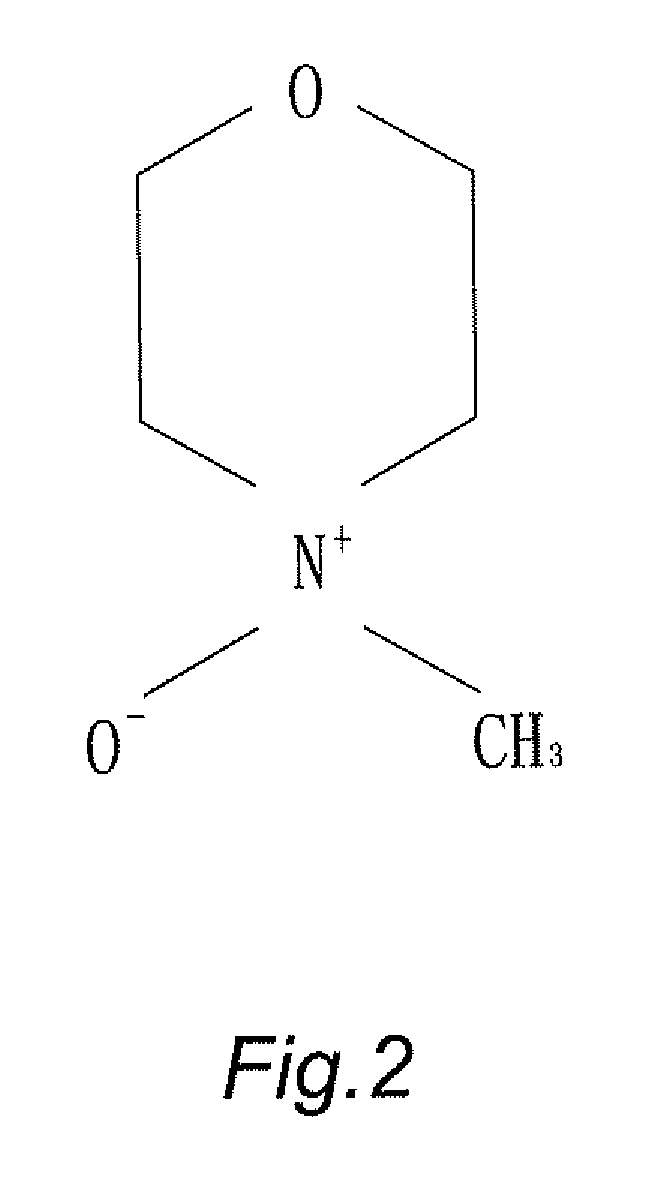
N-Methylmorpholine N-oxide (more correctly 4-methylmorpholine 4-oxide), NMO or NMMO is an organic compound. This heterocyclic amine oxide and morpholine derivative is used in organic chemistry as a co-oxidant and sacrificial catalyst in oxidation reactions for instance in osmium tetroxide oxidations and the Sharpless asymmetric dihydroxylation or oxidations with TPAP. NMO is commercially supplied both as a monohydrate C₅H₁₁NO₂·H₂O and as the anhydrous compound. The monohydrate is used as a solvent for cellulose in the Lyocell process to produce cellulose fibers.
Solution containing cellulose dissolved in n-methylmorpholine-n-oxide and high tenacity lyocell multifilament using the same
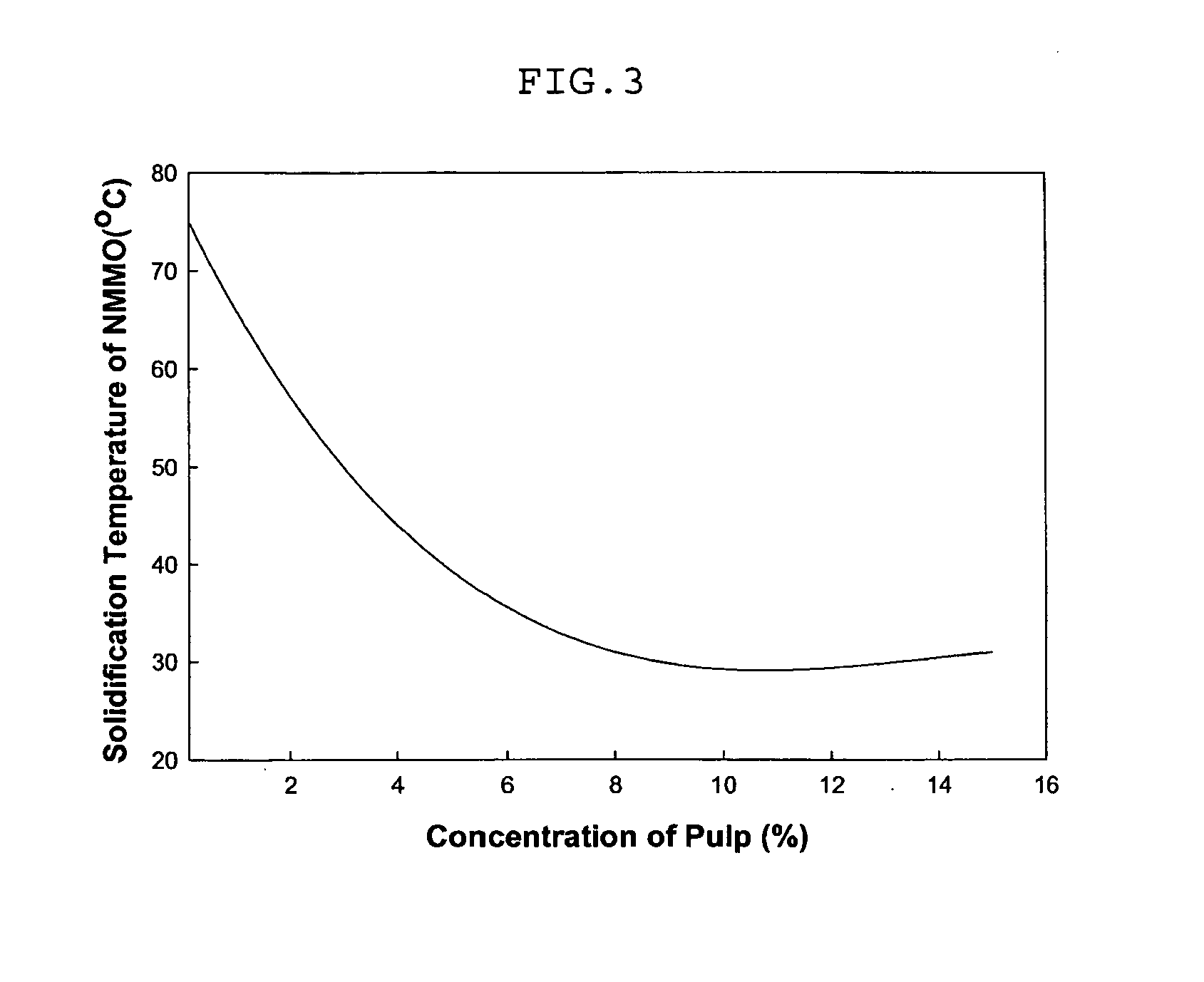
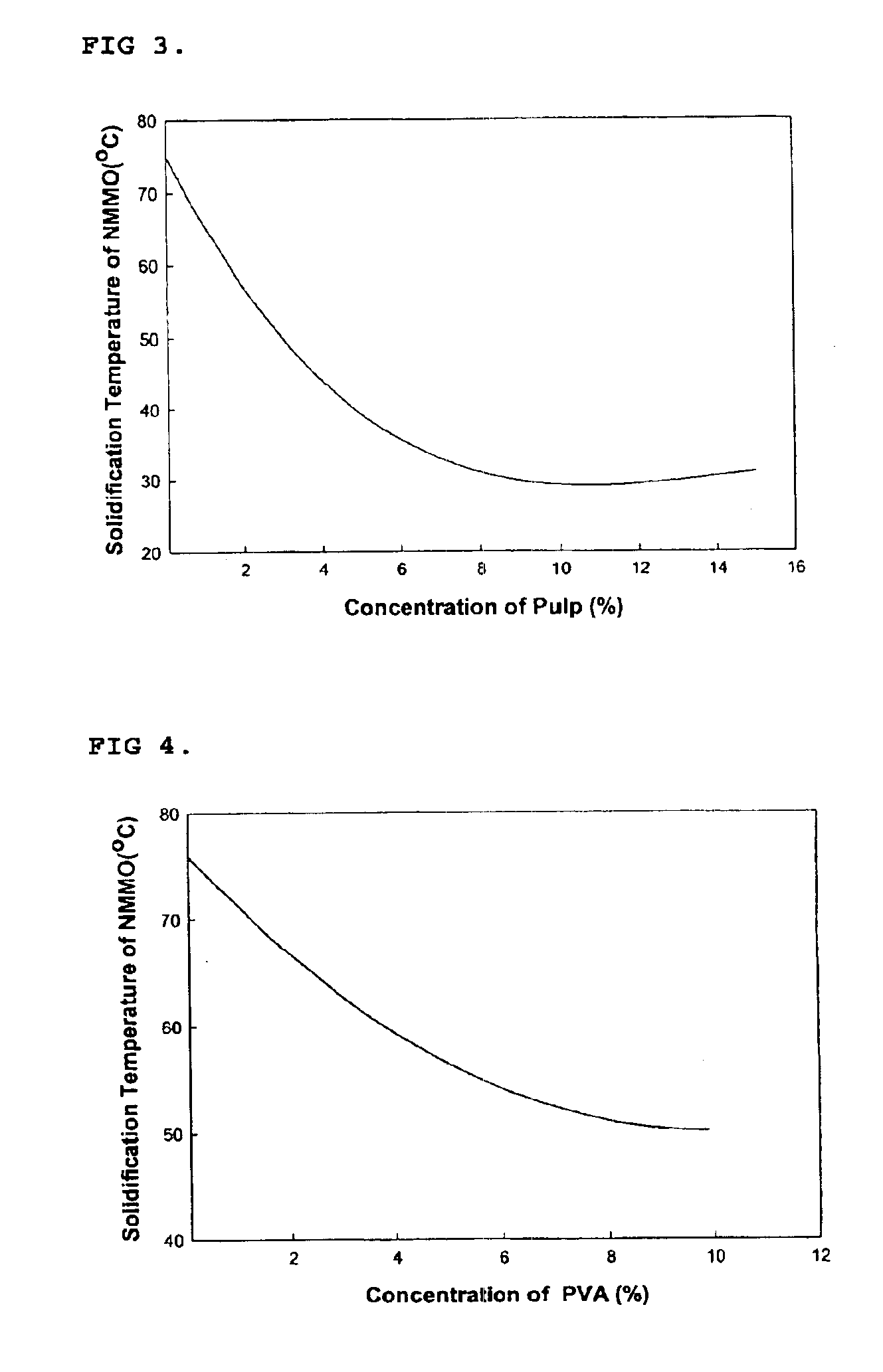
ActiveUS20050154093A1Solidifying temperatureIncrease flexibilityNon-fibrous pulp additionMonocomponent cellulose artificial filamentLiquid stateLyocell
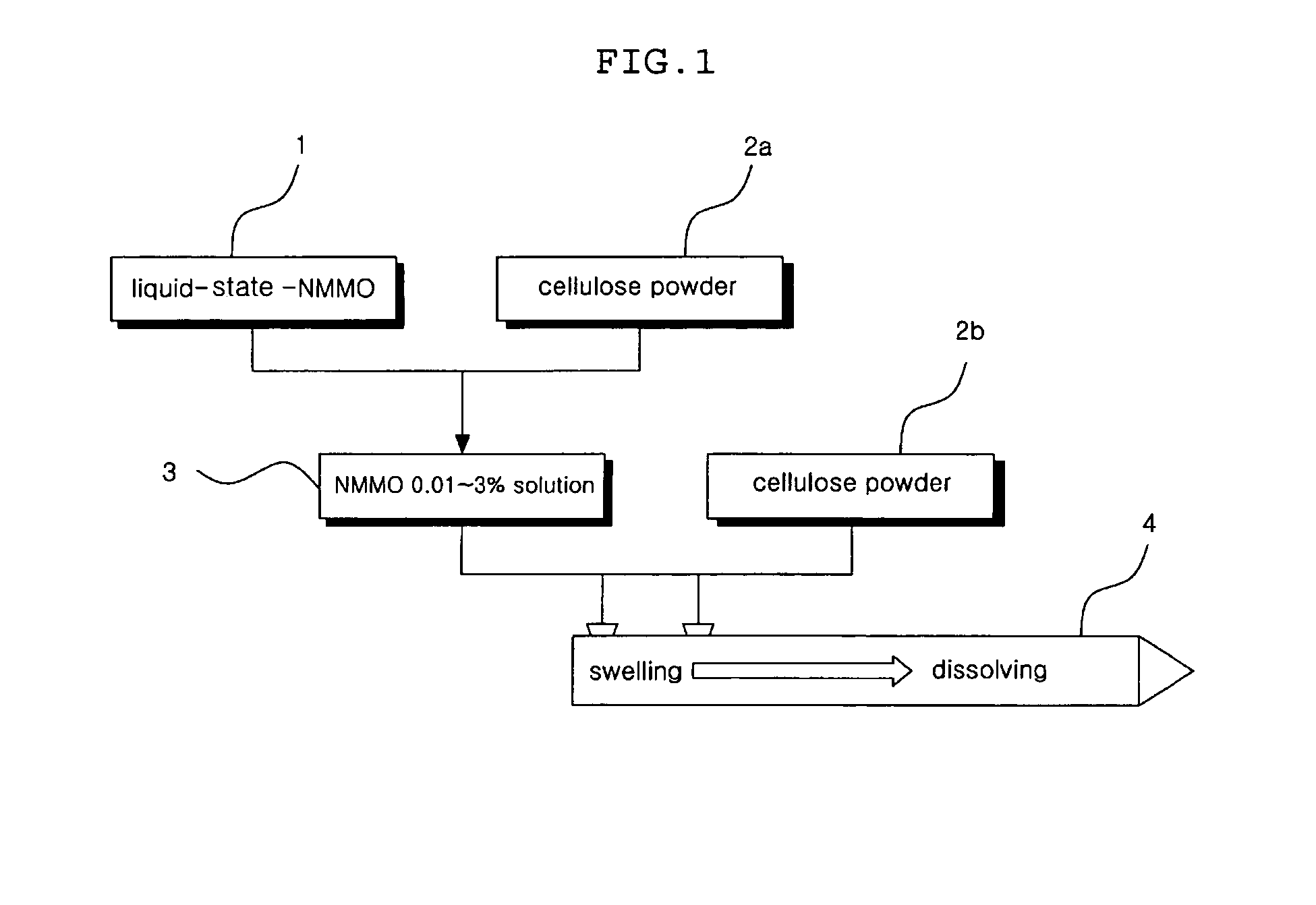
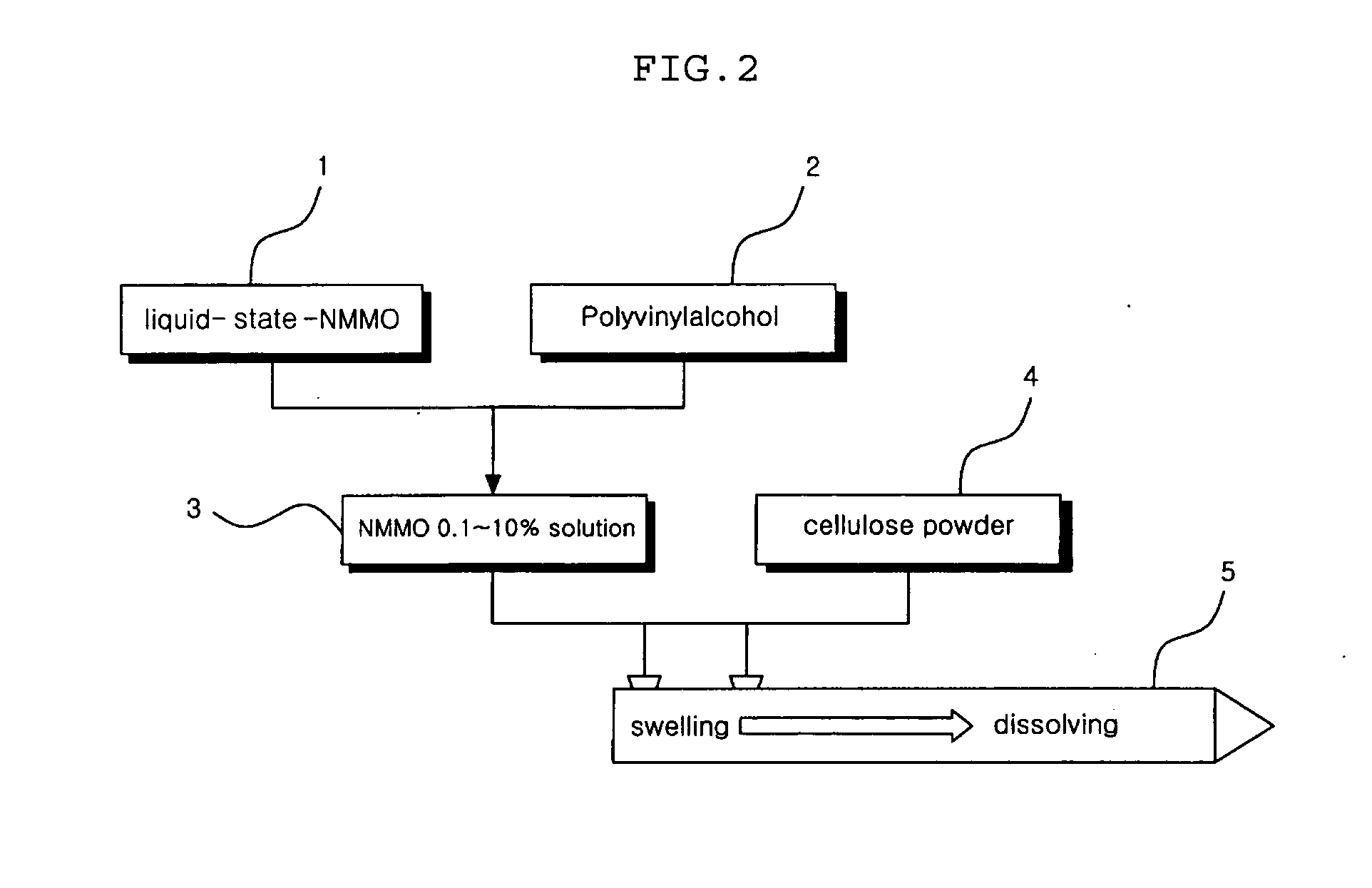
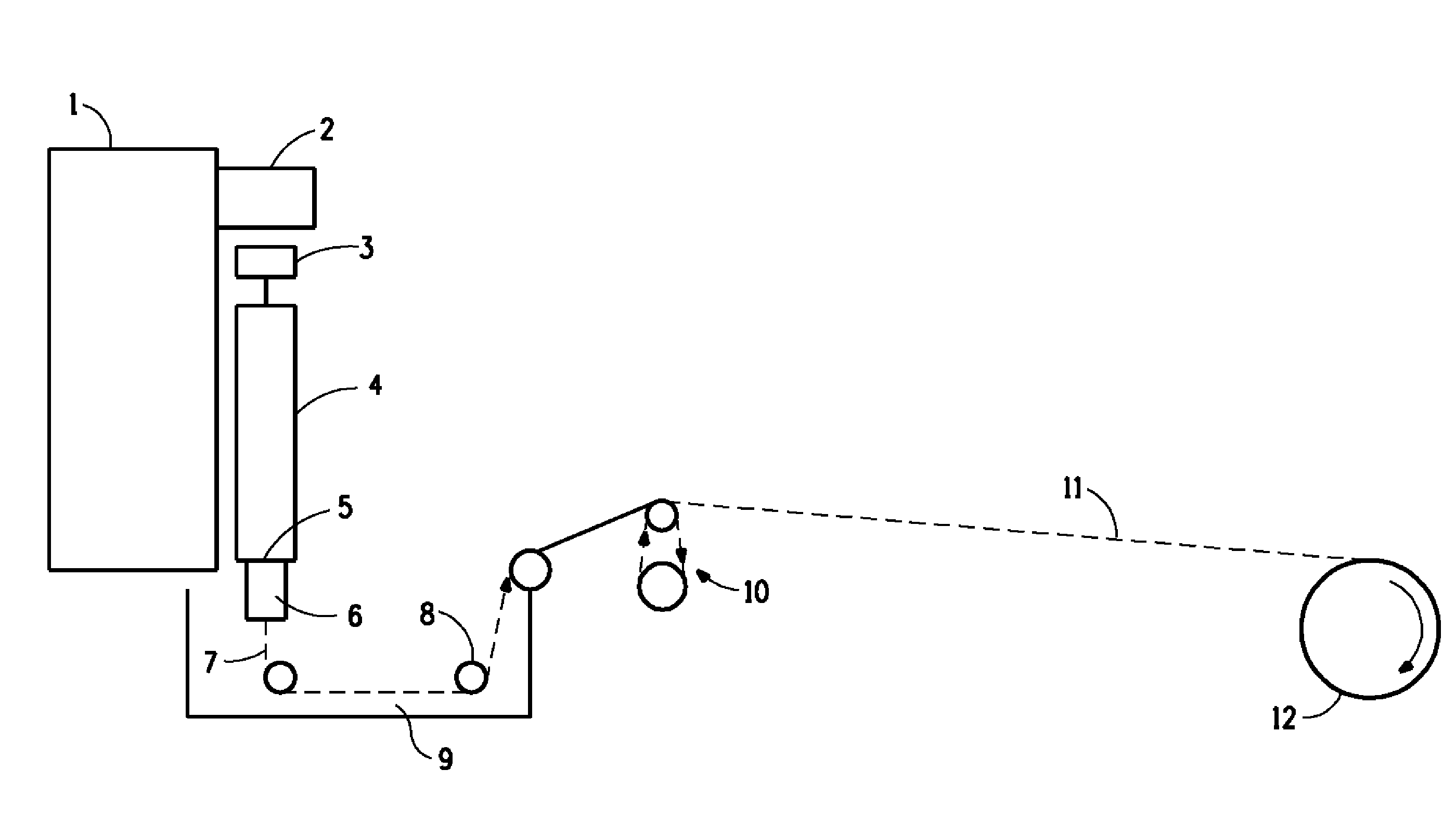
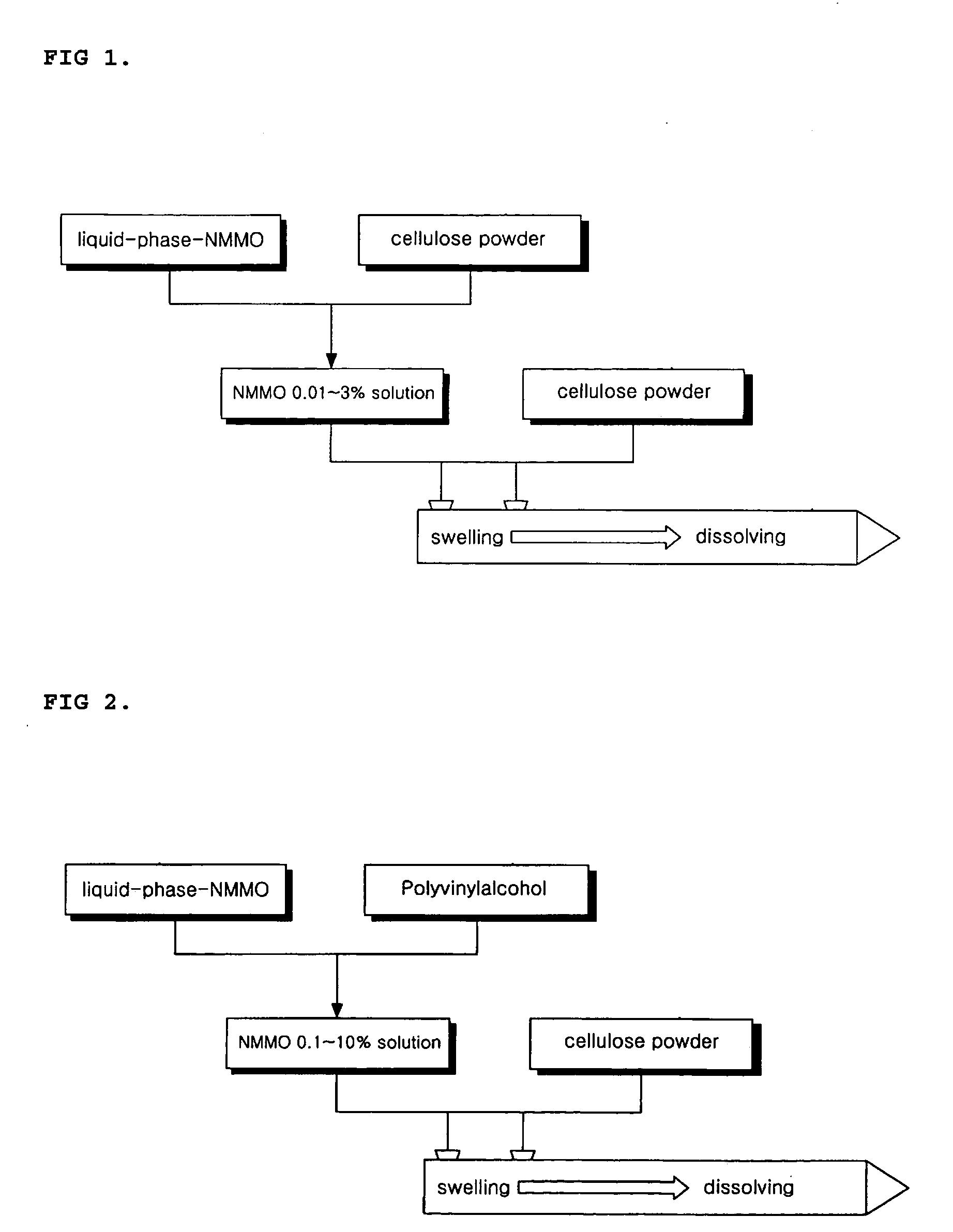
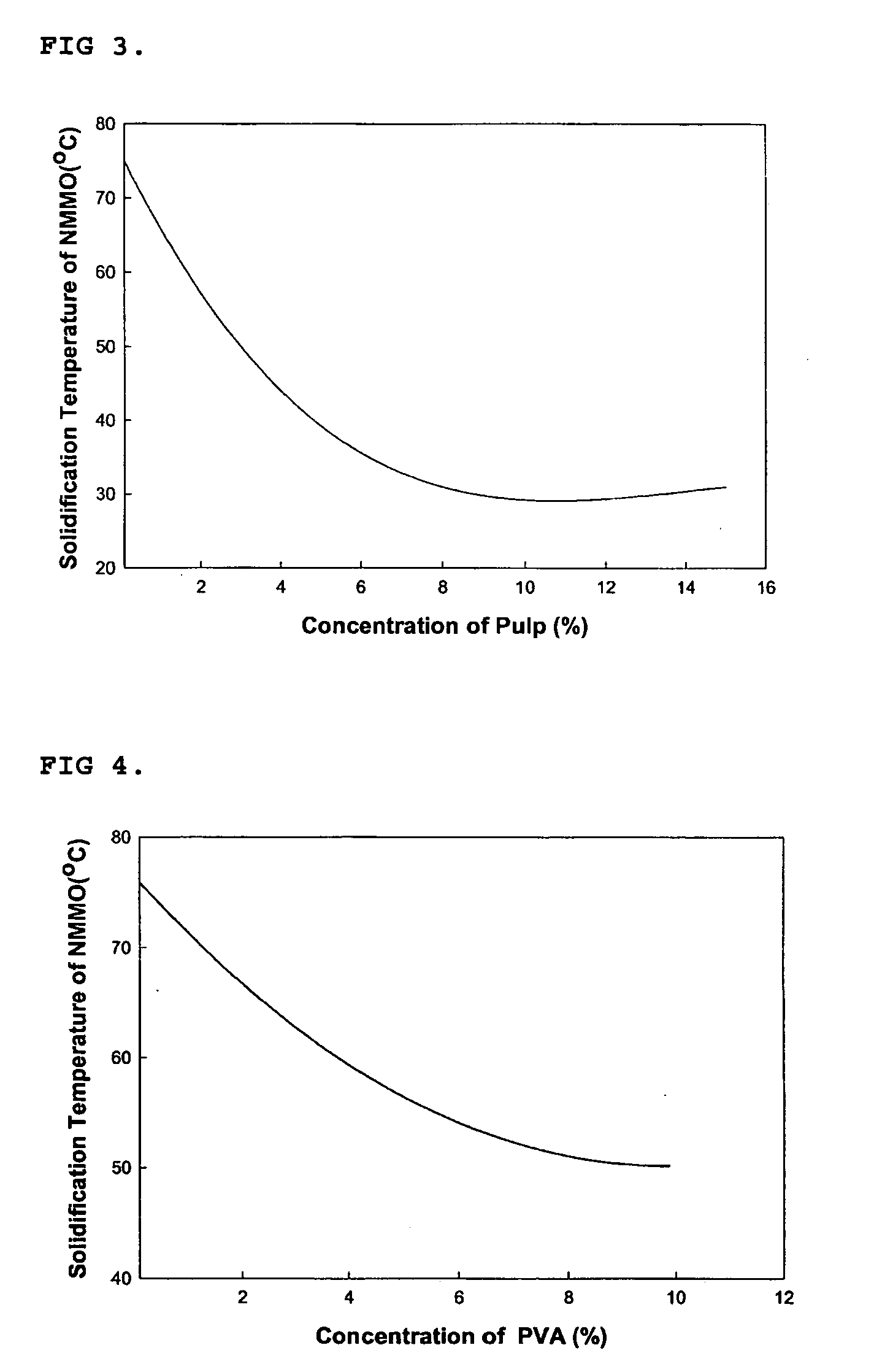
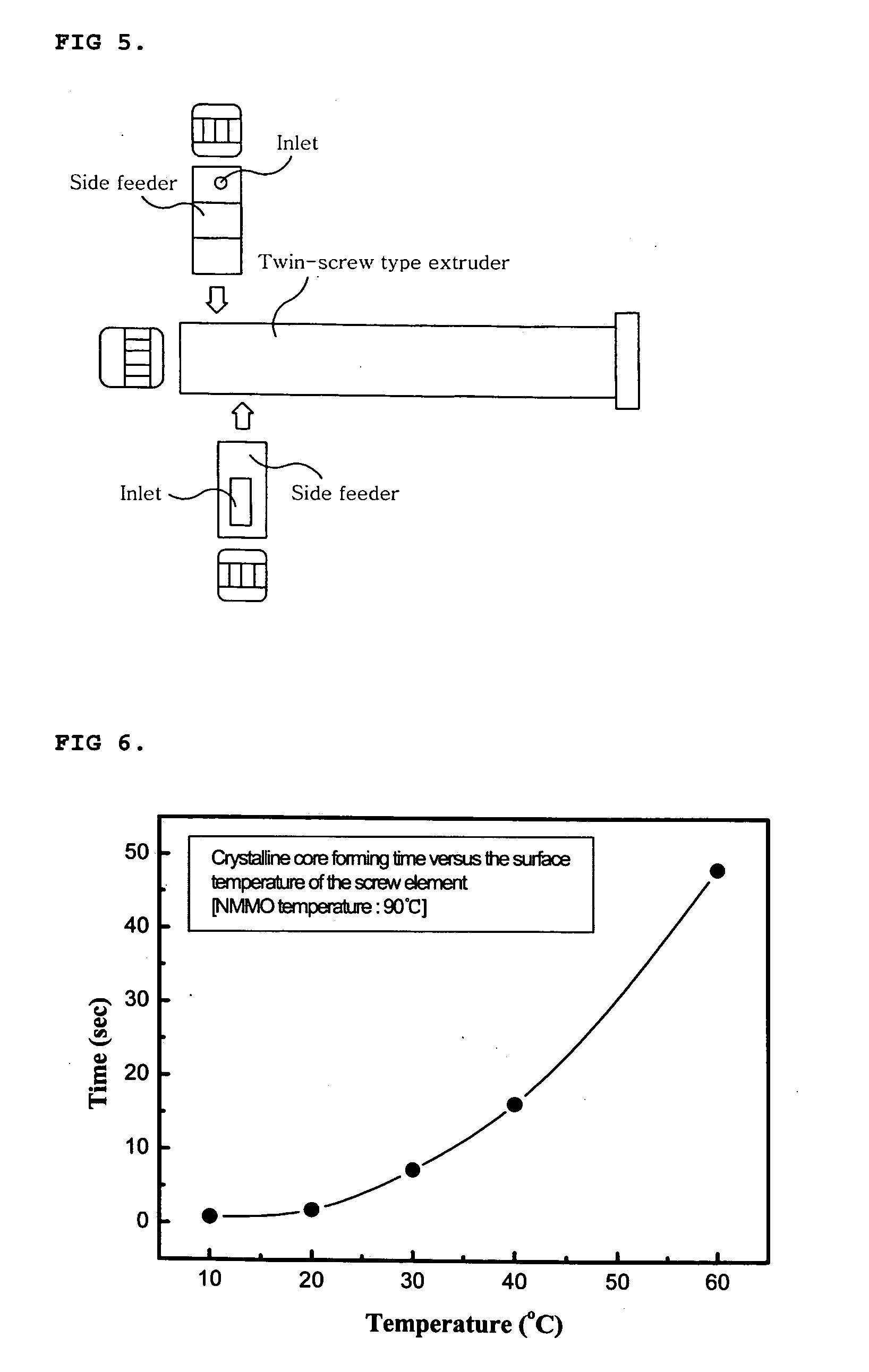
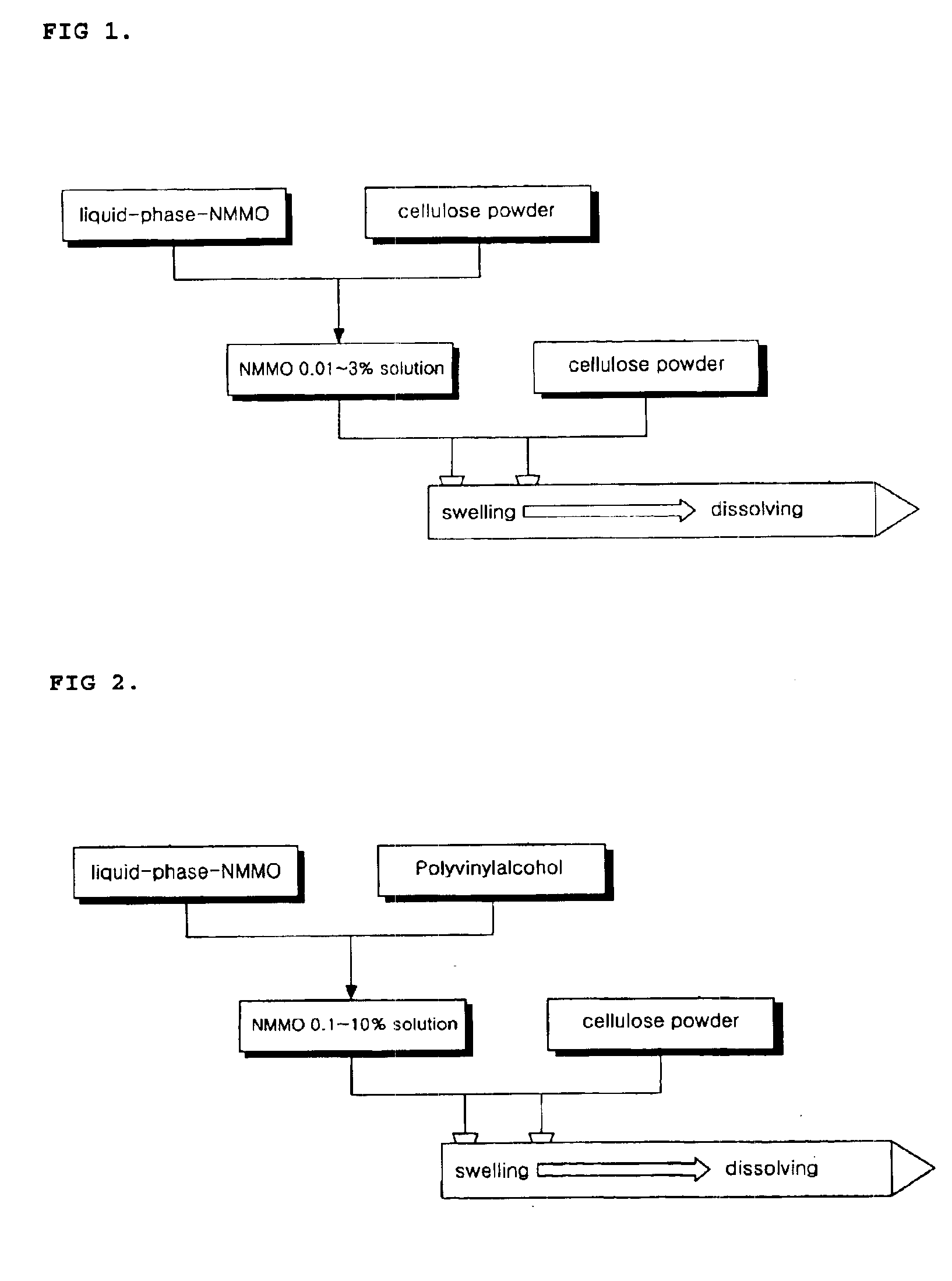
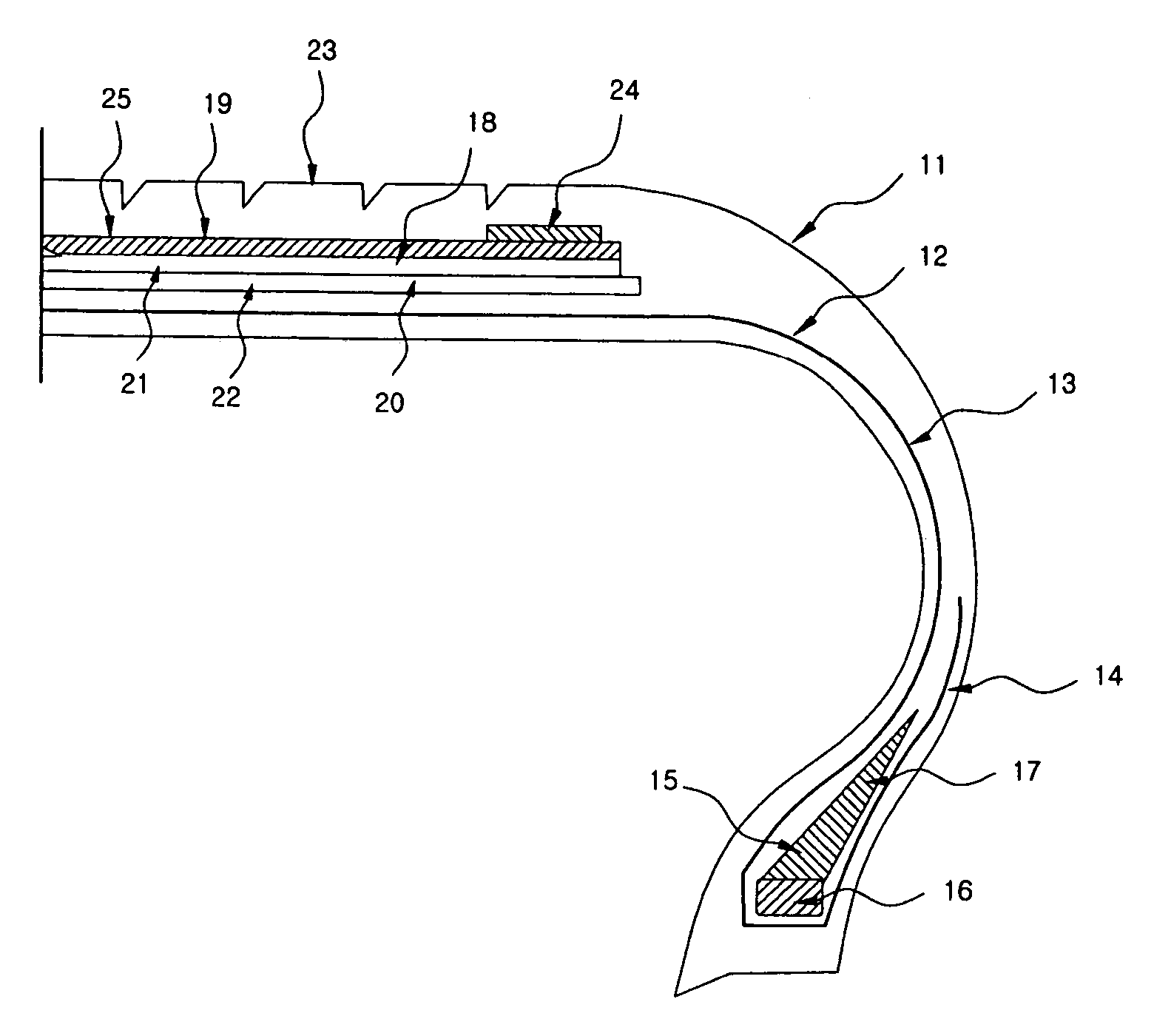
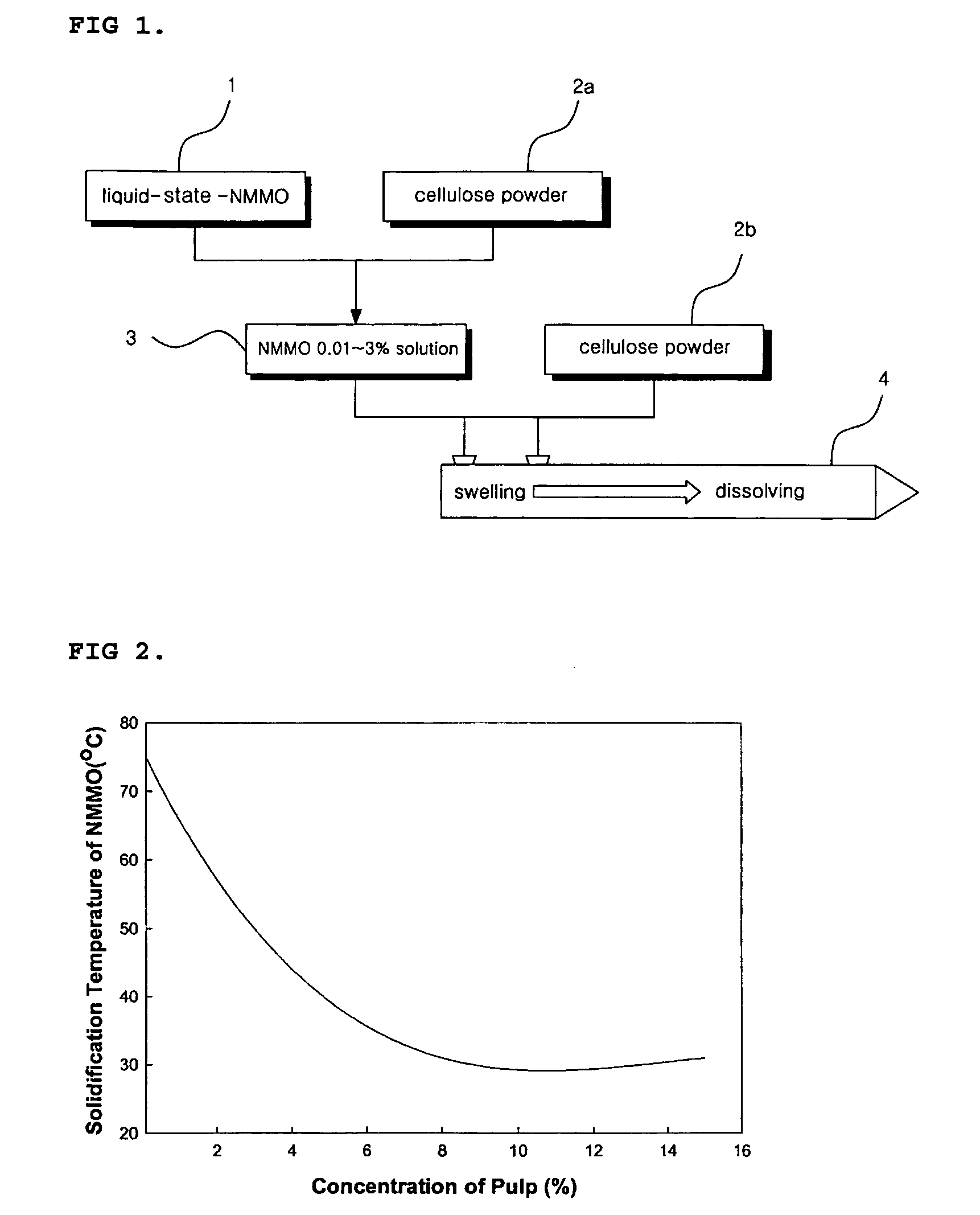
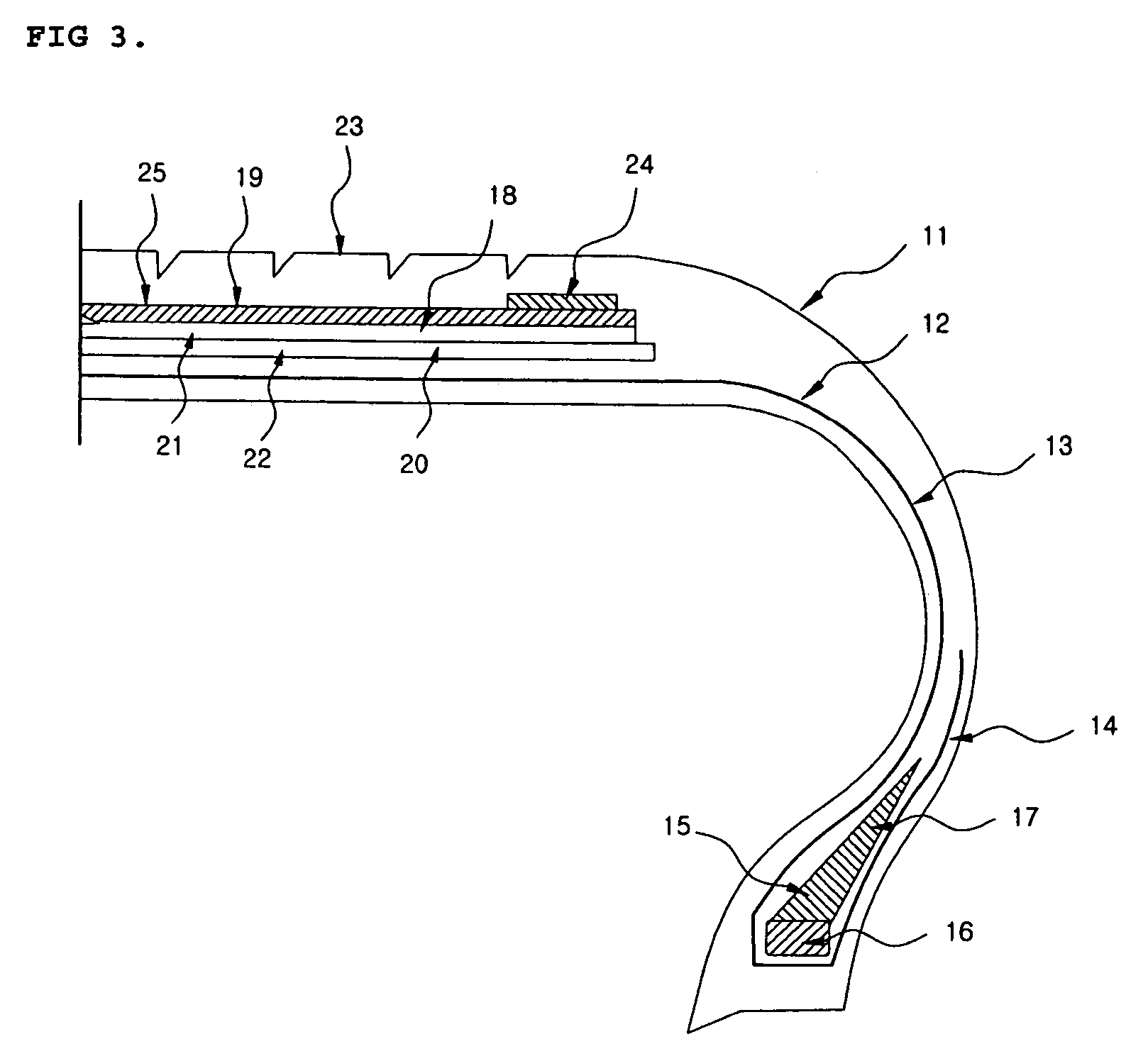
This invention relates to a method of preparing cellulose solution which is homogeneous at relatively low temperature, in which a small amount of cellulose powder or polyvinylalcohol is dissolved in the liquid-state, concentrated N-methylmorpholine-N-oxide (hereinafter, referred to as ‘NMMO’) so as to lower the solidifying temperature of NMMO, and then, the resulting solution and cellulose powder are fed into an extruder so as to be mixed, swollen and melted in the extruder.
Owner:HYOSUNG ADVANCED MATERIALS CORP
Novel Composition for Preparing Polysaccharide Fibers
This invention pertains to a novel process for preparing fibers from poly(α(1→3) glucan). The fibers prepared according to the invention, have“cotton-like” properties, are useful in textile applications, and can be produced as continuous filaments on a year-round basis. The process comprises solution spinning from a novel solution of poly(α(1→3) glucan) in a mixture of water and N-methylmorpholine-N-oxide followed by coagulation in a liquid coagulant that comprises a liquid that is not water.
Owner:NUTRITION & BIOSCIENCES USA 4 INC
Regenerated cellulosic fibers and process for producing the same
InactiveUS6183865B1Reduce stretchImprove the immunityMonocomponent cellulose artificial filamentCellulosic plastic layered productsLiquid crystallinePolymer science
It is an object of the present invention to overcome the problem of fibrillation which is a drawback found in solvent-spun regenerated cellulosic fibers and to thereby provide high-quality regenerated cellulosic fibers. The regenerated cellulosic fibers are produced by the use of a spinning dope of cellulose dissolved in a solvent containing N-methylmorpholine N-oxide under the conditions that the average degree of polymerization of cellulose contained in the spinning dope is held to 400 or lower and 5% to 30% by weight of the cellulose is adjusted to a degree of polymerization of 500 or higher. Thus a pseudo-liquid-crystalline phenomenon can be allowed to occur in the stretched filaments during spinning, so that the resulting regenerated cellulosic fibers have improved resistance to fibrillation as well as improved dyeability and feeling.
Owner:TOYOBO CO LTD
Lyocell multifilament
ActiveUS20050019564A1Low modulusLow tenacity lowMonocomponent cellulose artificial filamentCellulosic plastic layered productsYarnEngineering
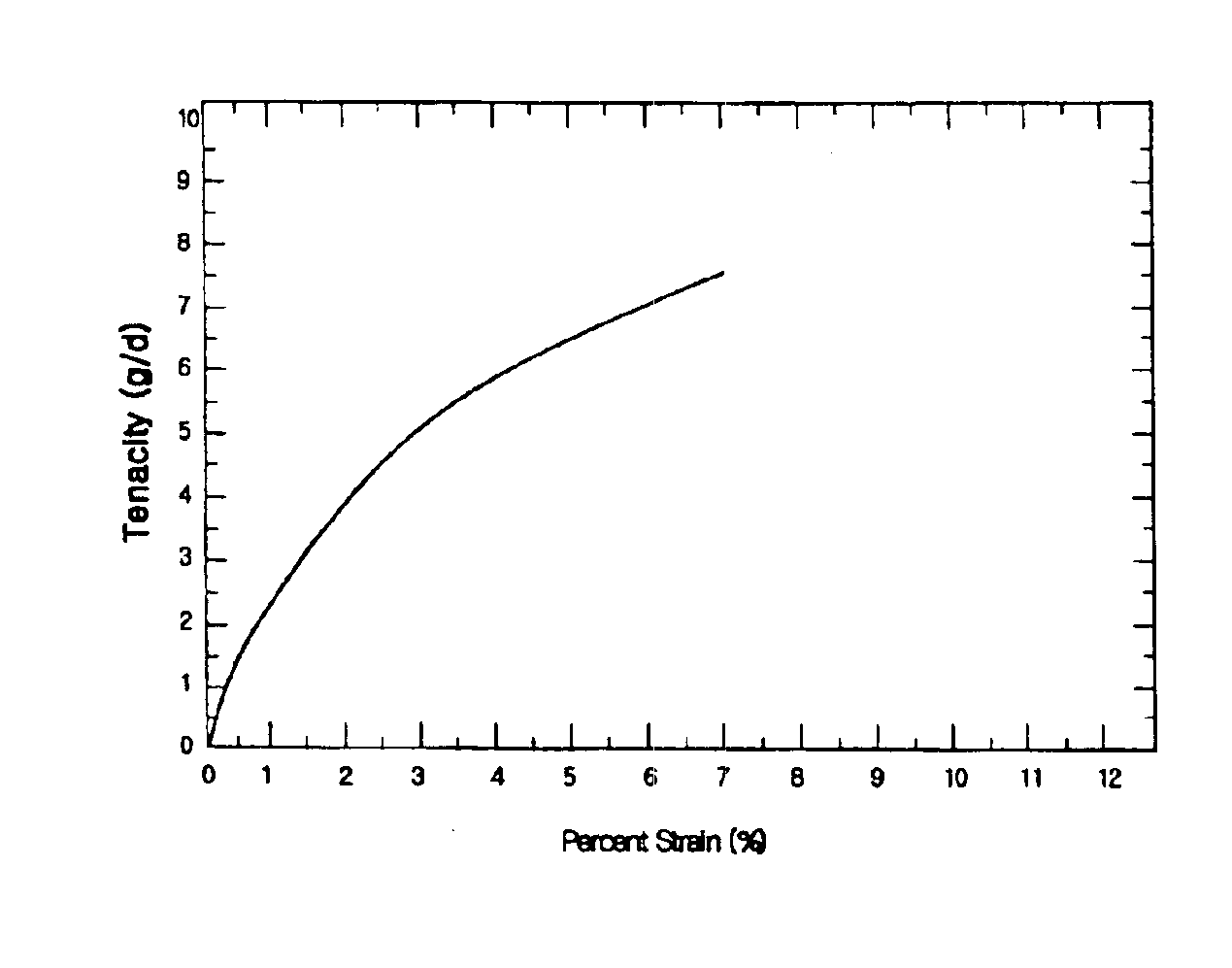
The present invention relates to a high tenacity, high modulus and low shrinkage lyocell multifilament yarn suitable for use in tire cords and MRG (mechanical rubber goods). The lyocell multifilament yarn is a cellulose-based fiber for industrial applications, which is produced by dissolving pulp having a degree of polymerization (DPW) of 700-2,000 and preferably 800-1,400, and a α-cellulose content of more than 90% and preferably more than 92%, in N-methylmorpholine N-oxide (NMMO) hydrate, at a pulp concentration of 5-15% by weight and preferably 8-13% by weight. The lyocell monofilament according to the present invention is characterized by the following stress-strain profile: (1) the lyocell monofilament analyzed after drying is elongated by less than 3.0% and has an initial modulus of 150-400 g / d, when it was subjected to an initial stress of 3.0 g / d; (2) it is elongated by 3.0-7.0% when it was subjected to a stress greater than the initial stress but smaller than 6.0 g / d; and (3) it is elongated from a tensile tenacity of at least 6.0 g / d until the yarn is broken.
Owner:HYOSUNG ADVANCED MATERIALS CORP
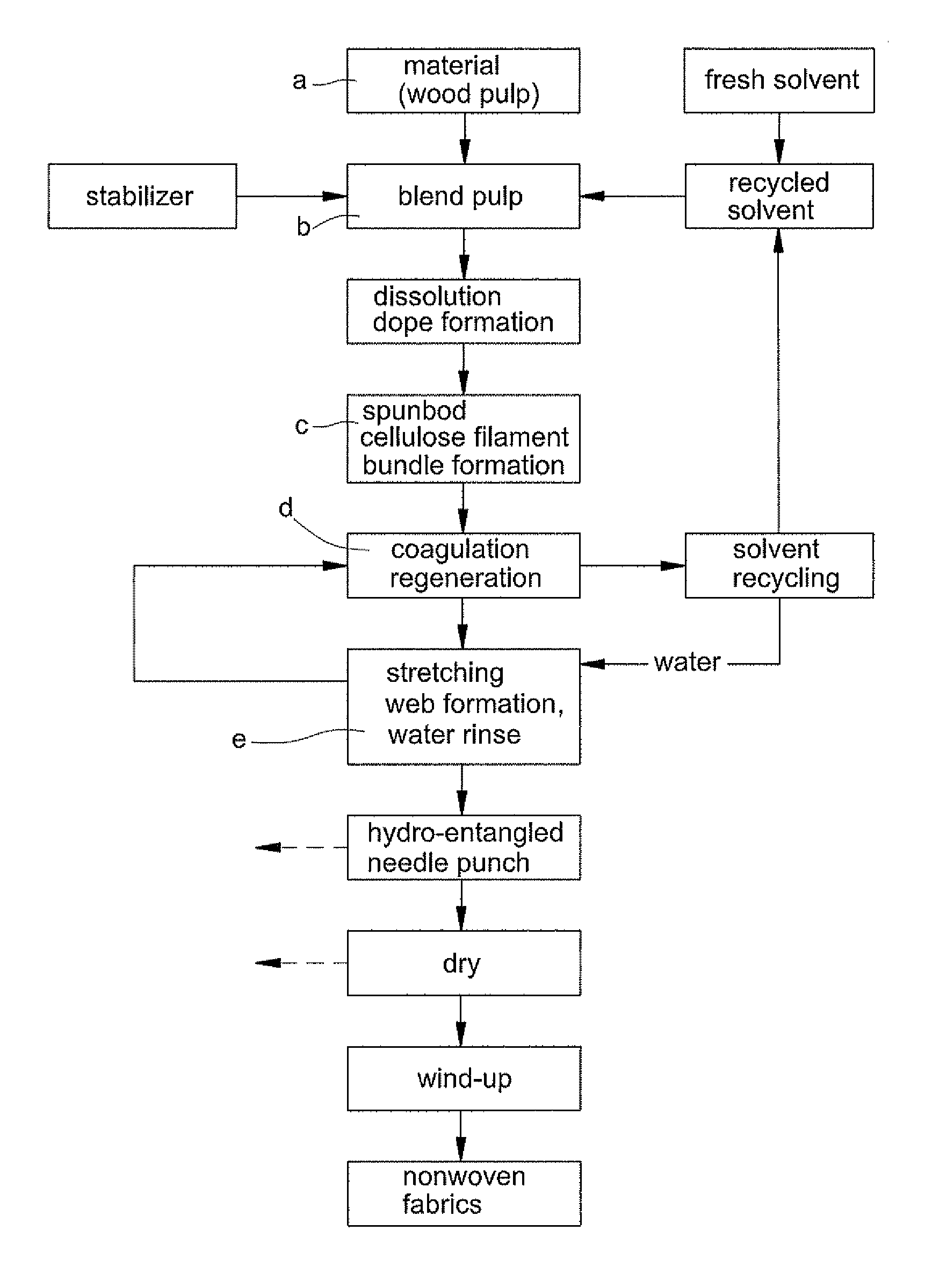
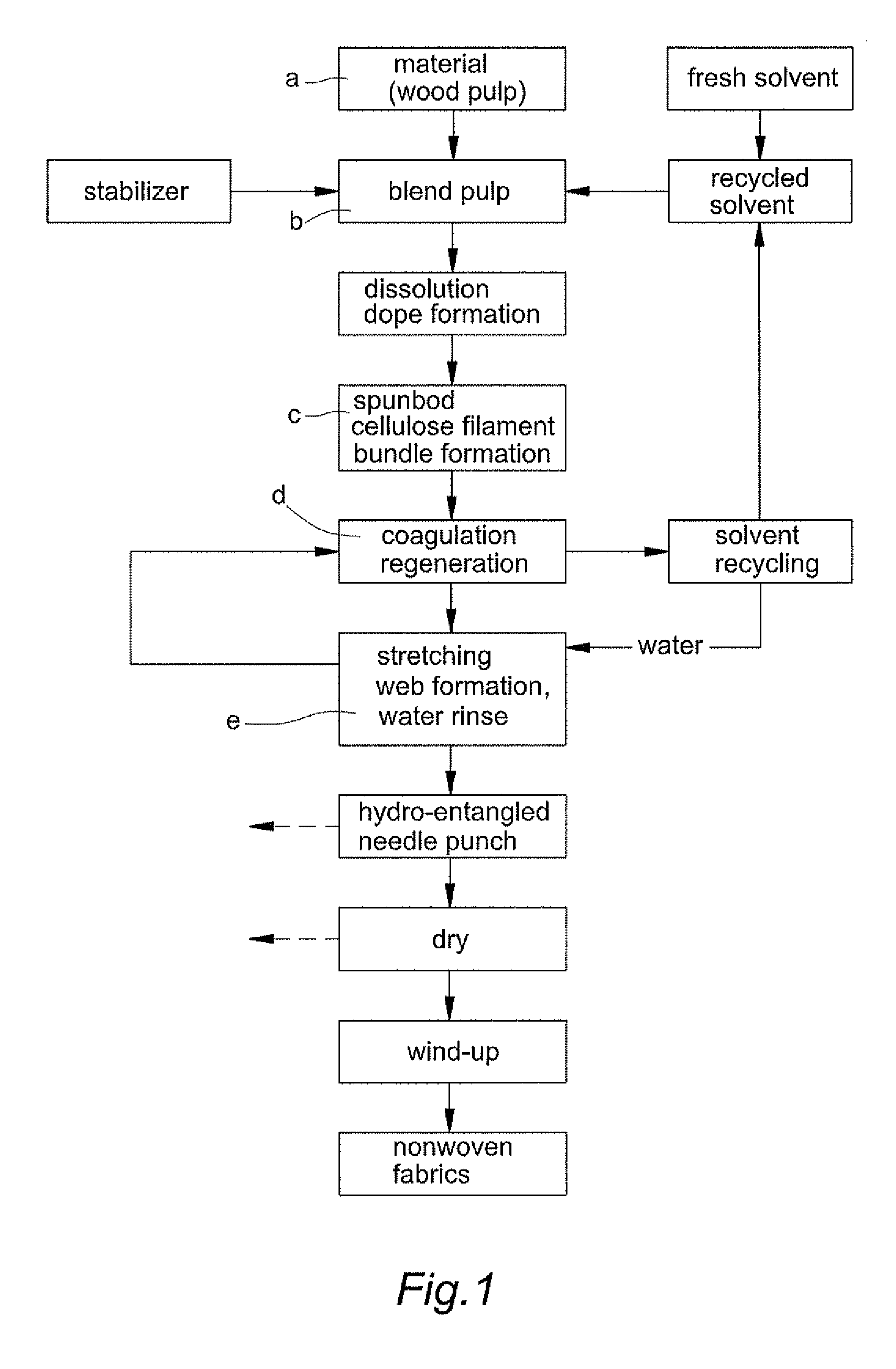
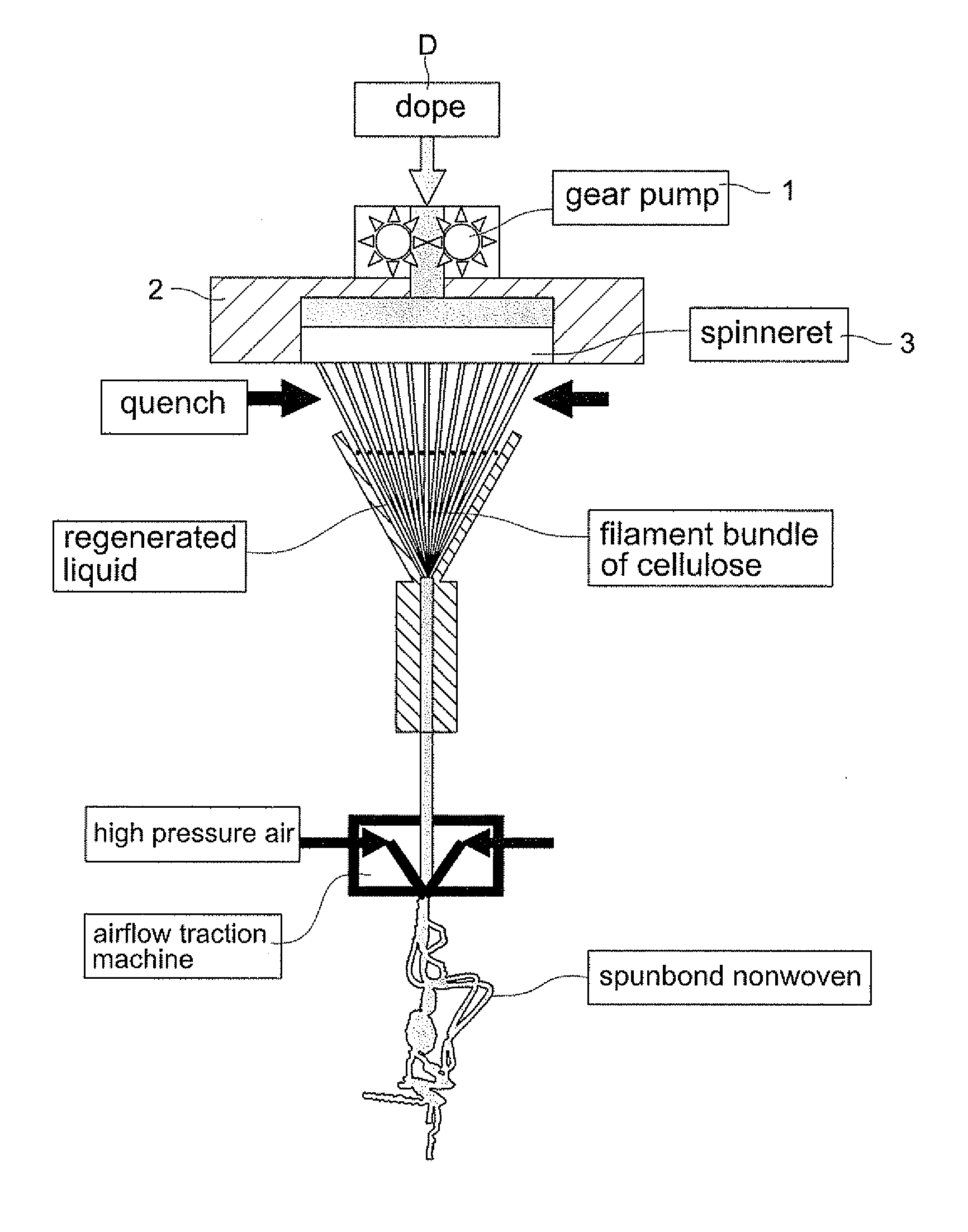
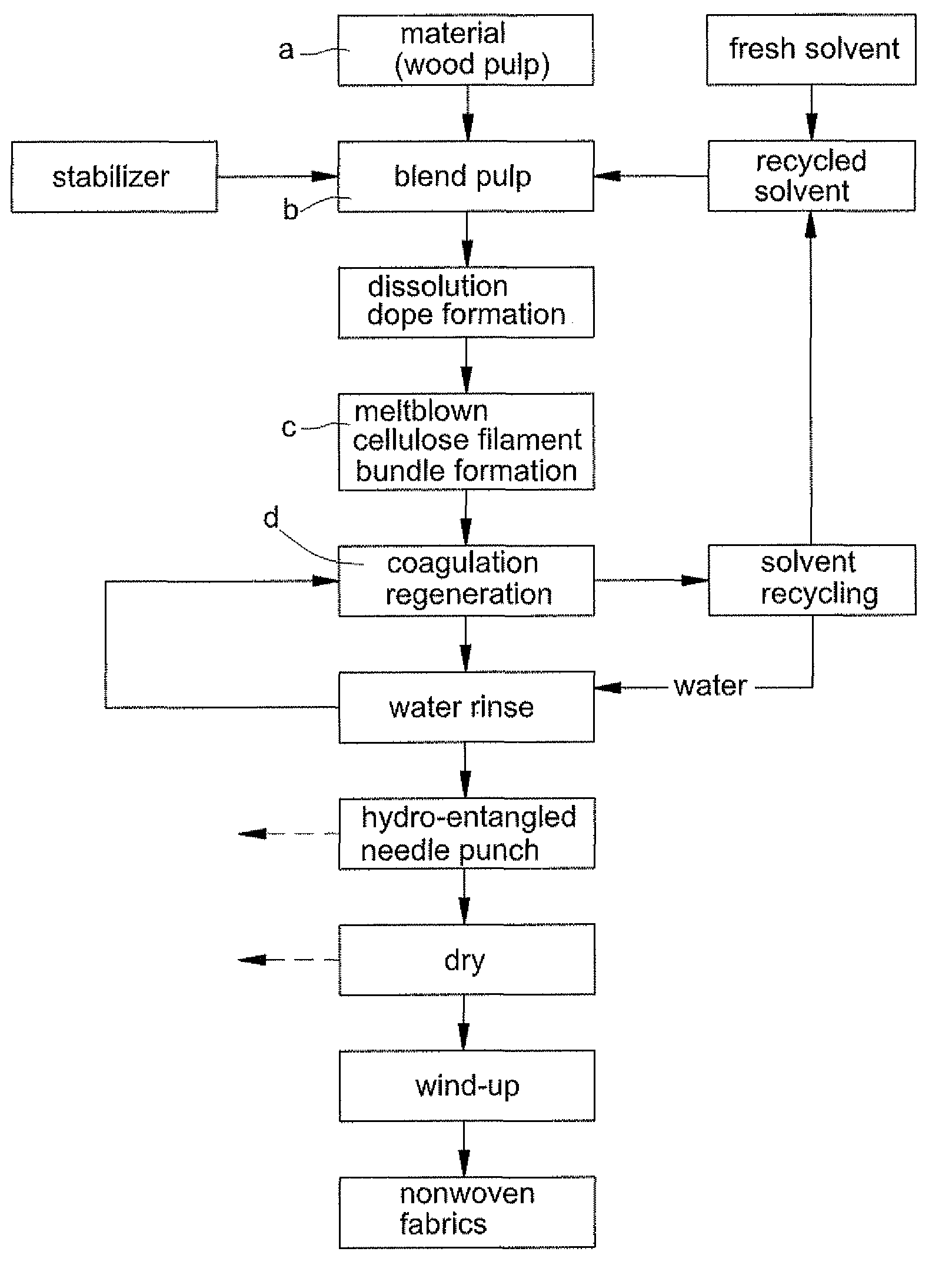
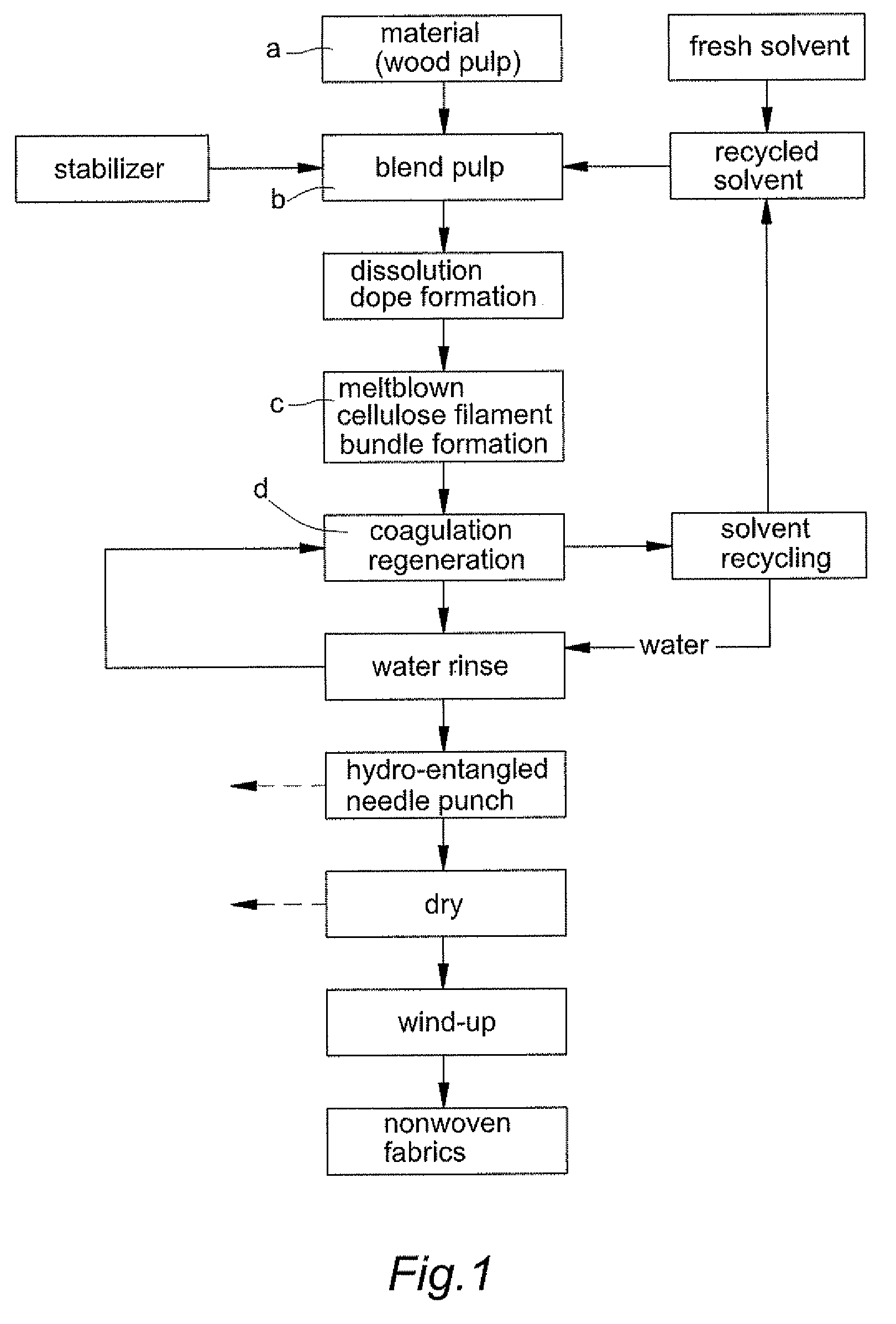
Spunbond wetlaid method for producing non-woven fabrics from natural cellulose
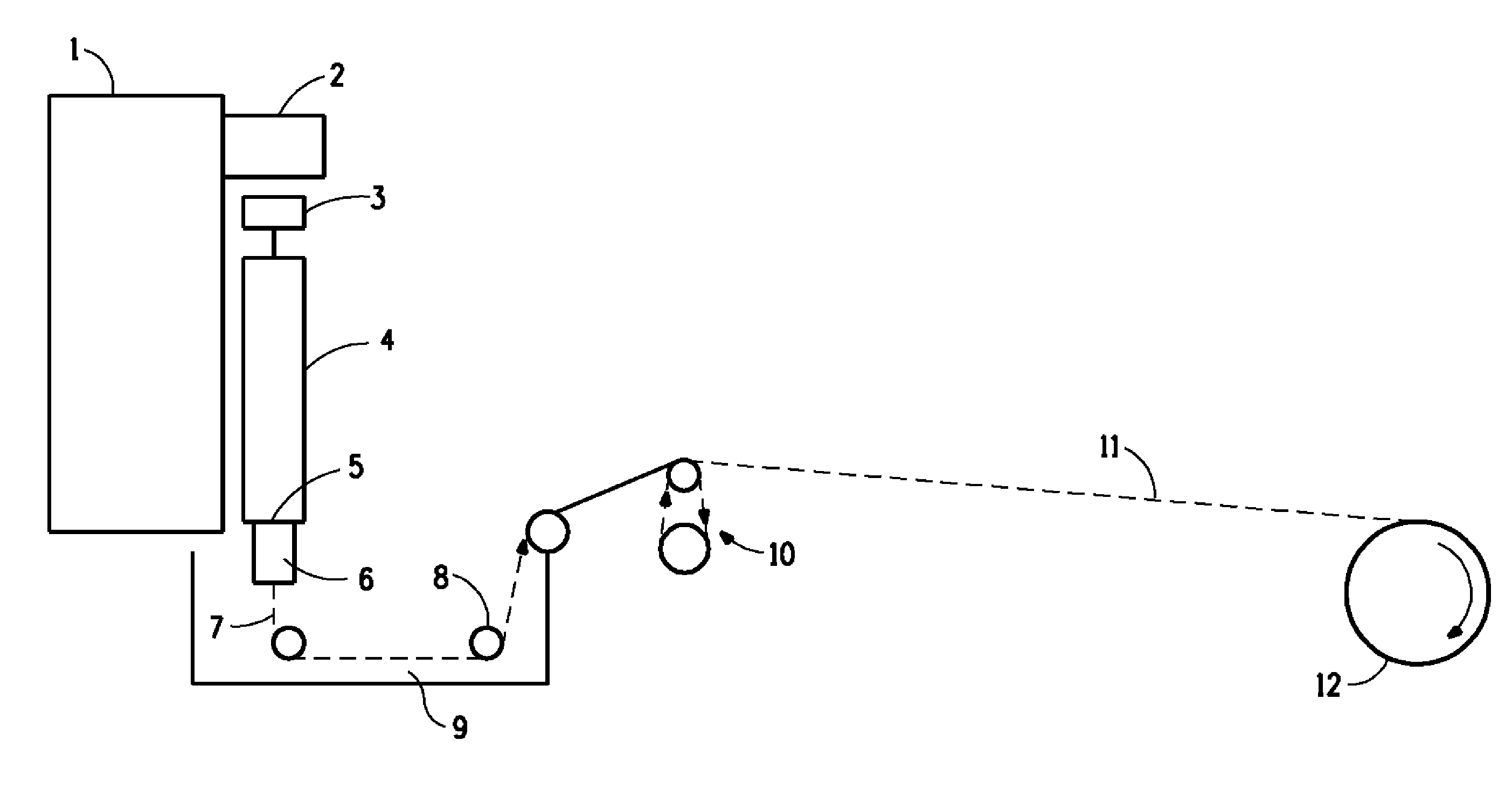
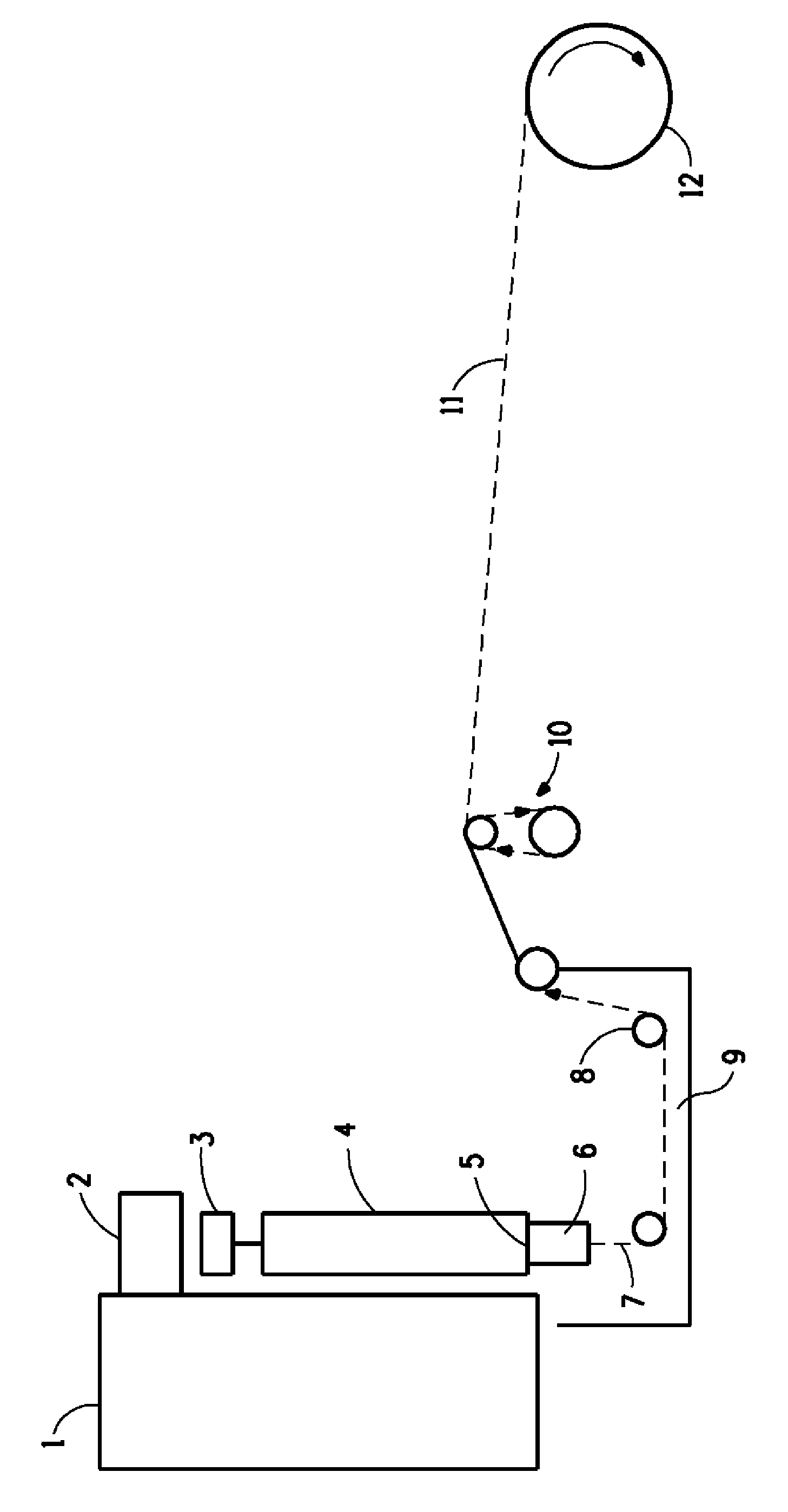
ActiveUS8366988B2Reduce manufacturing costDegree of air permeabilityArtificial filaments from cellulose solutionsPattern makingPunchingWater rinsing
Owner:LIN CHIH HSIN
Process for producing regenerated cellulosic fibers
InactiveUS6527987B1Maintain good propertiesImprove the immunityArtificial filaments from cellulose solutionsHollow filament manufactureLiquid crystallinePolymer science
It is an object of the present invention to overcome the problem of fibrillation which is a drawback found in solvent-spun regenerated cellulosic fibers and to thereby provide high-quality regenerated cellulosic fibers. The regenerated cellulosic fibers are produced by the use of a spinning dope of cellulose dissolved in a solvent containing N-methylmorpholine N-oxide under the conditions that the average degree of polymerization of cellulose contained in the spinning dope is held to 400 or lower and 5% to 30% by weight of the cellulose is adjusted to a degree of polymerization of 500 or higher. Thus a pseudo-liquid-crystalline phenomenon can be allowed to occur in the stretched filaments during spinning, so that the resulting regenerated cellulosic fibers have improved resistance to fibrillation as well as improved dyeability and feeling.
Owner:TOYOBO CO LTD
Method of Preparing of Natural Graphene Cellulose Blended Meltblown Nonwoven Fabric
ActiveUS20170107650A1Avoiding health hazard associated with solutionAltered propertyArtificial filament recoveryGraphitePresent methodSlurry
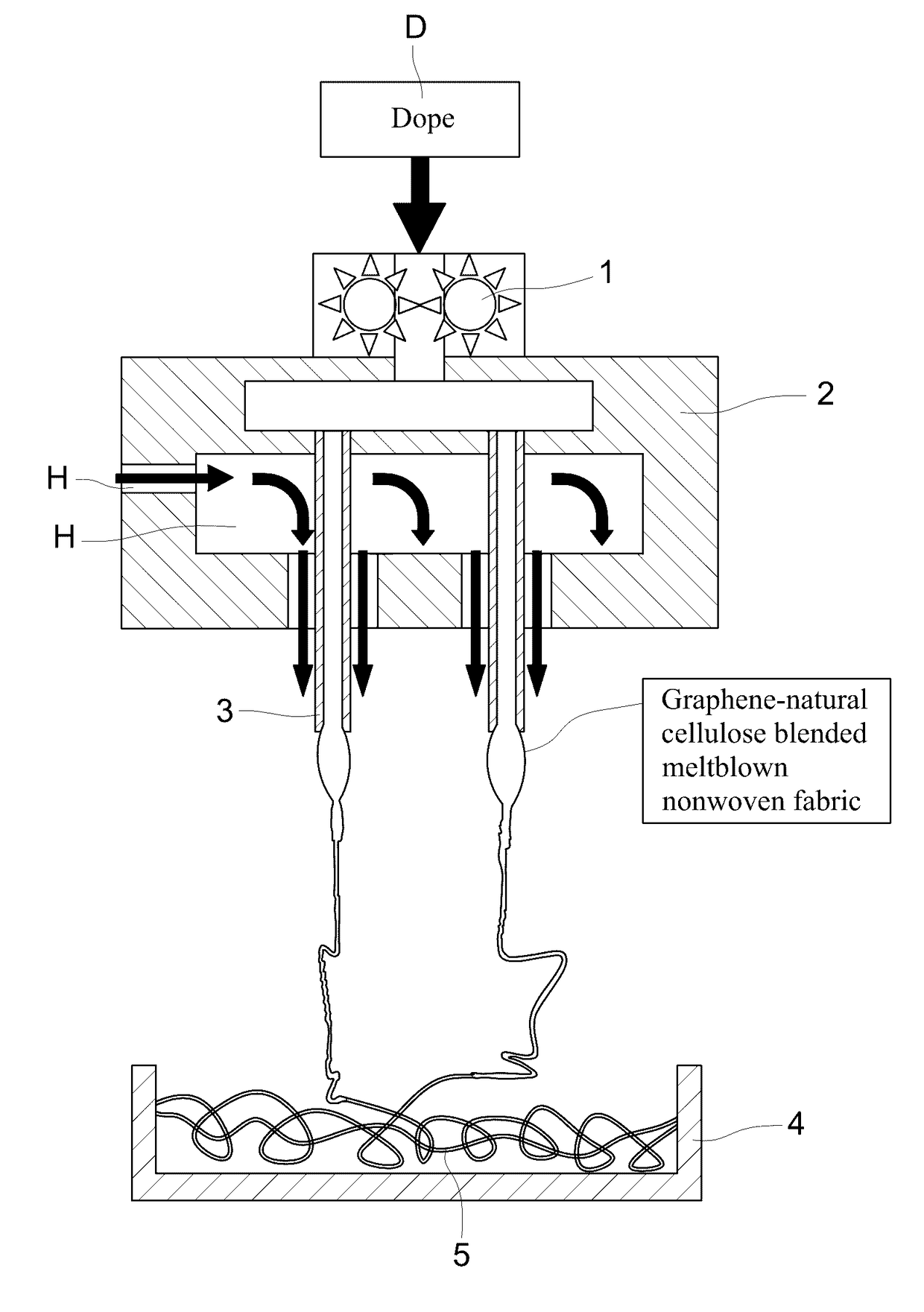
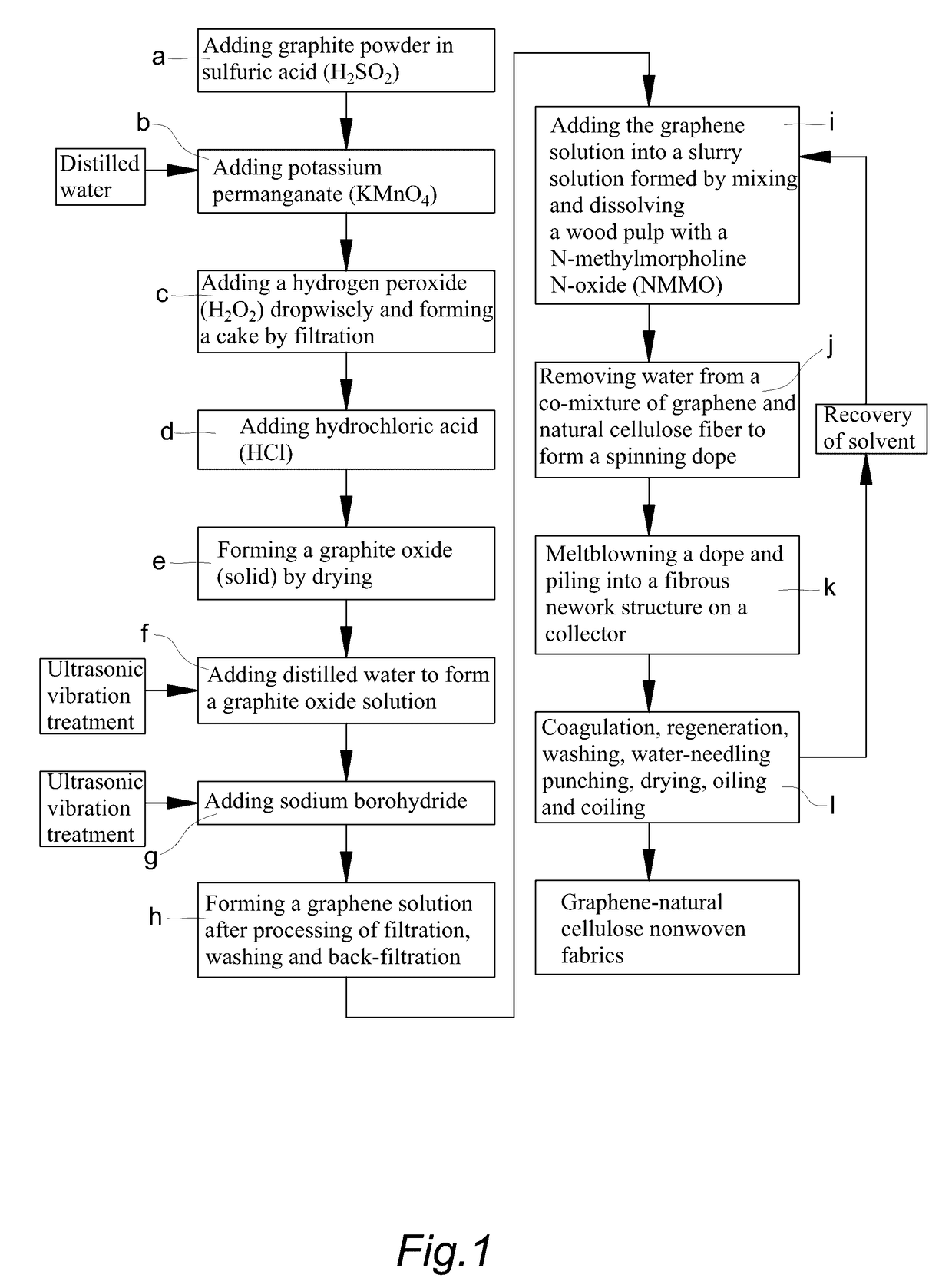
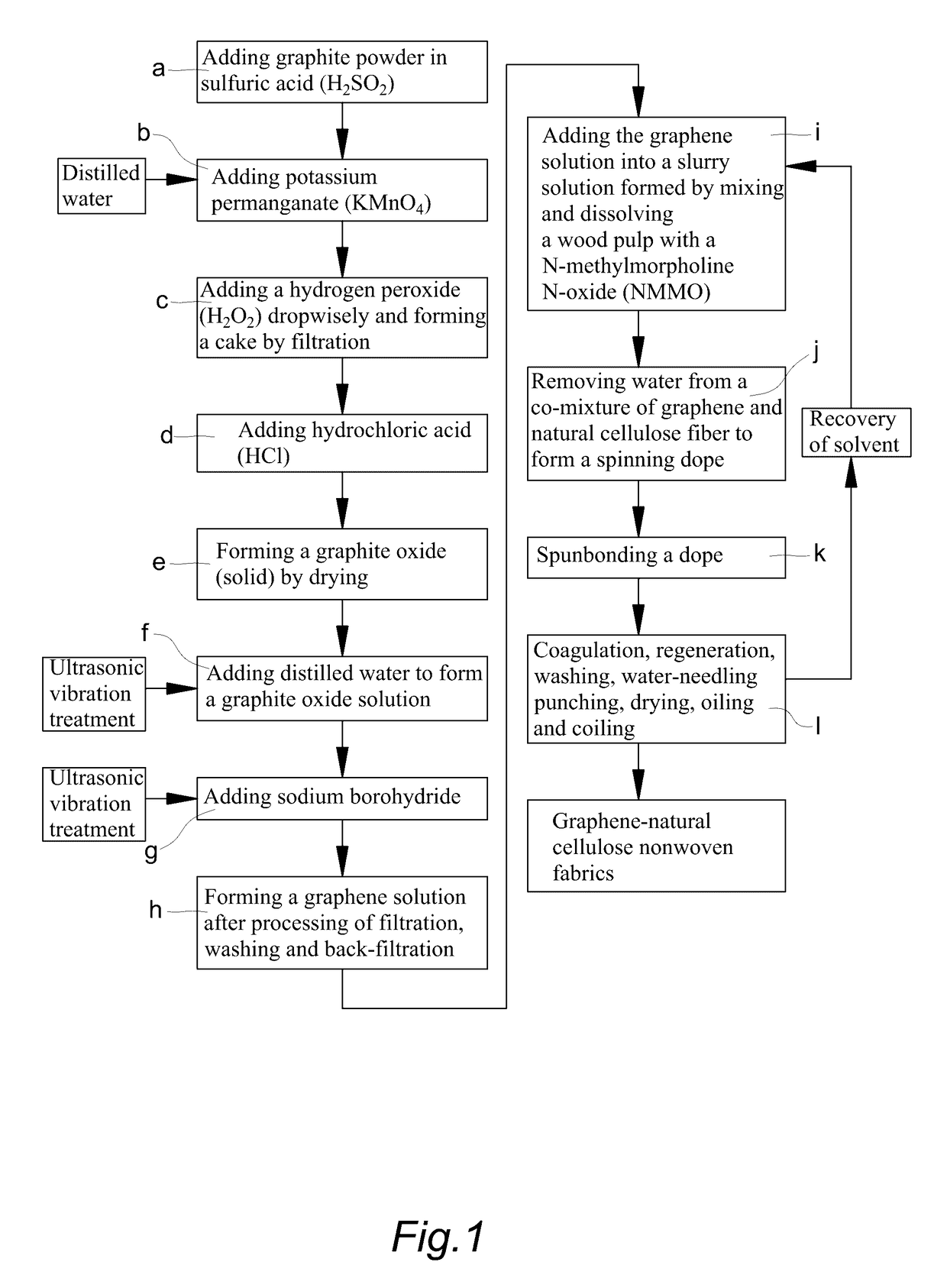
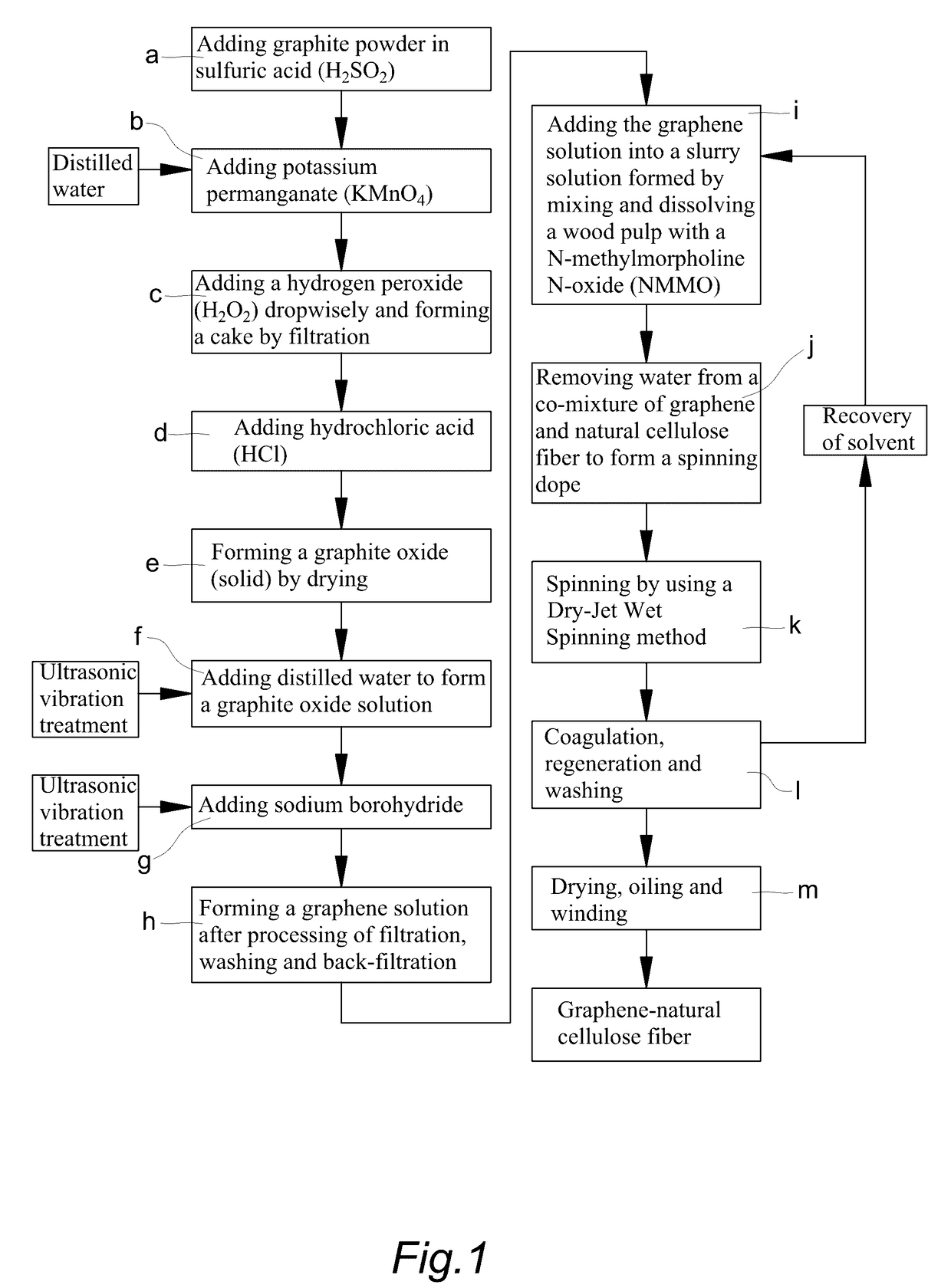
This application describes a method of preparation of a natural graphene cellulose blended meltblown nonwoven fabric, which comprises using a graphite powder as a raw material for preparing a graphene solution, adding the graphene solution to a slurry formed by mixing and dissolving a wood pulp with N-methylmorpholine N-oxide (NMMO), removing the water content thereof to form a spinning dope, and then directly preparing the natural graphene cellulose blended meltblown nonwoven fabric by a meltblown process. The present method does not require a highly toxic hydrazine hydrate solution. Further, by increasing the adding ratio of the graphene solution in the manufacturing process, control of the antistatic properties and thermal transferring function can be achieved, and thereby various requirements of different consumers can be satisfied. Besides, the fabric can decompose naturally after being used, and thus the product is harmless, natural, and environmentally friendly.
Owner:LIN CHIH HSIN
Spunbond wetlaid method for producing non-woven fabrics from natural cellulose
ActiveUS20110156303A1Reduce manufacturing costShort processMonocomponent cellulose artificial filamentWet spinning methodsPunchingWater rinsing
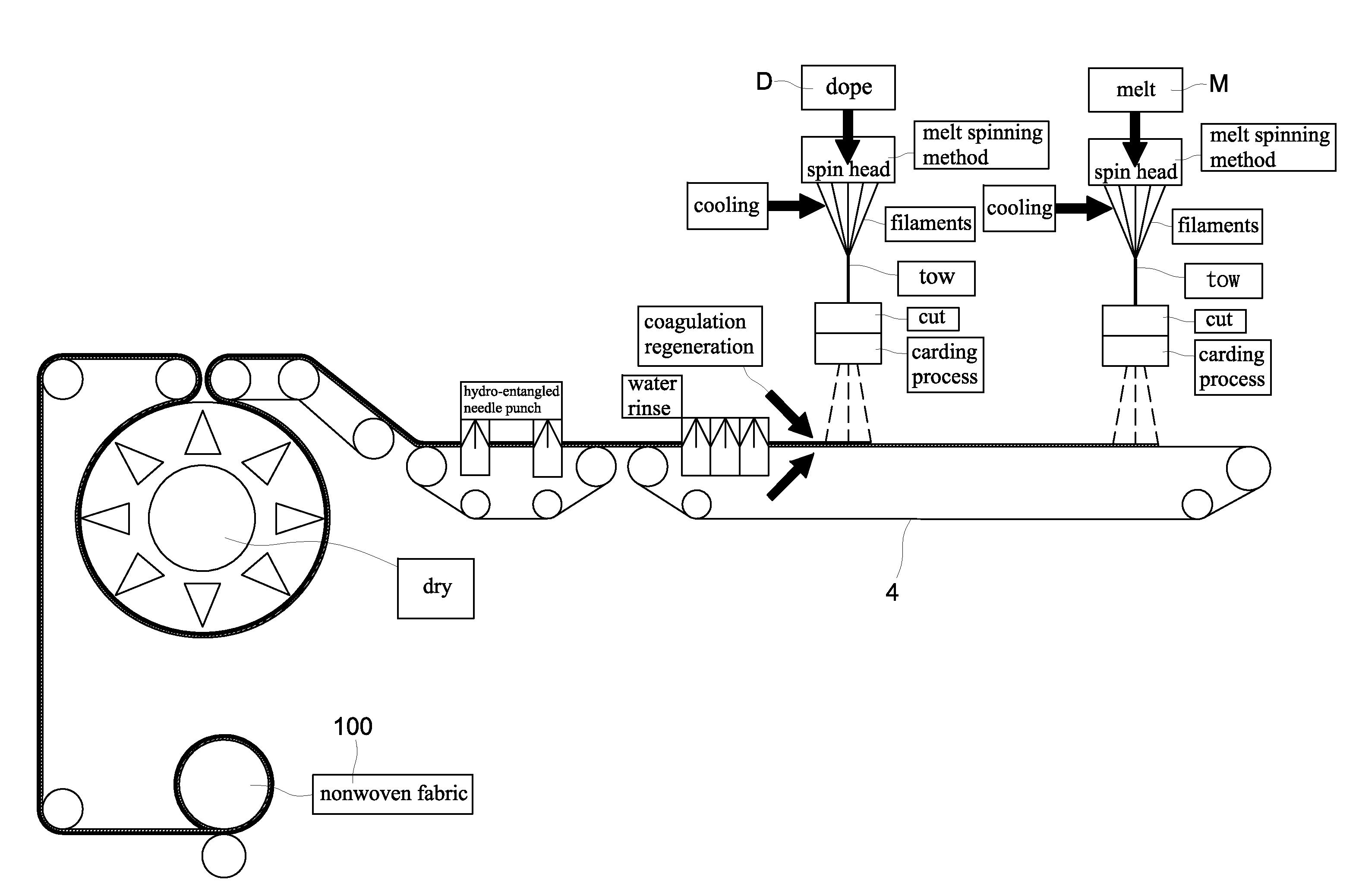
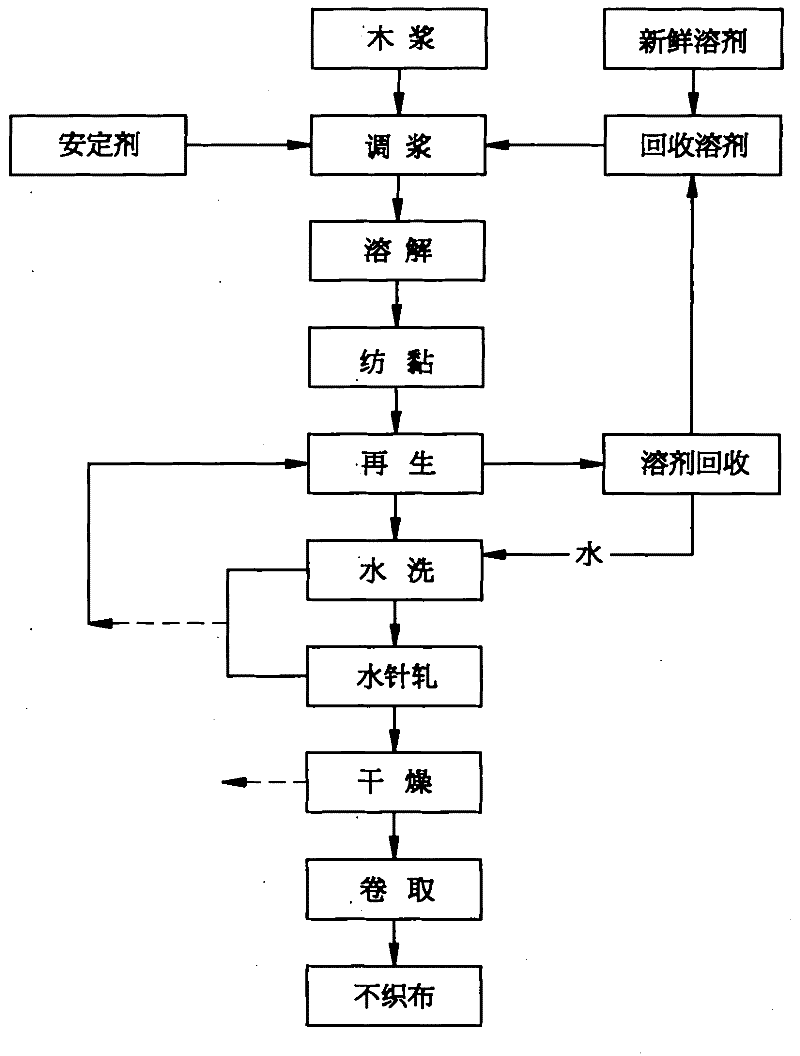
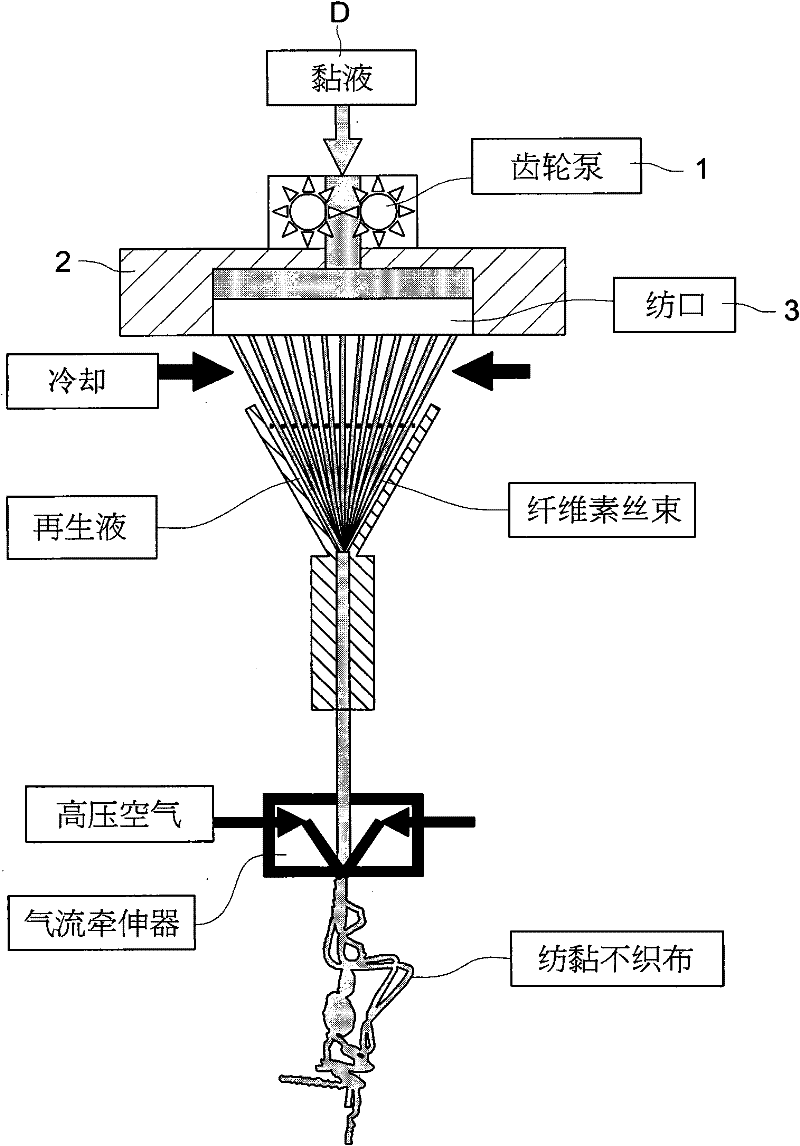
The present invention provides a “spunbond wetlaid method for producing non-woven fabrics from natural cellulose” using pulp as raw material and N-methylmorpholine N-oxide (NMMO) as solvent for dissolving into dope. Then, the dope is extruded out of a spinneret to form filament bundle by spunbond method. The dope is extruded out of a spinneret bank of grouped spinnerets to form filament bundle for further stretching process under quench condition. The filament bundle is coagulated with regeneration in a coagulating solution. The coagulated filament bundle is rapidly stretched under high pressure by an air draw-off machine. The stretched filament bundle is collected and stacked on a collecting net as web nonwoven. After post treatments of water rinsing, hydro-entangled needle punching, drying, winding-up and the like have been orderly applied then final product of nonwoven fabrics with continuous filament are produced from natural cellulose.
Owner:LIN CHIH HSIN
Method for producing a cellulose suspension
ActiveUS20150007952A1Operational securityPulp properties modificationArtificial filaments from cellulose solutionsOrganic solventN-Methylmorpholine N-oxide
Owner:LENZING AG
Cellulose/polylactic acid blend material and preparation method thereof
The invention discloses a blend material of cellulose and a polylactic acid. The blend contains 0.1-99.9% of cellulose and 99.9-0.1% of polylactic acid. The method comprises the following steps: with a 30-100% N-methylmorpholine-N-oxide (NMNO) water solution as a solvent, adding cellulose and a polylactic acid to the NMMO solution; dissolving at constant temperature of 35-150 DEG C for 0.1-100 hours; completely dissolving the cellulose and the polylactic acid, so as to prepare the mixed solution of the cellulose and the polylactic acid; precipitating a molding product of the mixed solution by a precipitant; and pelletizing and drying the obtained blend in vacuum, so as to prepare the blend material of the cellulose and the polylactic acid. The raw material of the cellulose is any one or a mixture of more than two of straws, bagasse, wood fiber, jute fiber, beet pulp, bamboo fiber, cotton pulp, hemp pulp, bamboo pulp and recycled cellulose, and the polylactic acid is a homopolymer, a copolymer or a blend thereof.
Owner:NANJING FORESTRY UNIV
Composition for preparing polysaccharide fibers
This invention pertains to a novel process for preparing fibers from poly(α(1→3) glucan). The fibers prepared according to the invention, have “cotton-like” properties, are useful in textile applications, and can be produced as continuous filaments on a year-round basis. The process comprises solution spinning from a novel solution of poly(α(1→3) glucan) in a mixture of water and N-methylmorpholine-N-oxide followed by coagulation in a liquid coagulant that comprises a liquid that is not water.
Owner:NUTRITION & BIOSCIENCES USA 4 INC
Graphene tencel composite fiber and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN106884210AHigh strengthGood flexibilityElectroconductive/antistatic filament manufactureMonocomponent cellulose artificial filamentYarnFiber
The invention discloses a graphene tencel composite fiber and a preparation method thereof. The graphene tencel composite fiber is prepared by mixing a graphene oxide solution and cellulose pulp into NMMO (N-methylmorpholine-N oxide) and water, dissolving, filtering, spinning by virtue of a dry-wet spinning process and then finishing by virtue of silk yarns and a graphene oxide finishing solution. The tencel composite fiber contains graphene and is prepared by the following steps: preparing a spinning solution, spinning, and finishing the yarns by virtue of graphene. The obtained yarns can sufficient integrate the excellent characteristics of tencel and graphene, has excellent physical properties of the tencel, such as moisture absorption performance, dyeing performance, comfort, high strength and the like, also improves the flexibility, conductivity, and bacteria resistance of the grpahene, and are ideal fibers for clothes. The preparation process and a production process are pollution-free to the environment, the fiber product waste can be naturally degraded, damage to the environment can be avoided, and a recyclable resource is easy to form.
Owner:常州市卓盛纺织有限公司
Method of Preparing of Natural Graphene Cellulose Blended Spunbond Nonwoven Fabric
ActiveUS20170107644A1Avoiding health hazard associated with solutionAltered propertySpinning solution de-aeratingCarbon compoundsPresent methodSlurry
This application describes a method of preparation of a natural graphene cellulose blended spunbond nonwoven fabric, which comprises using a graphite powder as a raw material for preparing a graphene solution, adding the graphene solution to a slurry formed by mixing and dissolving a wood pulp with N-methylmorpholine N-oxide (NMMO), removing the water content thereof to form a spinning dope, and then directly preparing the natural graphene cellulose blended spunbond nonwoven fabric by a spunbond process. The present method does not require a highly toxic hydrazine hydrate solution. Further, by increasing the adding ratio of the graphene solution in the manufacturing process, control of the antistatic properties and thermal transferring function can be achieved, and thereby various requirements of different consumers can be satisfied. Besides, the fabric can decompose naturally after being used, and thus the product is harmless, natural, and environmentally friendly.
Owner:LIN CHIH HSIN
Production method of cellulose non-woven fabric with functions of mildew proofing, antibiosis and deodorization through wet-type meltbrown
ActiveCN102127841AChance of infectionReduce the chance of being infected by microorganismsMonocomponent cellulose artificial filamentWet spinning methodsSlurryNatural fiber
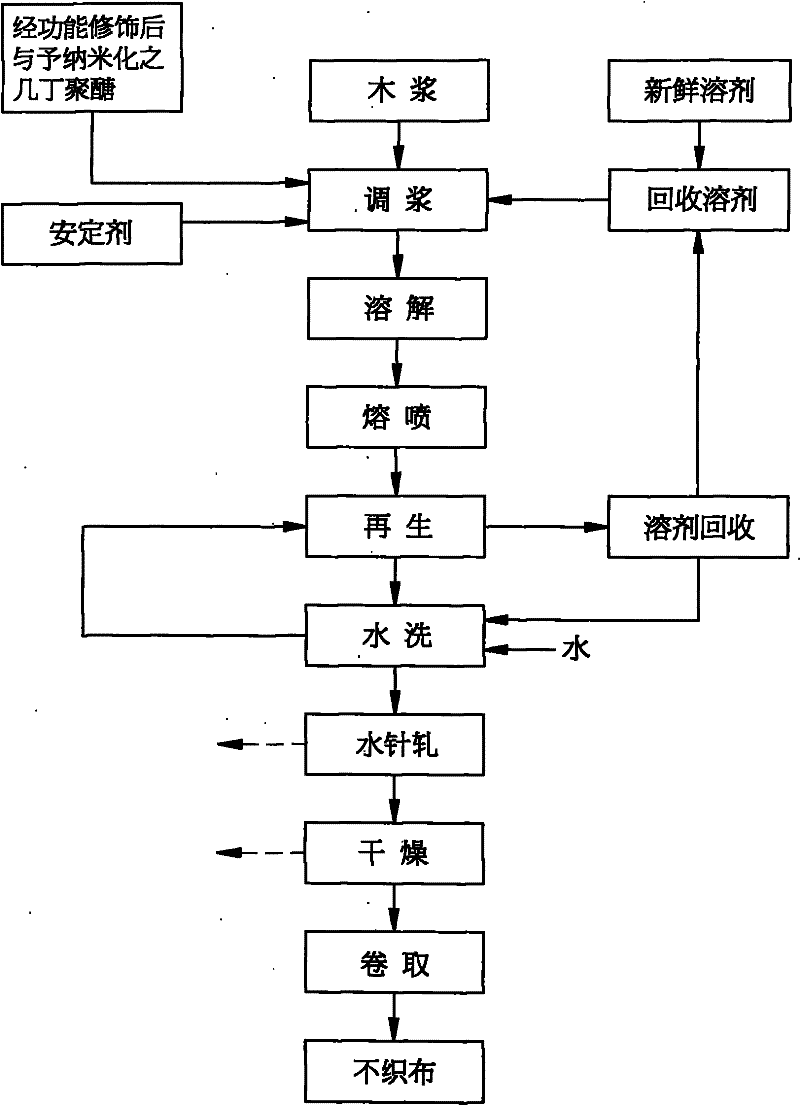
The invention provides a production method of a cellulose non-woven fabric with functions of mildew proofing, antibiosis and deodorization through wet-type meltbrown, comprising the following steps of: adding natural chitosan macromolecules subjected to functionalized modification and nanocrystallization into a size prepared from pulp and N-methylmorpholine N-oxide (short for NMMO) to be mixed and dissolved to form a dope; then spraying the dope from a spinning nozzle in a meltbrown way to form a non-woven fabric silk net, and carrying out water mist solidification and regeneration; and finally, washing with water, rolling with a squirt cut, drying, rolling and carrying out other procedures to obtain a natural cellulose non-woven fabric with functions of mildew proofing, antibiosis and deodorization and a continuous filament form. The cellulose non-woven fabric with functions of mildew proofing, antibiosis and deodorization can be applied to wiping textiles, medical consumables, filtering materials, biotechnical materials, photoelectric wafers and the like with functions of mildew proofing, antibiosis and deodorization.
Owner:张文波
Lyocell Fiber
The invention concerns a Lyocell fiber, containing a material selected from the group consisting of pearl powder, ground nacre and mixtures thereof. For the manufacture of the fiber according to the invention, a process is used comprising the steps ofmanufacturing a spinning solution of cellulose in an aqueous tertiary amine oxide, preferably N-methylmorpholine-N-oxide (NMMO)spinning the spinning solution to fibers,and being characterized in that a material selected from the group consisting of pearl powder, ground nacre and mixtures thereof is admixed to the spinning solution and / or to a precursor thereof.
Owner:LENZING AG
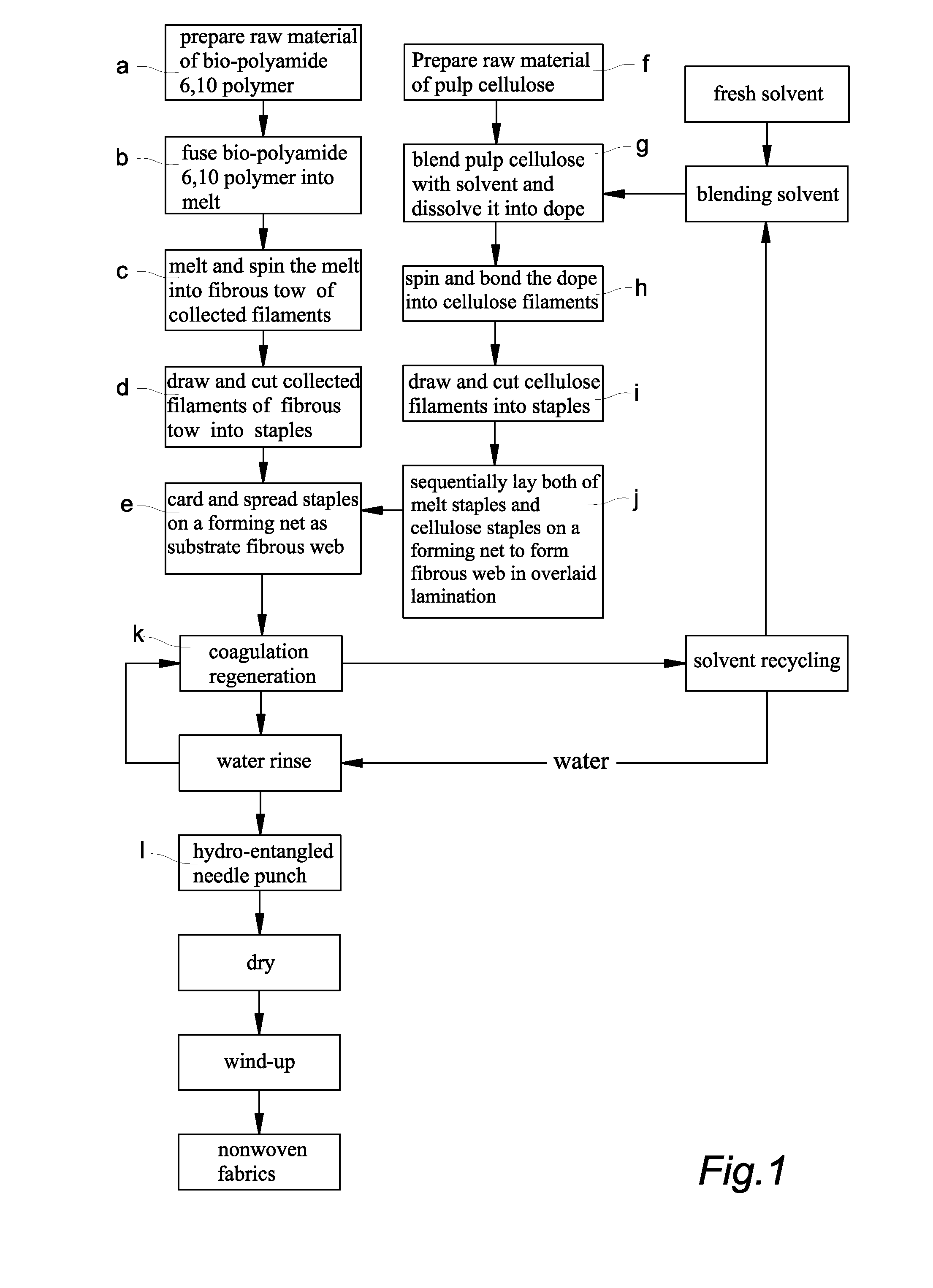
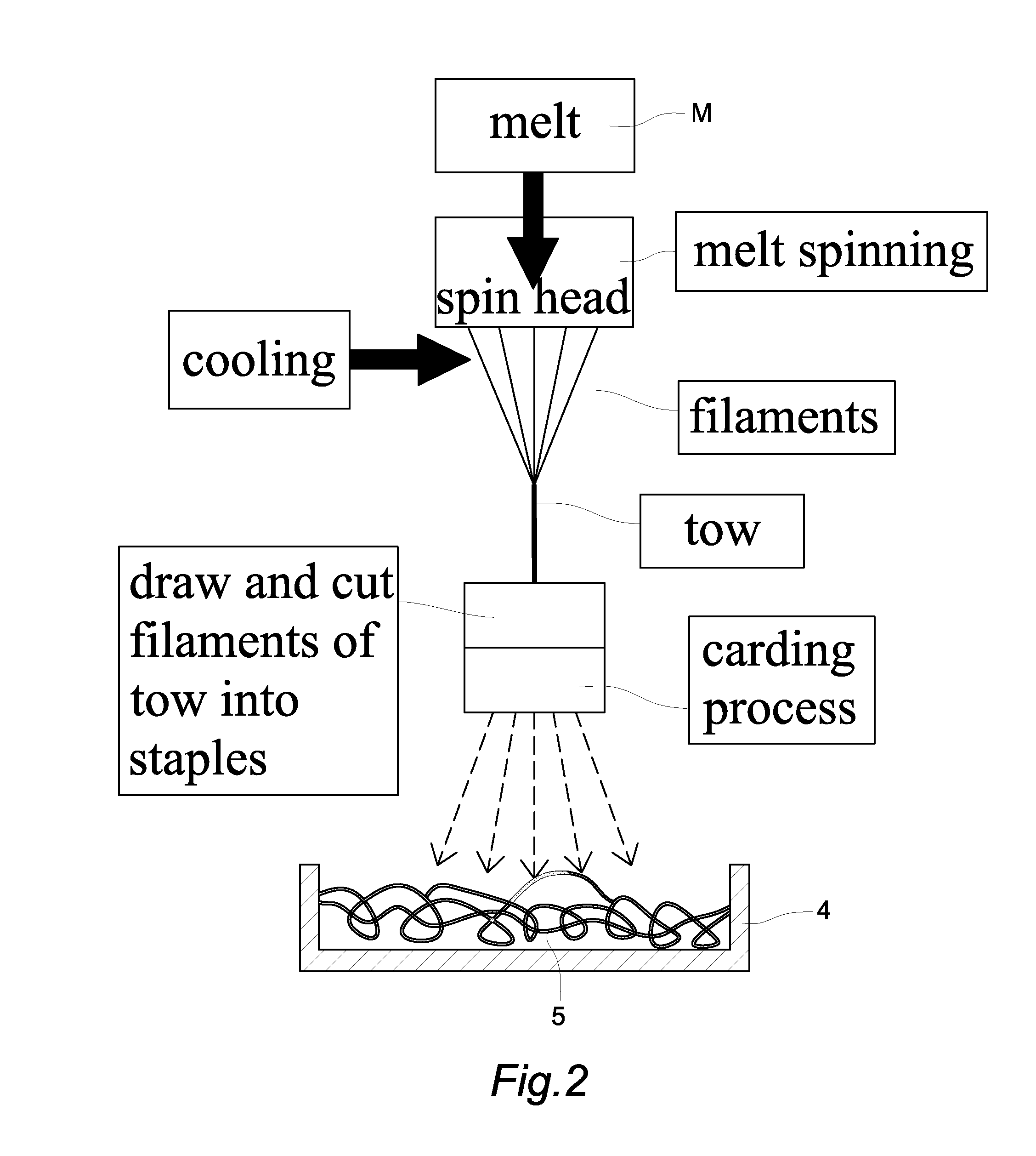
Stapled melt spinning method for producing non-woven fabrics with hygroscopic metastatic feature
ActiveUS20160145781A1Improve water absorptionReduce water contentPattern makingMonocomponent cellulose artificial filamentPunchingPolyamide
A stapled melt spinning method for producing nonwoven fabrics with hygroscopic metastatic feature. Firstly, fuse bio-polyamide 6,10 into melt, extrude and spin it out spin heads of extruder into filaments, cool, draw and collect filaments into tow, then extend, cut and card the filaments into the staples, and spread the staples on a conveyer to form fibrous web. Next, blend and dissolve pulp by N-methylmorpholine N-oxide (NMMO) dissolving solvent, dehydrate it to form dope, and extrude and spin it out spin heads of extruder into filaments, then cool, draw and collect filaments into tow, and extend, cut and card filaments into staples, then overlay the staples over existing fibrous web to form a composite fibrous web of bio-polyamide 6,10 and cellulose filaments. Finally, coagulate, regenerate and convert fibrous composite of bio-polyamide 6,10 and natural cellulose into nonwoven fabric with hygroscopic metastatic feature by hydro-entangled needle punching, drying, winding-up processes.
Owner:LIN CHIH HSIN
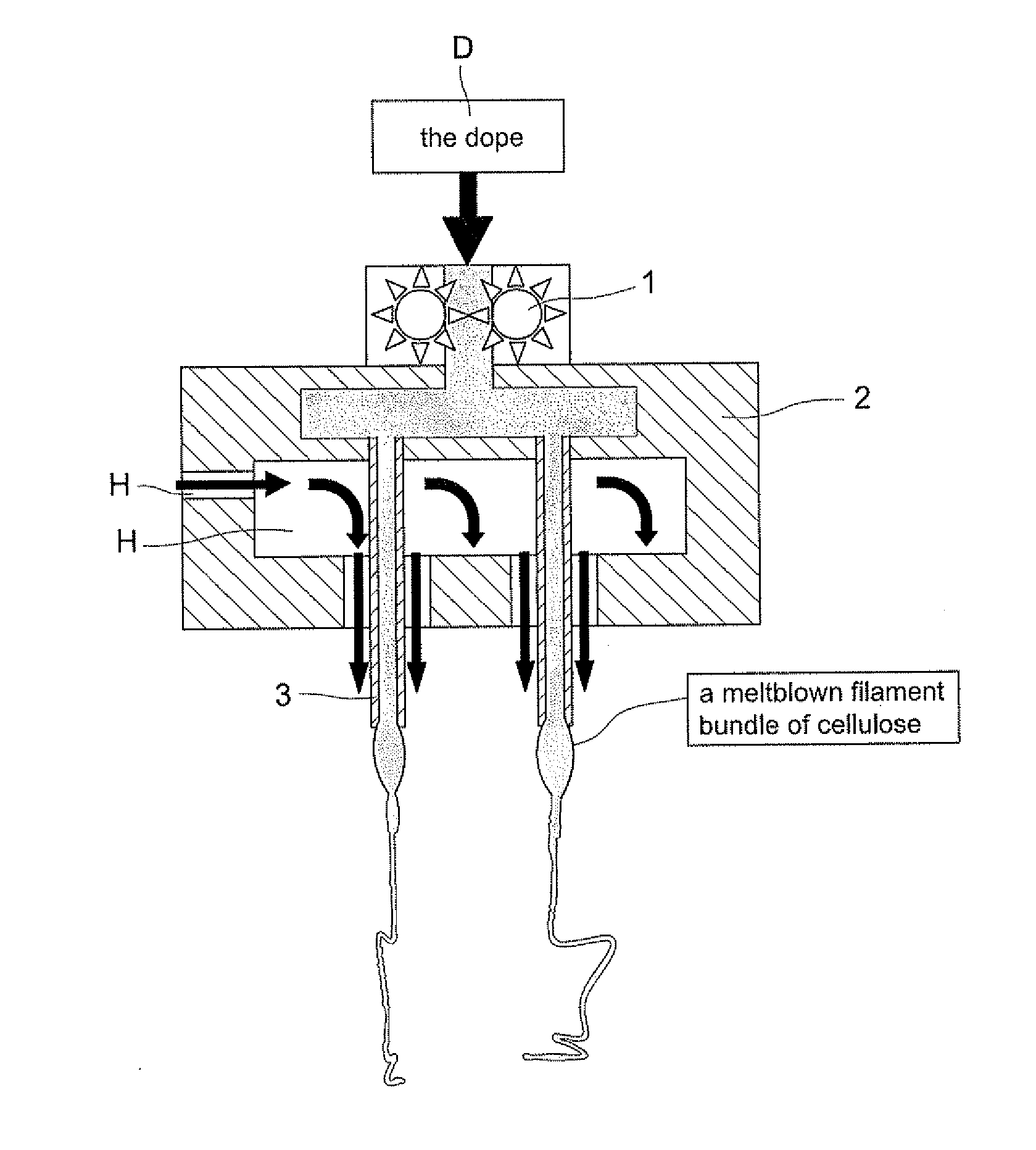
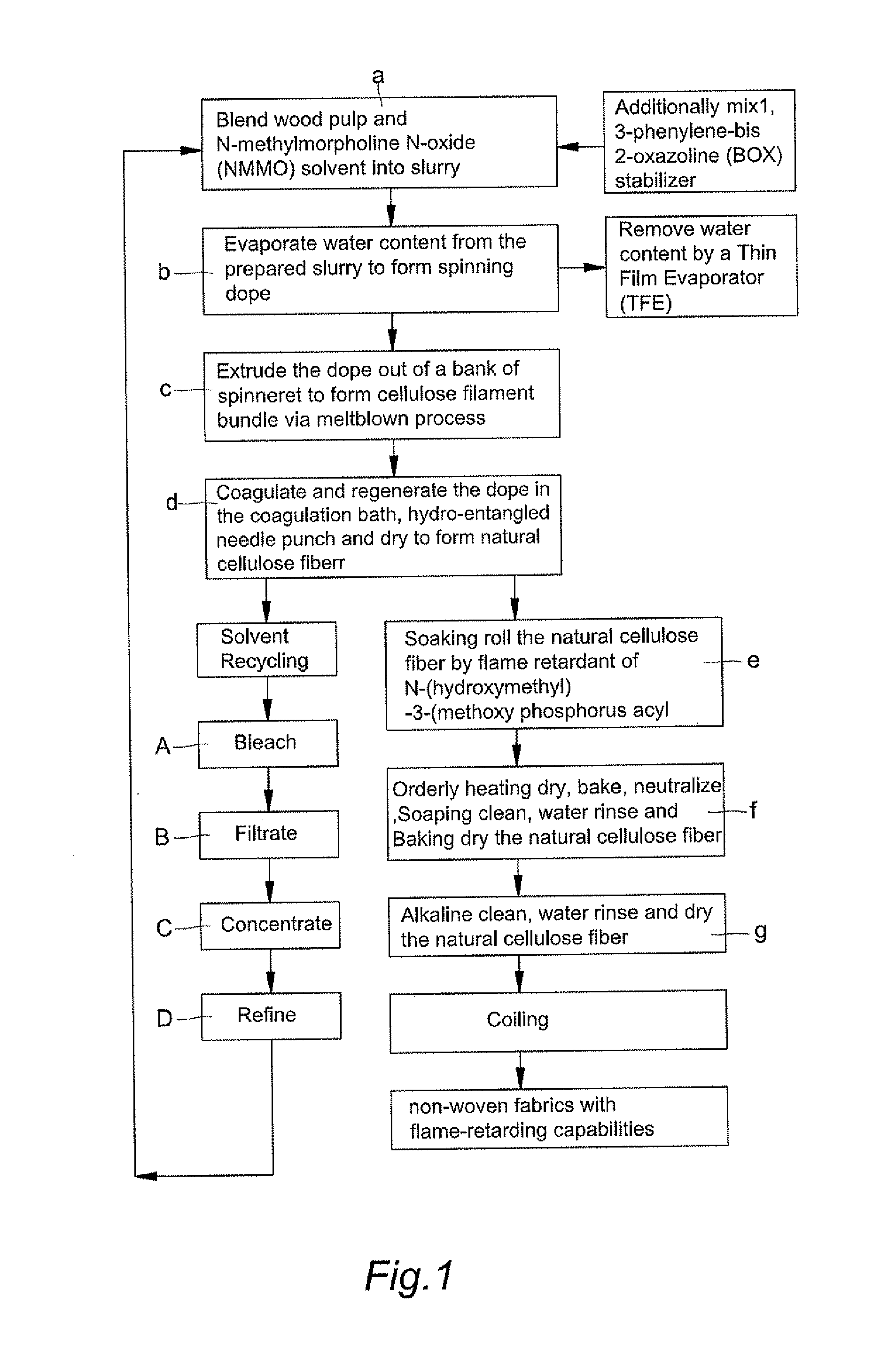
Fabrication of natural cellulose fiber with flame-retarding capability
ActiveUS20130228949A1Reduce solvent recycling costSimple facilitiesArtificial filaments from cellulose solutionsFlame-proof filament manufactureCross-linkSlurry
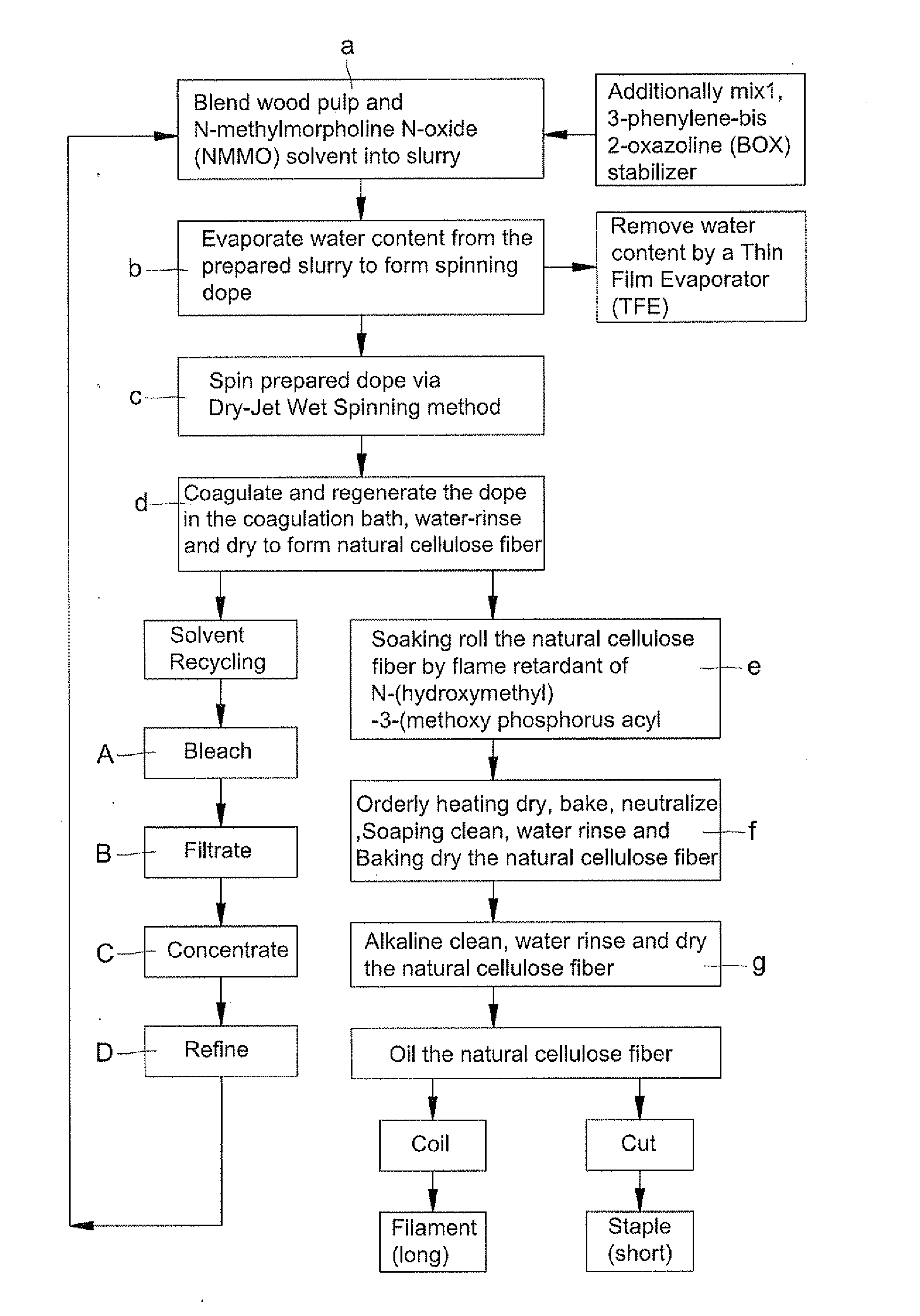
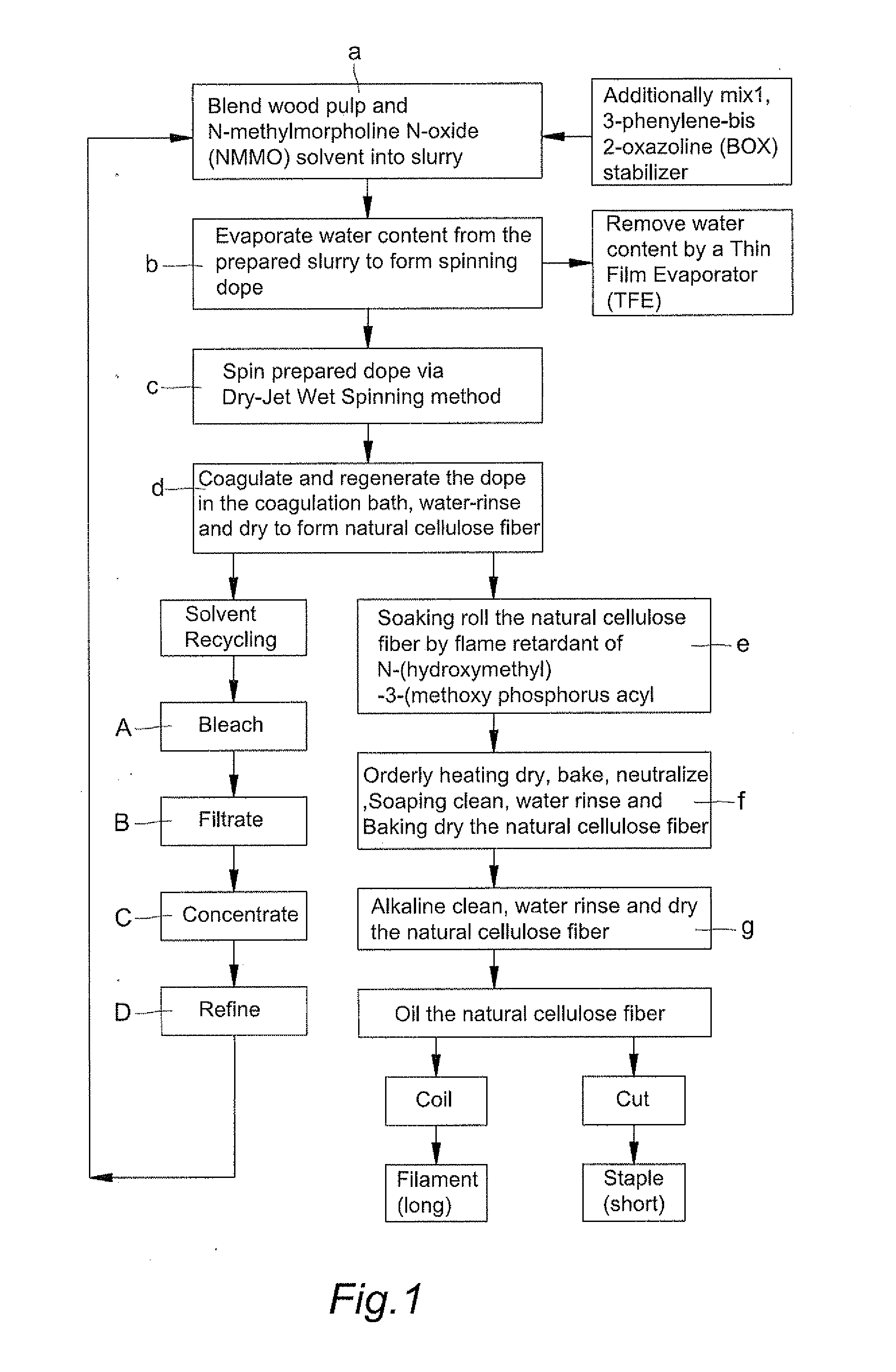
A fabrication of natural cellulose fiber with flame-retarding capability comprises following steps. Blend pulp and solvent of N-methylmorpholine N-oxide (NMMO) to form slurry. Evaporate extra water content from slurry by a Thin Film Evaporator (TFE) to form dope. By Dry-Jet Wet Spinning, spin and extrude dope for coagulating and regenerating. Water-rinse and dry to form natural cellulose fiber. Soaking roll natural cellulose fiber by flame retardant of N-(hydroxymethyl)-3-(methoxy phosphorus acyl). Orderly dry, bake, neutralize, soaping clean, water rinse, baking dry, soaking rolled, alkaline clean, water rinse, dry and oil the natural cellulose fiber to produce natural cellulose fiber of flame retarding capacity. Because of cross-linking reaction for the flame retardant of N-(hydroxymethyl)-3-(methoxy phosphorus acyl) with natural cellulose fiber, the flame-retarding capability thereof meet requirements of testing standards in American ASTM D6413-1999 and ASTM D2863-1995. Moreover, the wastes thereof meet the requirements of environment protections without harm.
Owner:ACELON CHEM & FIBER
Lyocell multifilament
ActiveUS6902804B2Low modulusLow tenacity lowMonocomponent cellulose artificial filamentCellulosic plastic layered productsYarnEngineering
The present invention relates to a high tenacity, high modulus and low shrinkage lyocell multifilament yarn suitable for use in tire cords and MRG (mechanical rubber goods). The lyocell multifilament yarn is a cellulose-based fiber for industrial applications, which is produced by dissolving pulp having a degree of polymerization (DPW) of 700-2,000 and preferably 800-1,400, and a α-cellulose content of more than 90% and preferably more than 92%, in N-methylmorpholine N-oxide (NMMO) hydrate, at a pulp concentration of 5-15% by weight and preferably 8-13% by weight.The lyocell monofilament according to the present invention is characterized by the following stress-strain profile: (1) the lyocell monofilament analyzed after drying is elongated by less than 3.0% and has an initial modulus of 150-400 g / d, when it was subjected to an initial stress of 3.0 g / d; (2) it is elongated by 3.0-7.0% when it was subjected to a stress greater than the initial stress but smaller than 6.0 g / d; and (3) it is elongated from a tensile tenacity of at least 6.0 g / d until the yarn is broken.
Owner:HYOSUNG ADVANCED MATERIALS CORP
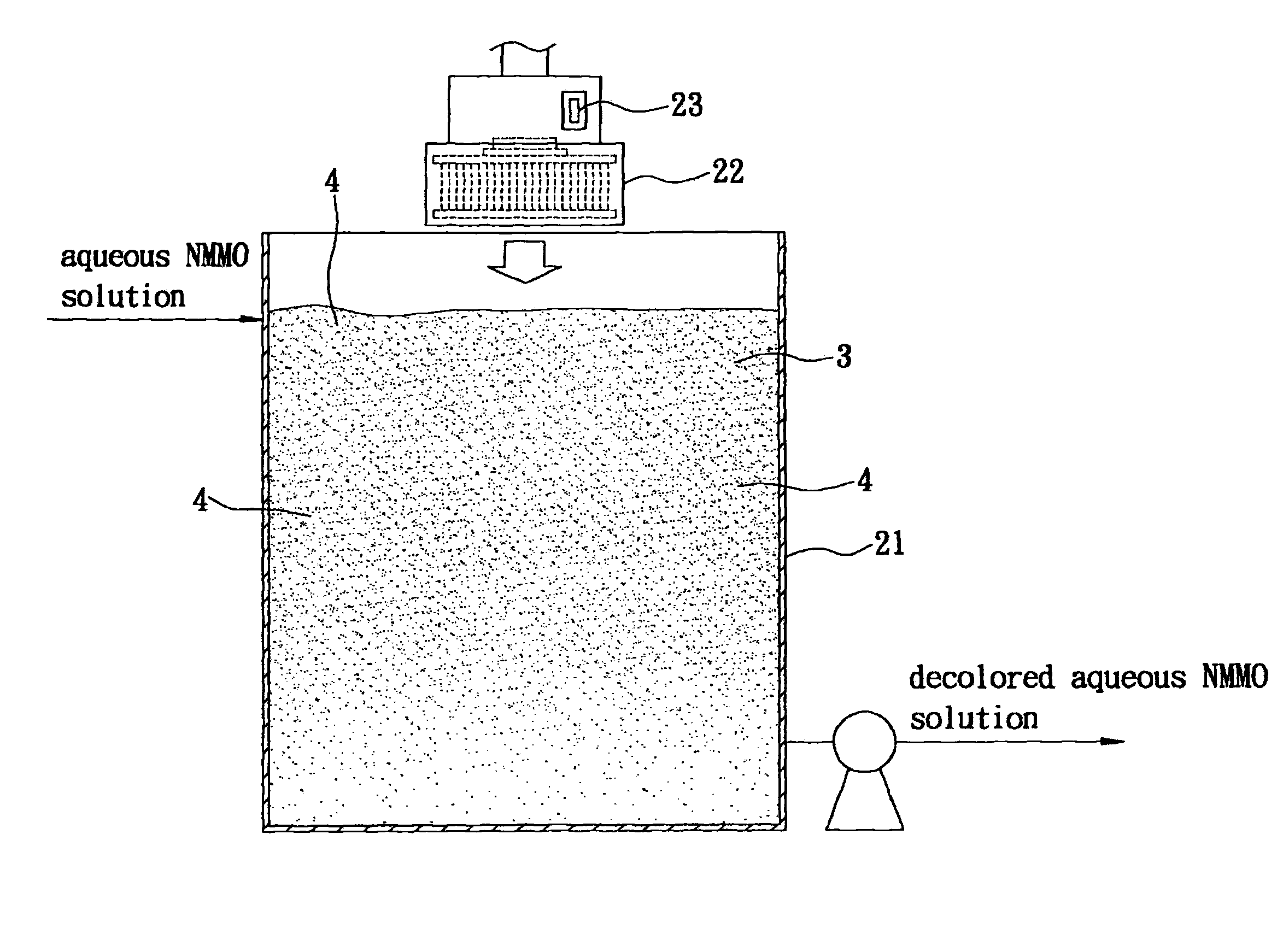
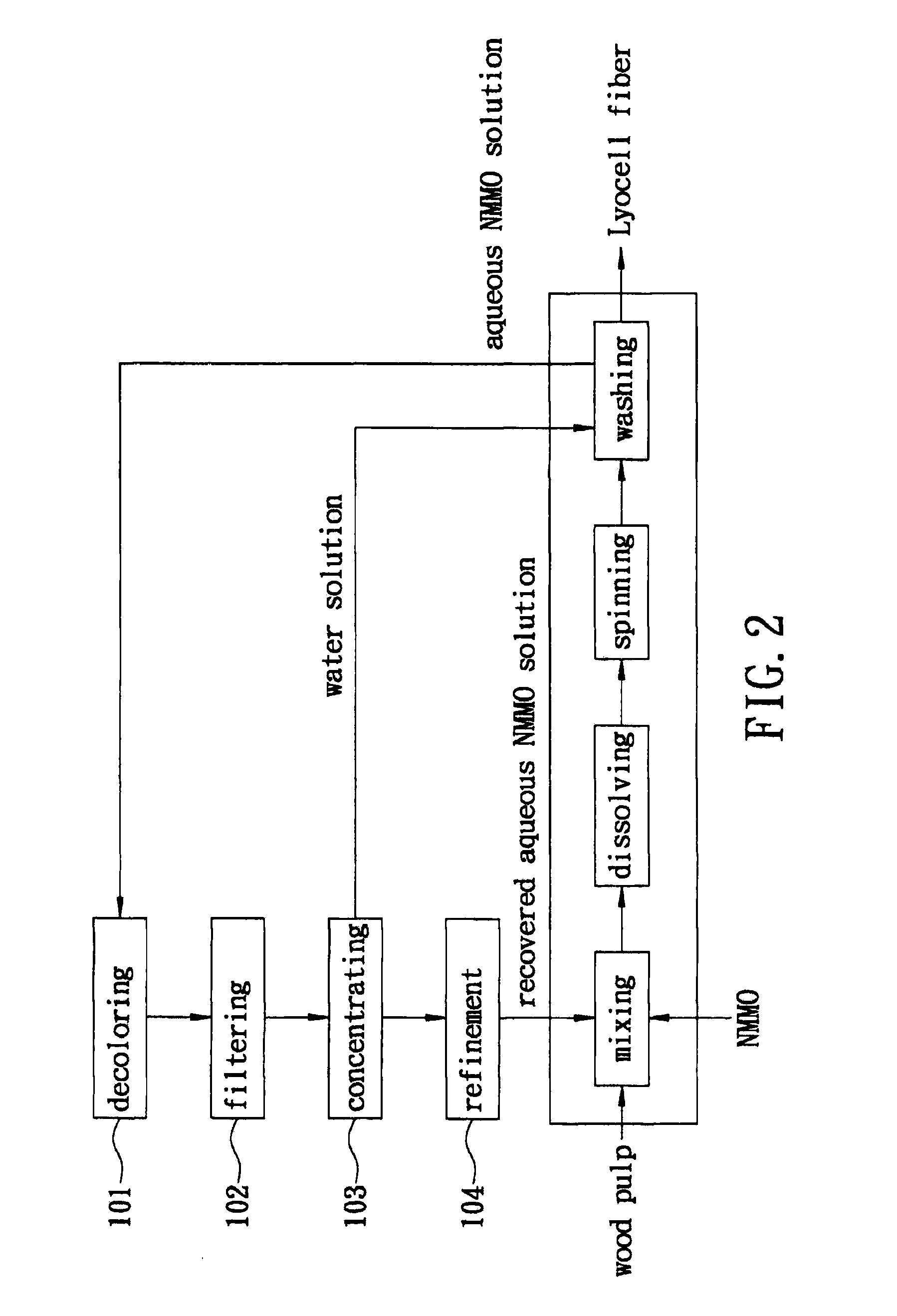
Method of Recovering Aqueous N-methylmorpholine-N-Oxide Solution Used in Production of Lyocell Fiber
InactiveUS20110226427A1Facilitate NMMO recoveryImprove recycling efficiencyArtificial filament recoveryTextile/flexible product manufactureFiberActivated carbon
A method of recovering an aqueous N-methylmorpholine-N-oxide (NMMO) solution used in production of Lyocell fiber includes: decoloring the aqueous NMMO solution by mixing the same with activated carbon using an agitation blower and by alternately energizing and de-energizing the agitation blower to contact the activated carbon with the aqueous NMMO solution thoroughly in an energy-efficient manner; filtering the aqueous NMMO solution which has been decolored through coarse filtration followed by ultrafiltration to remove the activated carbon and impurities from the aqueous NMMO solution; and concentrating the aqueous NMMO solution which has been filtered using one of a mechanical vapor recompression evaporator and a triple effect evaporator to remove water from the aqueous NMMO solution.
Owner:ACELON CHEM & FIBER
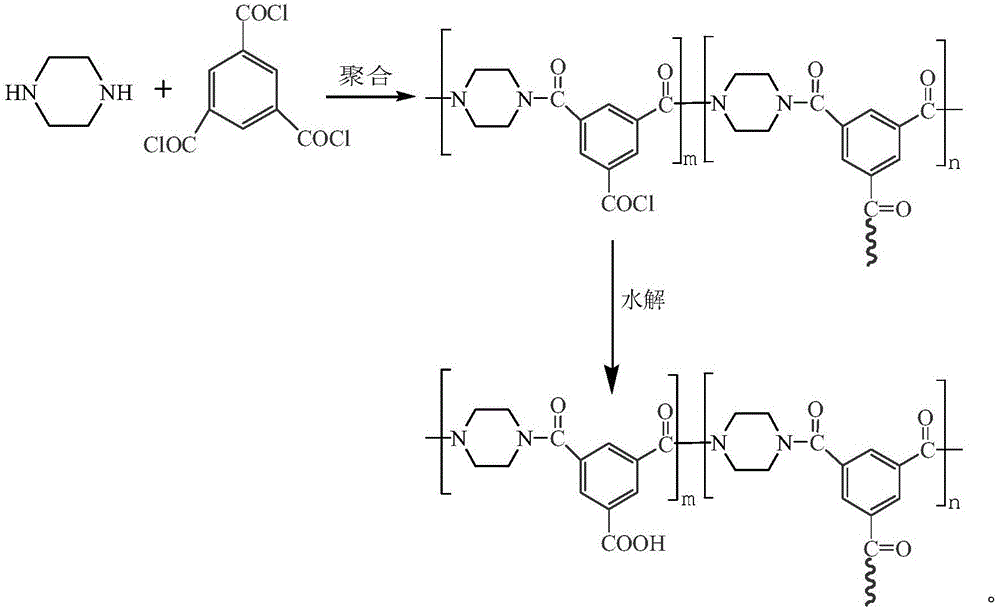
Preparation method of antibacterial cellulose flat nanofiltration membrane
ActiveCN106474944AWide variety of sourcesLow costMembranesWater contaminantsMoistureAntibacterial agent
The invention provides a preparation method of an antibacterial cellulose flat nanofiltration membrane. An N-methylmorpholine-N-oxide solvent with moisture content of 10%-16%, propyl gallate, a nanometer SiO2 pore-foaming agent, a nanometer TiO2 antibacterial agent (or a nanometer silver antibacterial agent) and cellulose pulp serve as raw materials, and a homogenous and transparent cellulose membrane casting solution is prepared; sequentially an antibacterial porous cellulose membrane is prepared by means of the immersion gel method; afterwards a poly piperazine aqueous solution and an N-hexane organic solution containing trimesoyl chloride are prepared, operation is conducted to make a crosslinking product obtained by polymerization of poly piperazine and trimesoyl chloride uniformly attached to membrane holes and membrane surfaces, and finally the antibacterial cellulose flat nanofiltration membrane is obtained. The whole preparation process is simple, cost is low, the prepared antibacterial cellulose flat nanofiltration membrane can be used for removing multivalent ions, a part of salts with monovalent ions and organics with molecular weight larger than 300, and has the advantages of being high in retention and water flux, selective in adsorption and friendly to the environment.
Owner:FUJIAN AGRI & FORESTRY UNIV
Meltblown wetlaid method for producing non-woven fabrics from natural cellulose
ActiveUS8420004B2Reduce manufacturing costDegree of air permeabilityArtificial filaments from cellulose solutionsPattern makingPunchingWater rinsing
The present invention provides a meltblown wetlaid method for producing non-woven fabrics from natural cellulose using pulp as raw material and N-methylmorpholine N-oxide (NMMO) as solvent for dissolving into dope. The dope is then extruded out of a spinneret to form filament bundle by meltblown method. Subsequently, by means of ejecting mist aerosol of water, the filament bundle is coagulated with regeneration. Via post treatments of water rinsing, hydro-entangled needle punching, drying, winding-up and the like have been orderly applied, then final product of nonwoven fabrics with continuous filament are produced from natural cellulose.
Owner:LIN CHIH HSIN
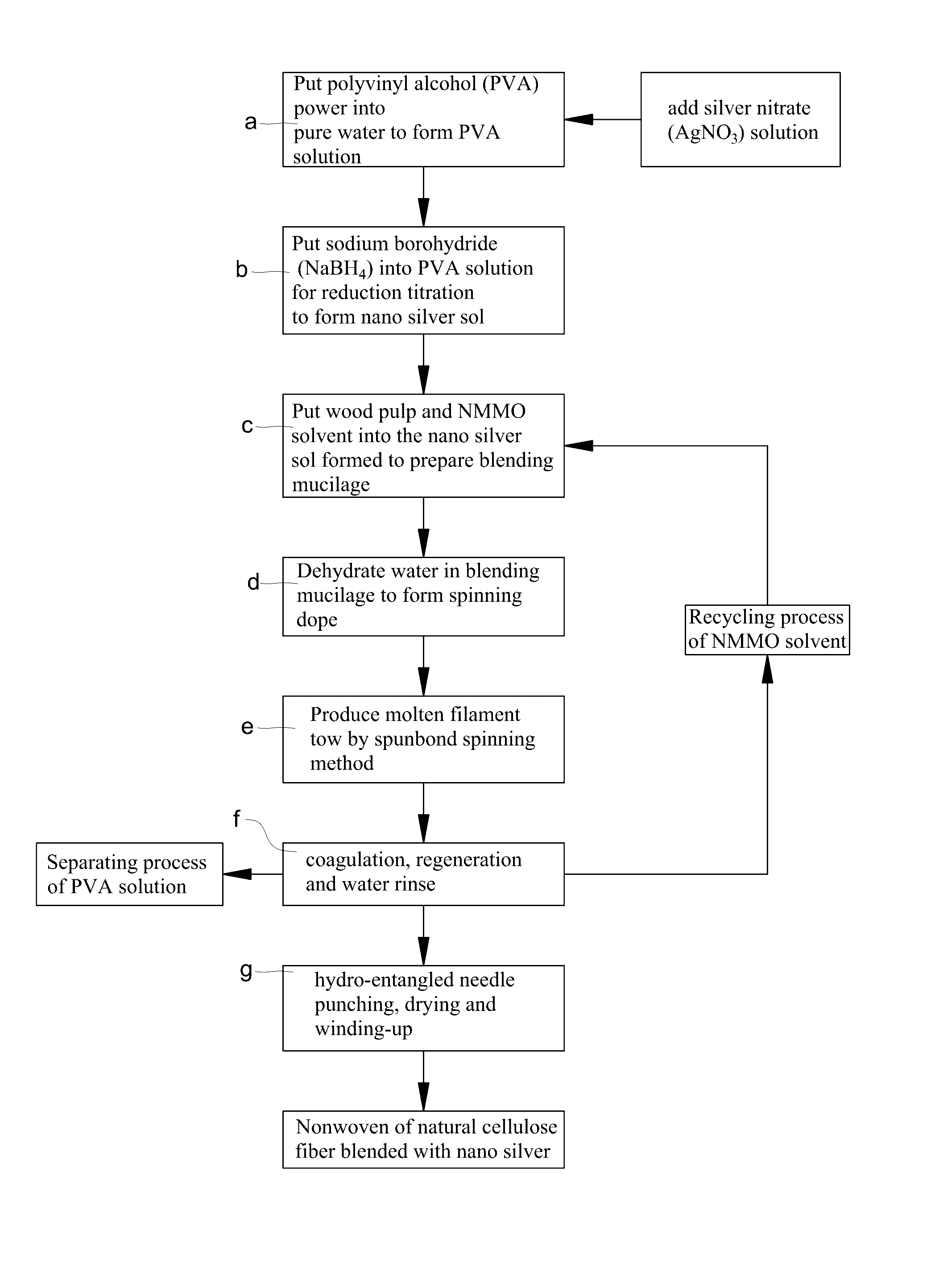
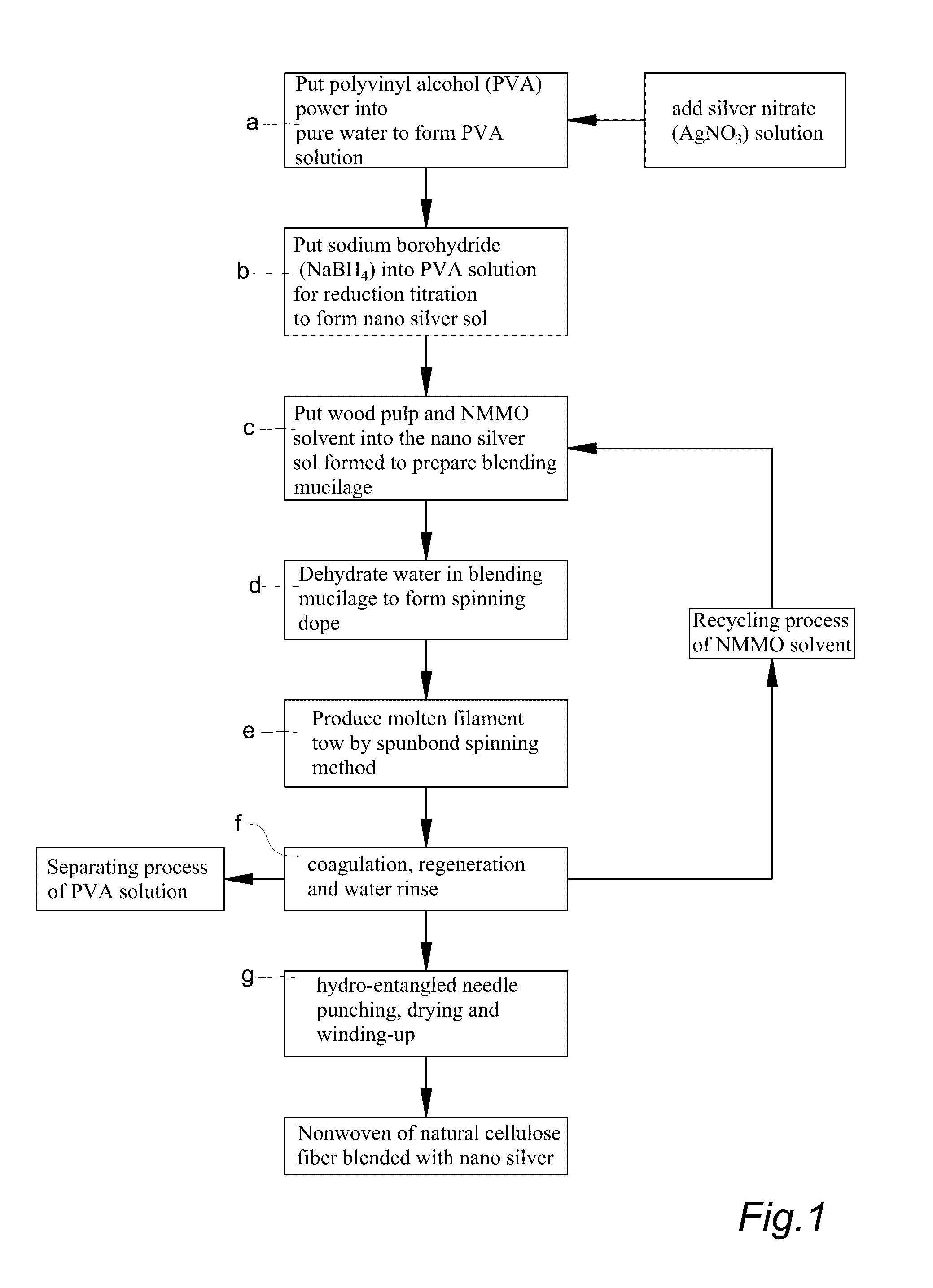
Fabricating method for natural cellulose fiber blended with NANO silver
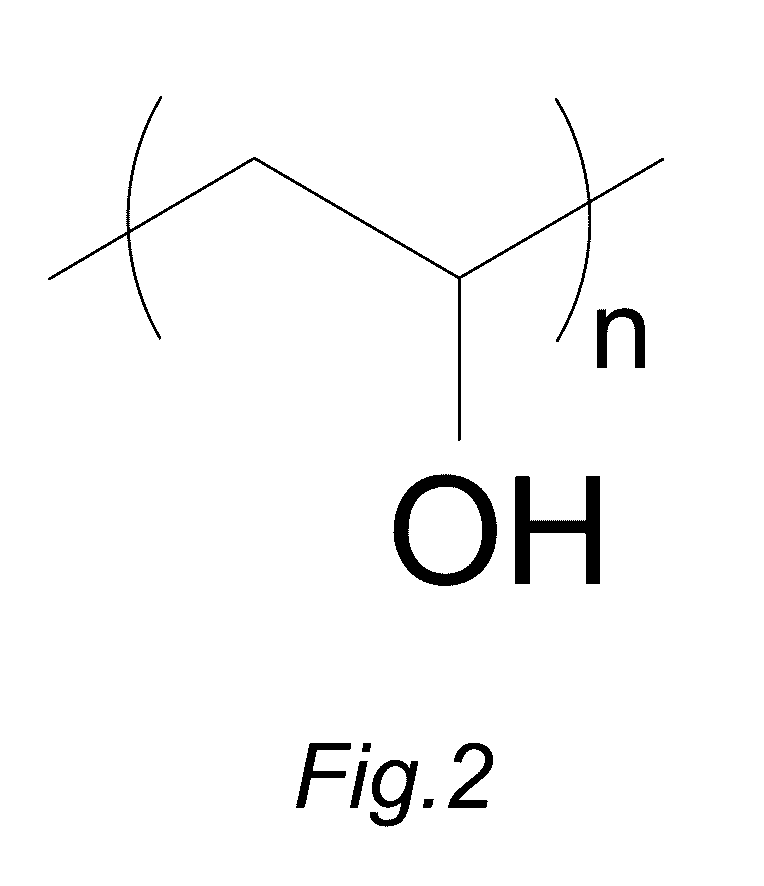
ActiveUS20160333498A1Improve antibacterial propertiesPromote healthfulArtificial filaments from cellulose solutionsArtificial filament recoveryPolyvinyl alcoholCellulose fiber
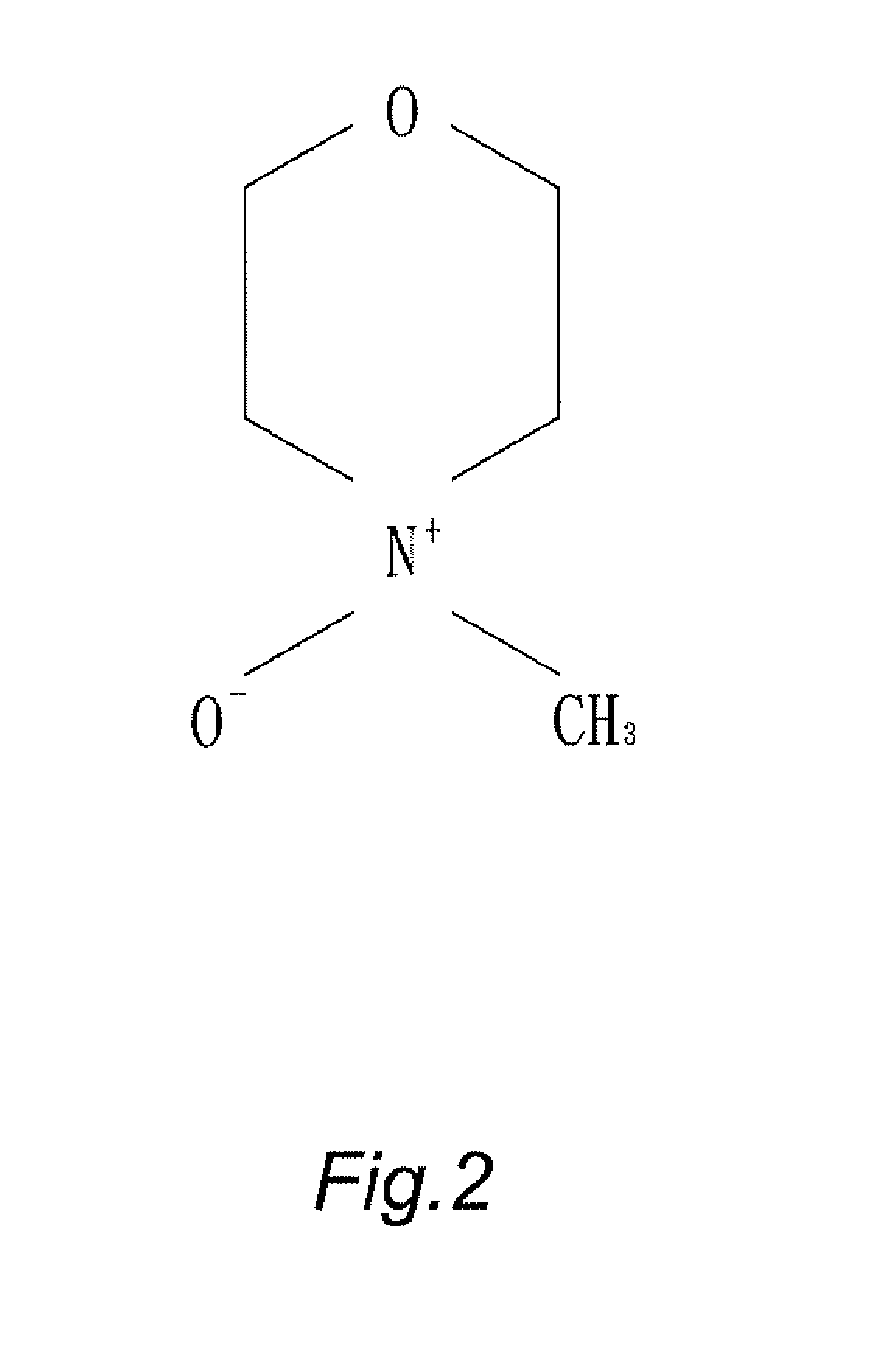
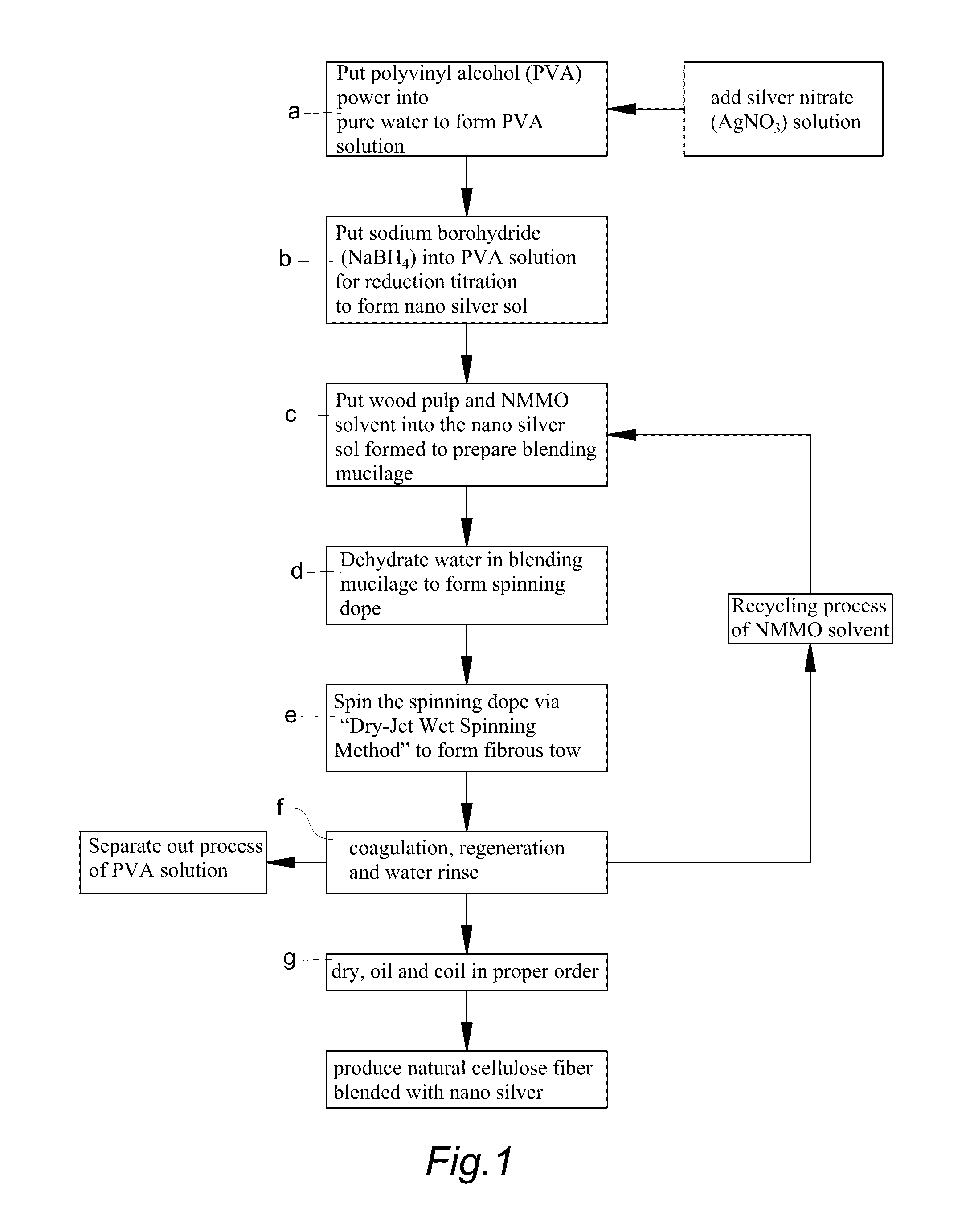
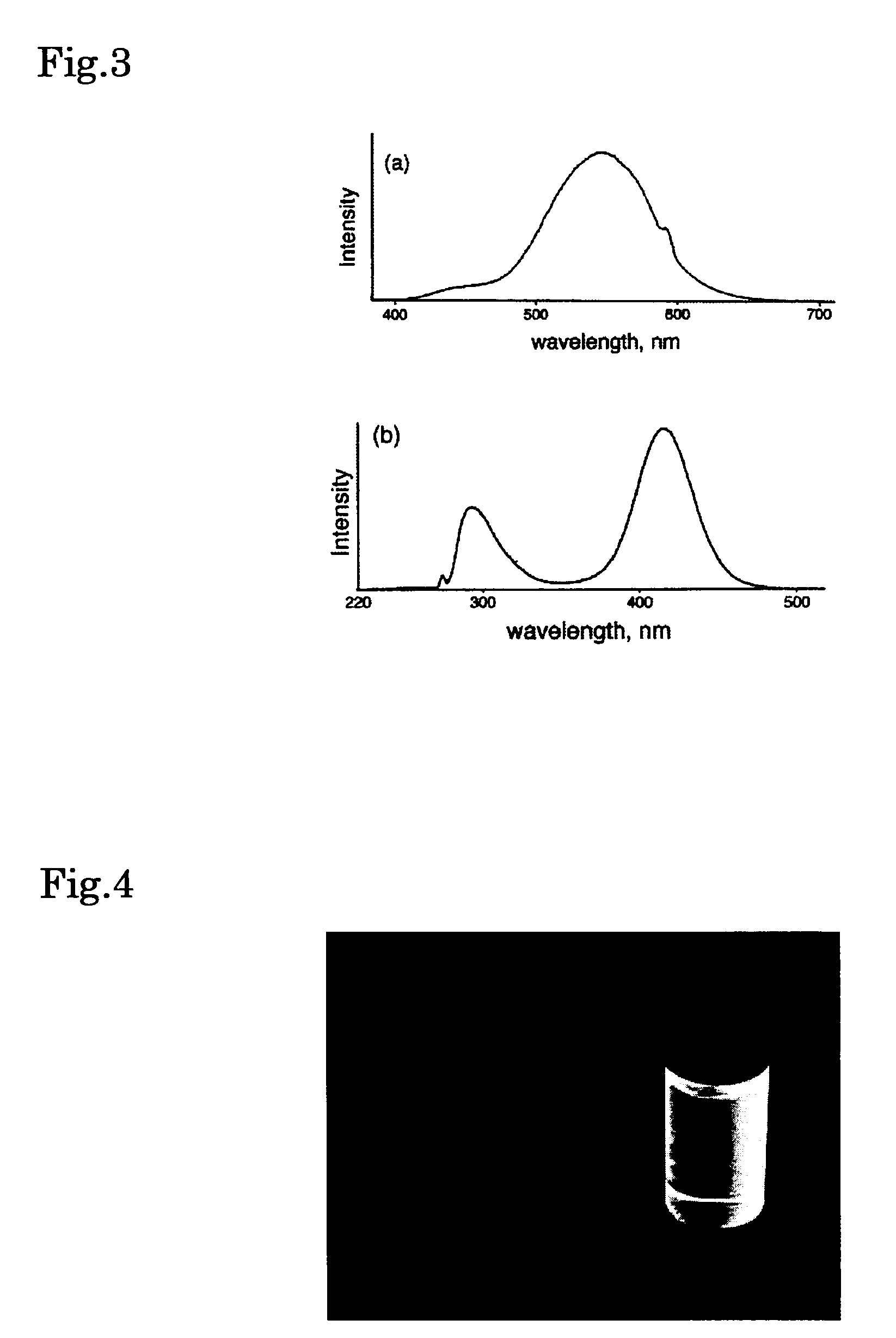
The present invention provides a fabricating method for natural cellulose fiber blended with nano silver.The fabricating method comprises following steps:Firstly, prepare nano silver colloidal sol by reduction titration for mixture of polyvinyl alcohol (PVA), silver nitrate (AgNO3) and sodium borohydride (NaBH4).Secondly, prepare mixing cellulose serum by blending agitation for mixture of wood pulp, N-methylmorpholine N-oxide (NMMO) and stabilizer.Thirdly, produce spinning dope by blending and dehydrating the nano silver colloidal sol and mixing cellulose serum.Fourthly, produce fibrous tow by Dry-Jet Wet Spinning method in association with coagulation, regeneration in coagulation bath, and water rinse.Finally, obtain final product of natural cellulose fiber blended with nano silver by post treatments of dry, oil and coil in proper order.
Owner:LIN CHIH HSIN
Method for preparing natural cellulose non-woven fabric in wet spunbond mode
ActiveCN102127840AWill not polluteShort processMonocomponent cellulose artificial filamentNon-woven fabricsCellulose fiberPulp and paper industry
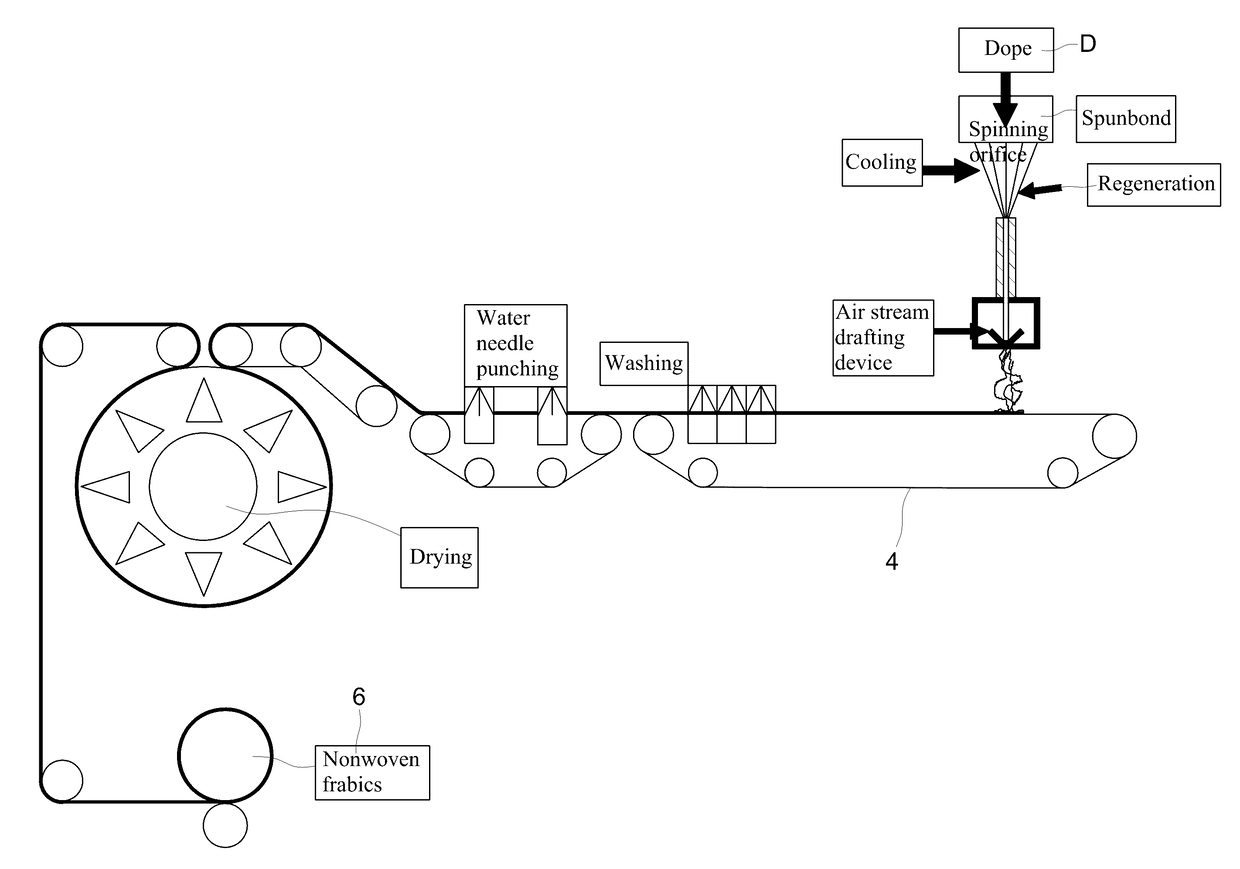
The invention provides a method for preparing a natural cellulose non-woven fabric in a wet spunbond mode, which comprises the following steps of: adding an N-methylmorpholine N-oxide (NMMO) solvent into pulp serving as a raw material, and mixing and dissolving to form dope; extruding the dope from a spinning nozzle in a spunbond mode to form a long cellulose strand, and performing cold stretching on the long cellulose strand through an air gap; adding into solidification liquid for solidification and regeneration; stretching at a high speed by using an air drafting device, and stacking into a net on a collecting net to form the non-woven fabric; and washing the non-woven fabric, rolling by using a squirt, drying, winding and the like to prepare the natural cellulose fiber non-woven fabric with a continuous long fiber pattern.
Owner:张文波
Polyrotaxane-containing solution and use thereof
InactiveUS20090149579A1Solve low usageLiquid carbonaceous fuelsBulk chemical productionAlkaline earth metalLithium chloride
An object of the present invention is to provide a polyrotaxane-containing solution by finding a good solvent for polyrotaxanes, and more particularly, to provide a polyrotaxane-containing solution by finding a good solvent for polyrotaxanes with a cyclodextrin as the cyclic molecule(s).The present invention provides a polyrotaxane-containing solution comprising polyrotaxane dissolved in a solvent selected from the group consisting of a nitrogen-containing organic solvent and an ionic liquid. In particular, a nitrogen-containing organic solvent such as N-methylmorpholine-N-oxide or hydrate thereof; a solution of a nitrogen-containing organic solvent such as N,N-dimethylacetamide containing as solute an alkali metal halide or alkaline earth metal halide such as lithium chloride; or an ionic liquid such as an N,N′-dialkylimidazolium salt or N-alkylpyridinium salt, is a good solvent for polyrotaxanes.
Owner:THE UNIV OF TOKYO
Fabricating method for spunbond nonwoven from natural cellulose fiber blended with NANO silver
ActiveUS20160333508A1Improve antibacterial propertiesPromote healthfulMaterial nanotechnologyMonocomponent cellulose artificial filamentPolyvinyl alcoholCellulose fiber
The present invention provides a fabricating method for spunbond nonwoven from natural cellulose fiber blended with nano silver, which comprises following steps.Firstly, prepare nano silver colloidal sol by reduction titration for mixture of polyvinyl alcohol (PVA), silver nitrate (AgNO3) and sodium borohydride (NaBH4).Secondly, prepare mixing cellulose serum by blending agitation for mixture of wood pulp, N-methylmorpholine N-oxide (NMMO) and stabilizer.Thirdly, prepare blending mucilage from mixing cellulose serum via blending process.Fourthly, produce spinning dope by blending and dehydrating the nano silver colloidal sol and mixing cellulose serum.Fifthly, produce molten filament tow by spunbond spinning method in association with coagulation, regeneration, water rinse and high-speed stretching process.Finally, by post treatments of hydro-entangled needle punching, drying, winding-up processes in proper order, obtain final product of spunbond nonwoven from natural cellulose fiber blended with nano silver, which is biodegradable with features of antibacterial and antistatic capabilities.
Owner:LIN CHIH HSIN
Method of preparing natural graphene cellulose blended fiber
This application describes a method of preparation of a natural graphene cellulose blended fiber, which comprises using a graphite powder as a raw material for preparing a graphene solution, adding the graphene solution to a slurry formed by mixing and dissolving a wood pulp with N-methylmorpholine N-oxide (NMMO), removing the water content thereof to form a spinning dope, and then spinning the spinning dope by a Dry-Jet Wet method to manufacture a natural graphene cellulose blended fiber. The present method does not require a highly toxic hydrazine hydrate solution. Further, by increasing the adding ratio of the graphene solution in the manufacturing process, control of the antistatic properties and thermal transferring functions can be achieved, and thereby various requirements of different consumers can be satisfied. Besides, the fibers can decompose naturally after being used, and thus the product is harmless, natural, and environmentally friendly.
Owner:LIN CHIH HSIN
Method of preparing Lyocell by taking bamboos as raw material
ActiveCN109234826AStrong performance close toReduce pollutionMonocomponent cellulose artificial filamentWet spinning methodsYarnFiber
The invention relates to a method of preparing Lyocell by taking bamboos as a raw material. The method comprises the following steps: by taking bamboos as the raw material, extracting cellulose from the bamboos by means of process methods such as degumming, lignin removal, and hemicelluloses removal and the like, and then dissolving bamboo cellulose in an N-methylmorpholine-N-oxide aqueous solution to prepare a spinning solution; feeding the spinning solution into a spinning system, vertically stretching sprayed silk yarns in air, and feeding the silk yarns to a condensing bath to be condensedto fibers; and preparing the Lyocell from the fibers through the processes such as alcohol washing, bleaching, washing, oiling and drying. The dry breaking strength of the Lyocell prepared by the method is between 44 cN / tex and 47 cN / tex, the dry elongation at break thereof is between 13% and 15%, the wet breaking strength thereof is between 29 cN / tex and 32 cN / tex, the wet elongation at break thereof is between 15% and 17%, and the strong performance thereof is close to that of purchased Lyocell.
Owner:WUHAN TEXTILE UNIV
Meltblown process for producing non-woven fabrics with flame-retarding capability from natural cellulose
ActiveUS20130234354A1Simple and effective processing facilityReduce solvent recycling costArtificial filaments from cellulose solutionsArtificial filament recoveryCross-linkEngineering
A Meltblown process for producing non-woven fabrics with flame-retarding capability from natural cellulose comprises following steps. Blend pulp and solvent of N-methylmorpholine N-oxide (NMMO) to form slurry. Evaporate water content from slurry by a Thin Film Evaporator to form dope. Extrude the dope off spinneret bank to form filament bundle via meltblown process. Coagulating regenerate, water rinse, hydro-entangled needle-punch and dry the filament bundle to form normal natural cellulose nonwoven. Soaking roll formed nonwoven by flame retardant of N-(hydroxymethyl)-3-(methoxy phosphorus acyl). Orderly dry, bake, neutralize, soaping clean, water rinse, baking dry, soaking roll, alkaline clean, water rinse, dry and coil the nonwoven to produce modified natural cellulose nonwoven of flame retarding capacity. Because of cross-linking reaction between foregoing flame retardant and natural cellulose nonwoven, the flame-retarding capability thereof meet requirements of testing standards in American ASTM D6413-1999 and ASTM D2863-1995. Moreover, the wastes thereof meet environmental protection requirements.
Owner:LIN CHIH HSIN
Nanometer microcrystalline cellulose preparation method
The present invention discloses a nanometer microcrystalline cellulose preparation method, which comprises: (1) adopting N-methylmorpholine-N-oxide and an ion liquid to treat microcrystalline cellulose; and (2) recovering the treatment agent. According to the present invention, the nanometer microcrystalline cellulose preparation method has the following advantages that: microcrystalline cellulose is adopted as a raw material, and can be extracted from plants, such that the source is wide, and the natural plant fiber utilization rate is substantially increased; the N-methylmorpholine-N-oxide and the ion liquid are subjected to coupling use, and the treatment is performed to obtain the fragmented nanometer microcrystalline cellulose; the N-methylmorpholine-N-oxide and the ion liquid can be recycled after being treated so as to reduce the nanometer microcrystalline cellulose production cost; and the nanometer microcrystalline cellulose preparation process has characteristics of simpleness, easy performing and green environmental protection, and no corrosion on equipment, environmental pollution and other problems exists.
Owner:JIANGSU UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Cellulose dip cord produced from highly homogeneous cellulose solution and tire using the same
ActiveUS6983779B2Smoothly swollenGood physical propertiesMonocomponent cellulose artificial filamentCellulosic plastic layered productsYarnN-Methylmorpholine N-oxide
The present invention relates to, and more particularily, to a lyocell dip cord and tire produced by a method comprising the steps of: (A) dissolving 0.01 to 3 wt % of cellulose powder in portions in concentrated liquid N-methylmorpholine N-oxide (NMMO) to prepare cellulose-containing NMMO solution; (B) feeding the NMMO solution and cellulose powder into an extruder having a screw to be subjected to dispersing, mixing, shearing, kneading, melting and measuring ability in the extruder to prepare a swollen and homogenized cellulose solution; (C) spinning the cellulose solution through a spinning nozzle, passing the spinning solution through an air gap to a coagulation bath and coagulating the spinning solution to obtain a multifilament; (D) subject the multifilament to water-wash, drying and oil-treatment, followed by winding; and (E) twisting the wound yarn with a twisting machine to prepare a greige cord, weaving the greige cord and dipping the woven cord in a dipping solution.
Owner:HYOSUNG ADVANCED MATERIALS CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com