Pipe insulation product with charge dissipater
a technology of dissipation device and pipe insulation, which is applied in the direction of film/foil adhesive, pipe, synthetic resin layered products, etc., can solve the problems of loss of efficiency of cooling unit, increased time and/or expense in operating system, and reduced system efficiency, so as to reduce static charge generation, reduce shipping damage, and dissipate charge
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
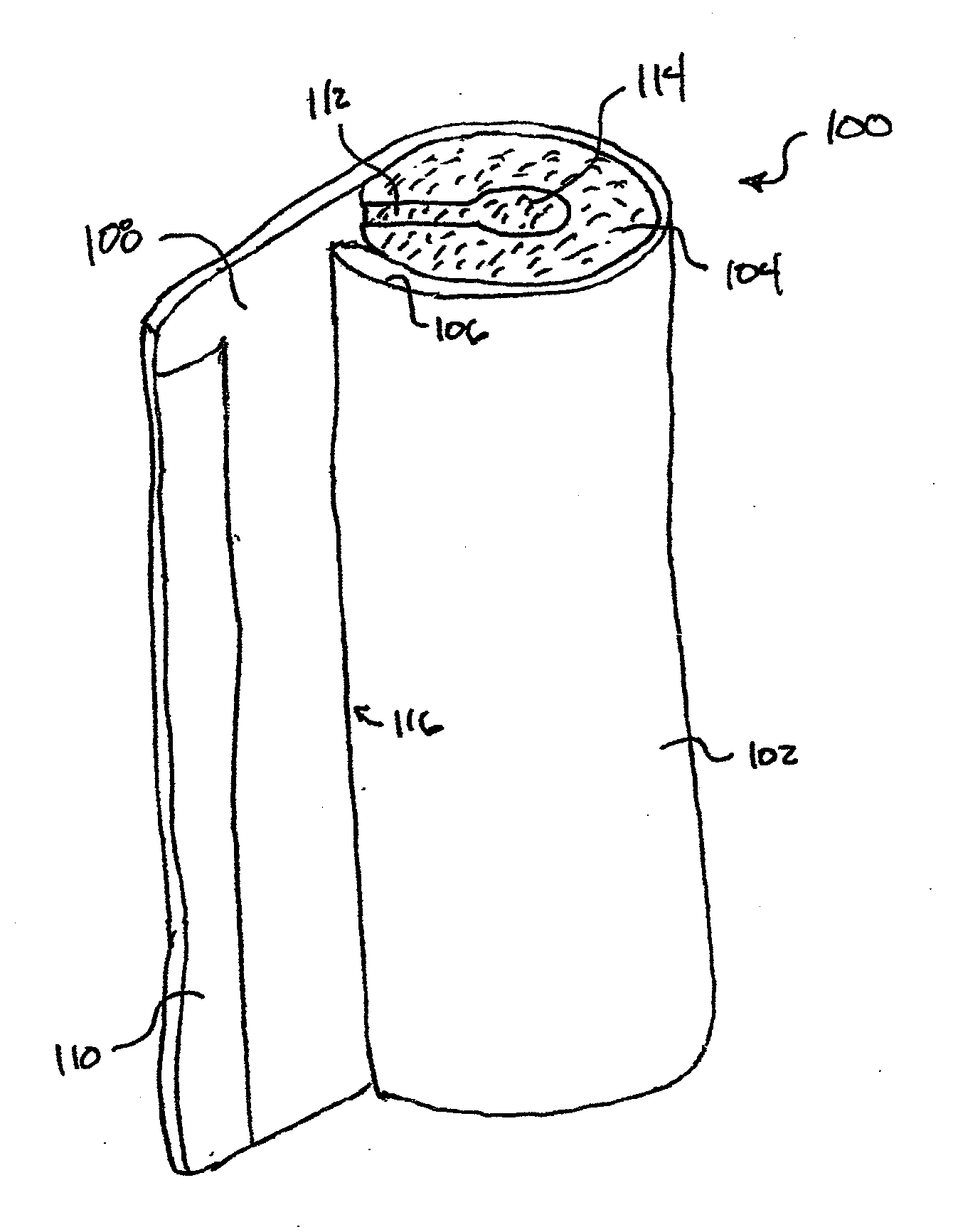
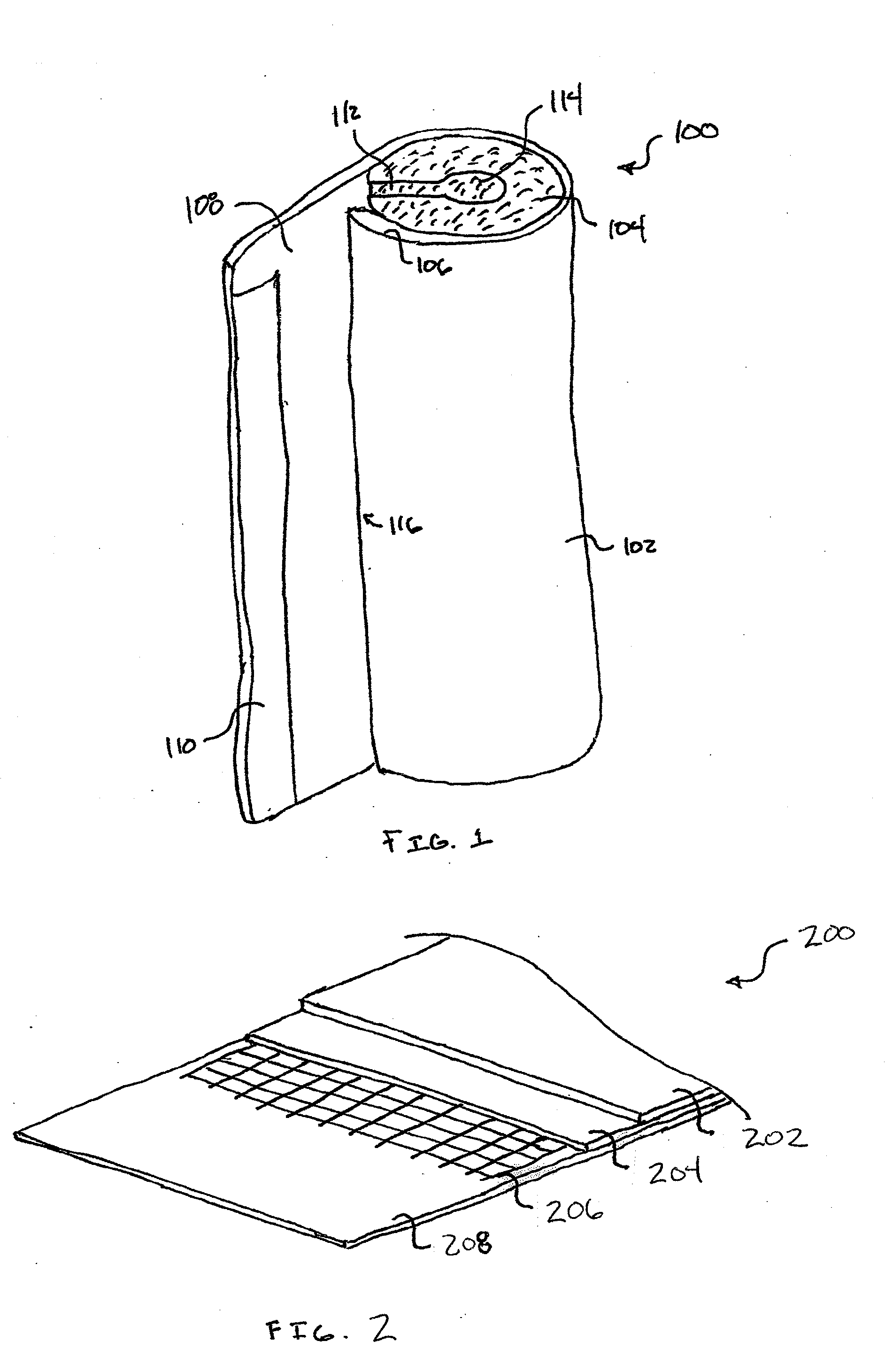
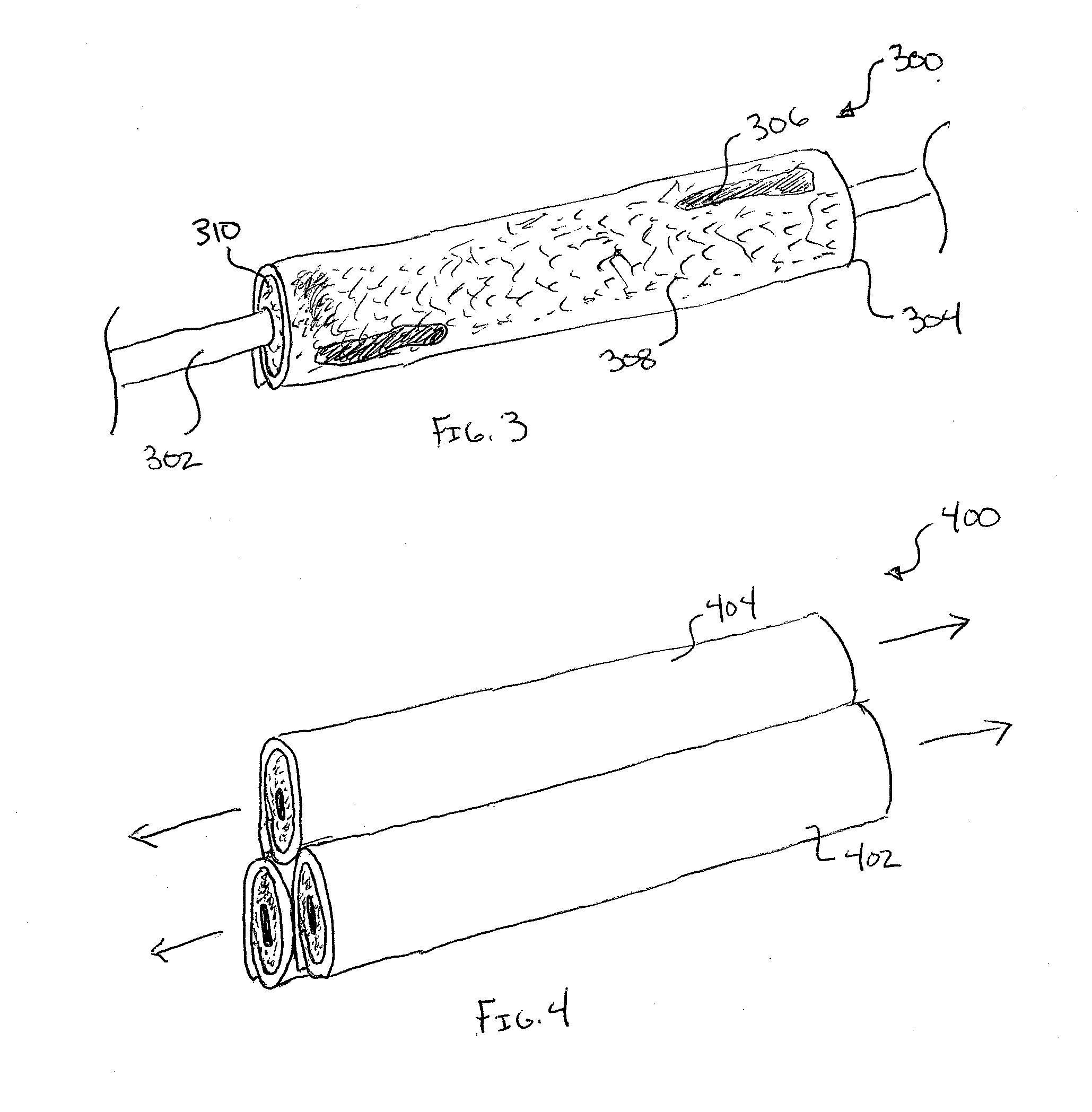
[0026]The present invention includes a pipe insulation product that is used to insulate and / or protect one or more sections of pipe. For example, in addition to minimizing heat transfer between the insulated sections of pipe and the surrounding environment, the pipe insulation product may also shield or protect the pipe from one or more environmental elements (e.g., water vapor). The protection / shielding function minimizes potential risks for the pipe and / or for surrounding objects (e.g., condensation of water vapor on the pipes; mold, mildew, and / or fungal growth; water drip damage; loss of the pipe insulation product's insulating value; etc.).
[0027]The pipe insulation product may also serve an aesthetic purpose when fitted about pipe sections. For example, pipe insulation products are often designed to provide a smooth, finished, and visually appealing outer surface to enhance the visual appeal of the piping systems. The pipe insulation product, however, may be susceptible to one ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| length | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com