Laser activated nanothermolysis of cells
a laser-activated nanothermolysis and cell technology, applied in the field of electromagnetic radiation and nanoparticles medical treatments, can solve the problems of selective and increased thermomechanical damage to the targeted biological body, selective and increased thermomechanical damage to the targeted cancer cell, and not to the normal cells comprising the sampl
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
In Vitro Laser Activated Nanothermolysis of Tumor Cells Using Nanospheres
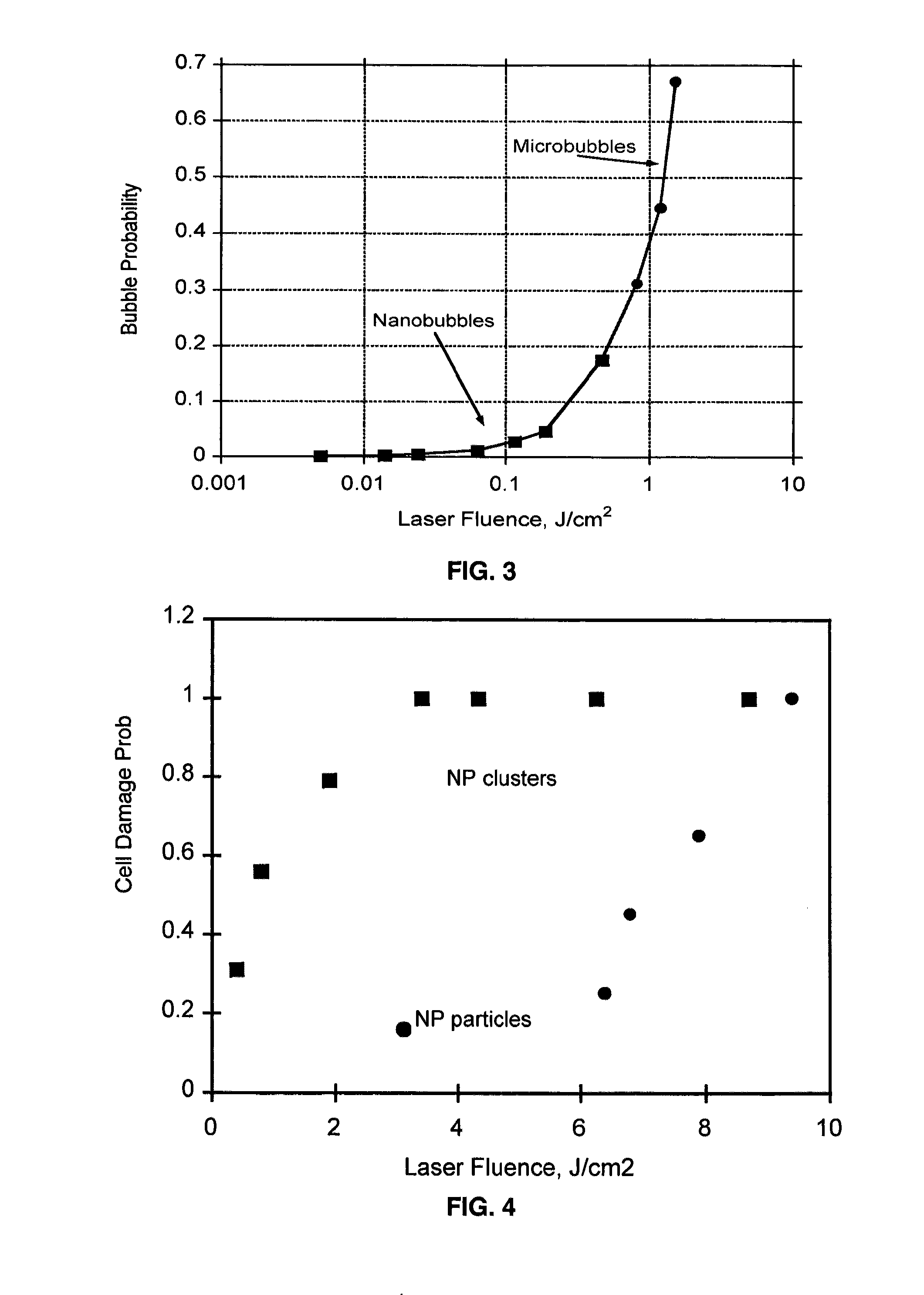
[0174]An in vitro model with myeloid K562 cell line, cryopreserved human cells, tumor cells (patient-derived acute B lymphoblast leukemia), both referred to as tumor cells, and normal stem cells are used. Well-defined specific MABs are used as primary MAB for targeting, i.e., CD15 and Glycophorin-A for K562 cells and CD19 for acute B-lymphoblast leukemia cells. Selection of MABs was realized by using flow cytometry. MABs CD 15 and Glycophorin A were selected for K562 cells based on their superior level of expression on surface of those cells. CD 19 was selected in the same way for acute B lymphoblast leukemia (ALL) cells. For controls for the single-cell model, untreated K562 cells are used and for the suspension model, normal stem cells are used.
Specific Targeting Protocol
[0175]Cells at a concentration of 800,000 / ml in phosphate buffer solution (PBS) with 1% fetal bovine serum (FBS) were preincubated with two ...
example 2
[0189]Ex Vivo LANTCET of Human Normal and ALL Leukemia Cells Using Spherical Nanoparticles
[0190]Cryopreserved samples of human bone marrow (BM) taken either from normal donors or patients with the diagnosis of acute B-lymphoblast leukemia (ALL) were used. Suspensions of normal and tumor cells were not mixed. Normal BM samples had no tumor cells and ALL tumor samples consisted mainly of tumor cells where the level of B-lymphoblasts was 94% to 98% in samples from different patients. Three normal and three tumor samples were all obtained from different patients. Normal and tumor samples were prepared and analyzed as separate samples though the same treatment protocol was used for each. Leukemia cells express diagnosis-specific genes that were determined individually for each ALL patient by using standard clinical protocols [53]. Specific MAB, raised against cell membrane receptors corresponding to specific genes, were used for each sample of tumor cells. Phenotyping was performed with ...
example 3
LANTCET of Human Normal and Tumor Cells Using Nanorods or Nanoshells
[0215]Cells and Antibody Conjugates
[0216]K562 cells that have high level of expression of CD33 antigens were used. Primary samples of human bone marrow (BM) taken either from normal donors or patients with the diagnosis of acute myeloid leukemia (AML) were used in experiments. All AML (tumor) samples consisted mainly of tumor cells where the level of B-lymphoblasts was 94 to 98% in samples from different patients. AML cells expressing diagnosis-specific CD-33 genes were determined with flow cytometry.
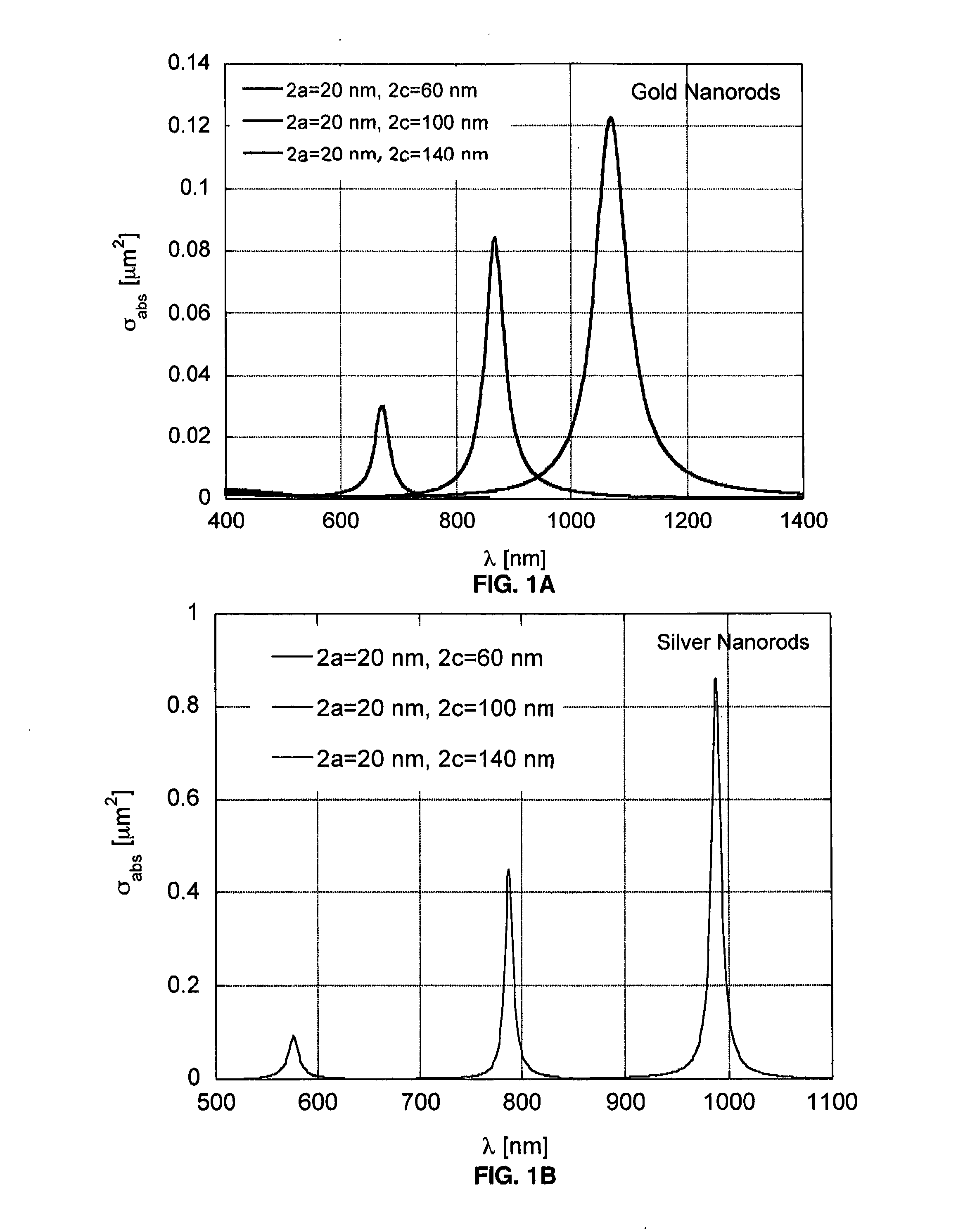
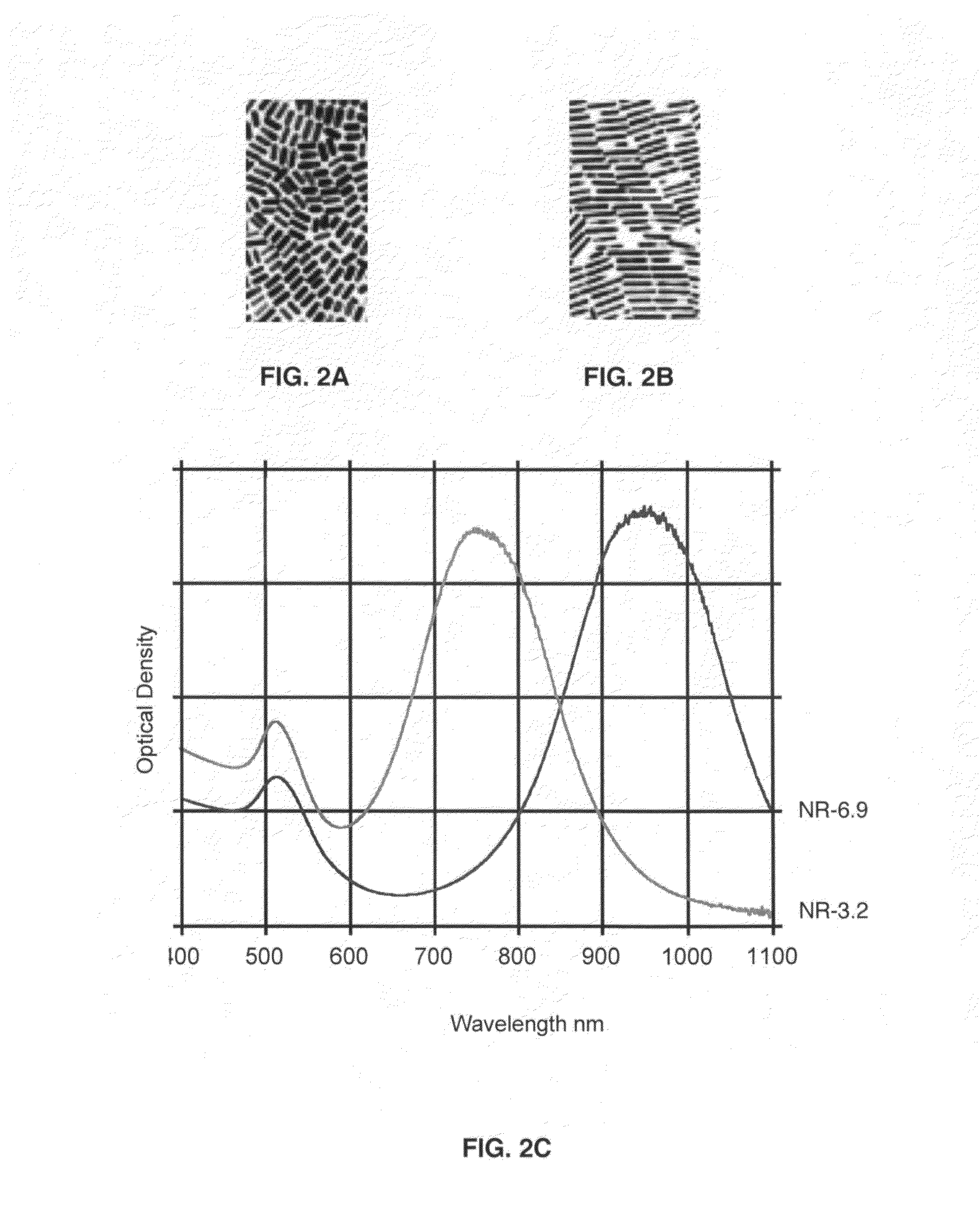
[0217]Conjugates of gold nanorods (NR) with and without antibodies to CD33 were used. AML and K562 cells were incubated for 30 min at 37° C. with the gold nanorods with dimensions 45×14 nm and absorption maximum at 780 nm. Then living and fixed cells were used as suspensions for bubble generation and detection.
[0218]Solid tumor cells were prepared as the monolayers of living EGF-positive carcinoma cells (Hep-2C) that we...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com