Protection factor rating system for protective eyewear
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
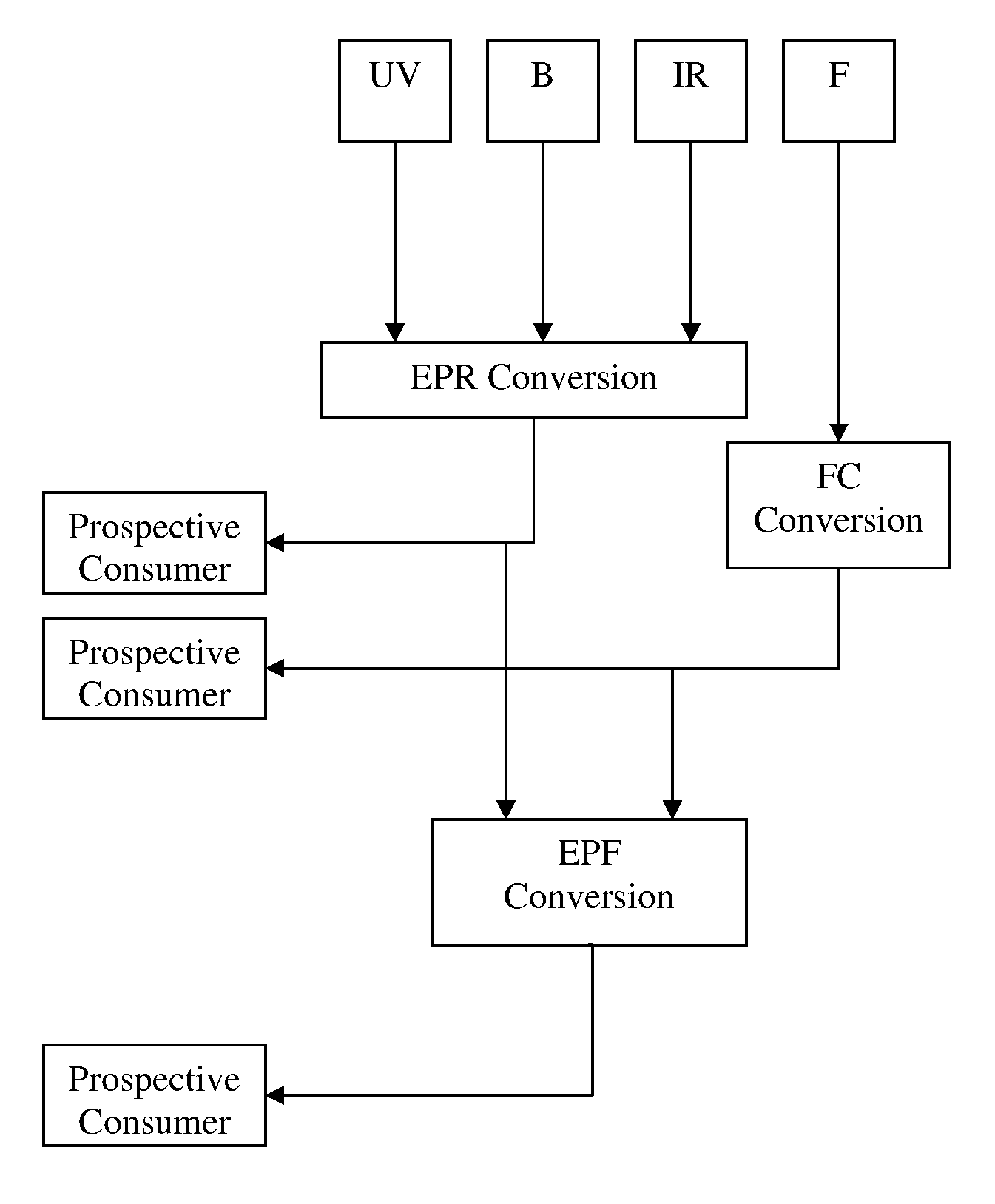
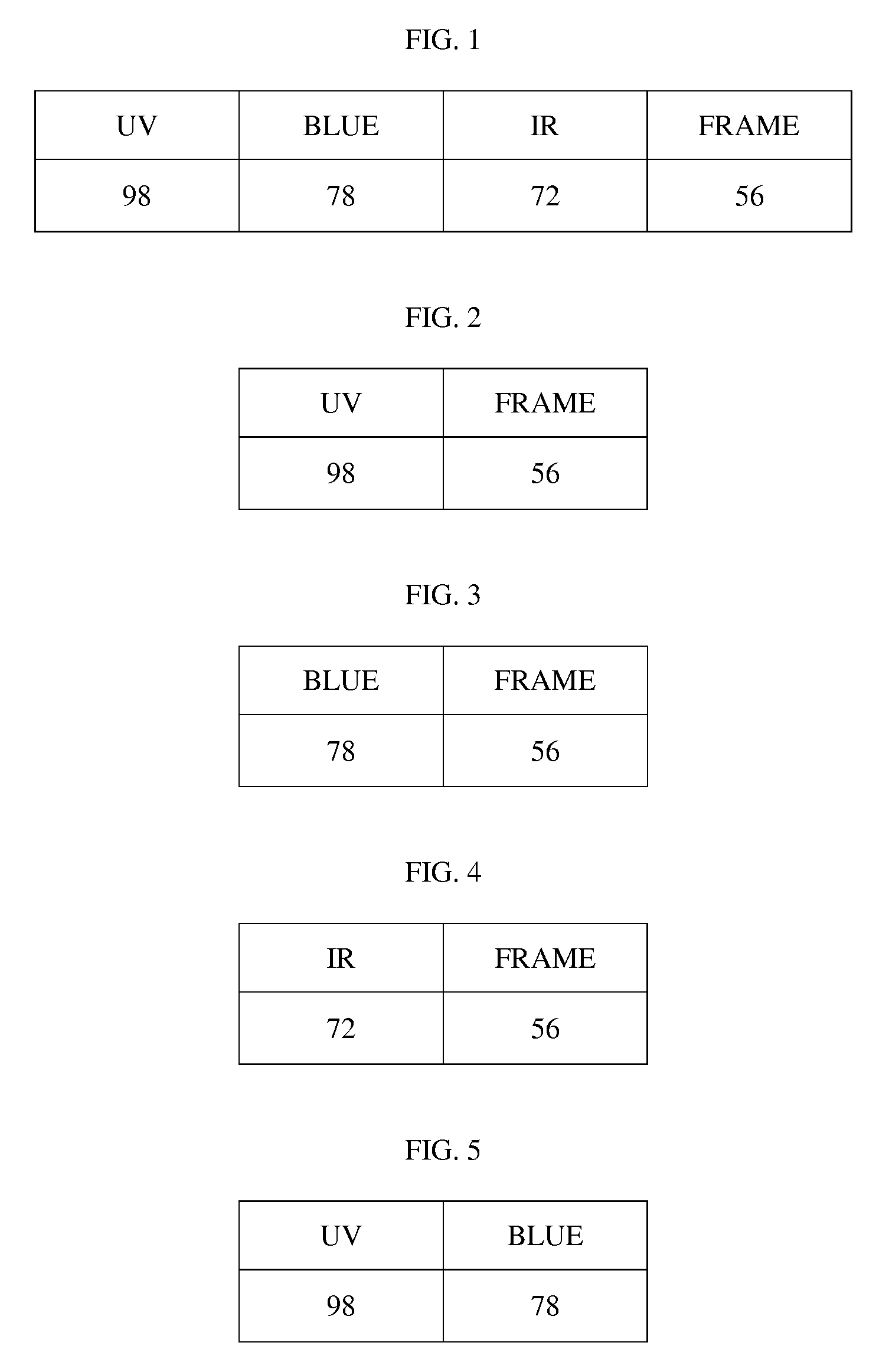
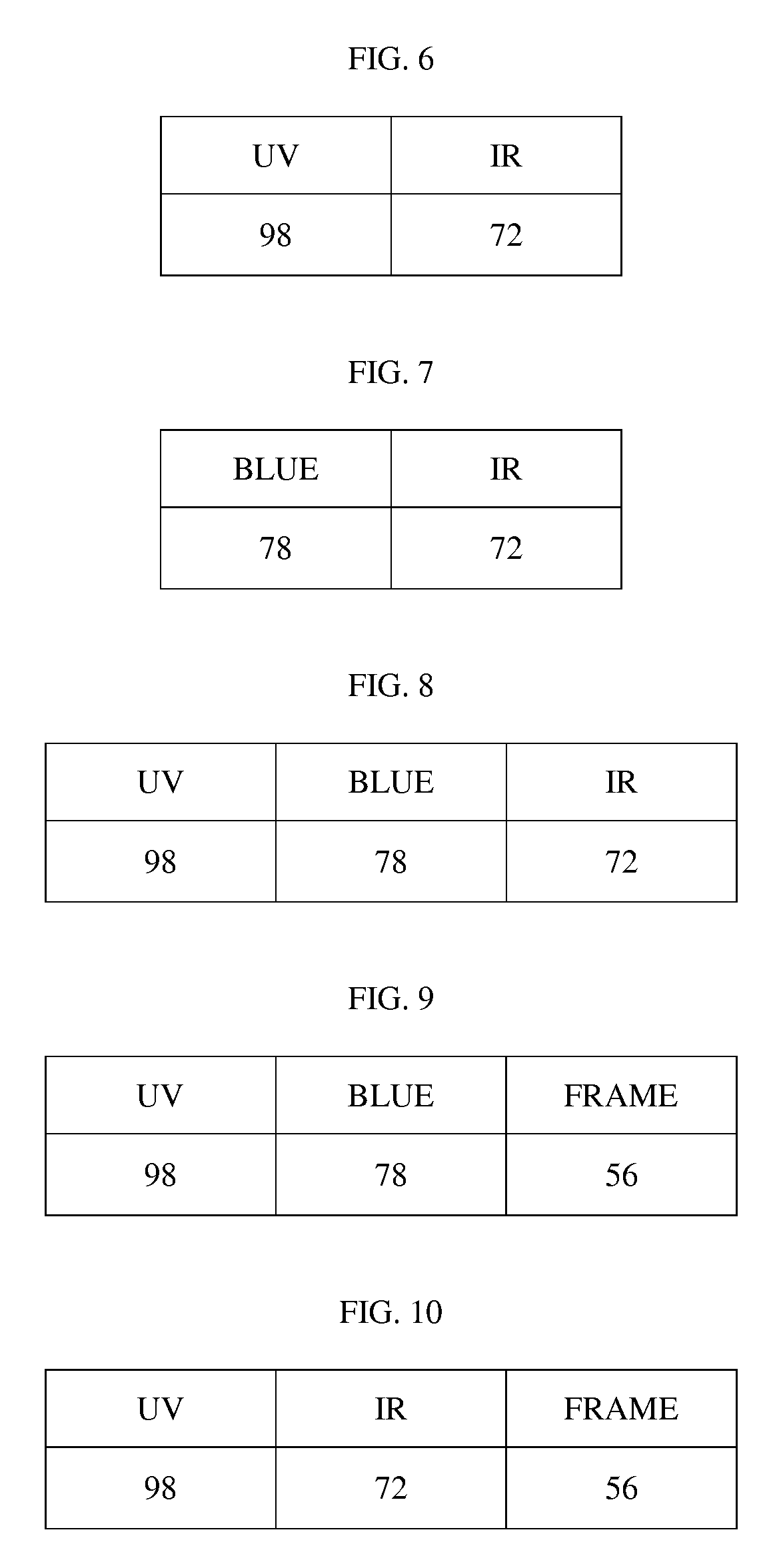
[0036]According to the principle of the invention, a method for rating eye protection includes measuring physical properties of eyewear and transforming those measured properties into values that can then be related and displayed to a prospective consumer for informational purposes. This method provides the consumer of the eyewear with valuable information concerning the value or rating of major protective variables or factors of the eyewear. The consumer is then able to use this information to make a more informed decision when purchasing eyewear such as sunglasses, snow goggles, swim goggles, corrective glasses, and the like.
[0037]Developing a rating system for protective eyewear is difficult because of the number of variables involved, including the sensitivity of different eye tissues to different radiation, the effects on radiation passing through different tissues, the distance of the eyewear from the eyes, the shape of the eyewear, and other factors. The issues are more compl...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com