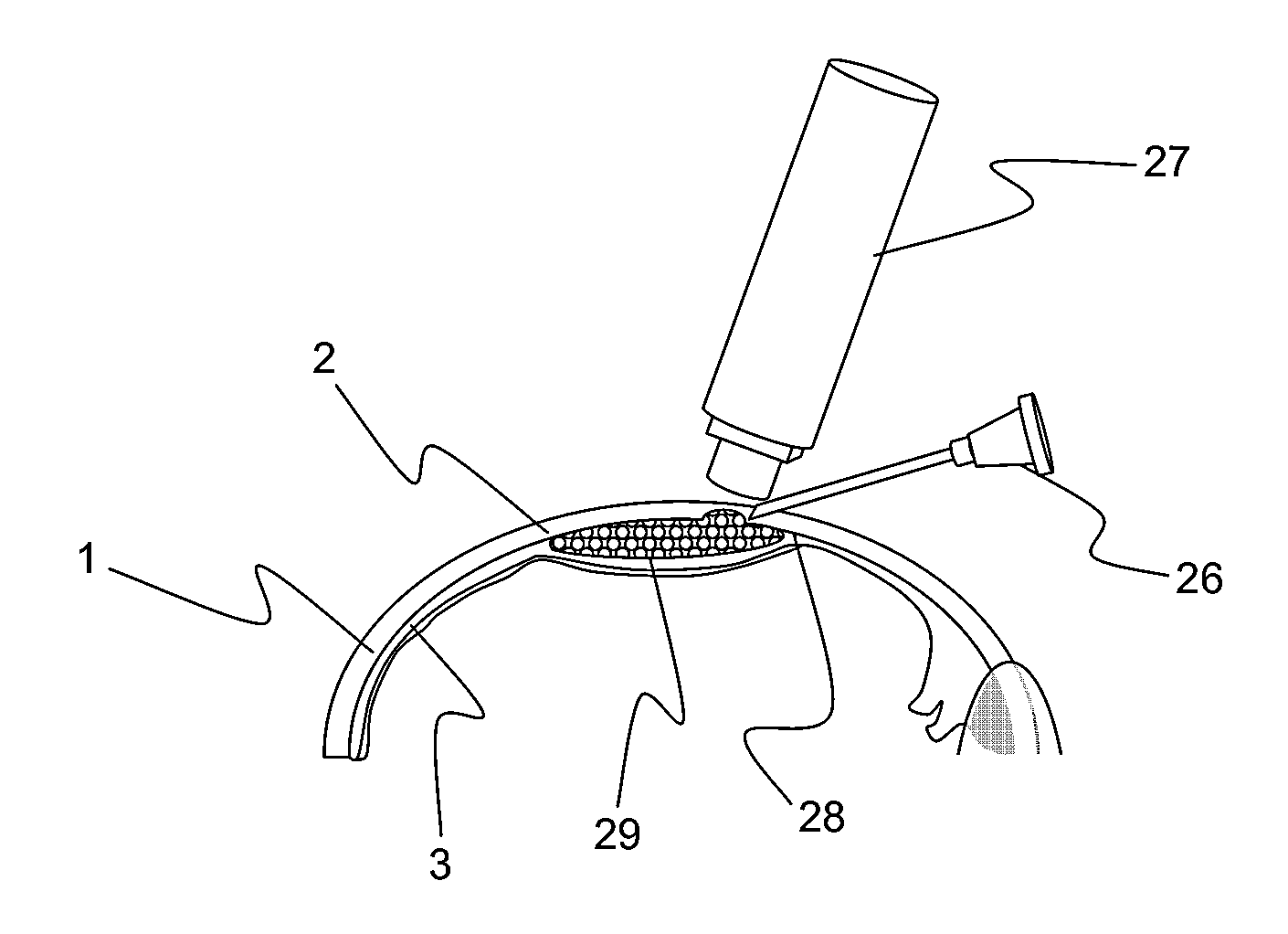
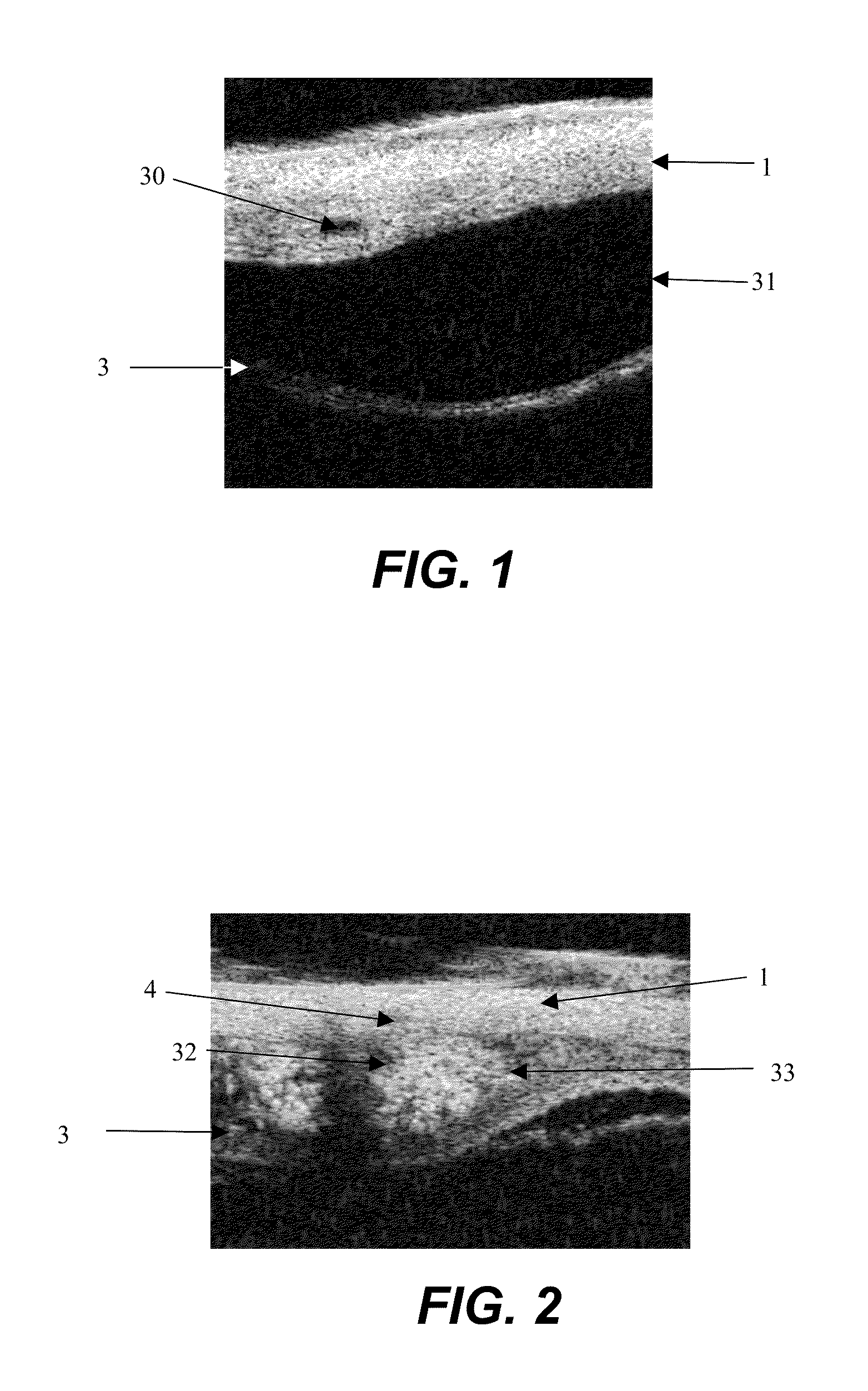
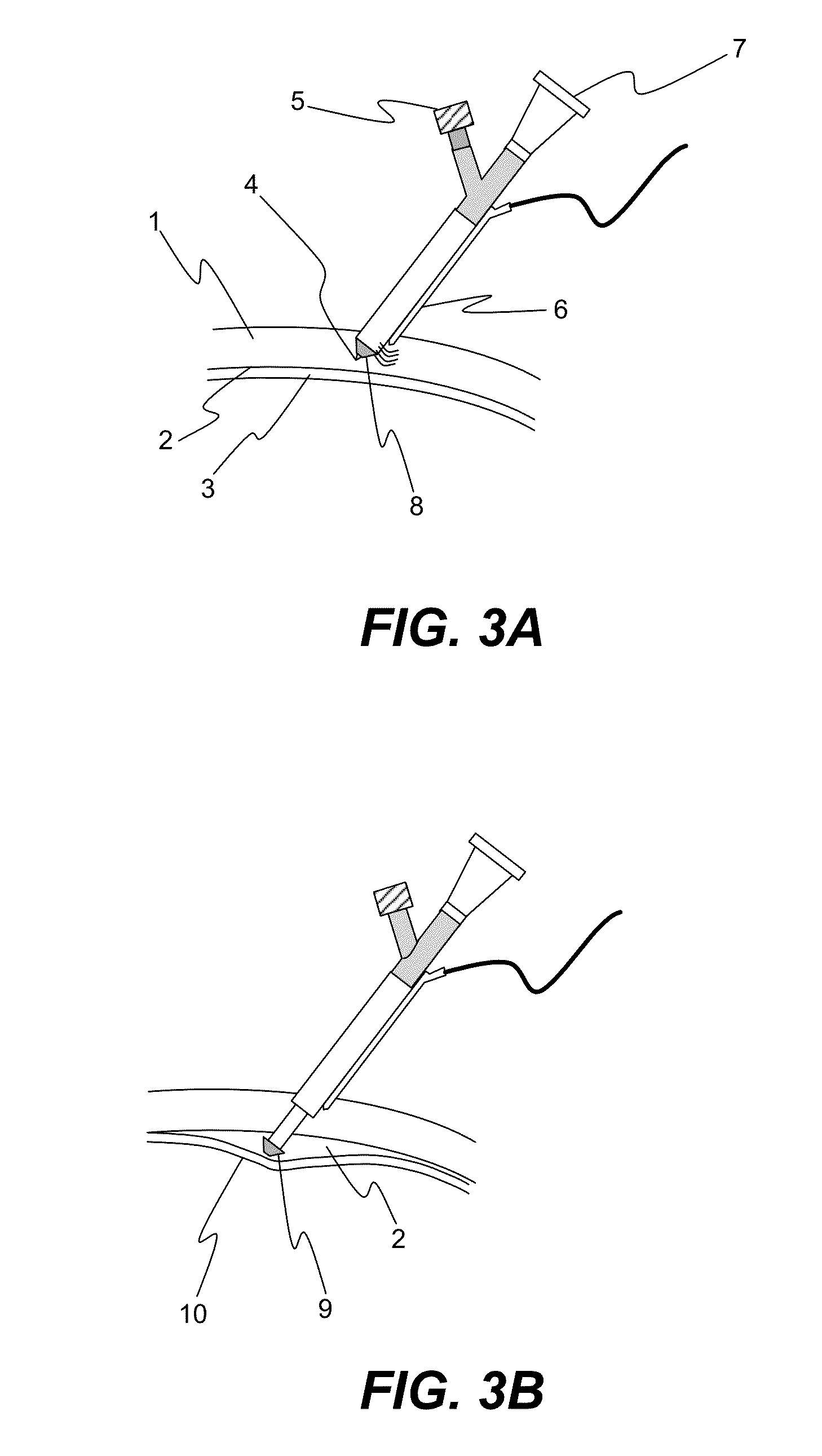
Apparatus and formulations for suprachoridal drug delivery
a technology of suprachoridal and appendix, which is applied in the field of eye drug delivery, can solve the problems of limiting treatment options, affecting the access to the eye for medical treatment, and the delicate nature of the tissues, so as to prevent trauma
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
[0054]Fluorescent dyed polystyrene microspheres (Firefli™, Duke Scientific, Inc., Palo Alto, Calif.) suspended in phosphate-buffered saline were used as model drug to evaluate the size range in which particulates will migrate in the suprachoroidal space from the anterior region to the posterior region.
[0055]An enucleated human cadaver eye was radially incised to the choroid in the pars plana region, which is in the anterior portion of the eye. Using a syringe terminated with a blunt 27 gauge needle, 0.15 mL of a 1% by volume microsphere suspension (mean diameter 6 micron) was delivered into the anterior region of the suprachoroidal space. The needle was withdrawn and the incision sealed with cyanoacrylate adhesive.
[0056]The eye was then perfused for 24 hours with phosphate buffered saline at 10 mm Hg pressure by introducing into the anterior chamber a 30 gauge needle attached to a reservoir via infusion tubing. The reservoir was placed on a lab jack and elevated to provide constant ...
example 2
[0059]The experiment of Example 1 was repeated, except that a mixture of 6 and 33 micron diameter fluorescent microspheres as a model drug was suspended in a polymeric excipient comprising a surgical viscoelastic (Healon 5, Advanced Medical Optics, Inc.), a 2.3% concentration of sodium hyaluronic acid of 4,000,000 Daltons molecular weight, with thixotropic properties of a zero shear viscosity of 7,000,000 mPas and 400 mPas viscosity at 1000 s−1 shear rate. The mixture was introduced into the suprachoroidal space in the manner of Example 1. After 24 hour perfusion, the microspheres resided solely in the suprachoroidal space at the anterior instillation site and did not show evidence of migration, demonstrating the localizing effect of the thixotropic polymeric excipient.
example 3
[0060]To demonstrate the effect of polymeric excipient viscosity on drug localization, the experiment of Example 1 was repeated, except that bevacizumab (Avastin™, Genentech), an anti-VEG antibody, was adsorbed onto 5 micron diameter carboxylated fluorescent microspheres and mixed at equal volumes with one of three hyaluronic acid based surgical viscoelastics (Healon, Healon GV, Healon 5, Advanced Medical Optics, Inc.), each with a different viscosity and thixotropic properties. (Healon, 300,000 mPas viscoscity at zero shear rate, 150 mPas viscosity at 1000 s-1 shear rate; Healon GV, 3,000,000 mPas viscosity at zero shear rate, 200 mPas at 1000 s-1 shear rate; Healon 5, 7,000,000 mPas viscosity at zero shear rate, 400 mPas viscosity at 1000 s-1 shear rate.) Each mixture was introduced into the anterior region of the suprachoroidal space at the pars plana in the anterior region of the eye in the manner of Example 1. After 24 hours perfusion, the microspheres in Healon and Healon GV w...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com