Methods of Treating Mitochondrial Dysfunction
a mitochondrial dysfunction and treatment method technology, applied in the field of mitochondrial dysfunction treatment methods, can solve the problems of tissue or organ dysfunction symptoms, drug side effects, and the effect of drugs only for a limited time period
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
General Methods
[0097]Materials.
[0098]All chemicals, including PJ34 (Garcia et al., 2001), were from Sigma-Aldrich unless stated otherwise.
[0099]Animal Experiments.
[0100]Male PARP-1+ / + and PARP-1− / − mice on a pure C57Bl / 6J background (Menissier-de Murcia et al., 1997) were used. Mice were housed separately, had ad libitum access to water and standard rodent chow (10 kcal % of fat, Safe, Augy, France) or to a high calorie, high fat diet (60 kcal % of fat, Research Diets, New Brunswick, N.J., USA), and were kept under a 12 h dark-light cycle. In other animal experiments, 8 weeks-old male C57Bl / 6J mice were purchased from Charles River and powder chow (D12450B) and high fat (D12492) diets were from Research Diets Inc (New Brunswick, N.J., USA). 80 ml of water per kg of powder CD were used to make food pellets. 40 ml of water per kg of powder HFD were used to make food pellets. For NR, NMN and NA supplemented diets, the appropriate amount of these compounds was added to the water used to...
example 2
PARP-1− / − Mice are Leaner and Display Increased Energy Expenditure
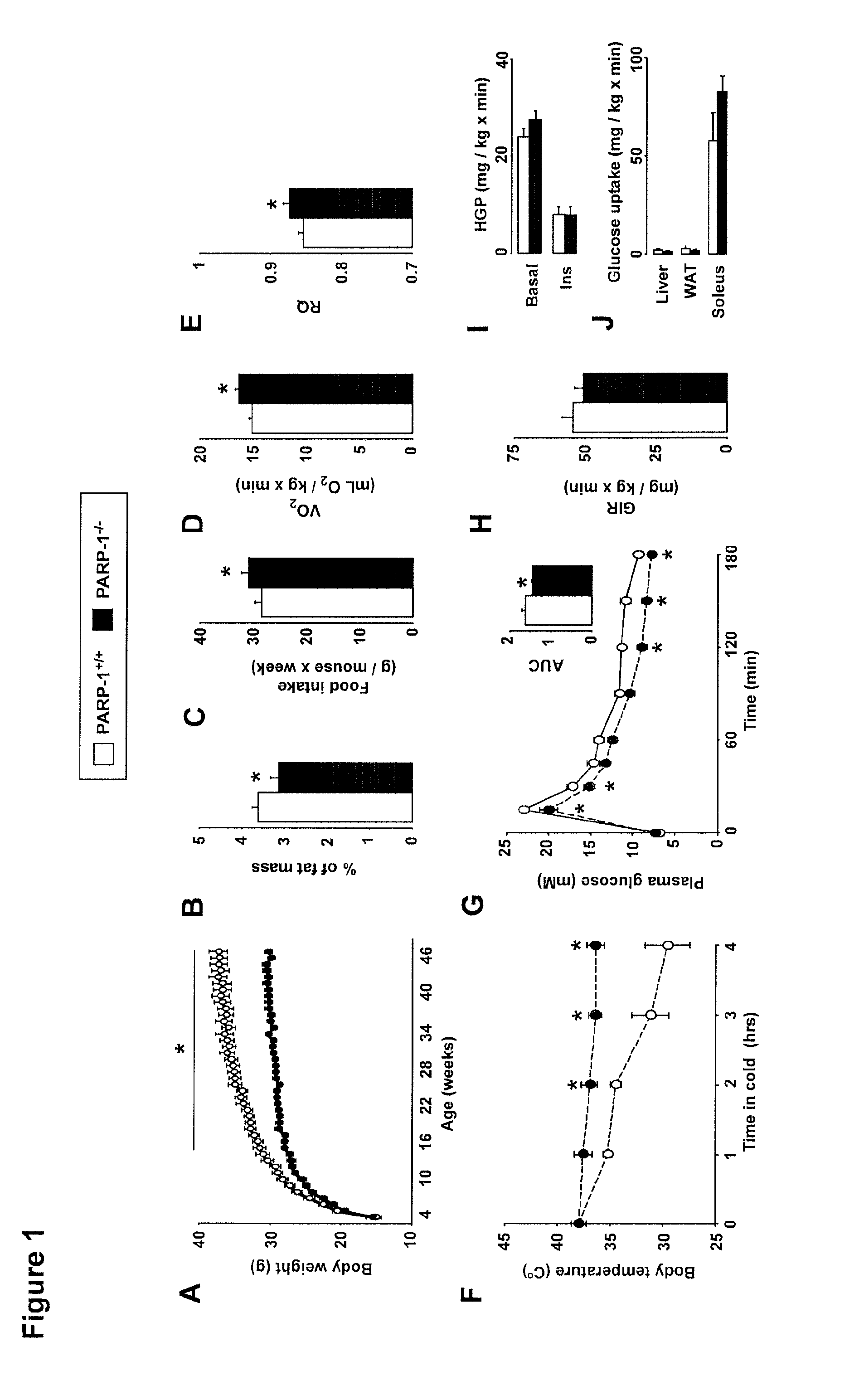
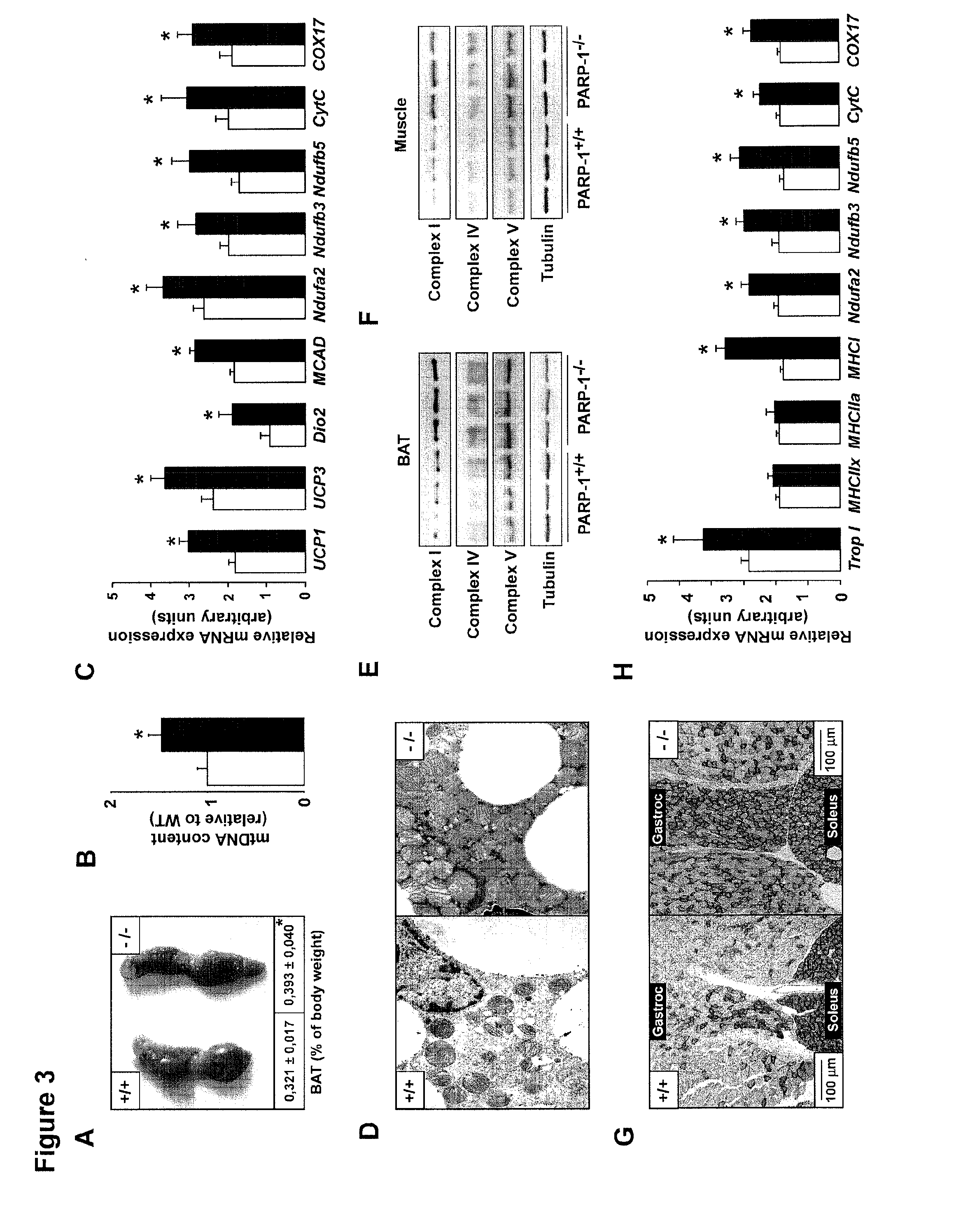
[0158]A striking initial observation was that PARP-1− / − mice on chow weighed less (FIG. 1A) and accumulated less fat than wild-type (WT, PARP-1+ / +) littermates upon aging (FIG. 1B). This happened despite the fact that the PARP-1− / − mice consumed significantly more food (FIG. 1C). The effects of PARP-1 deletion on body mass and food intake were observed in both males and females (data not shown). During indirect calorimetry, PARP-1− / − mice also consumed more O2 (FIG. 1D), suggesting that their decreased body weight might be a consequence of increased energy expenditure (EE). Interestingly, resting energy expenditure (REE) was not different (FIG. 8), suggesting that the increase could be attributed to changes at night, when the mice are active. In line with this, spontaneous locomotor activity was significantly increased at night in PARP-1− / − mice (FIG. 8B). Consistently, the respiratory quotient was also higher in PARP...
example 3
PARP-1 Protein Levels and Activity are Regulated by Metabolic Challenges
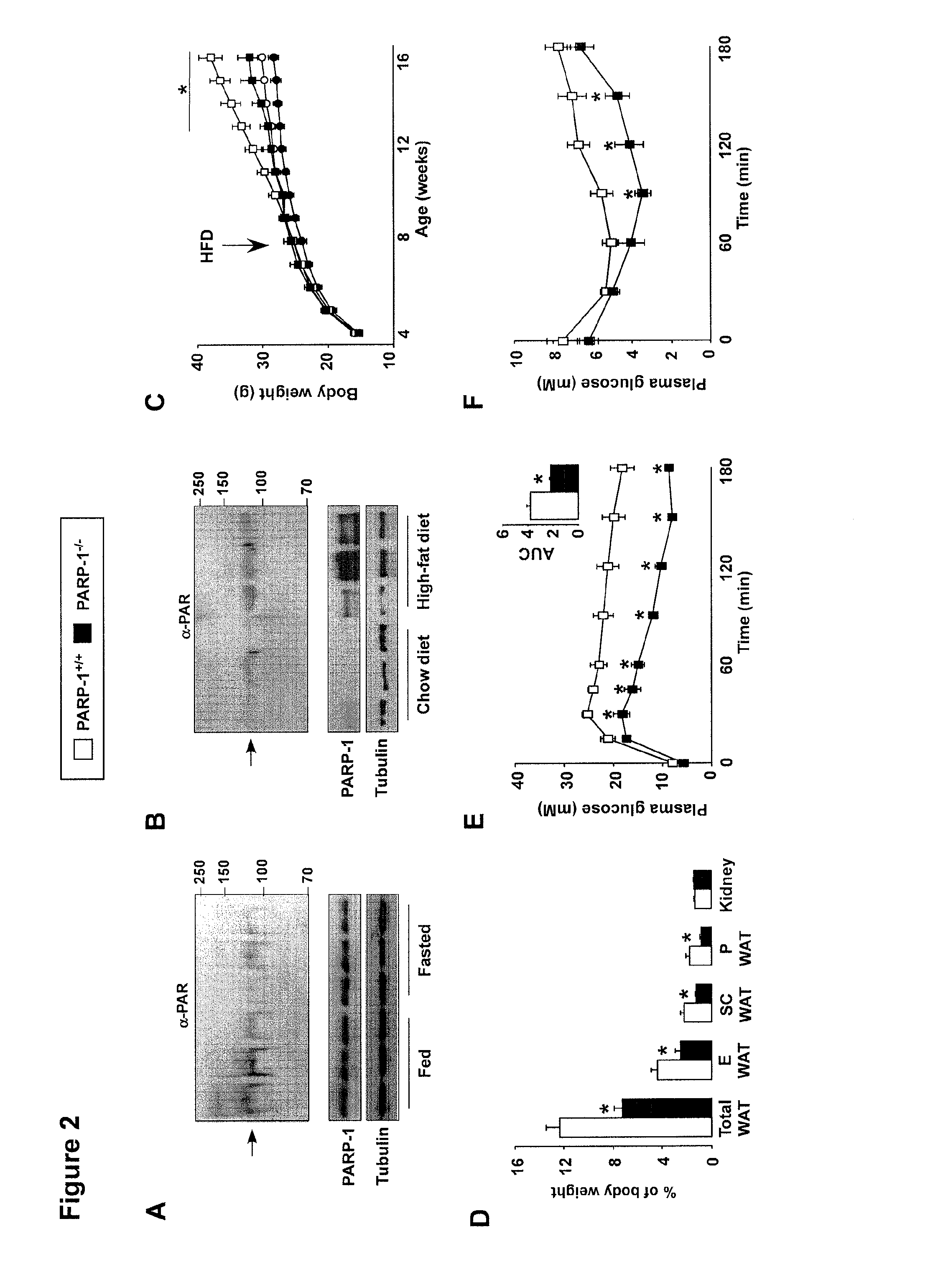
[0160]The striking impact of PARP-1 deletion on metabolism made us wonder whether PARP activity would be dynamically regulated in normal mice upon physiological changes in nutrient availability. To test this hypothesis we analyzed whether nutrient scarcity (fasting) or overload (high-fat diet) would have an effect on PARP-1 activity. A 24-hr fast promoted a significant reduction in PARP activity, as manifested by the lower PARP-1 autoPARylation levels, which reflect global PARylation activity (Adamietz, 1987) (FIG. 2A). This change happened in the absence of changes in total PARP-1 levels, suggesting a lower activity of the enzyme (FIG. 2A). In contrast, nutrient overload induced by high-fat feeding promoted a robust increase in PARP-1 protein levels and PARP activity (FIG. 2B). Together, these data indicate that PARP-1 levels and activity are positively regulated by nutrient availability.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Concentration | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Disorder | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com