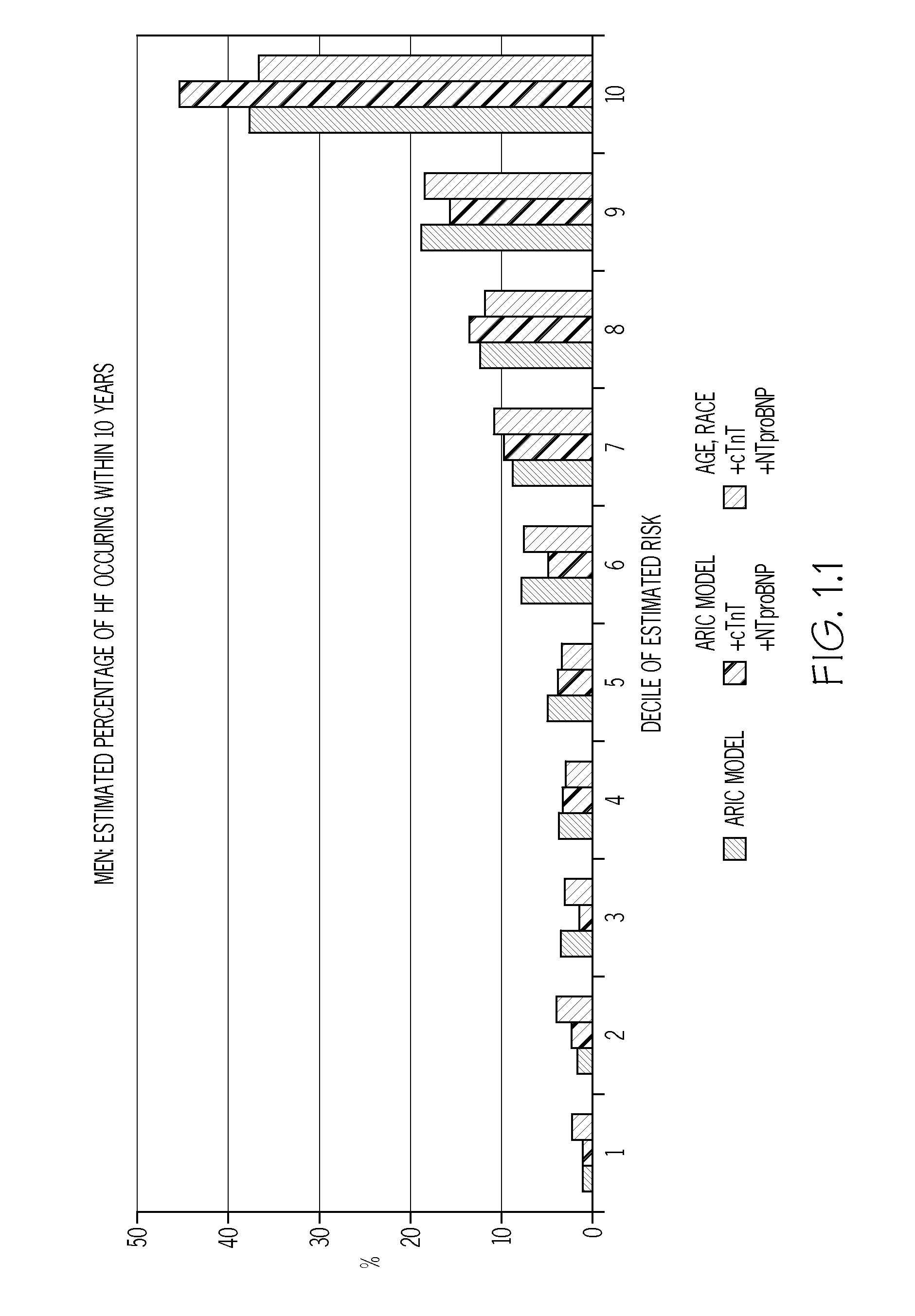
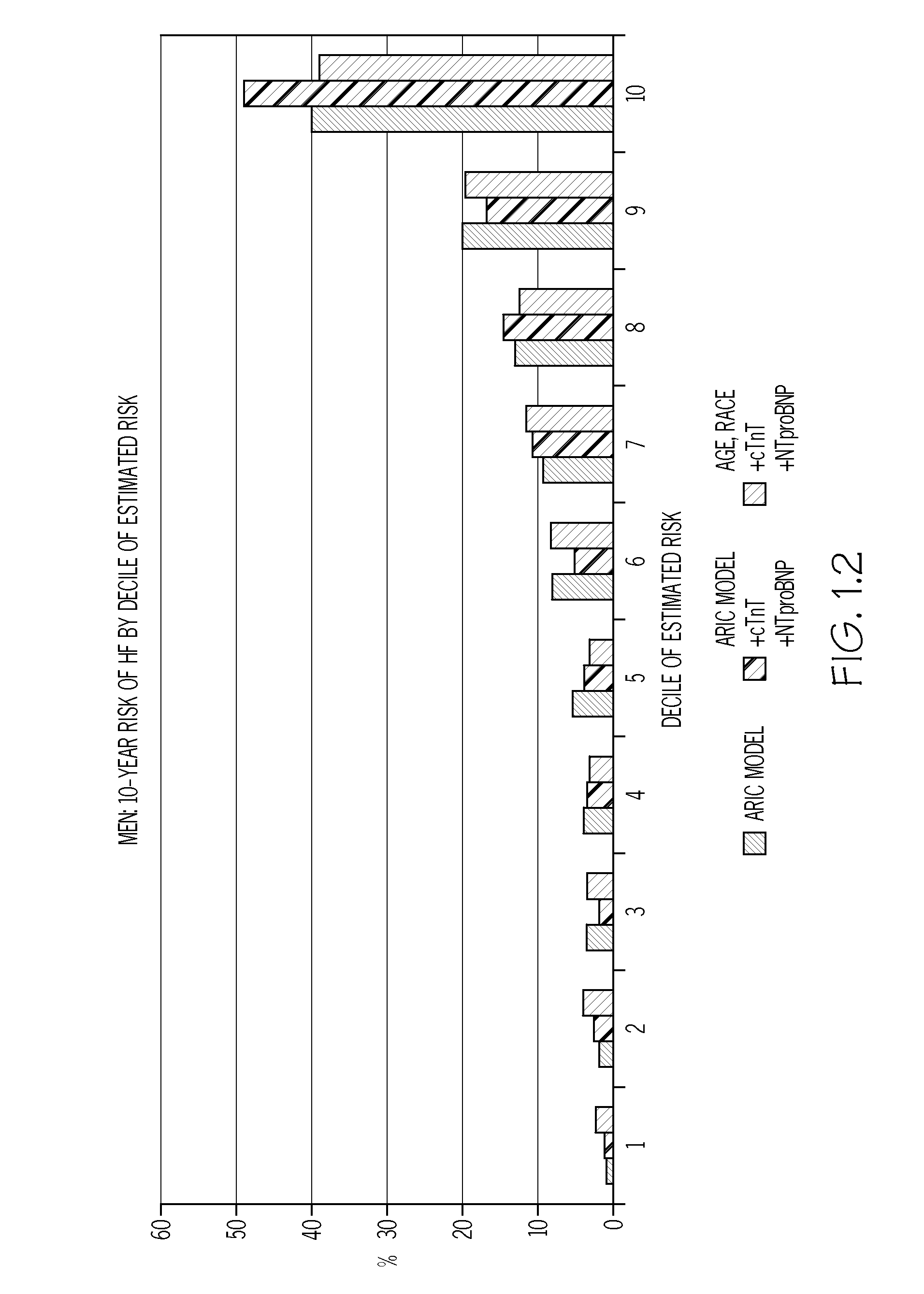
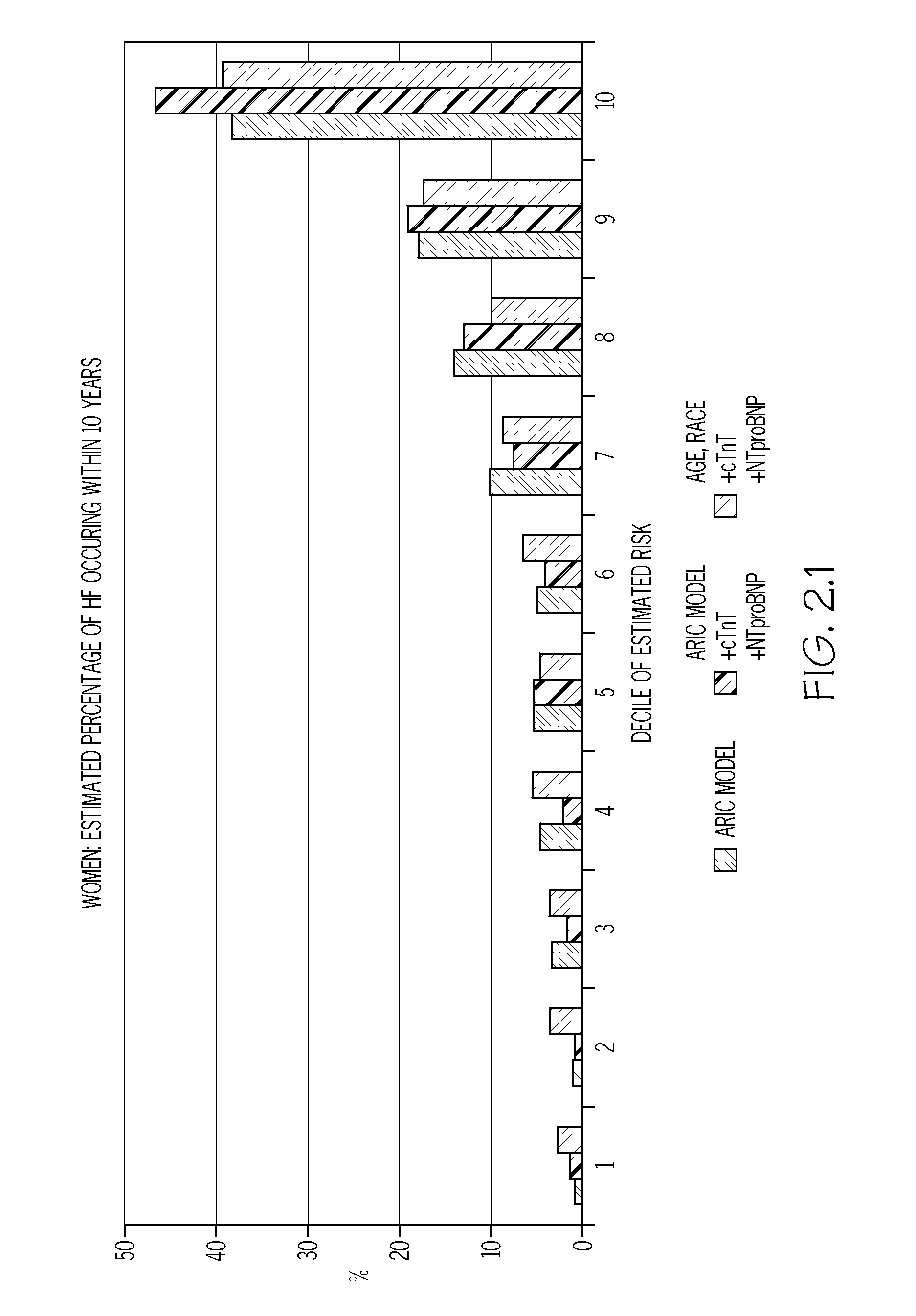
Biomarkers to improve prediction of heart failure risk
a biomarker and risk technology, applied in the field of laboratory diagnostics, can solve the problems of reducing the likelihood of heart failure in a patient, and the difficulty of diagnosing patients at risk for heart failure, so as to improve the risk of heart failure, and improve the diagnosis of hf risk.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
ARIC Study Population
[0078]The study population was generated using data obtained following the fourth ARIC examination (1997-99). From the 11,656 eligible individuals, those whose race was neither Black nor White (n=31), Black participants from the Washington County, Md. or Minneapolis centers (n=38), those with prevalent HF at examination 1 (n=410), those missing HF status at examination 1 (n=199), those missing covariates for ARIC HF model (n=354), those with HF hospitalization between examination 1 and 4 (n=229), those missing covariates for ARIC HF model (n=354), cTnT values (n=365), or NT-proBNP values (n=9), and those with extreme NT-proBNP≧6025 pg / ml (n=6), or not having given full consent (n=249) were excluded, leaving 9,868 individuals with adequate sample eligible for the analysis. Participants with biomarker levels below the detectable limit were assigned half the lower limit of detection. The mean age of the study population was 62.7 years; 44% were males, and ˜79.5% we...
example 2
Determination of cTnT and NT-proBNP Levels of ARIC Participants
[0079]Cardiac troponin T (cTnT) and NT-proBNP levels were measured using stored blood samples collected during the fourth ARIC examination described in Example 1.
[0080]Assays: Cardiac troponin T (cTnT) was measured using a 5th Generation, highly sensitive assay (Elecsys® Troponin T hs; Roche Diagnostics, Indianapolis, Ind. U.S.A.) (Hermsen, D. et al. 2007, Clin Lab.,53(1-2): 1-9). A cobas e 411 automated analyzer (Roche Diagnostics) was used to quantify the amount of cTnT. A detailed report on sources of variability, interassay reliability coefficients, repeatability of measurements and coefficients of variation in the ARIC study has been previously described (Agarwal et al., 2012, Circ Heart Fail. 5(4): 422-29; Saunders, A. T. et al., 2011, Circulation. 123(13): 1367-76). Briefly, the lower and upper limits of detection of the cTnT assay are 3 and 10,000 ng / L, respectively, and the limit of quantitation (the lowest anal...
example 3
Determination of Cox Hazard Ratios
[0083]Using Cox proportional hazards models, the hazard ratio for the association of cTnT (Table 2) and NT-proBNP (Table 3) with incident of HF was determined. Model factors were adjusted for age, race and cTnT (Table 3) or NT-proBNP (Table 2). Hazard ratios were also determined when model factors were adjusted for all components of the ARIC heart failure risk prediction model, and either cTnT (Table 3) or NT-proBNP (Table 2).
TABLE 2Hazard Ratios for Association of Troponin T (cTnT) with Heart Failure:The ARIC Study, 4th ExaminationTroponin categories (ng / L)MenWomenAge, race,Full ARIC,Age, race,Full ARIC,Model FactorsNT-proBNPNT-proBNPNT-proBNPNT-proBNPUndetectable11113 to ≦51.55 (1.00, 2.43)1.59 (1.02, 2.49)1.09 (0.82, 1.43)1.11 (0.84, 1.46)6 to ≦81.83 (1.19, 2.81)1.91 (1.24, 2.95)2.01 (1.54, 2.63)1.70 (1.29, 2.24) 9 to ≦132.28 (1.49, 3.50)2.14 (1.39, 3.30)3.10 (2.32, 4.15)2.47 (1.84, 3.33)14 to ≦254.78 (3.12, 7.33)3.80 (2.46, 5.88)6.03 (4.22, 8.62...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com