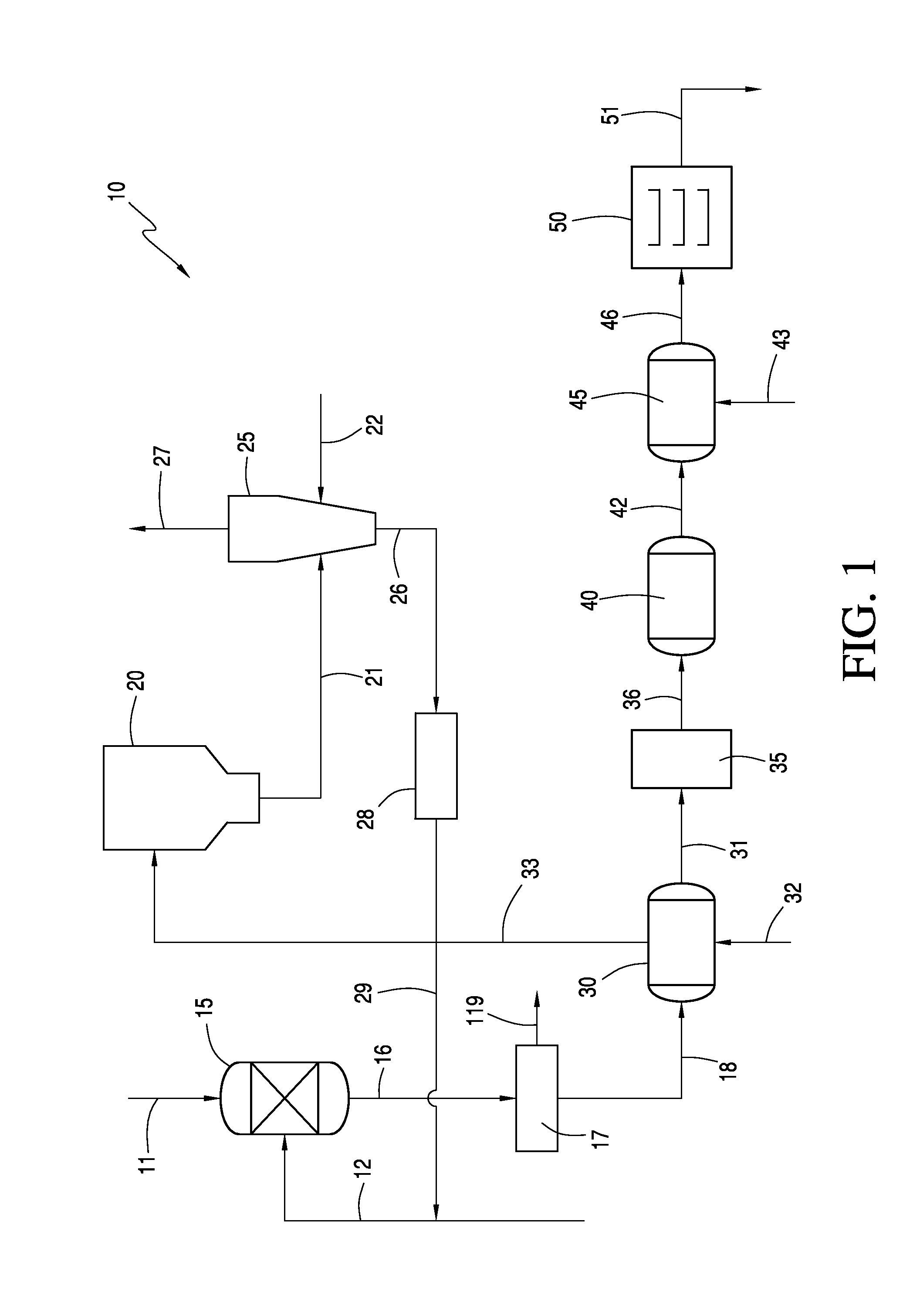
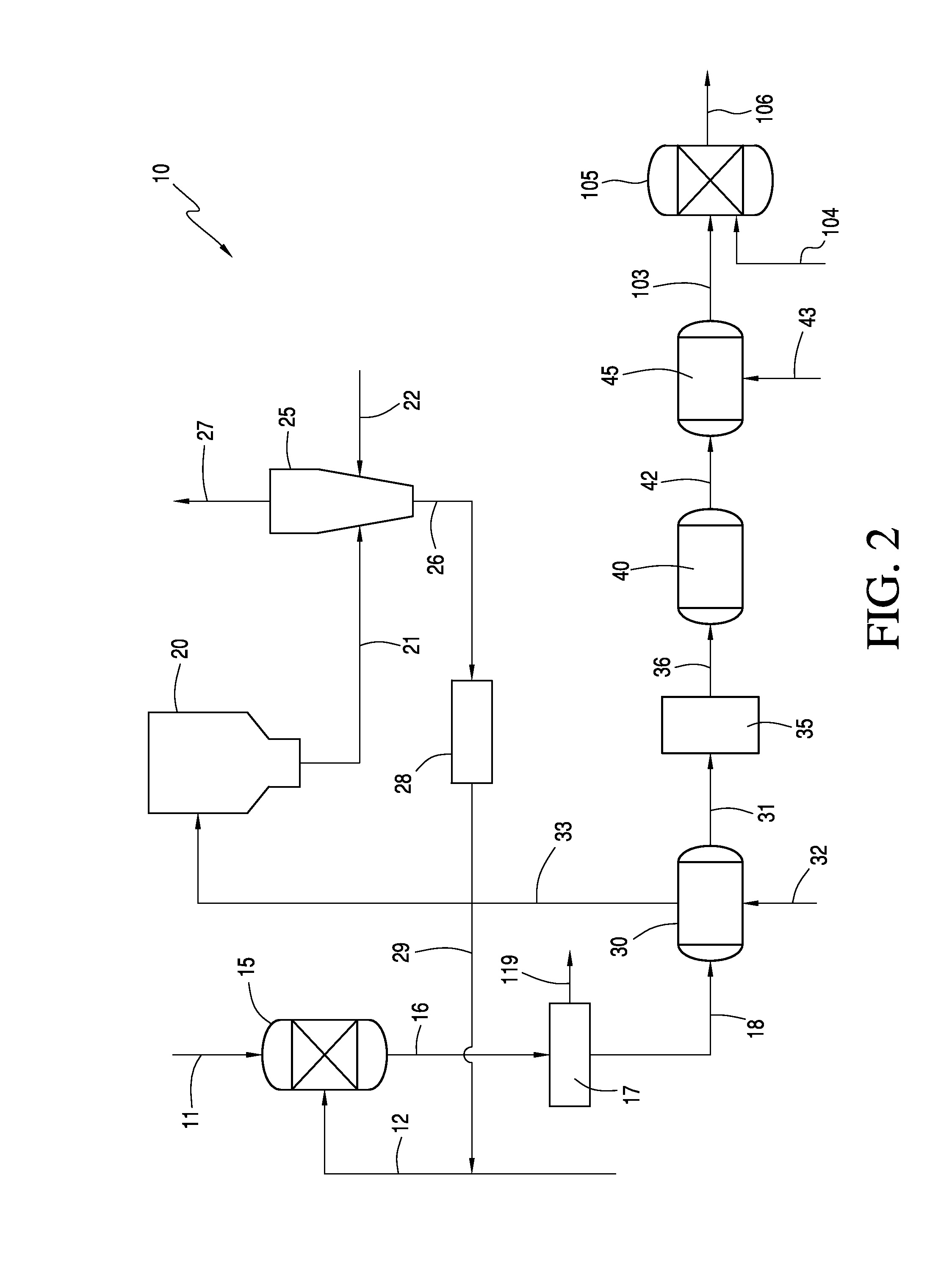
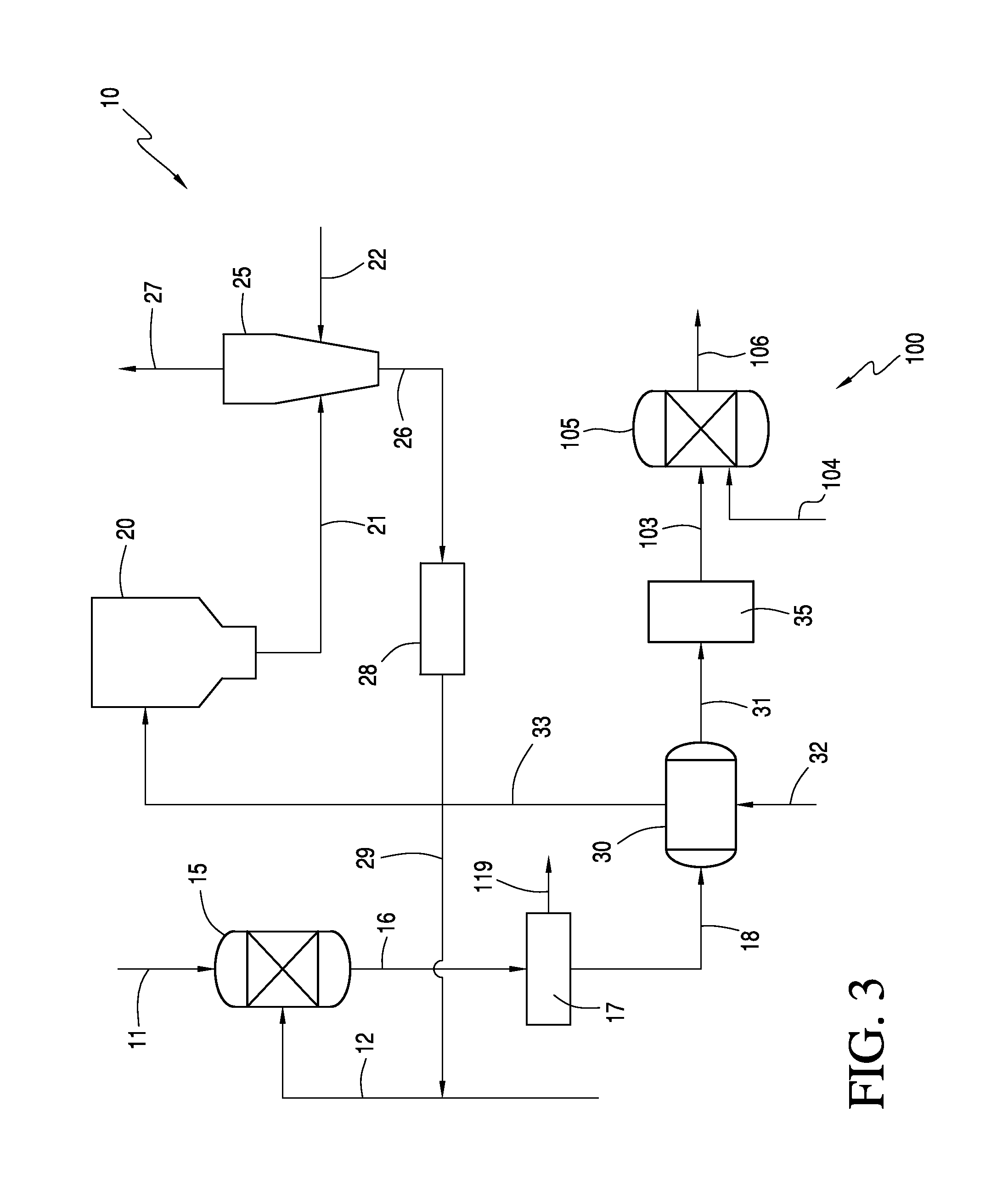
Integrated Processes for Purifying a Cellulosic Material
a cellulosic material and integrated technology, applied in pulp by-product recovery, pulp liquor regeneration, papermaking, etc., can solve the problems of high cost of such so-called cellulose produced in commercial pulp processes, incompatible with certain industrial uses, and inability to achieve dmdo. to achieve the effect of reducing the cost of dmdo
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
[0159]A wet pulp, simulating a wet pulp from a kraft or sulfite pulping process, was pre-extraction washed with DMSO to reduce the water content. Excluding any DMSO from this pre-extraction wash, a pulp comprising 74.8 wt. % cellulose, 18.7 wt. % hemicellulose and 6.5 wt. % water was fed to an extraction unit. Separately, an extractant comprising 3.5 wt. % EMIM Ac and 96.5 wt. % DMSO was fed to the extraction unit. The extraction was conducted at a temperature of 90-110° C. and a pressure of 90-110 kPa. An extraction mixture comprising 3.6 wt. % cellulose, 0.89 wt. % hemicellulose, 0.31 wt. % water, 3.3 wt. % ionic liquid and 91.9 wt. % DMSO was removed from the extractor and sent through a vacuum filter and washed with an extractant wash to remove an extraction filtrate comprising extractant and hemicellulose. The extractant wash was water and was fed at a 10:1 mass ratio of water to pulp. The washed cellulosic material, e.g., the intermediate cellulosic material, comprised 24.5 wt...
example 2
[0162]The finished cellulosic product and the finished hemicellulose product were prepared as in Example 1, except that the extraction process was completed in 82-stage counter-current operation. The extraction time was dropped to 60 minutes at a temperature of 90° C. for dissolving the same amount of hemicellulose, which was indicated by the UV absorbance value of 1.2 at 277 nm wavelength, or equivalently 2.8 wt. % hemicellulose.
example 3
[0163]The finished cellulosic product and the finished hemicellulose product were prepared as in Example 1, except that the extractant wash comprised 90 wt. % acetic acid and 10 wt. % water. The value of UV absorbance at 277 nm for the final pulp is 0.98, or equivalently 1.9 wt % hemicellulose.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| wt. % | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| wt. % | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| wt. % | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com