Treatment of AMD using aav sflt-1
a technology of amd and sflt, which is applied in the direction of viruses, peptide/protein ingredients, unknown materials, etc., can solve the problems of retinal neovascularization and vision loss, severe visual impairment, and cumulative risk increas
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
rAAV.sFlt-1
[0362]One example recombinant virus is rAAV.sFlt-1. It encodes a vector and a human form of the truncated, soluble VEGF receptor 1 (sFLT-1). The vector is a recombinant, replicative-deficient adeno-associated viral (rAAV) vector, of serotype 2.
[0363]The rAAV.sFlt-1 was manufactured under Good Manufacturing Practices (cGMP). At the manufacture site, the final product was aliquoted into sterile, low-virus-binding microcentrifuge tubes (individually wrapped, low-retention, sterilised flat cap vials) according to the protocol requirements (i.e. 200 μl of 1×1010 or 1×1011 viral genomes) and stored at −80° C. to await final product release. Each vial contained enough vector for use in a single patient (100 μl to be administered).
[0364]The recombinant virus, rAAV.sFlt-1, is a recombinant adeno-associated virus 2 (rAAV2) vector carrying the soluble VEGFR receptor 1 (VEGFR1) or sFLT-1 driven by the human cytomegalovirus (CMV) promoter. The rAAV.sFlt-1 vector and intact AAV2 genome...
example 2
In Vitro Inhibition of VEGF-Induced Endothelial Cell Proliferation
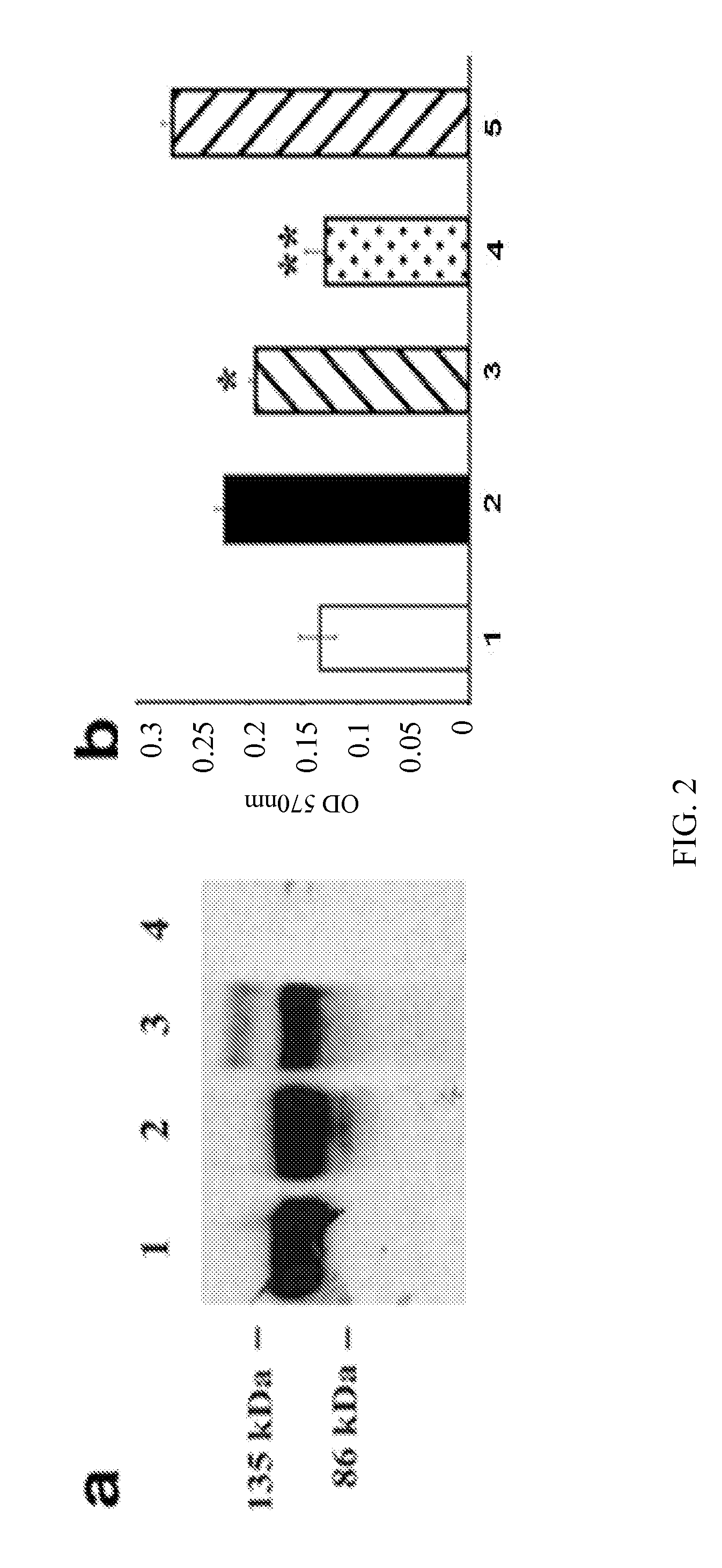
[0371]Studies were performed to assess VEGF-induction of human umbilical vein endothelial cell (HUVEC) proliferation and to determine whether VEGF-induced HUVEC proliferation would be inhibited by rAAV-mediated sFLT-1. The presence of sFLT-1 in transduced cells was first confirmed by Western blot analysis of conditioned media (FIG. 2, panel a). Conditioned medium from rAAV.sFlt-1-transduced and rAAV.gfp-transduced 293 cells were added to VEGF-treated HUVECs in increasing dilutions. A control starvation medium (normal HUVEC growth medium without bovine endothelial growth factor) only was also included. Heparin was added to each well at 100 μg / mL. The relative VEGF-induced proliferation of HUVECS treated with VEGF and the different conditioned media was assayed by addition 25 μL of 3-(4,5-dimethythiazol-2-yl)-2,5-diphenyltetrazolium bromide (MTT, 5 mg / mL, Sigma) to each well for 4 hours at 37° C. The secreted sFLT-1 enc...
example 3
rAAV.sFlt-1 Studies in Mice
[0375]Transgenic mice (trVEGF029) with slow, but stable retinal neovascularization induced by transgenic expression of human VEGF from photoreceptor cells were used as a model for retinal neovascularization. Two separate studies with these mice have been conducted.
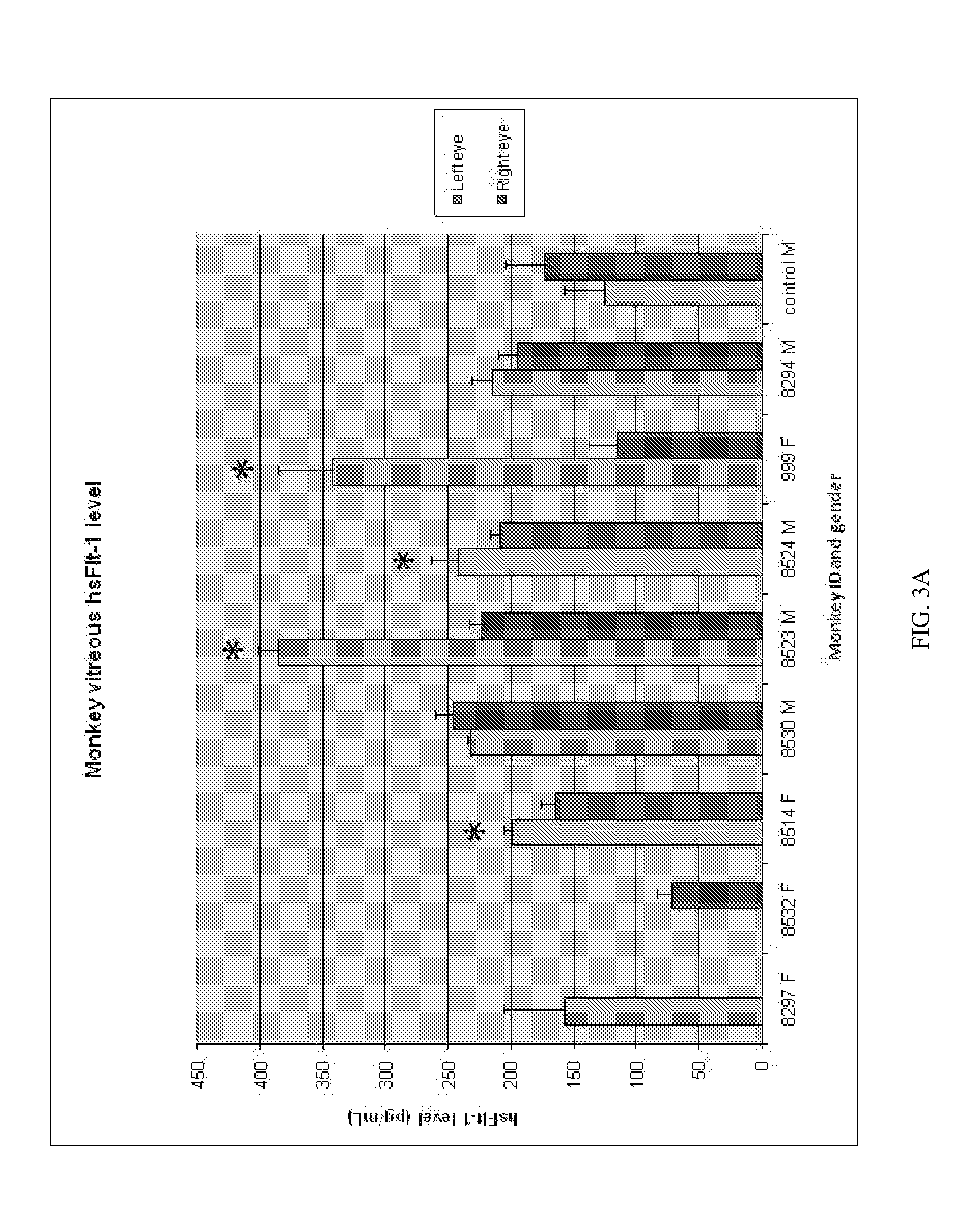
[0376]In the first mouse study, 13 transgenic mice were assessed for ocular neovascular changes before and after administration of the rAAV.sFlt-1 vector (1×1011 vector particles) in one eye and control vector in the contralateral eye. Eyes were assessed for neovascular changes using fluorescein angiography at one, three and eight months after injection. The extent, intensity and stage of neovascularization were graded (0-4) by three observers, masked to the treatment received in the eyes examined There was a statistically significant overall reduction in the neovascular grading from a median grade of ‘3’ (before injection) to a median grade of ‘1’ at one month after injection (P=0.012). This red...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com