Parametric system for risk sharing of critical illness risks and corresponding method thereof
a risk sharing and risk technology, applied in the field of parametric system for risk sharing of critical illness risks, can solve the problems of many systems failing to take over risk transfer, suffering from high blood pressure, etc., and achieve the effect of improving operational and financial stability of the system, improving diagnosis or treatment, and improving system stability
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
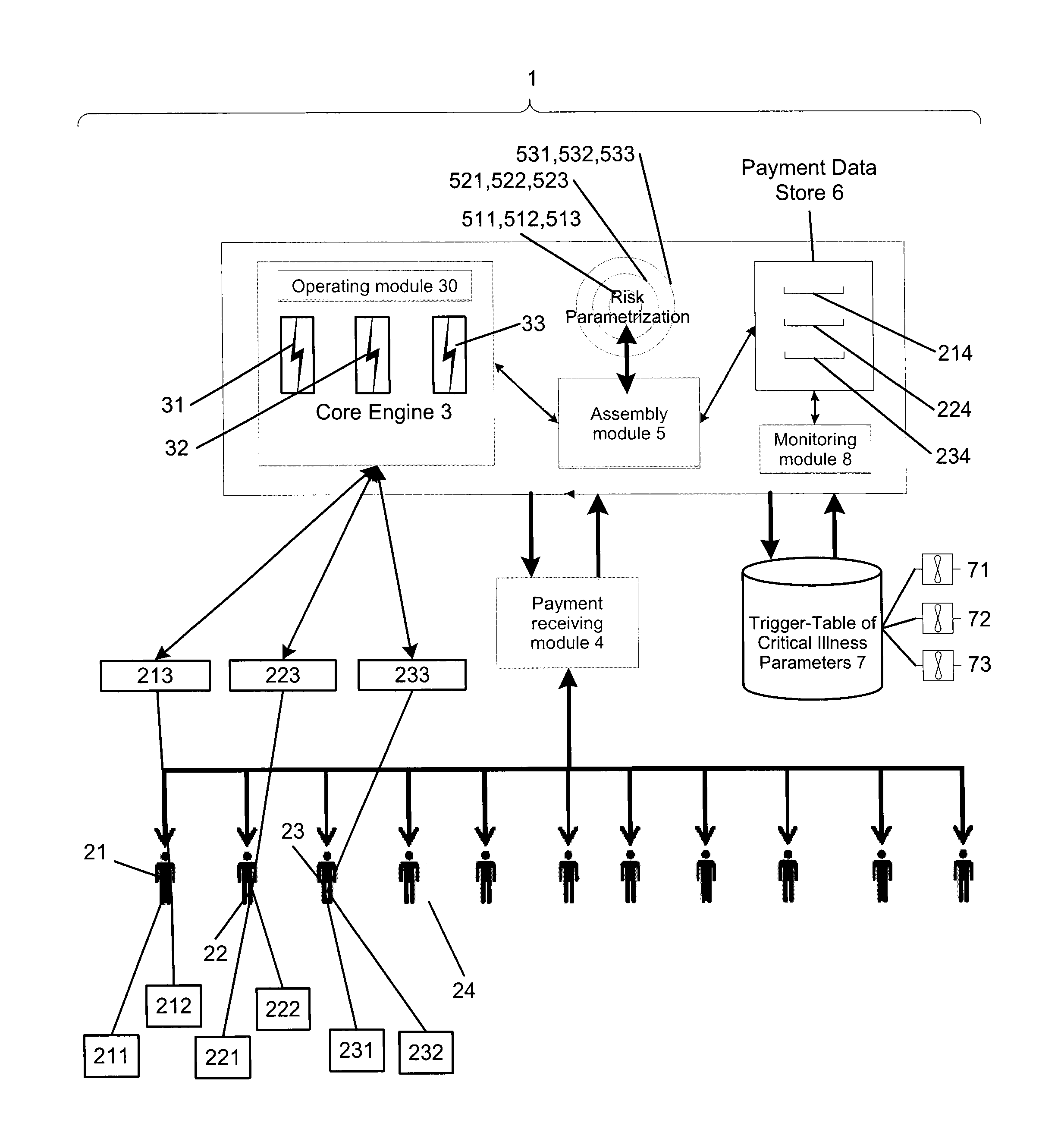
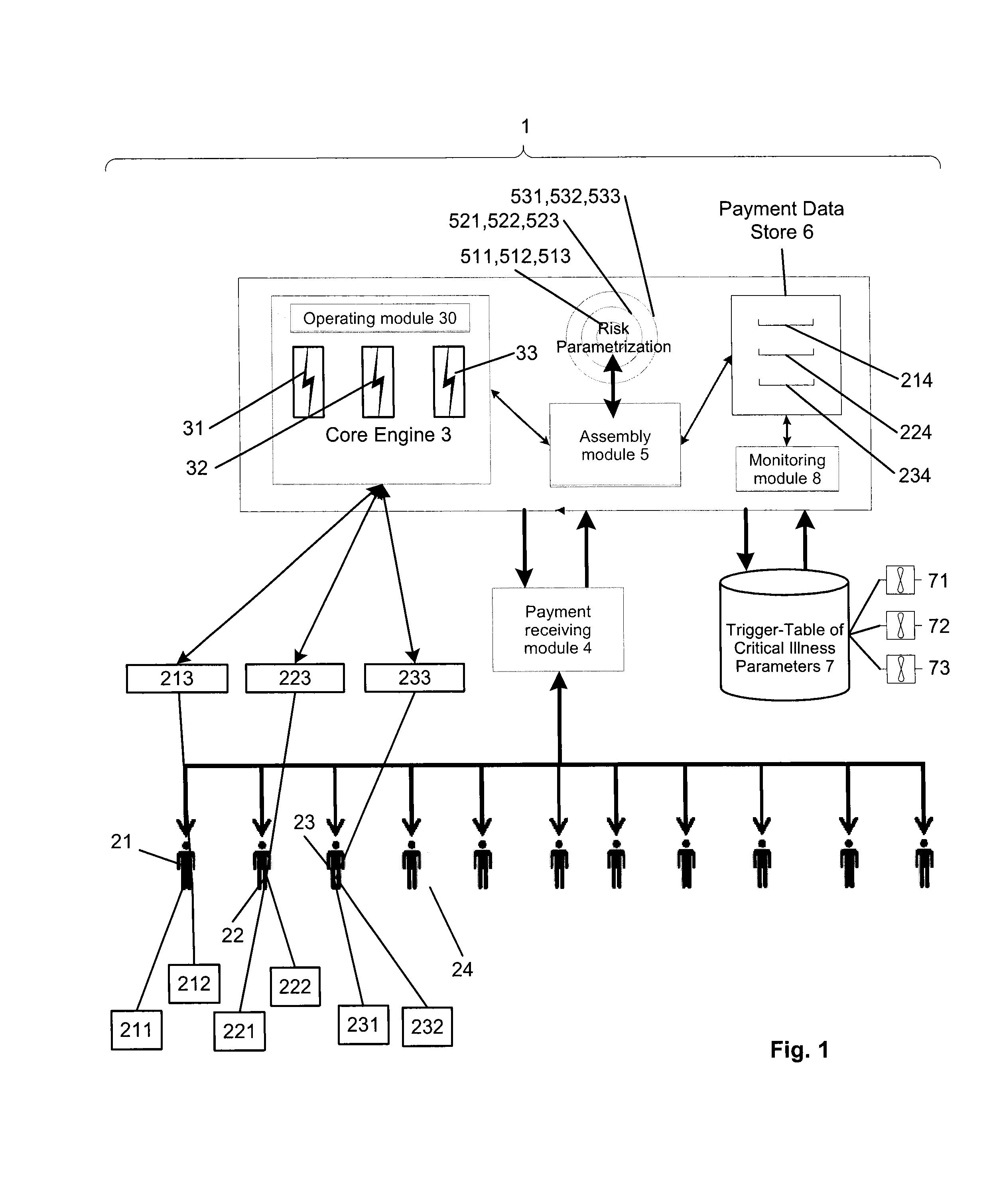
[0022]FIG. 1 illustrates, schematically, an architecture for a possible implementation of an embodiment of the parametric, event-driven resource-pooling system 1 for risk sharing of critical illness risks. In FIG. 1, reference numeral 1 refers to the resource-pooling system for risk sharing of the risk exposure components 21, 22, 23 . . . The resource-pooling system 1 provides a dynamic self-sufficient risk protection and corresponding risk protection structure for a variable number of risk exposure components 21, 22, 23, i.e.; persons or individuals, by its means. The system 1 includes at least one processor and associated memory modules. The system 1 can also include one or more display units and operating elements, such as a keyboard, and / or graphical pointing devices as a computer mouse. The resource-pooling system 1 is a technical device comprising electronic means that can be used by service providers in the field of risk transfer or insurance technology for risk transfer rela...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com