Low, immune enhancing, dose mtor inhibitors and uses thereof
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
Effects of mTOR Inhibition on Immunosenescence in the Elderly
[0459]One of the pathways most clearly linked to aging is the mTOR pathway. The mTOR inhibitor rapamycin has been shown to extend lifespan in mice and improve a variety of aging-related conditions in old mice (Harrison, D E et al. (2009) Nature 460:392-395; Wilkinson J E et al. (2012) Aging Cell 11:675-682; and Flynn, J M et al. (2013) Aging Cell 12:851-862). Thus, these findings indicate that mTOR inhibitors may have beneficial effects on aging and aging-related conditions in humans.
[0460]An age-related phenotype that can be studied in a short clinical trial timeframe is immunosenescence. Immunosenescence is the decline in immune function that occurs in the elderly, leading to an increased susceptibility to infection and a decreased response to vaccination, including influenza vaccination. The decline in immune function with age is due to an accumulation of immune defects, including a decrease in the ability of hematopoie...
example 2
Enhancement of Immune Response to Vaccine in Elderly Subjects
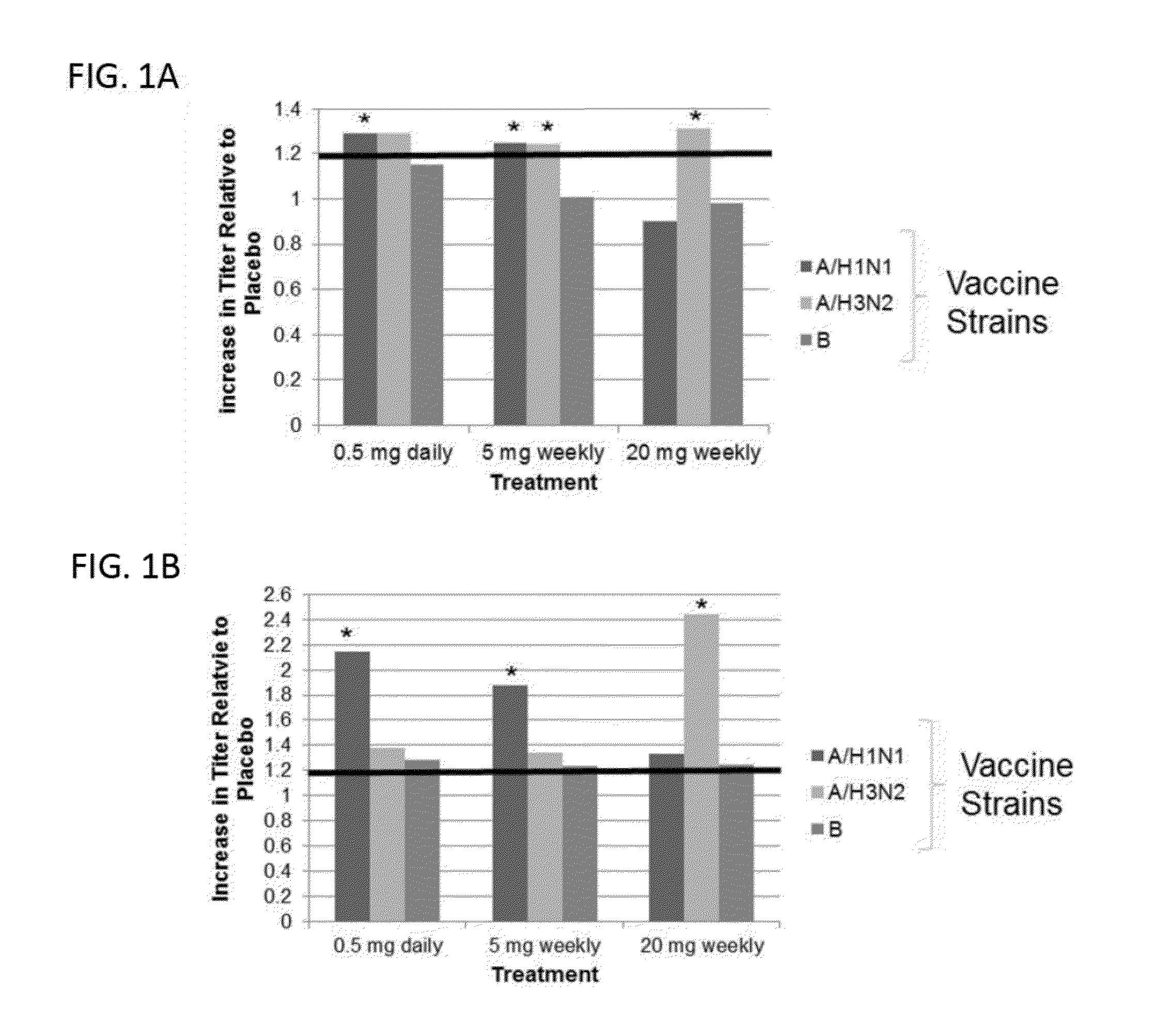
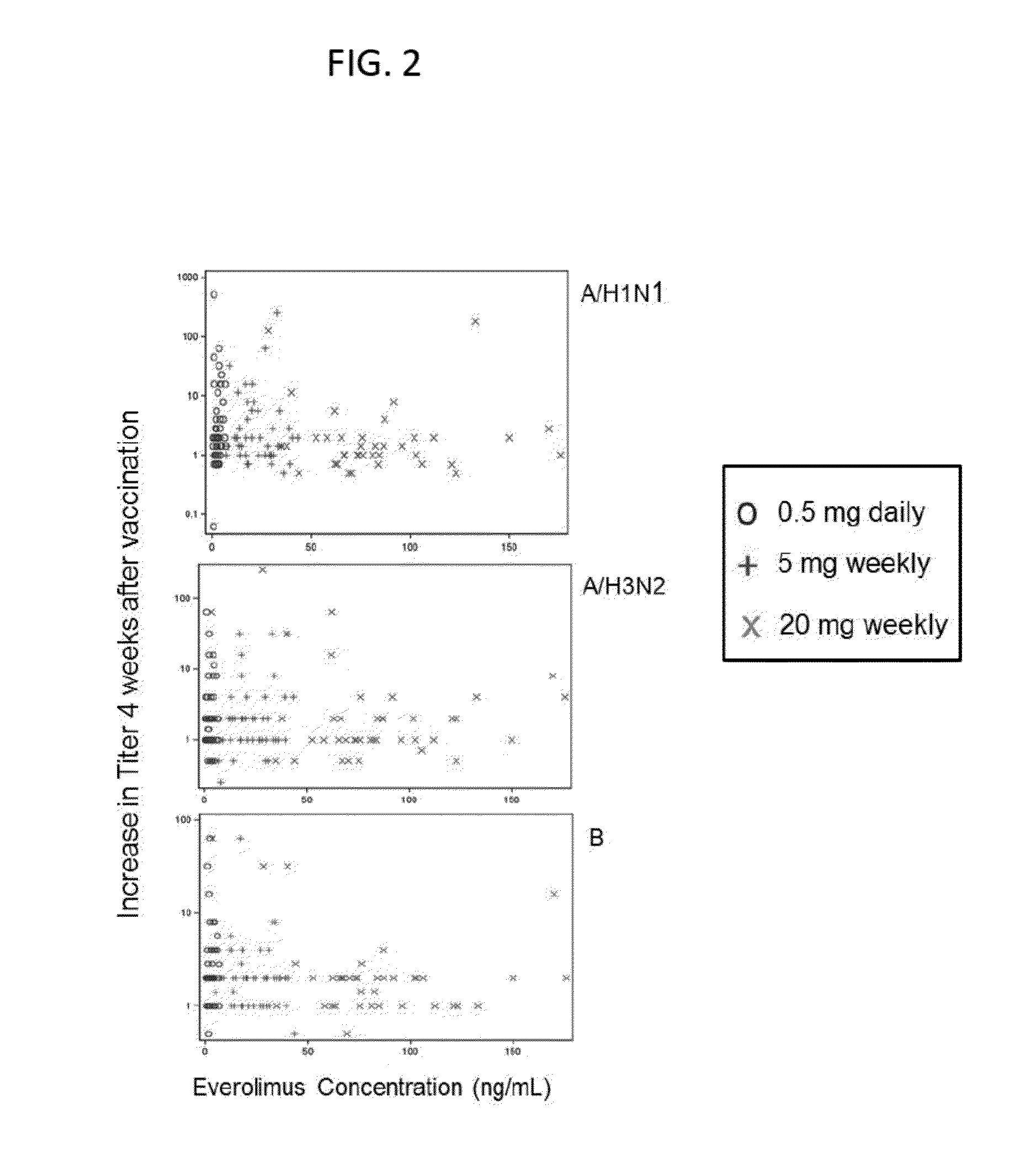
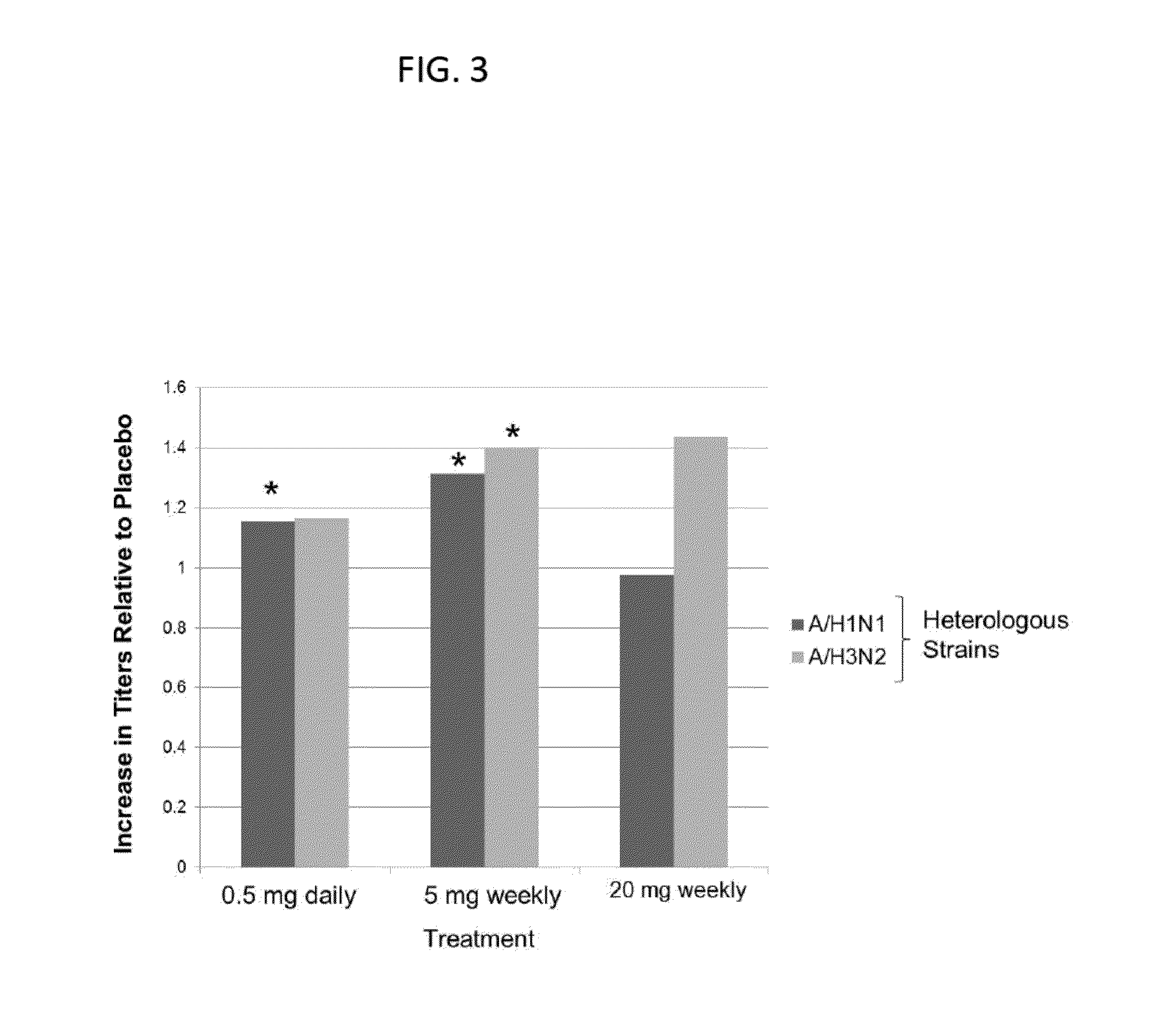
[0493]Immune function declines in the elderly, leading to an increase incidence of infection and a decreased response to vaccination. As a first step in determining if mTOR inhibition has anti-aging effects in humans, a randomized placebo-controlled trial was conducted to determine if the mTOR inhibitor RAD001 reverses the aging-related decline in immune function as assessed by response to vaccination in elderly volunteers. In all cases, appropriate patent consents were obtained and the study was approved by national health authorities.
[0494]The following 3 dosing regimens of RAD001 were used in the study:
[0495]20 mg weekly (trough level: 0.7 ng / ml)
[0496]5 mg weekly (trough level was below detection limits)
[0497]0.5 mg daily (trough level: 0.9 ng / ml)
[0498]These dosing regimens were chosen because they have lower trough levels than the doses of RAD001 approved for transplant and oncology indications. Trough level is the low...
example 3
Low Dose mTOR Inhibition Increases Energy and Exercise
[0502]In preclinical models, mTOR inhibition with the rapalog rapamycin increases spontaneous physical activity in old mice (Wilkinson et al. Rapamycin slows aging in mice. (2012) Aging Cell; 11:675-82). Of interest, subjects in the 0.5 mg daily dosing cohort described in Example 2 also reported increased energy and exercise ability as compared to placebo in questionnaires administered one year after dosing (FIG. 7). These data suggest that partial mTOR inhibition with rapalogs may have beneficial effects on aging-related morbidity beyond just immune function.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Fraction | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Fraction | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Time | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com