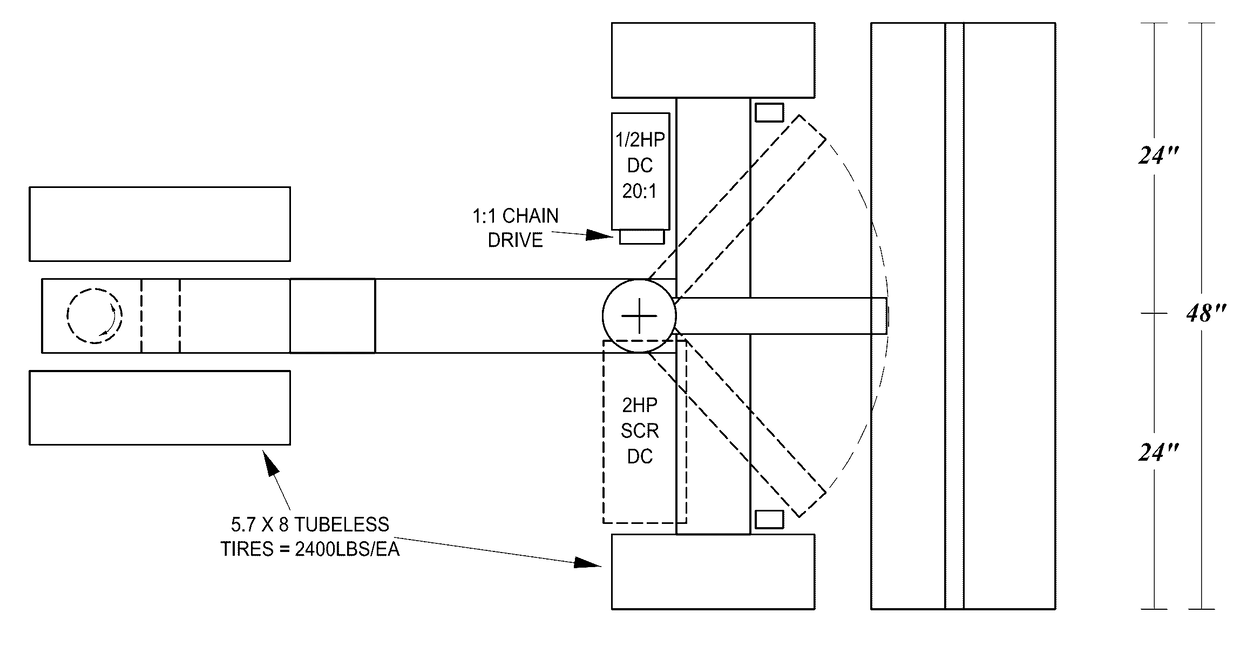
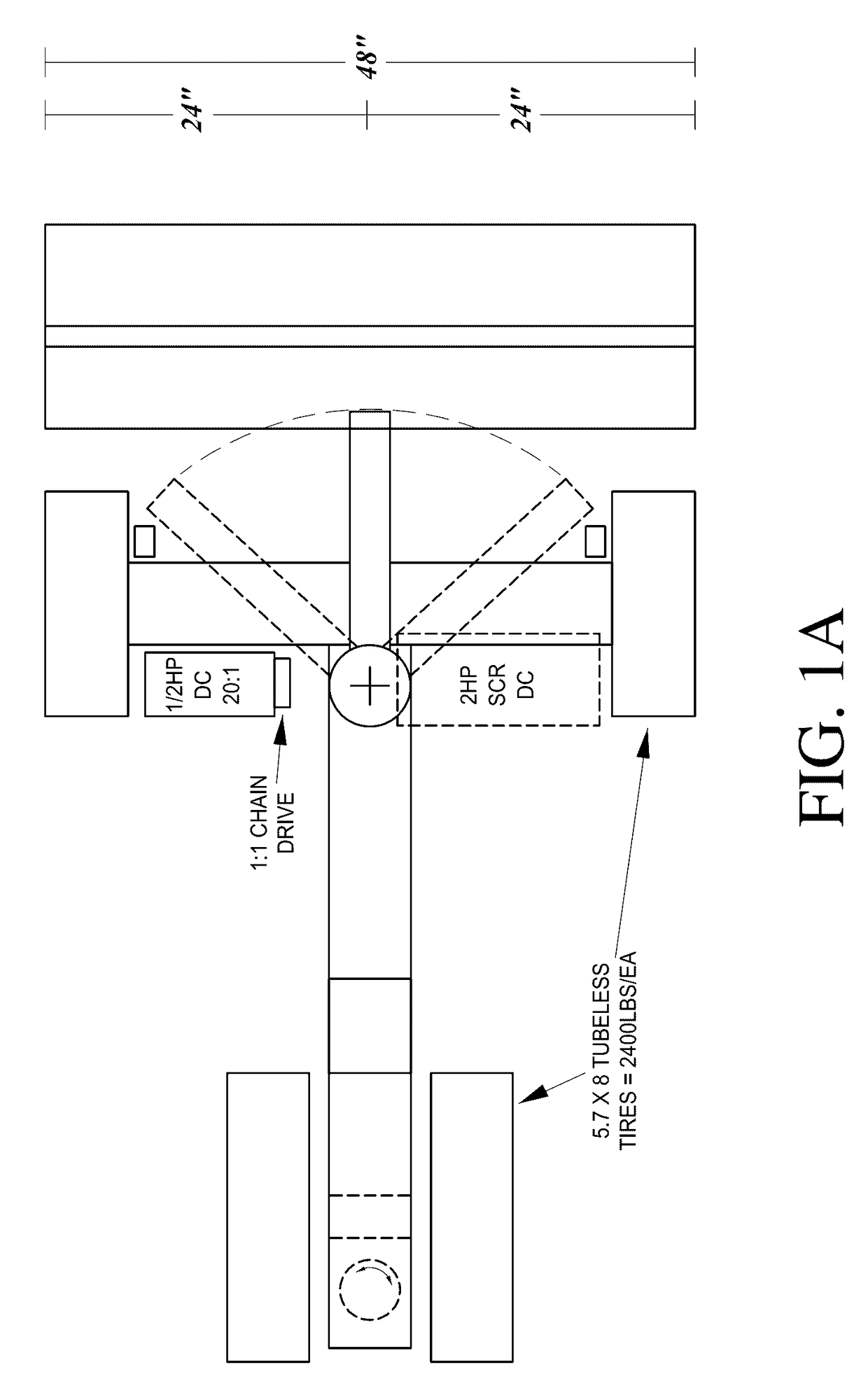
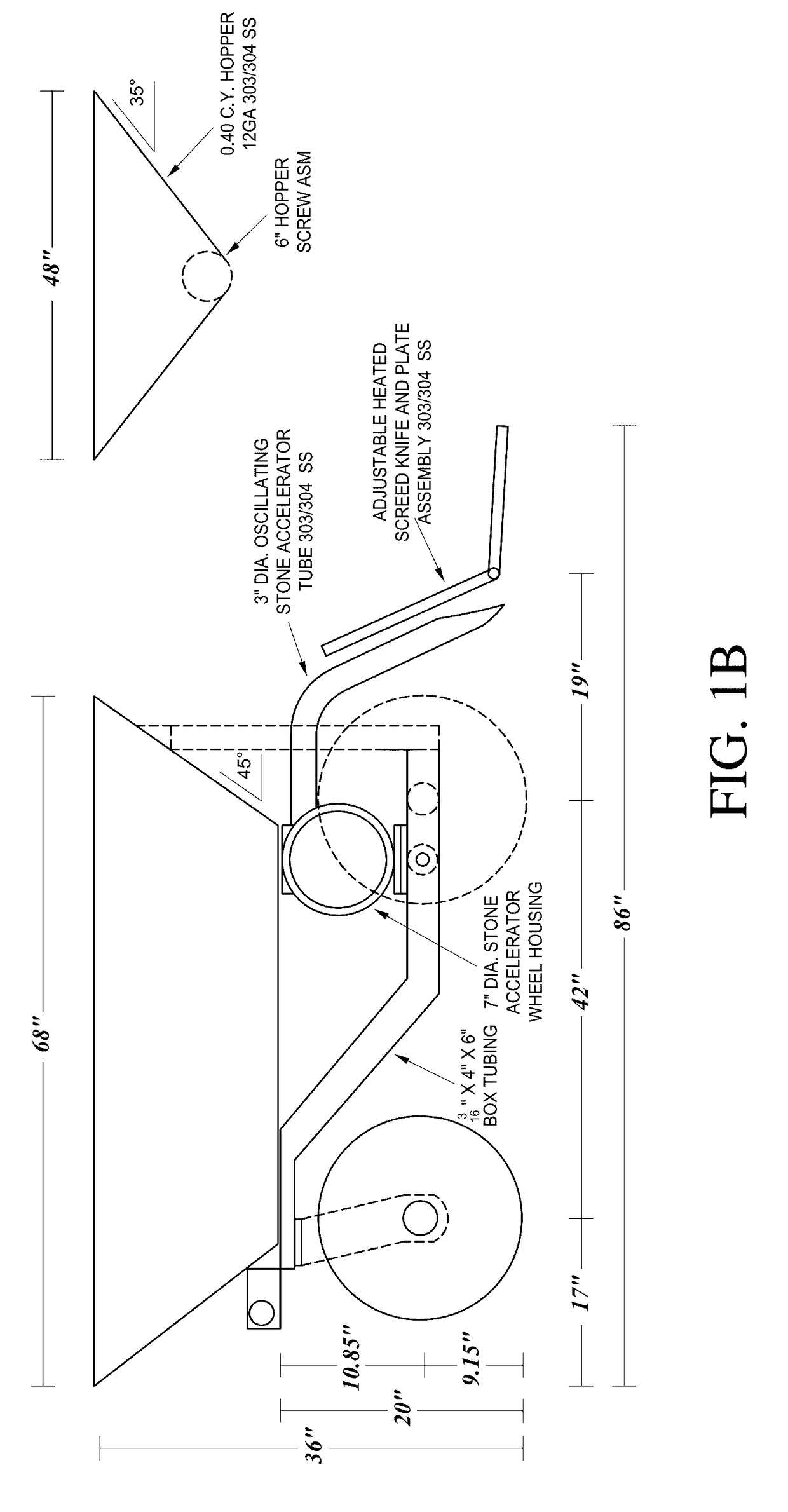
Pavement repair system
a technology of repair system and paving, which is applied in the direction of bridge construction, layered product treatment, foundation engineering, etc., can solve the problems of large technical and financial challenges in the repair and maintenance of civil infrastructure, including roads and highways of the united states, and quickly fail infrastructure, and achieve the effect of paving properties
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0081]The following description and examples illustrate a preferred embodiment of the present invention in detail. Those of skill in the art will recognize that there are numerous variations and modifications of this invention that are encompassed by its scope. Accordingly, the description of a preferred embodiment should not be deemed to limit the scope of the present invention.
[0082]Contrary to conventional methods, the systems of various embodiments and associated paving repair methods not only repair the pavement to a uniform surface with paving properties similar or superior to conventional or conventionally repaired asphalt paving, but also change the character of the underlying deteriorated road bed to minimize or eliminate the telegraphing of cracks. This character of the underlying pavement is a function of, e.g., the starting composition of the road, how the road was initially manufactured, exposure of the road to ambient conditions and different loads over time, and prior...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| peak wavelength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com